MOUTH & TONGUE
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
how is the mouth divided
the mouth can be divided into the:
vestibule - the sulci between the cheeks/ lips and the teeth
oral cavity proper - the space inside the mouth and including the teeth
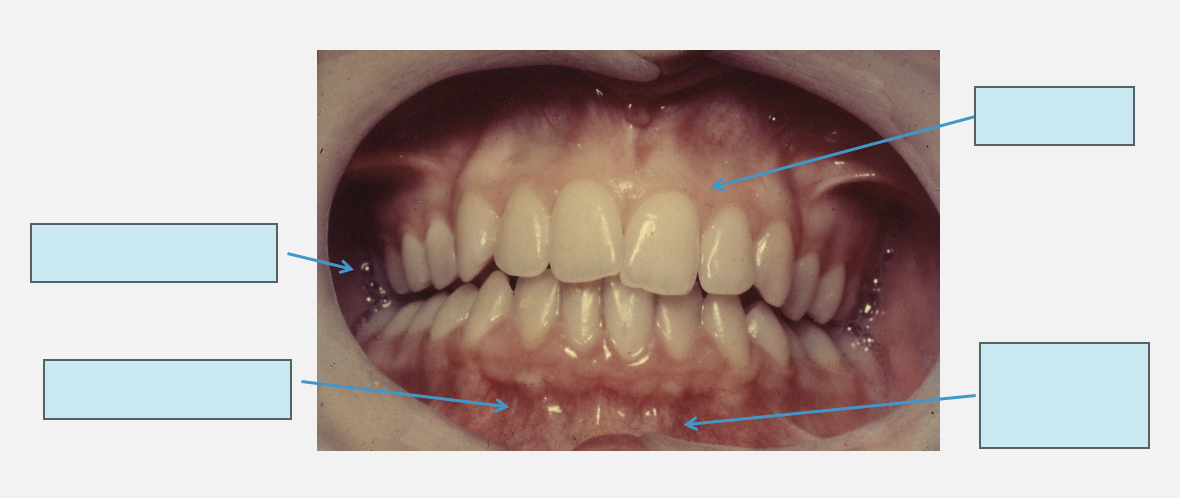
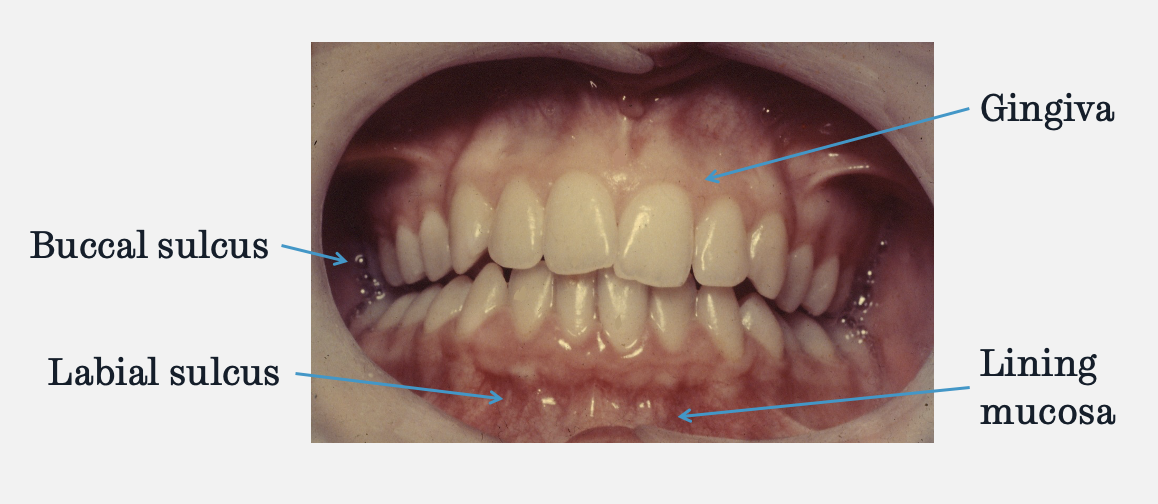
label the features of the vestibule
lining mucosa - quite transparent, can often see blood vessels
outline the palatoglossal arch
also known as the anterior pillars of fauces
forms the boundary between the mouth and oropharynx
everything in front = mouth
everything behind = oropharynx
extends from soft palate to the side of the tongue
paired
outline the palatopharyngeal arch
