D2.1 Mitosis*
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
All organisms need to produce new cells for
growth maintenance and reproduction
cell divition
A parent cell will divide to produce daughter cells
prokaryotes through
binary fission
eukaryotes through
mitosis - create somatic cells
meiosis - create gamates
cytokinesis
division of cytoplasm
cytokinesis in animals cells
Actin and myosin proteins form a contractile ring
Pinches the cell membrane together
Forms a cleavage furrow
Deepens and split the cytoplasm in two
cytokinesis in plant cells
Vesicles containing cell wall materials fuse to form a cell plate
Cell plate grows outwards until it reaches the existing cell wall
Fuses with existing cell wall to split the parent cell into two daughter cells
vesicle
phospholipid bilayer vacuole - use to transport substances
cellulose stored inside
division of cytoplasm is usually
equal
both daughter cells must what for cytokinesis
receive a mitochondrion and any other organelle that can only be made by dividing a pre-existing structure
ensure the same structure and the same function
unequal cytokinesis example
budding in yeast and oogenesis in humans
budding in yeast
Reproduce asexually through budding
Nucleus divides by mitosis
Small outgrowth (bud) on mother cell is formed
Receives one of the nuclei but only a small share of cytoplasm
Dividing wall constructed separating the two cells leaving a budding scar
Oogenesis in humans
Process of producing mature egg cells in humans
Begins with two divisions of a mother cell
First division produces one large cell with nearly all the cytoplasm and a small polar body
Large cell goes on to carry out the second division - unequal division again to form one large cell and one small polar body which does not develop further
what must occur before mitosis or meiosis
dna repllication
when does dna replication occur
interphase
After replication, each chromosome consists of
two genetically identical sister chromotids held tgt by a centromere
before nucelar division what happens
chromatin supercoils into condensed sturcture to enable efficient seperation of dna
chromatin
loosely packe dna with histones
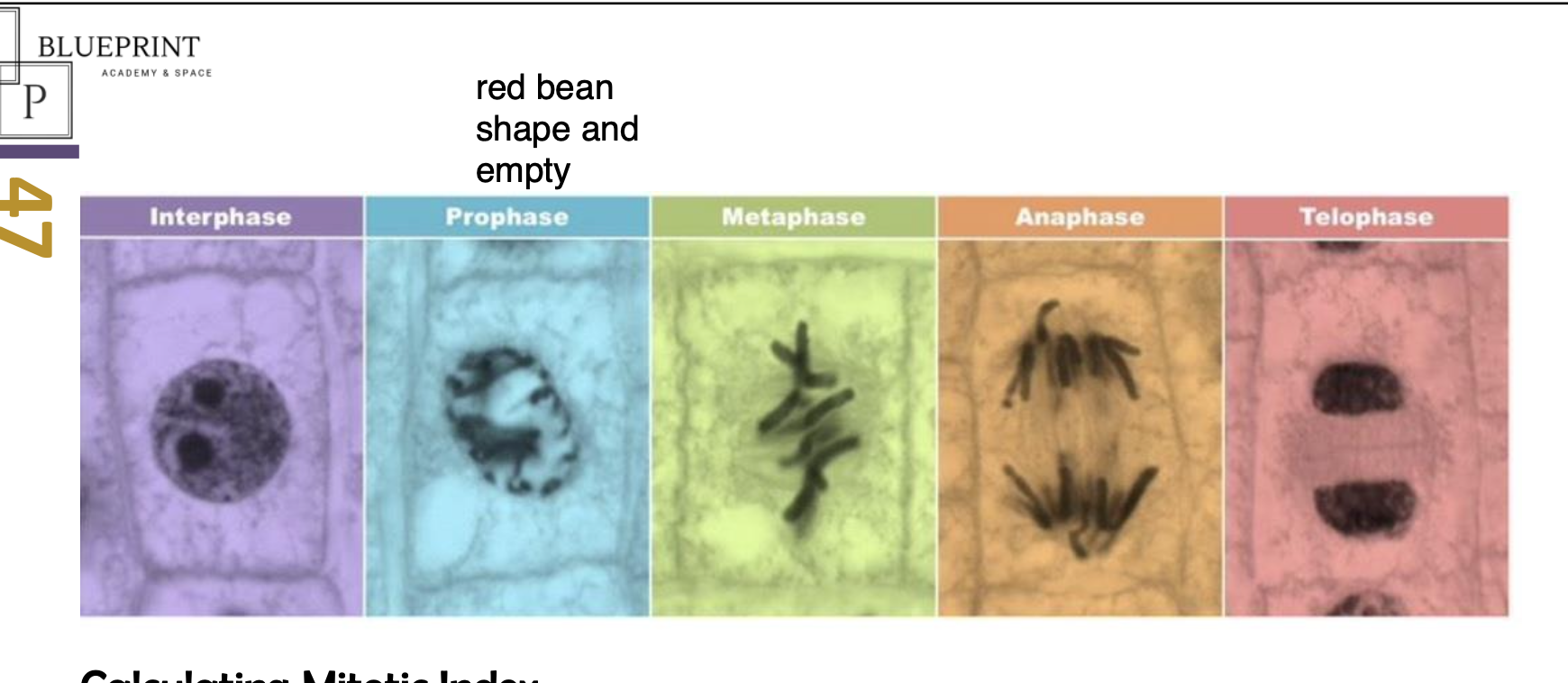
four phases of mitosis
prophase metaphase anaphase telophase
prophase
• DNA supercoil: chromatin condenses and becomes sister chromatids, which are visible
under the light microscope.
• Nuclear membrane is broken down and disappears
• Centrosomes move to the opposite poles of the cell and spindle fibres begin to form
metaphase
Spindle fibres (microtubules) from each of the centrosomes attach to the centromere of sister chromatids.
• Chromatids line up in the equator.
anaphase
• Contraction of the spindle fibres cause the separation of the sister chromatids
• The chromatids are now considered as chromosomes.
• Chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell.
telophase
• Chromosomes uncoil to become chromatin
• Spindle fibres break down and new nuclear membrane reform at opposite pole
cell elongates and prepares for cytokinesis
mitosis are diploid or haploid
diploid
interphase
prepration stage before mitosis and meiosis
containing g1 s g2
- G1 Phase:
obtain more nutrients—increase cytoplasm volume increase in cell size
s phrase
dna replication/synthesis
g2 phase
double the amount of organelle and protein synthesis
increase transcription and translation as well (cell size also increases).
any translation or transcription during mitosis?
no because dna supercoil
mutagens types
biological mutagens - viruses
chemical - cigarettes
physical - UV light
Protooncogenes
regulates the cell cycle - if mutagen - cause this gene to mutate - becomes oncogenes - leading to uncontrolled division
primary tumor
- Oncogenes / mutagen / Tumor suppressor gene
Secondary tumor -
migration of cancer cells (metastasis)
when transcription and translation occur
g2
movement of chromosomes include what 2 structures
microtubules and microtubule motors
Microtubule motors
Specialised proteins that bind to microtubules and hydrolyse ATP
Provide energy to move chromosomes to either pole of the cell
Microtubules
Long, thin, cylindrical fibrous proteins that form the spindle apparatus during cell division
Responsible for pulling chromosomes apart during division
before nuclear division, what chromatin does
supercoils into condensed structures to enable efficient separation of replicated DNA
mitosis is haploid or diploid
diploid
mitosis somatic cells or gametes
somatic cells
mitotic index
measure of the proliferation status of a cell population
if mitotic index too high
cancer
if mitotic index too low
low repair rate
photos of 4 stages
calculate mitotic index
cells in mitosis/total number of cells