Unit 5: The Muscular System
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
A-band
an area where actin and myosin overlap
Actin
a muscle protein; a major component of the I-band and helps to compose the thin filaments
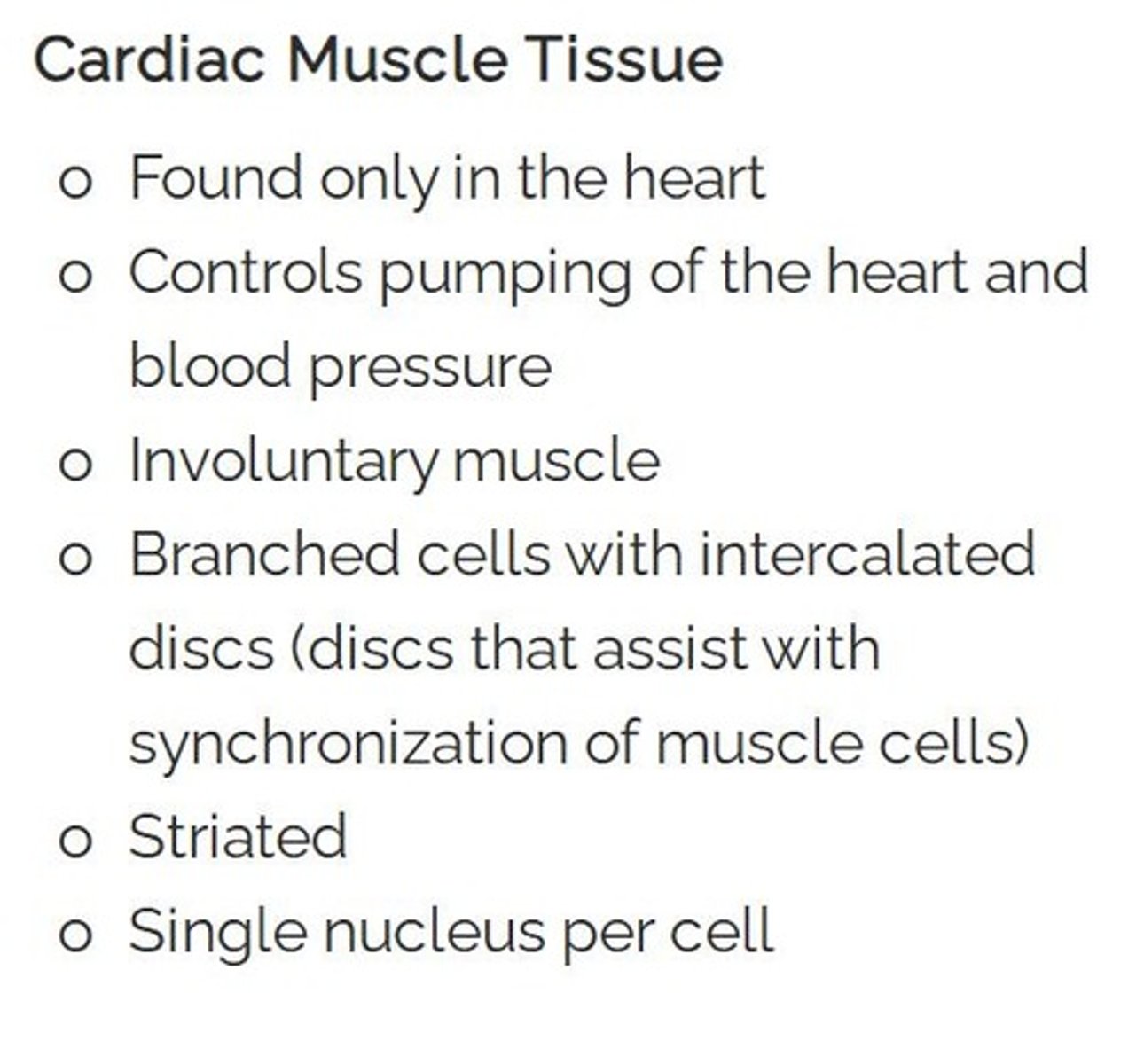
Cardiac muscle
the principal involuntary-muscle tissue of the vertebrate heart made up of striated fibers joined at usually branched ends and functioning in synchronized rhythmic contraction
Cramp
a painful, involuntary muscle contraction, usually caused by fatigue or strain
Fascia
a sheet of tissue that covers or connects parts inside the body (such as muscles)
I-band
the small gap between the myosin and the Z-band at the end of the sarcomere