behind the palatoglossal arch
also known as the posterior pillars of fauces
extends from the soft palate to the side of the pharynx
where are the palatine tonsils situated
between the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches
how can the uvula vary anatomically
can be notched
can be bifid
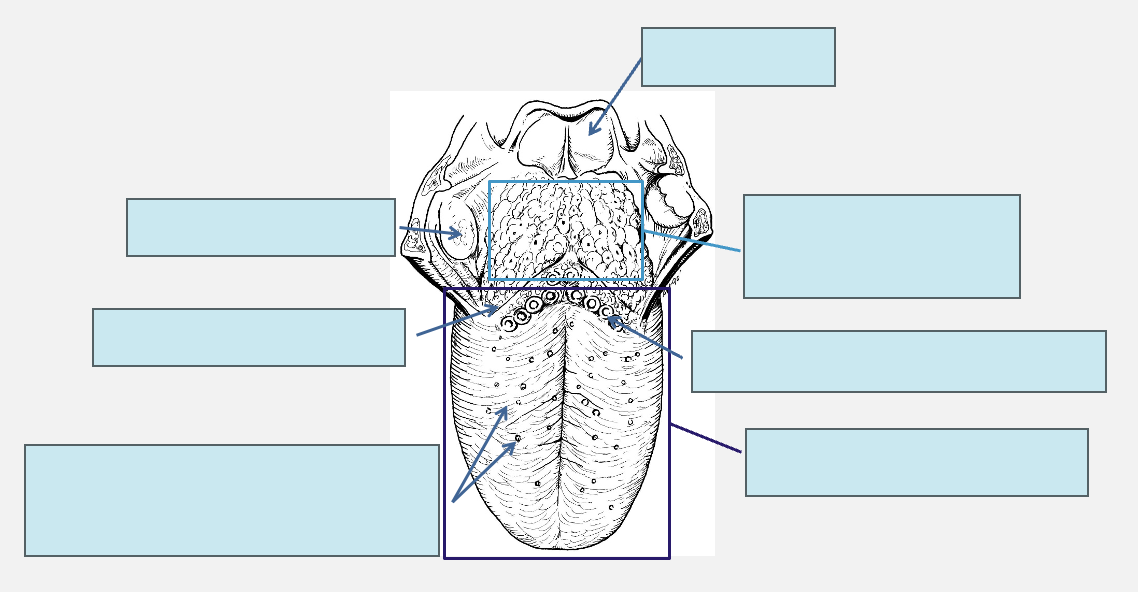
label the dorsal surface of the tongue
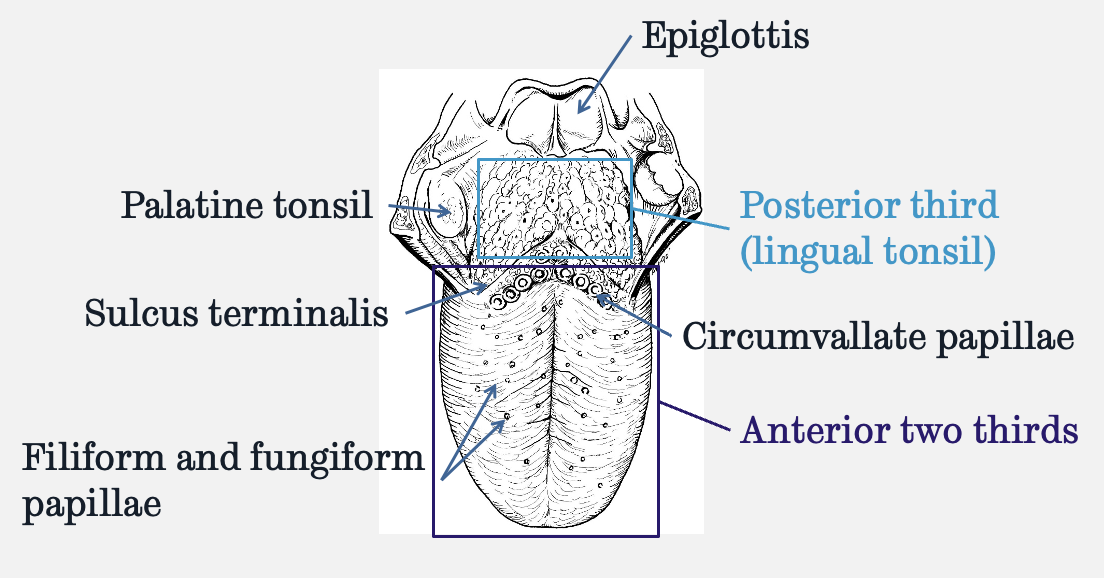
do circumvallate papillae contain taste buds?
yes
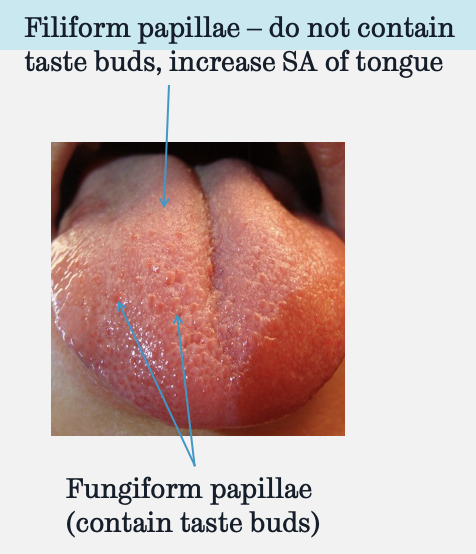
do filiform papillae contain taste buds?
no, they increase the surface area of the tongue
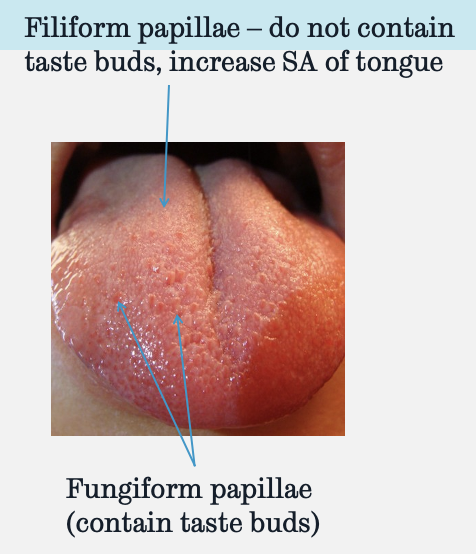
do fungiform papillae contain taste buds?
