long bones
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1st function of the bone
support - provide framework
2nd function of the bone
proetction - skull to brain, vertebrae to spinal cord, ribcage to heart/lungs
3rd function of the bone
anchorage - muscles attach to bones by tendons using bones as levers to move the body
4th function of the bone
mineral storage - resovoirs for calcium + phosphate and release them to the bloodstream
5th function of the bone
blood cell formation - hemtopolesisoccures in the red marrow
6th function of the bone
fat storage - stored in yellow marrow inside long bones
7th function of the bone
hormone production - produce osteocalcin
which bones are long bones
look like a traditional bone with a diaphysis (shaft) and epiphyses (ends) with medullary cavity inside.
examples of long bones
Humerus
Radius
Ulna
Metacarpals
Phalanges
Femur
Tibia
Fibula
Metatarsals
Phalanges
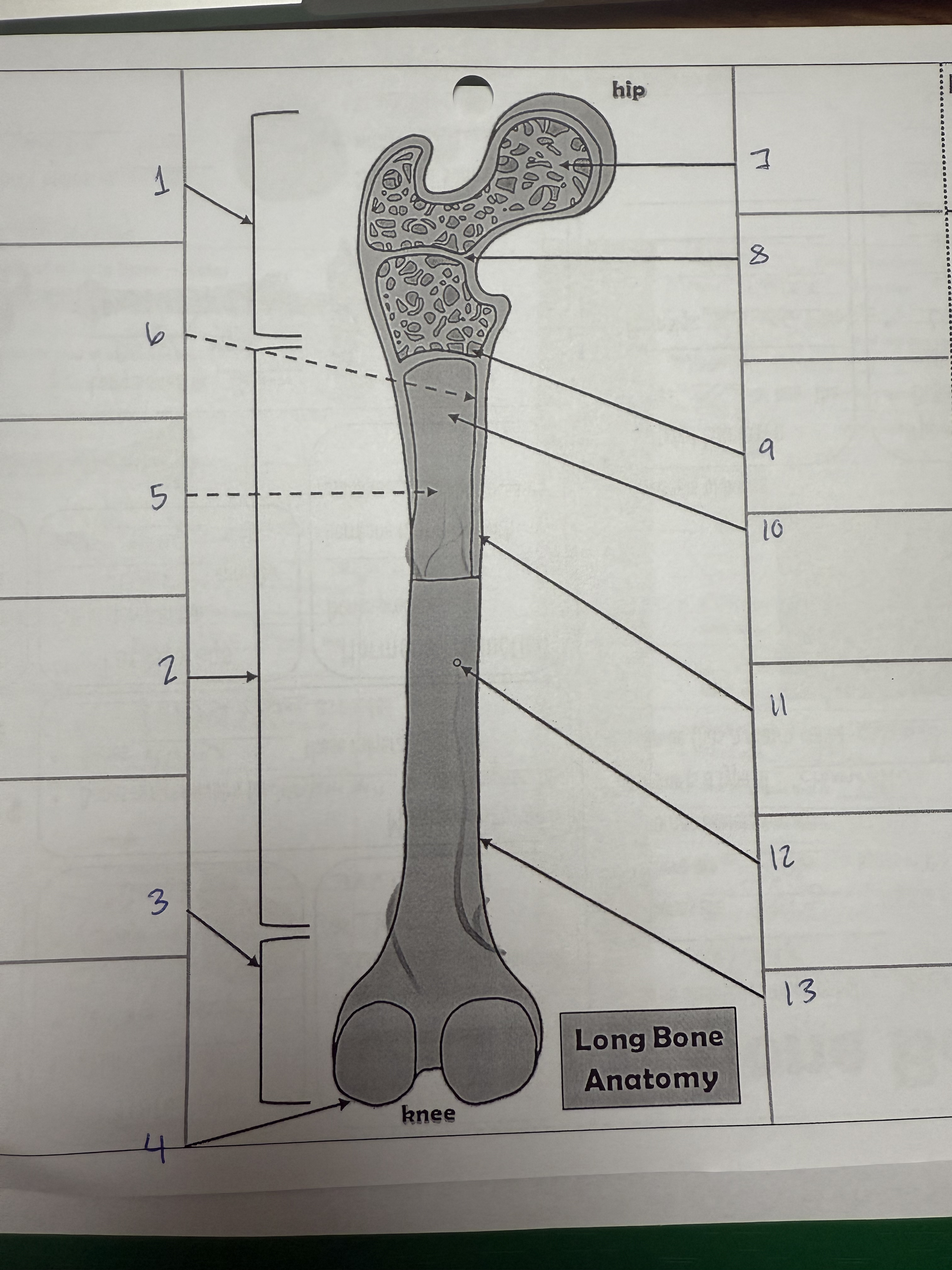
1
proximal epiphysis/metaphysis