Involuntary
a type of muscle that contracts without conscious control
Myocyte
muscle cell
Myofibril
located within the muscle cells; composed of thick (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments
Myosin
a muscle protein; a major component of the A-band; thick filaments
Muscle
a tissue that has the ability to contract to help with movement
Muscle contraction
when the sarcomere shortens and the Z-lines move closer together
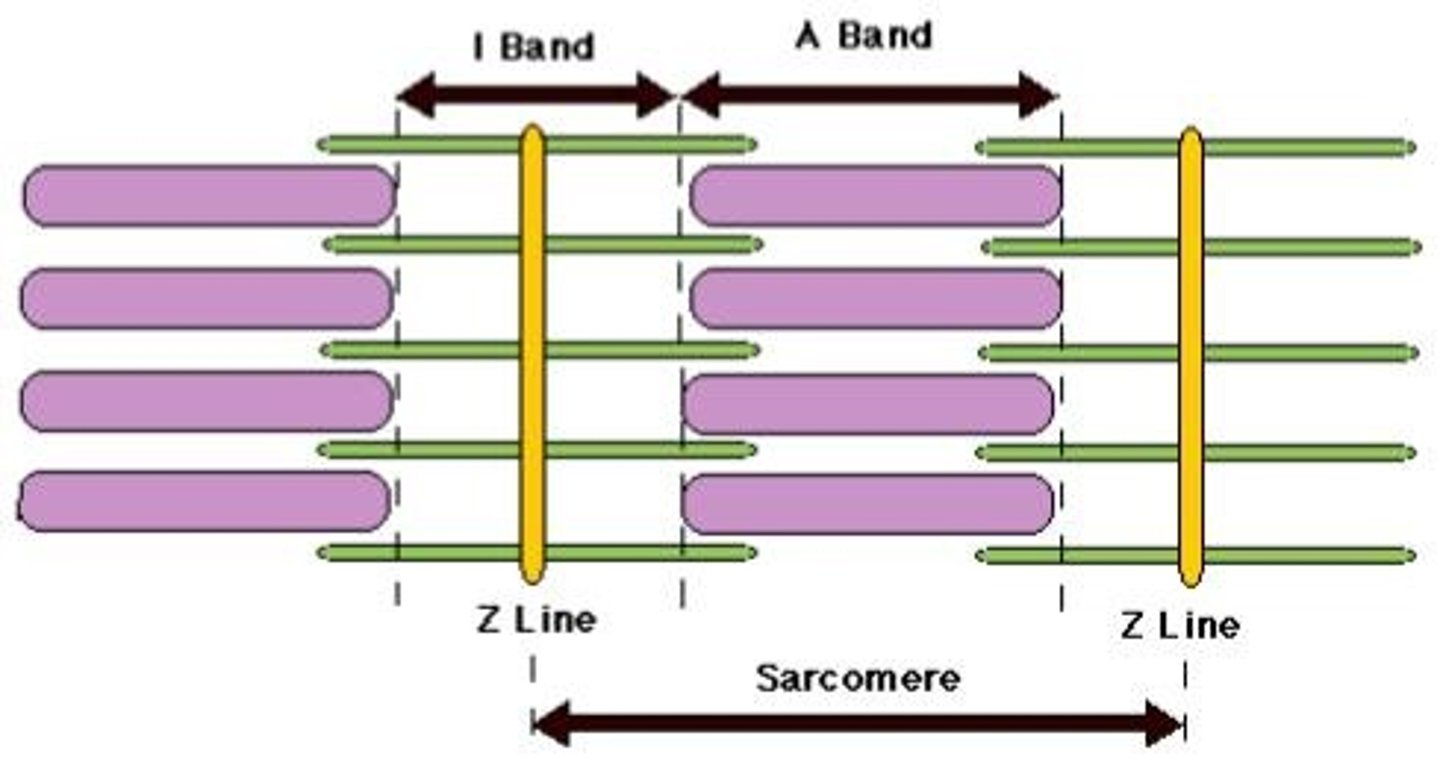
Sarcomere
the basic unit of muscle contraction; segment between two neighboring Z-lines
Skeletal muscle
striated muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and is usually under voluntary control.