yes
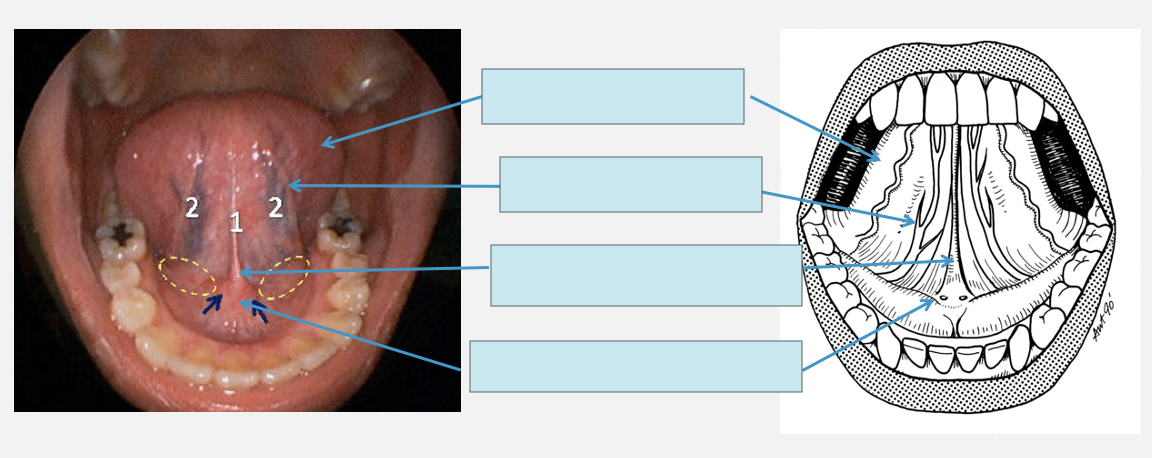
label the ventral surface of the tongue
lining mucosa: non-keratinised
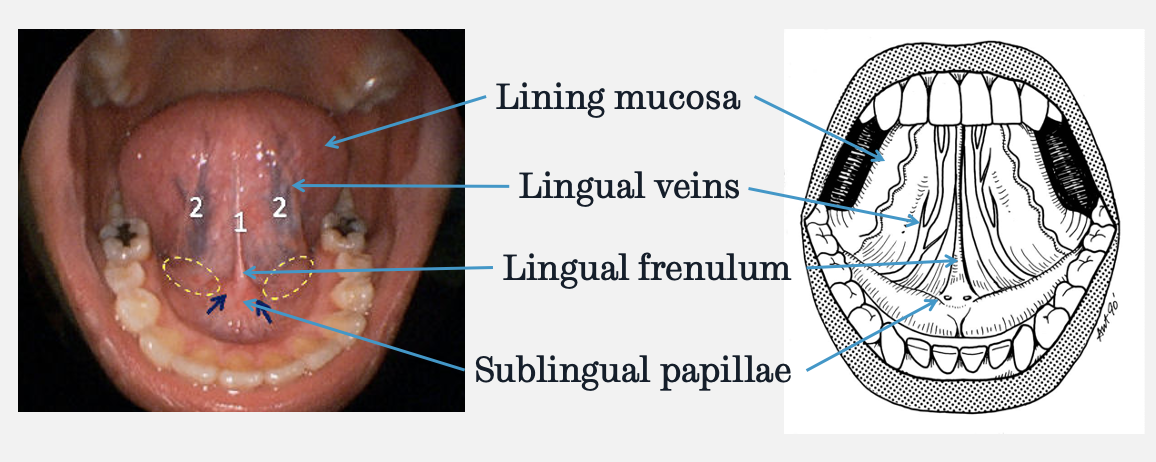
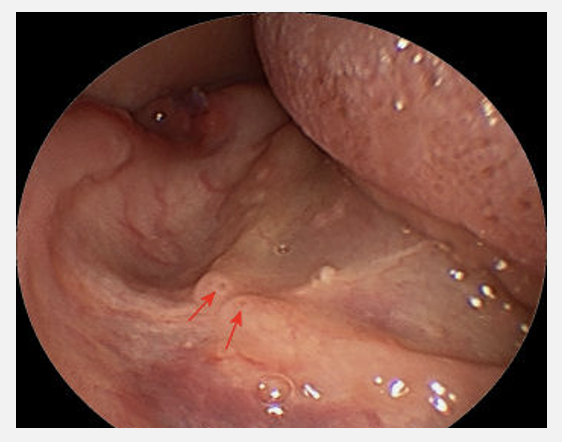
what do sublingual papillae contain
the opening of Wharton’s ducts (submandibular)
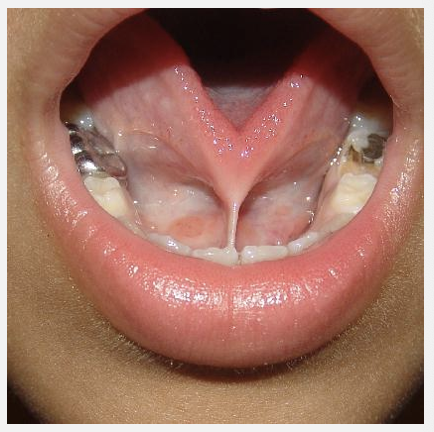
outline ankyloglossia
commonly known as tongue-tie
condition where the lingual frenulum is too short
this restricts tongue movements
what are the two sets of muscles of the tongue
extrinsic muscles
intrinsic muscles
state the attachments and functions of the extrinsic muscles of the tongue
extrinsic muscles of the tongue
attach to the skull and tongue
changes the position of the tongue
state the attachments and functions of the intrinsic muscles of the tongue
intrinsic muscles of the tongue
both attachments are within the tongue
changes the shape of tongue
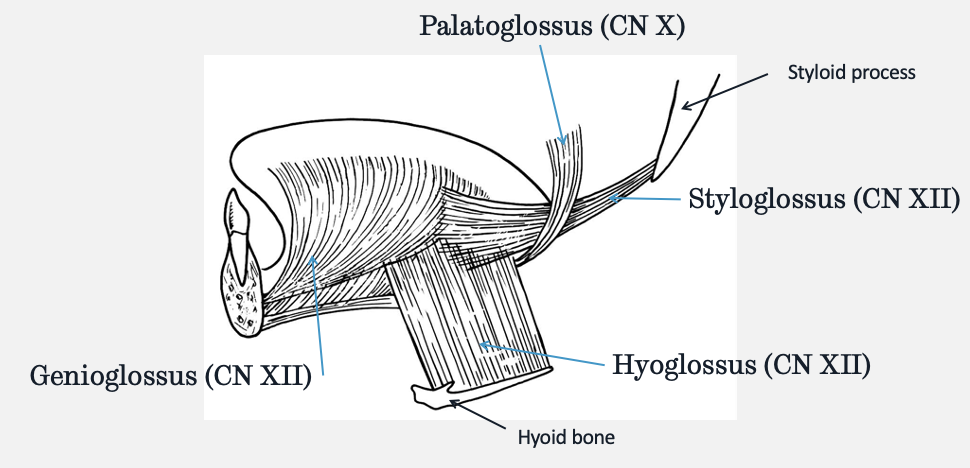
what are the extrinsic muscles of the tongue and which nerves supply their motor innervation
genioglossus - CN XII (hypoglossal)
palatoglossus - CN X
styloglossus - CN XII (hypoglossal)
hyoglossus - CN XII (hypoglossal)
what is the function of the genioglossus
wide range of actions
protrudes the tongue
depresses the tongue
deviates the tongue to the opposite side
what is the function of the palatoglossus
elevates posterior tongue
depresses the soft palate
what is the function of the styloglossus
retracts tongue
elevates the sides of the tongue
what is the function of the hyoglossus
depresses tongue
depresses the sides of the tongue
retracts the tongue
