Filtration
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Filtrate Formation and Modification: Processes
Involve in urine formation: several processes are involved in formation of filtrate and urine
Filtrate Formation:
-Filtration: blood fluid fenestration -> sending things out into nephron
-Reabsorption: taking things back that had been in _____(______)
-Secretion: take things from ___, but into____. Independent of filtration
-Excretion: waste we are talking about/ leaving system
-nephron
-the blood (glucose and ions)
- blood, filtrate
Tubular transport maximum (Tm)
Maximum rate at which a substance can be reabsorbed
Proximal Tubule Reabsorption and Secretion: Area of tubule that is close to glomerulus: take back into ____ what we but out during ______( ______ )
-not always happening with simple diffusion. May need a _____ (saturated)
- circulation, filtration
-(bicarbonate, glucose, nutrients)
-transported
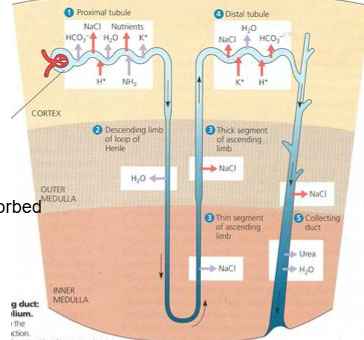
Distal tubule reabsorption and secretion
FINE TUNES
Reabsorbs: Na+, Cl-, Ca2+
Secretion: K+, H+
Collecting duct reabsorption and secretion
BULK RETURN
Reabsorbes: water and urea
Secretion or reabsorption: H+, HCO3 - Na+, K+
Collecting duct reabsorption and secretion: Production of dilute urine
Late distal tubule and collecting duct not reabsorbing H2O
Occurs when extracellular H2O is high (excess fluid)
Ions still absorbed as needed along way
_______ contributes to concentrating urine
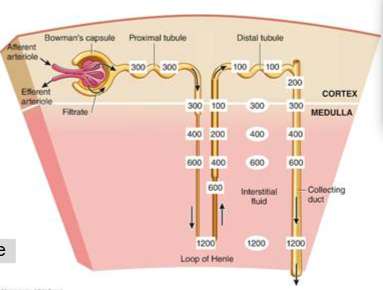
Countercurrent Mechanism
Production of dilute urine
-Start at 300, go down and it gets __________, come back up numbers go down
- Whats happening?: water is ____ as we go down (more conc), back up= no water moving but do see ______ (________)
-If take things out of solution (_____)
-Get to distal tubules, number ___ further because more water _____
-more concentrated
- coming out
-ion movement (active transport process)
-more dilute
-drops, leaves
Countercurrent mechanism contributes to concentrating urine: Where
-Nephron loop
-Uses energy (ATP) to create osmotic gradient
-Driving water reabsorption
Countercurrent mechanism contributes to concentrating urine: Thick ascending limb
Na+/k+/2Cl- symporter
NaCl pumped out of filtrate
interstitial fluid osmolarity increased
Countercurrent mechanism contributes to concentrating urine: Thin descending limb
Freely permeable to H2O
High interstitial osmolarity (NaCl and Urea) draw H2O out
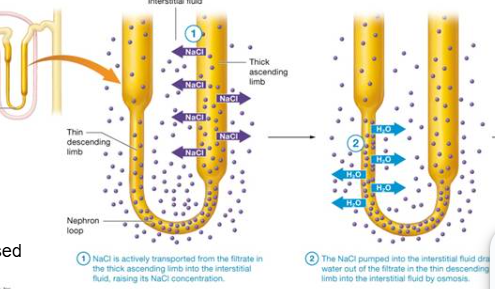
-Filtrate becomes _______ as it approaches bottom of nephron loop and _______ in the ascending limb
-High NaCl concentration in filtrate ____ symporter activity
-Symporter activity causes filtrate to become ______ as it ascends
-More activity near ____ and less as ascend the limb and NaCl _____ in filtrate
- more concentrated and less concentrated
-increases
-more dilute
-bottom and decreases
Medullary collecting duct and urea recycling contribute to
osmotic gradient
_____ contributes to interstitial osmolarity
Urea
-Urea _____ moves out of collecting duct (30-50% remains in filtrate and is excreted)
-Urea entering interstitium is_____ (maintains osmolarity); _____ highly involved
-passively
- recycled and Vasa recta
_____ is necessary to produce concentrated urine: Water moves according to gradient
Osmotic gradient
_____ and ______ maintain medullary osmotic gradient
Vasa recta and countercurrent exchange
Straight capillary bed surrounding nephron loop and collecting duct
Vasa Recta
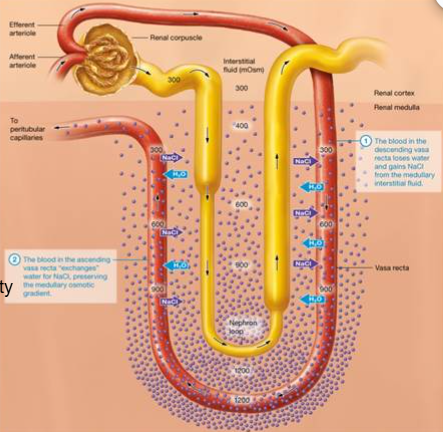
Countercurrent exchange…
-H2O and NaCl exchanged between nephron loop, interstitial fluid, and blood in vasa recta
-Sequence maintains interstitial osmolarity
-Drains into peritubular capillaires
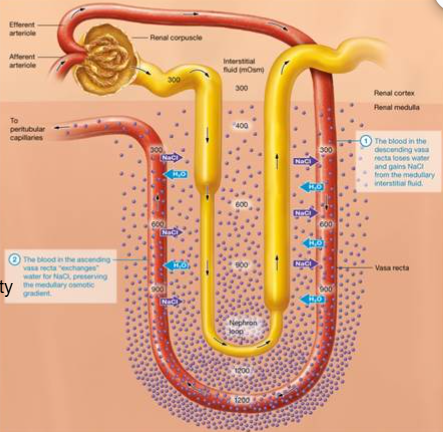
Why are capillaries around the loop and collecting duct advantageous? How? Result?
arrangements maintains interstitial osmolality at the same time that we are taking water away
How? As blood goes to medulla (opposite way of filtrate) it gets concentrated, go around loop (water is going out) pick up water and getting back to NaCl.
End Result: reclaimed water and most of salt back