Sliding filament theory
theory that explains how sarcomeres contract; myosin filaments use energy from ATP to 'walk' along the actin filaments with their cross bridges; myofilaments slide past one another and contract the myocyte
Smooth muscle
muscle tissue that lacks cross striations, is made up of elongated spindle-shaped cells having a central nucleus and is found especially in vertebrate hollow organs and structures (as the digestive tract and bladder) as thin sheets performing functions not subject to direct voluntary control
Sprain
an injury to the joints caused by overstretching
Strain
an injury to the muscle caused by overstretching
Superficial muscles
muscles that are located in the layer closest to the skin
Tendon
a tough piece of tissue in your body that connects a muscle to a bone
Visceral muscle
smooth muscle found in the digestive, respiratory and circulatory systems.
Voluntary
a type of muscle that is controlled by the individual, such as the striated muscle
Maintains posture
Muscles adjust continuously to provide coordination of movement, stabilizing joints.
Generating heat
As ATP is used to provide energy for muscle contraction, almost 75% of the energy escapes as heat, providing the majority of body heat needed for survival.
Myocytes
Muscle cells that make up every muscle in the body.
Voluntary muscles
Muscles that are under conscious control.
Involuntary muscles
Muscles that are not under conscious control.
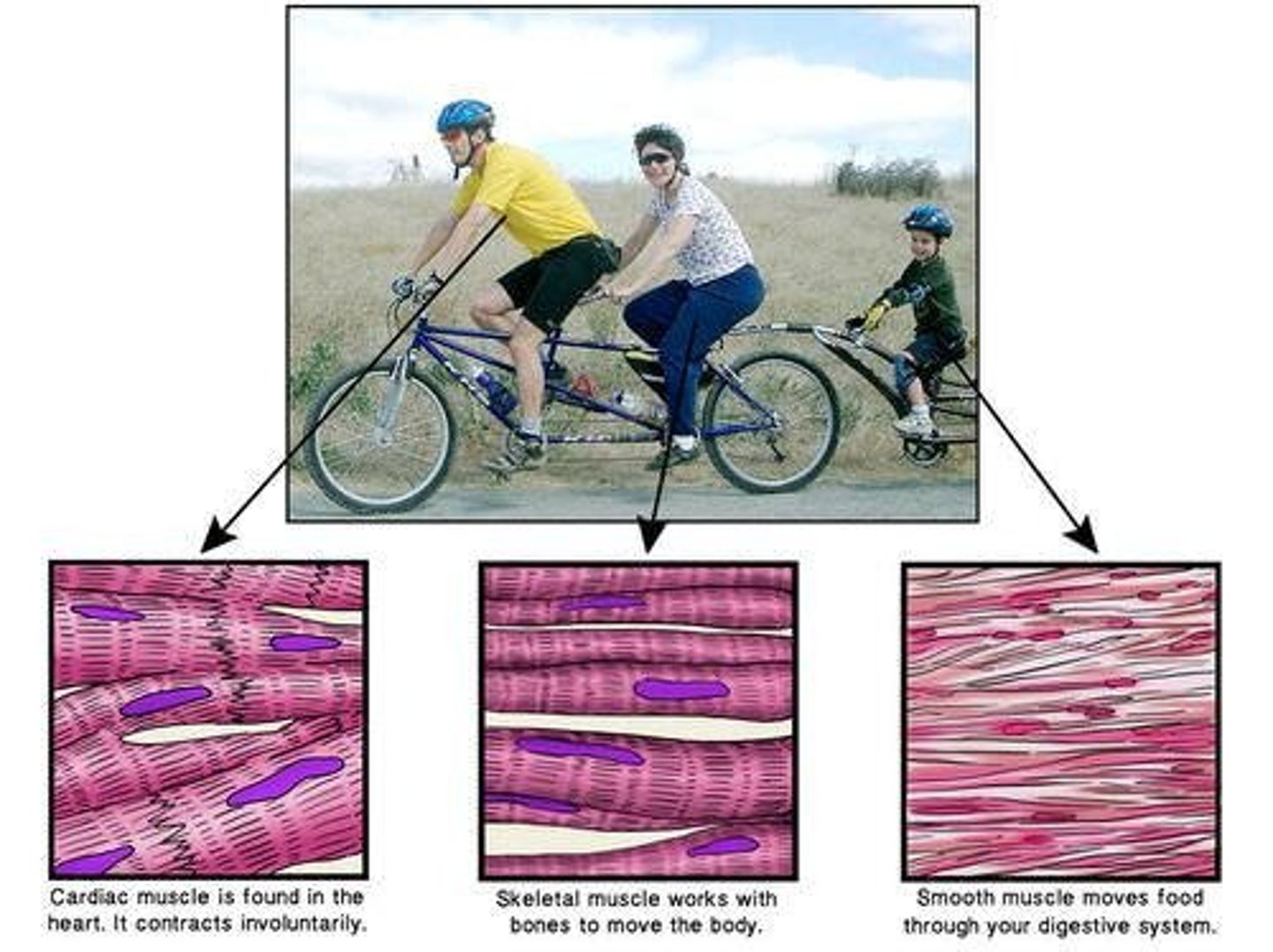
Types of muscles
There are three types of muscles in the body: skeletal (stratified), smooth, and cardiac.