what are the intrinsic muscles of the tongue and which nerves supply their motor innervation
superior longitudinal
inferior longitudinal
transverse
vertical
ALL INNERVATED BY CN XII (HYPOGLOSSAL)
what is the function of the superior longitudinal muscle
shortens tongue
curls apex and sides upwards
what is the function of the inferior longitudinal muscle
shortens tongue
curls apex downwards
what is the function of the transverse (lingual) muscle
narrows tongue
lengthens tongue
what is the function of the vertical (lingual) muscle
broadens the tongue
flattens the tongue
elongates the tongue
which nerve(s) supply the tongue with motor innervation
CN XII - hypoglossal
CN X - vagus (palatoglossus)
which nerve(s) supply the tongue with sensory innervation
CN IX - glossopharyngeal
CN VII - facial nerve
chorda tympani branch
CN V3 - mandibular branch of trigeminal nerve
lingual branch
which region of the tongue does CN IX (glossopharyngeal) supply and what sensation is felt
CN IX supplies sensory innervation to the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
taste sensation + general sensations e.g. heat, touch
what region of the tongue does CN VII (chorda tympani branch) supply and what sensation is felt
CN VII (chorda tympani branch) supplies sensory innervation to the anterior 2/3 of the tongue
taste sensation
what region of the tongue does CN V3 (lingual branch) supply and what sensation is felt
CN V3 (lingual branch) supplies sensory innervation to the anterior 2/3 of the tongue
general sensation e.g. heat, touch
describe the location of the chorda tympani in relation to the lingual nerve
the chorda tympani fuses to the lingual nerve outside of the oral cavity
the chorda tympani and lingual nerve therefore cannot be distinguished inside the tongue/ oral cavity
the lingual nerve runs close to the mucosa that lines the floor of the mouth so it can be found easily if the oral cavity was dissected
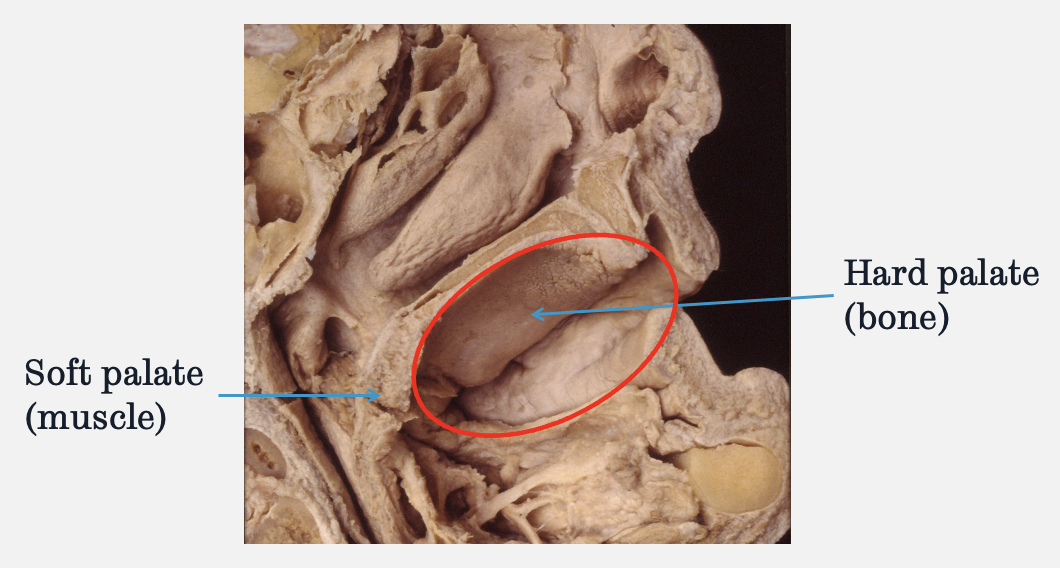
describe oral masticatory mucosa
tightly bound to the underlying bone incl. gingiva
midline of hard palate appears pale/ white
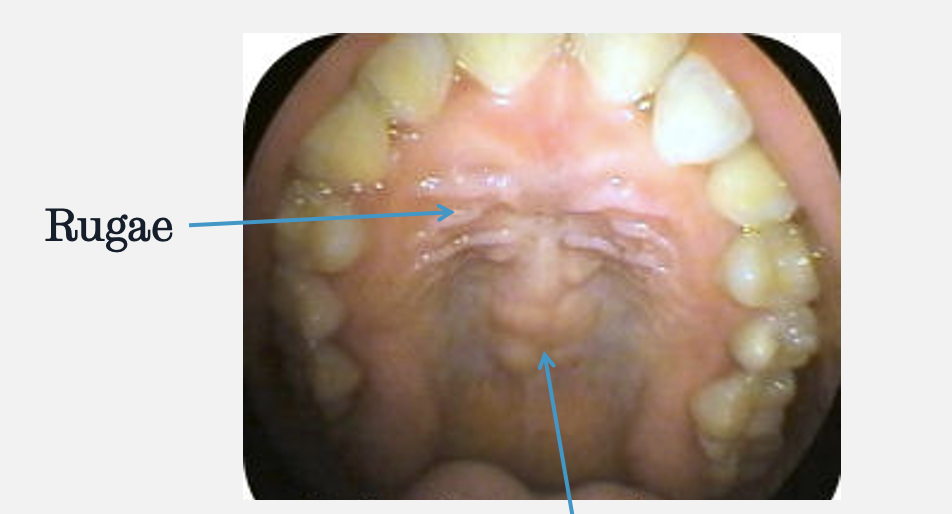
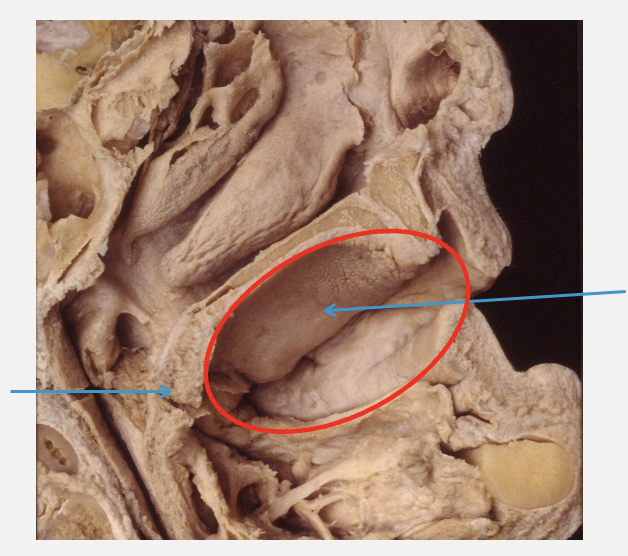
what do the arrows and red circle indicate
red circle = oral cavity proper
what are the muscles of the soft palate
levator veli palatini
tensor veli palatini
palatoglossus
palatopharyngeus
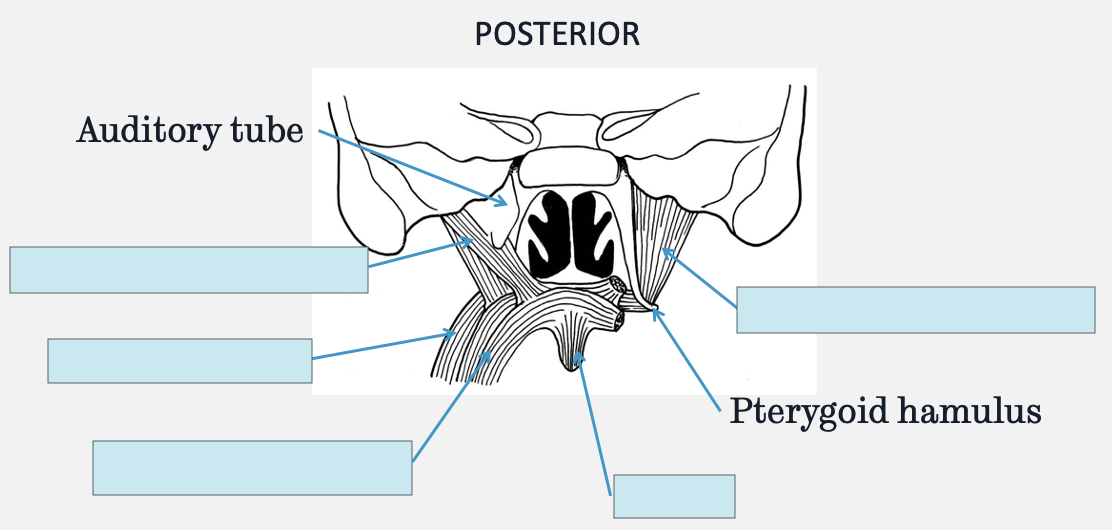
what is the function of the pterygoid hamulus
acts as a pulley for the tensor veli palatini
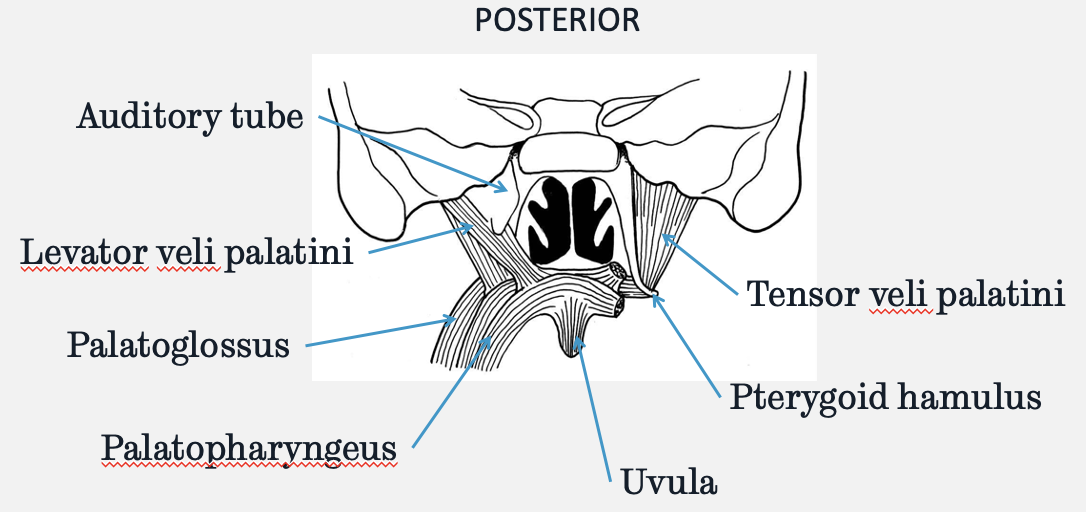
what is the function of the levator veli palatini
elevates soft palate
what is the function of the tensor veli palatini
tenses soft palate
what is the function of the palatoglossus
depresses soft palate
what is the function of the palatopharyngeus
depresses soft palate
what is the innervation of the muscles of the soft palate
all innervated by vagus, except the tensor veli palatini which is innervated by a branch of CN V3
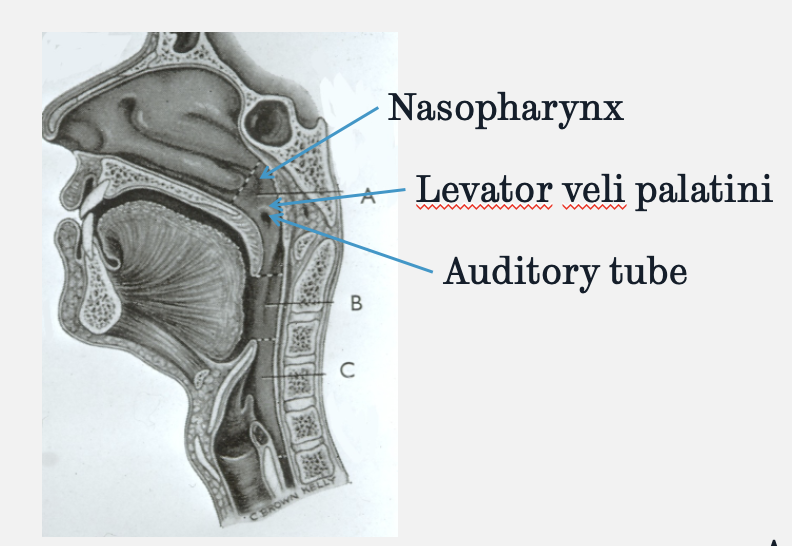
how are the auditory tube and levator and tensor veli palatini muscles associated
the attachments of the levator veli palatini and to a degree the tensor veli palatini are important in terms of opening the Eustachian tube