Muscle Cell Contraction
Muscle contraction starts with a signal from the nervous system.
Myofibrils
Hundreds of organelles contained in each muscle fiber.
Myofilaments
Bundles of contractile proteins that make up each myofibril.
Sarcomeres
Functional units arranged along the muscle fiber, and the basic unit of muscle contraction.
Z line
The area between two Z lines defines the sarcomere.
A band
The area in the sarcomere where myosin and actin overlap.
Muscle fiber contraction
A muscle fiber either contracts fully, or it doesn't contract at all.
Strength of muscular force
Determined by the number of fibers that contract; more fibers contracting at the same time results in greater force.
Skeletal muscle structure
Each skeletal muscle is an organ consisting of skeletal muscle tissue, connective tissue, nerve tissue, and vascular tissue.
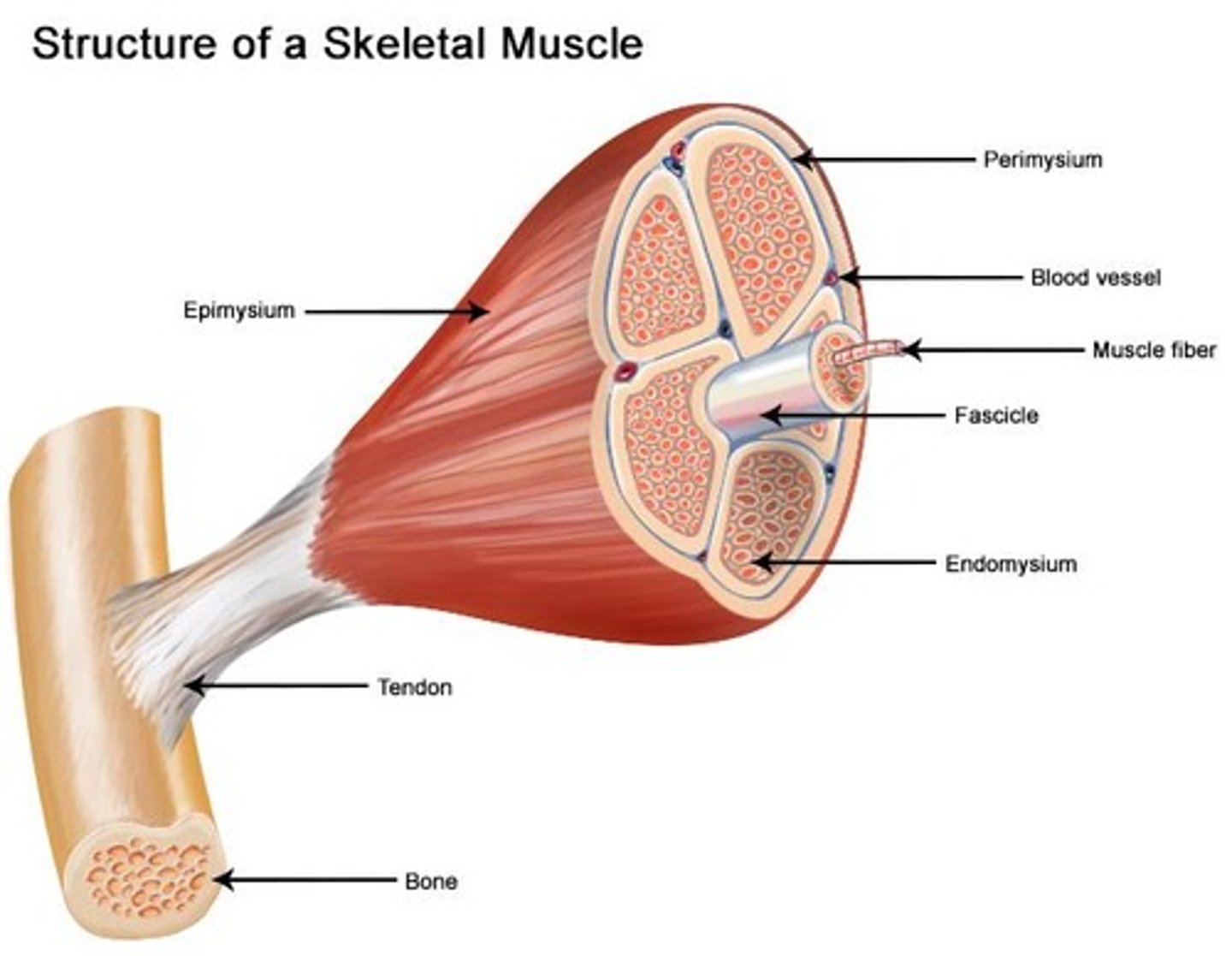
Endomysium
The connective tissue that wraps each individual muscle fiber.
Fascicles
Bundles in which muscle fibers are arranged.
Perimysium
The connective tissue that separates and surrounds fascicles.
Epimysium
The outermost layer of connective tissue that surrounds the fascicles.
Connective Tissue
Multiple layers of connective tissue give support and protection to the delicate muscle fibers and allow them to withstand the force of contraction.
Transport System
Active skeletal muscle needs an efficient transport system to provide the muscle with oxygen and nutrients needed for contraction and to remove waste products.
Origin
The bone that does not move during contraction.
Insertion
The bone that does move during contraction.
Flexion
An action that decreases the angle at a joint.
Flexor
A muscle that causes the angle of a joint to become smaller.
Extension
An action that straightens or extends a joint.
Extensor
A muscle that causes a joint to straighten out.
Antagonistic Pairs
Groupings of muscles that work against each other to move parts of the body in opposite directions.
Agonist
A muscle that causes a movement to occur through its own contraction.
Antagonist
A muscle that opposes the specific movement of the agonist muscle, controlling and slowing its motion.
Skeletal Muscle Variability
Skeletal muscles can vary in size, shape, and arrangement of fibers.
Parallel Fiber Pattern
Fibers run parallel to the direction of the muscle, functioning similarly to a single muscle fiber.
Convergent Fiber Pattern
Fibers fan out from a common point of attachment, allowing for a more versatile type of movement.
Pennate Fiber Pattern
Muscles have one or more tendons running through the body with fascicles forming an oblique angle to the tendons, able to generate greater tension.
Sphincter
Also known as circular muscles, arranged concentrically around an opening or recess, getting smaller as they contract.
Biceps Brachii
A muscle that, when contracted, pulls on the radius bone, causing the arm to move up.