they attach closely to the opening of the auditory tube so when they contract, the auditory tube opens
this is why in aeroplanes, chewing gum helps equalise the pressure in the ears
the chewing action causes muscles of the soft palate to contract which opens the Eustachian tube
how does cleft palate affect the muscles of the soft palate and the health of the ear
children born with cleft palate have:
weak action of TVP and LVP on the auditory tube because palatal attachment is ‘insecure’
auditory tube does not open efficiently
middle ear does not drain » ear infections
middle ear does not drain » glue ear » conductive hearing loss
what related structure is commonly found near lymphatic vessels
blood vessels
which lymphatic vessels collect lymph from the lymphatic capillaries
two sets of lymphatic vessels collect lymph from the lymphatic capillaries:
superficial - variable in distribution e.g. in the subcutaneous layer deep to the skin
deep - larger, more constant vessels that accompany deep arteries and veins supplying skeletal muscles and organs
where are lymph nodes found
lymph nodes are found along lymphatic vessels and have a high concentration of lymphocytes
label the lymph nodes of the head and neck
superficial cervical chain of nodes runs on top of sternocleidomastoid
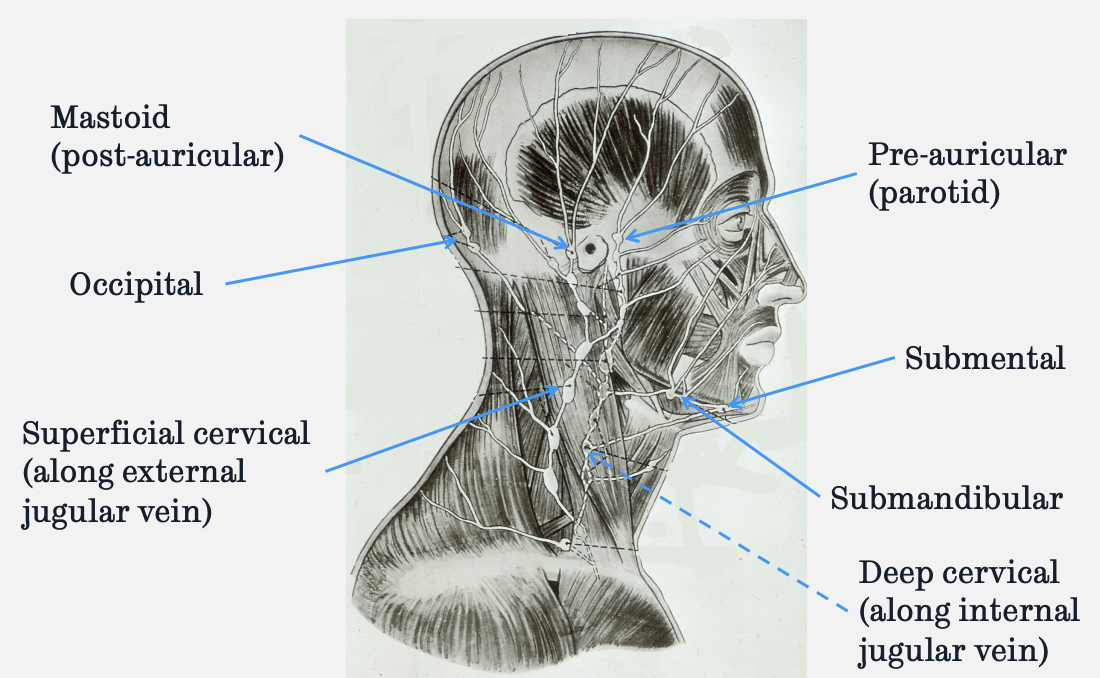
where does the pre-auricular/ parotid lymph node receive lymphatic drainage from
anterolateral scalp
eyelids
cheeks
where does the post-auricular lymph node receive lymphatic drainage from
posterolateral scalp
where does the occipital lymph node receive lymphatic drainage from
posterior scalp
neck
where does the submandibular lymph node receive lymphatic drainage from
face
gingivae
teeth
tongue
» receives majority of lymphatic drainage from the oral cavity
where does the submental lymph node receive lymphatic drainage from
central lower lip
chin
FOM
tip of tongue
incisor teeth
where does drainage from the occipital and post-auricular nodes pass to
the superficial cervical nodes and then to deep nodes
where does drainage from pre-auricular, submandibular and submental nodes pass to
the deep cervical nodes
where does lymph travel to from the deep cervical nodes
from the deep cervical nodes lymphatic vessels form the right and left jugular trunks
these empty into the right lymphatic duct (right side) or thoracic duct (left side)
diagram of intraoral lymphatic drainage
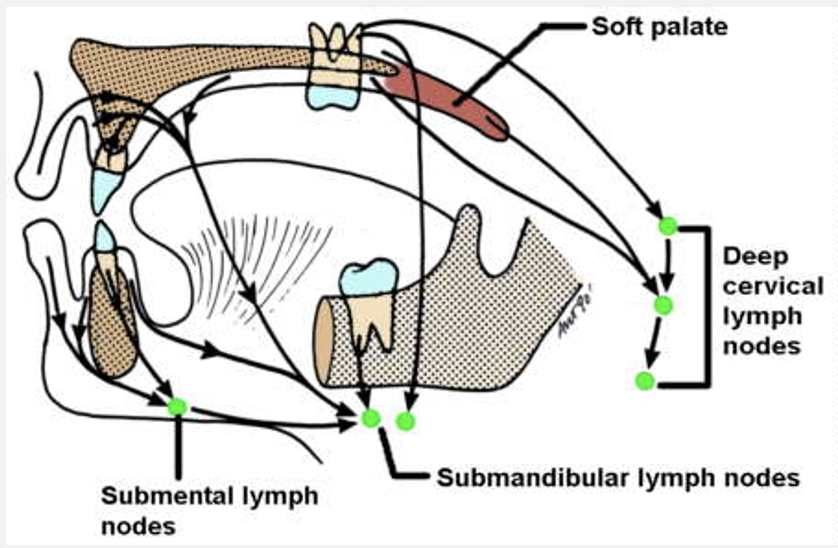
what introral structures do submental nodes drain
lower anterior teeth
central lower lip
small area of FOM behind incisor teeth
tip of tongue
what introral structures do submandibular nodes drain
remaining lower dentition and supporting tissues
remaining FOM
lateral part of lower lip
cheek
upper lip
upper anterior teeth
anterior 2/3 of tongue
what introral structures do upper deep cervical nodes drain
upper posterior teeth
hard palate
soft palate
where does the posterior 1/3 of the tongue drain into
directly into the jugulodigastric node of the deep cervical chain
where does the anterior 2/3 of the tongue drain into
directly into the deep cervical nodes