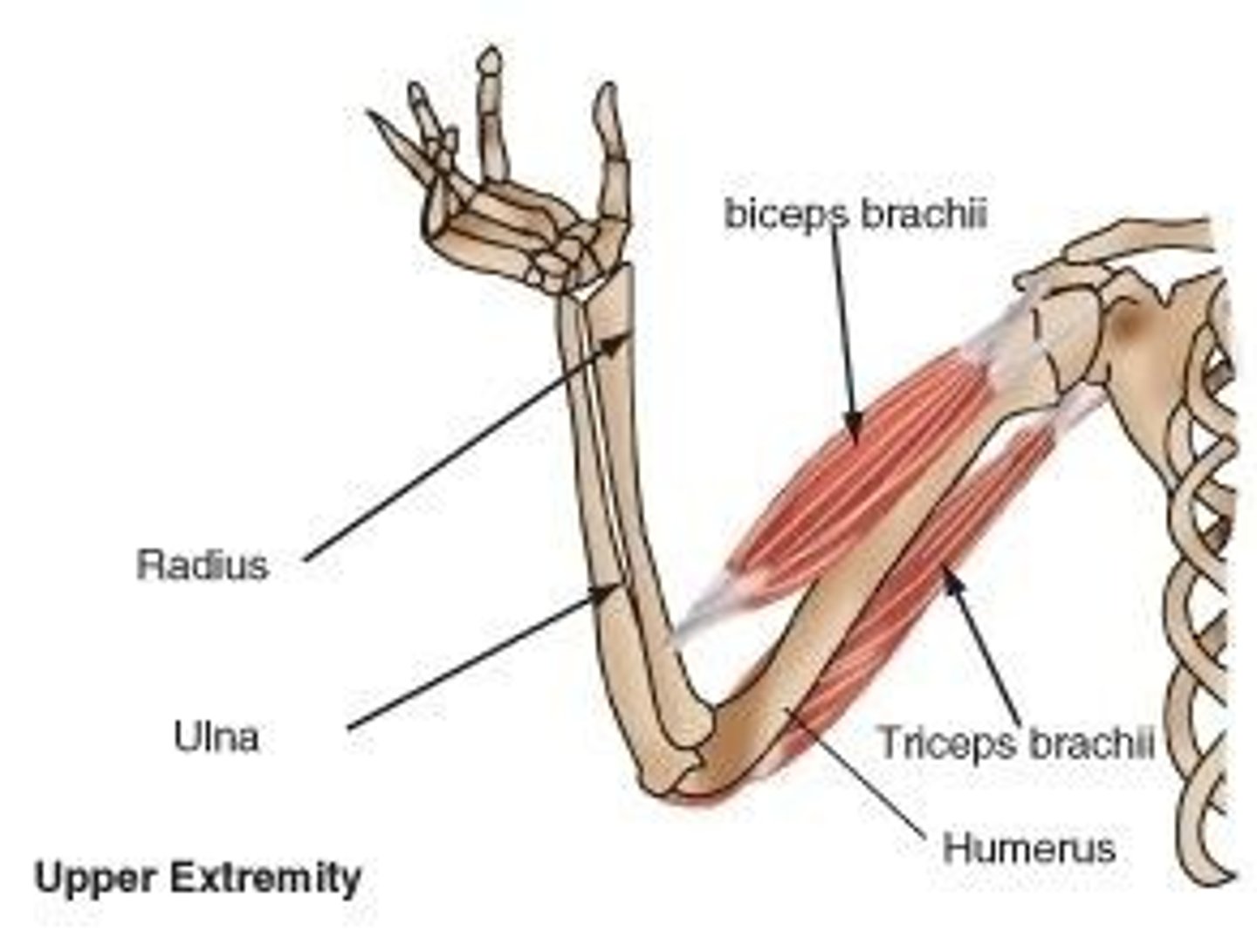
Triceps Brachii
A muscle that contracts to extend or straighten the arm, opposing the biceps brachii.
Prime Movers
Muscles that are primarily responsible for generating a specific movement.
Muscle Relaxation
Muscles extend after contraction only passively through relaxation.
Vastus
Huge
Maximus
Large
Longus
Long
Minimus
Small
Brevis
Short
Deltoid
Triangular
Rhomboid
Like a rhombus
Latissimus
Wide
Teres
Round
Trapezius
Like a trapezoid
Rectus
Straight
Transverse
Across
Oblique
Diagonally
Orbicularis
Circular
Pectoralis
Chest
Gluteus
Buttock or rump
Brachii
Arm
Supra-
Above
Infra-
Below
Sub-
Under or beneath
Lateralis
Lateral
Biceps
Two heads
Triceps
Three heads
Quadriceps
Four heads
Sternocleidomastoideus
Origin on the sternum and clavicle, insertion on the mastoid process
Brachioradialis
Origin on the brachium or arm, insertion on the radius
Abductor
To abduct a structure
Adductor
To adduct a structure
Levator
To lift or elevate a structure
Masseter
To chew
Muscle hypertrophy
The increase in muscle mass due to exercise, particularly weight training