indirectly via the submental and submandibular nodes
where does the tip of the tongue drain into
submental nodes and then onto the jugulo-omohyoid node (deep chain)
what is the term for the vertical midline of the tongue
midline raphe/ lingual septum
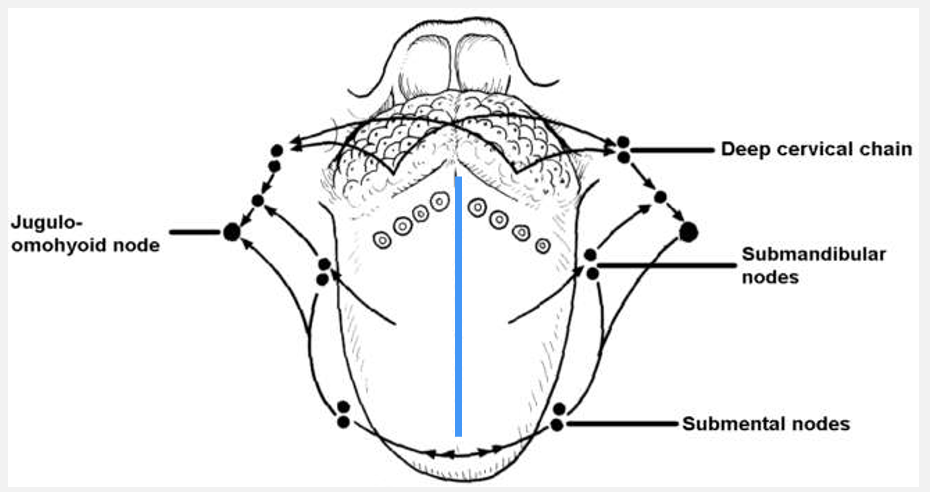
outline the midline raphe/ lingual septum and its relationship to lymphatic drainage of the tongue
forms an impervious lymph barrier that is deficient at the tip and posterior 1/3
this means that drainage is bilateral at the tip and posterior 1/3 but ipsilateral for the remaining anterior 2/3
—
» lymphatic fluid cannot cross the raphe
what can often spread through lymphatic vessels
infections
how do lymph nodes respond to infection
lymph nodes are placed at intervals in the lymphatic vessels
they produce a response to infection by enlarging as they produce lymphocytes
what is the term used to refer to enlarged lymph nodes
lymphadenopathy - lymph nodes may be palpable when enlarged
describe the appearance of malignant cells
malignant cells are usually atypical in appearance
they lose their desmosomal attachments to each other
they can therefore migrate
explain the association between cancer and lymphatic vessels
malignant cells often migrate through lymphatic vessels into lymph nodes where they form secondary growths i.e. metastasize
this is esp. true for head and neck cancers as other cancers spread through blood vessels instead
the lymph nodes may also be palpable
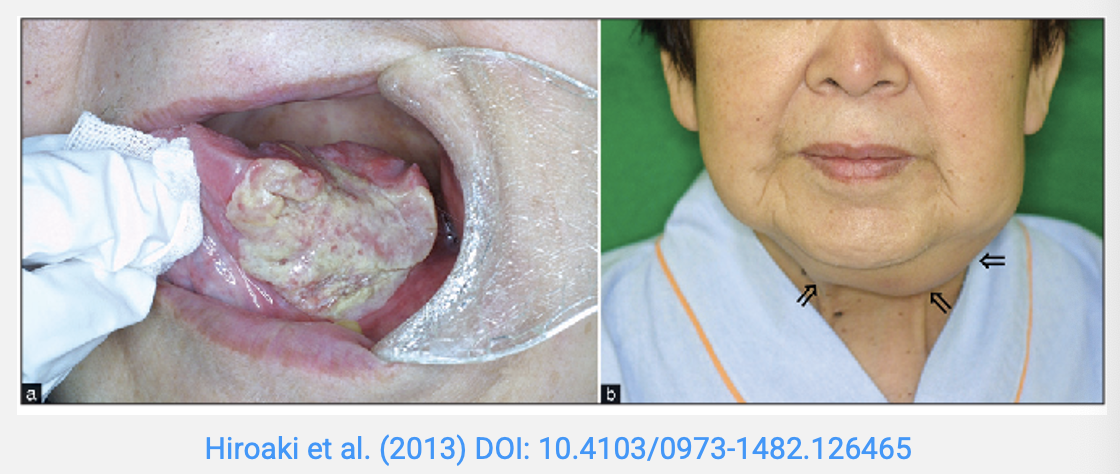
image of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) with lymph node involvement