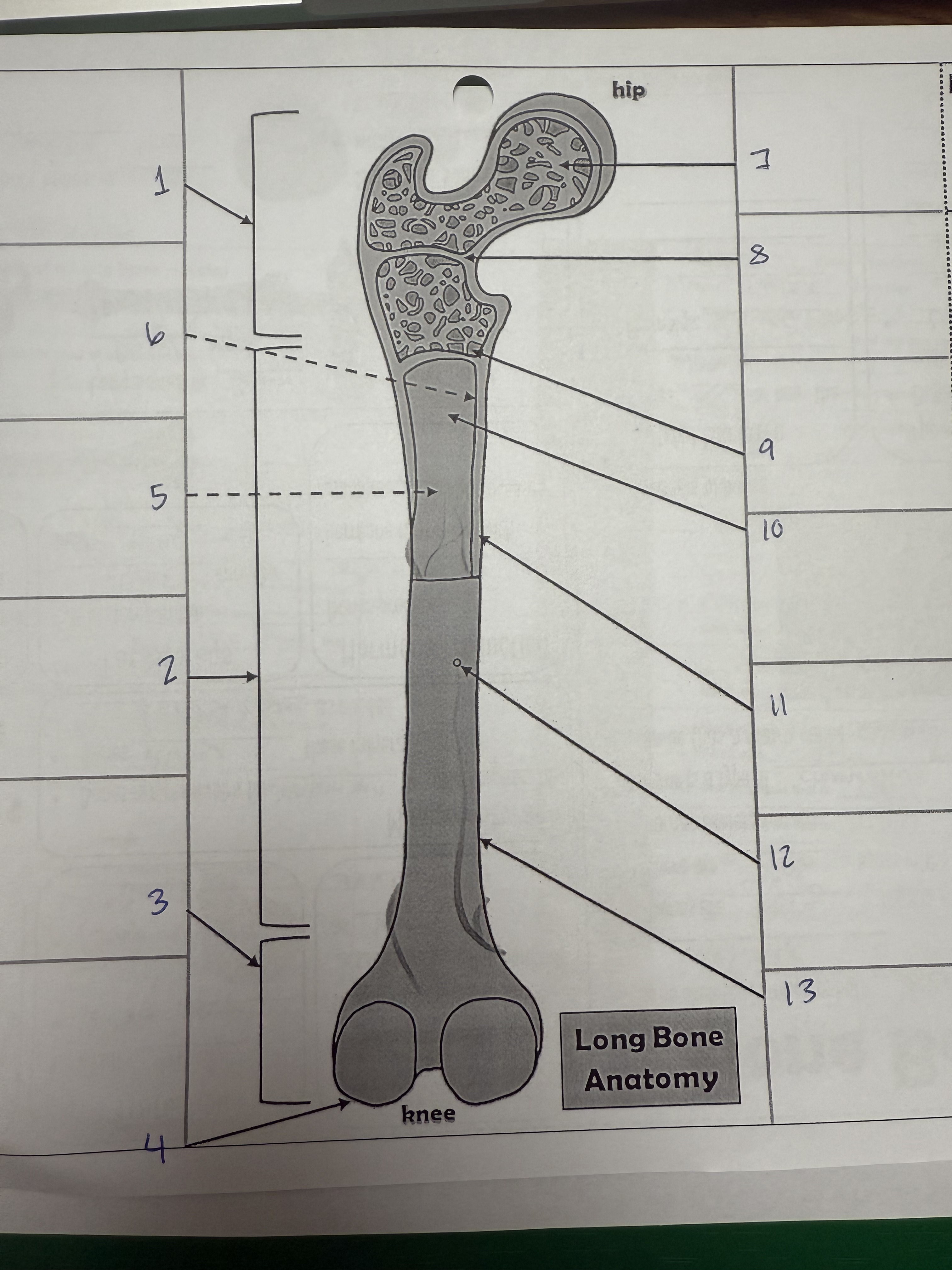
2
diphysis
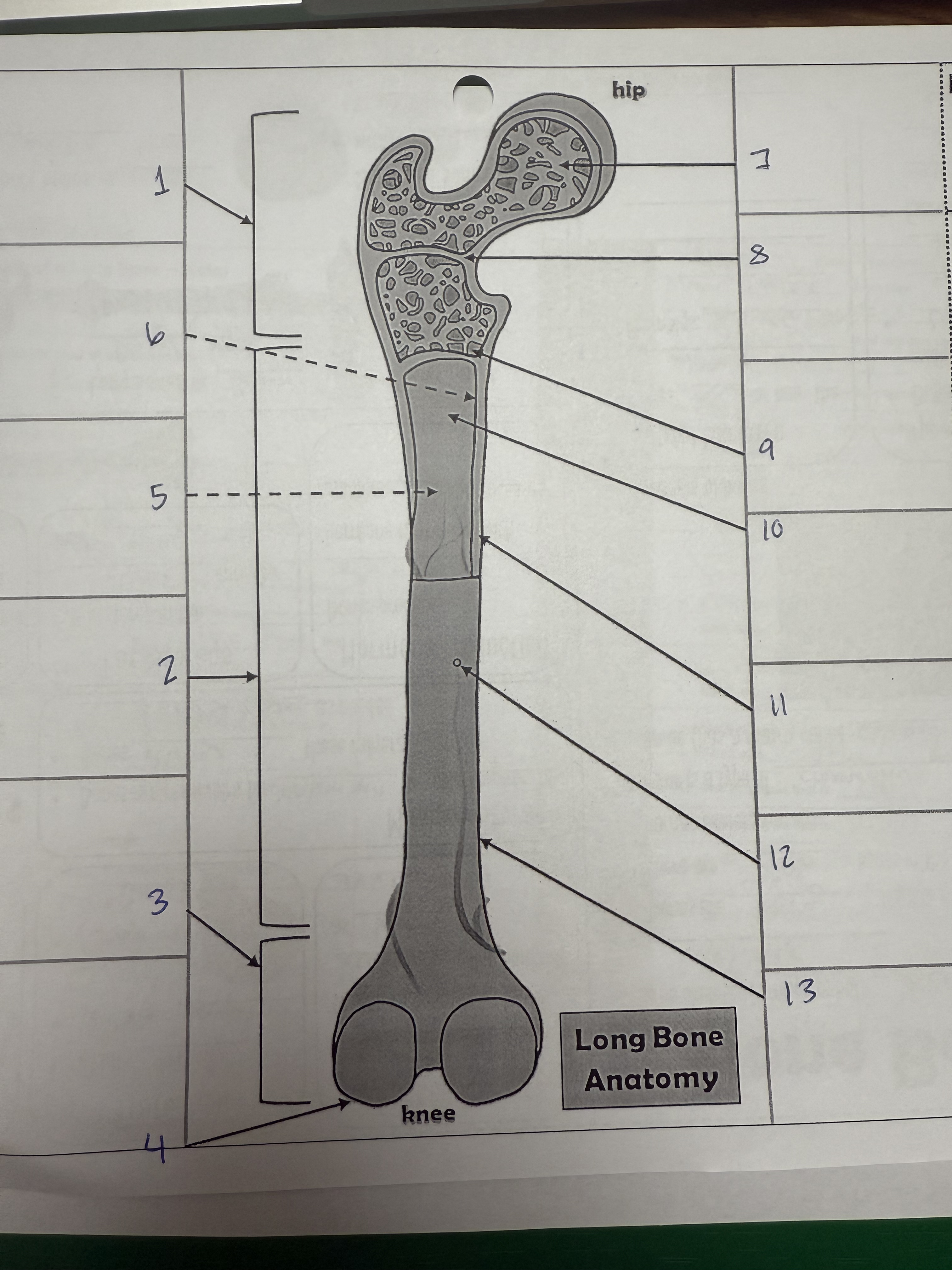
3
distal epiphysis/metaphysis
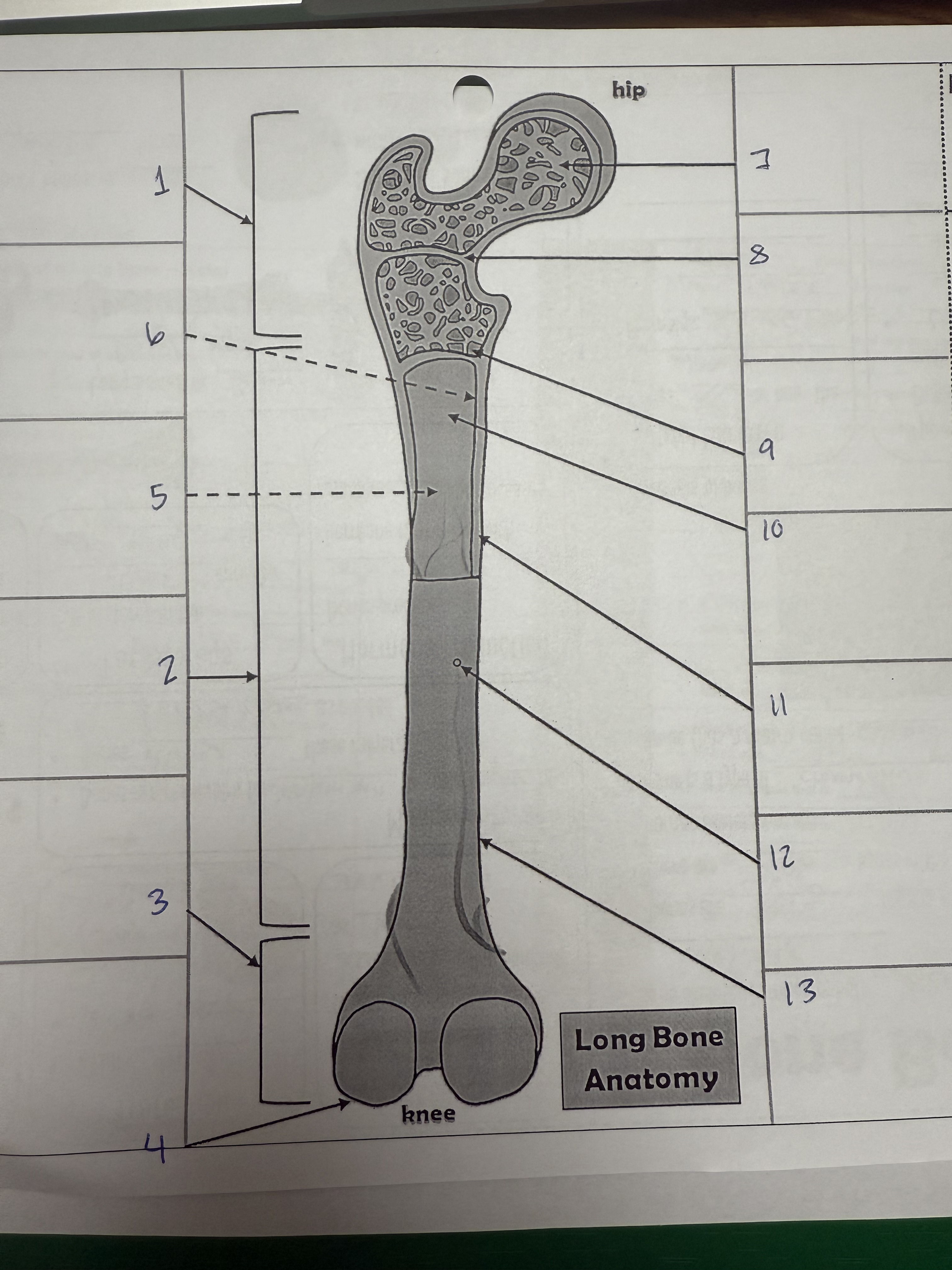
4
articular cartilage
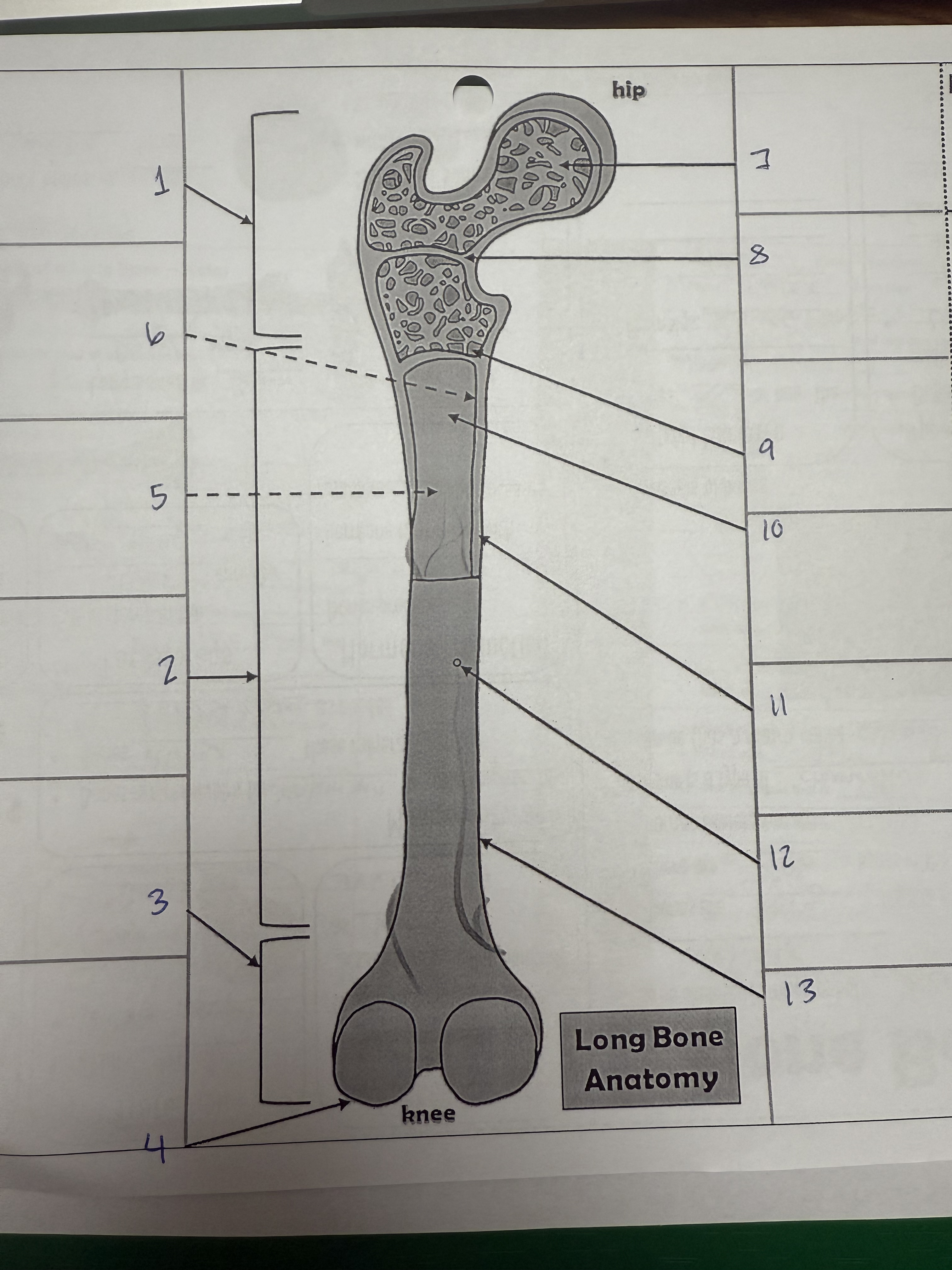
5
bone marrow adipose tissue
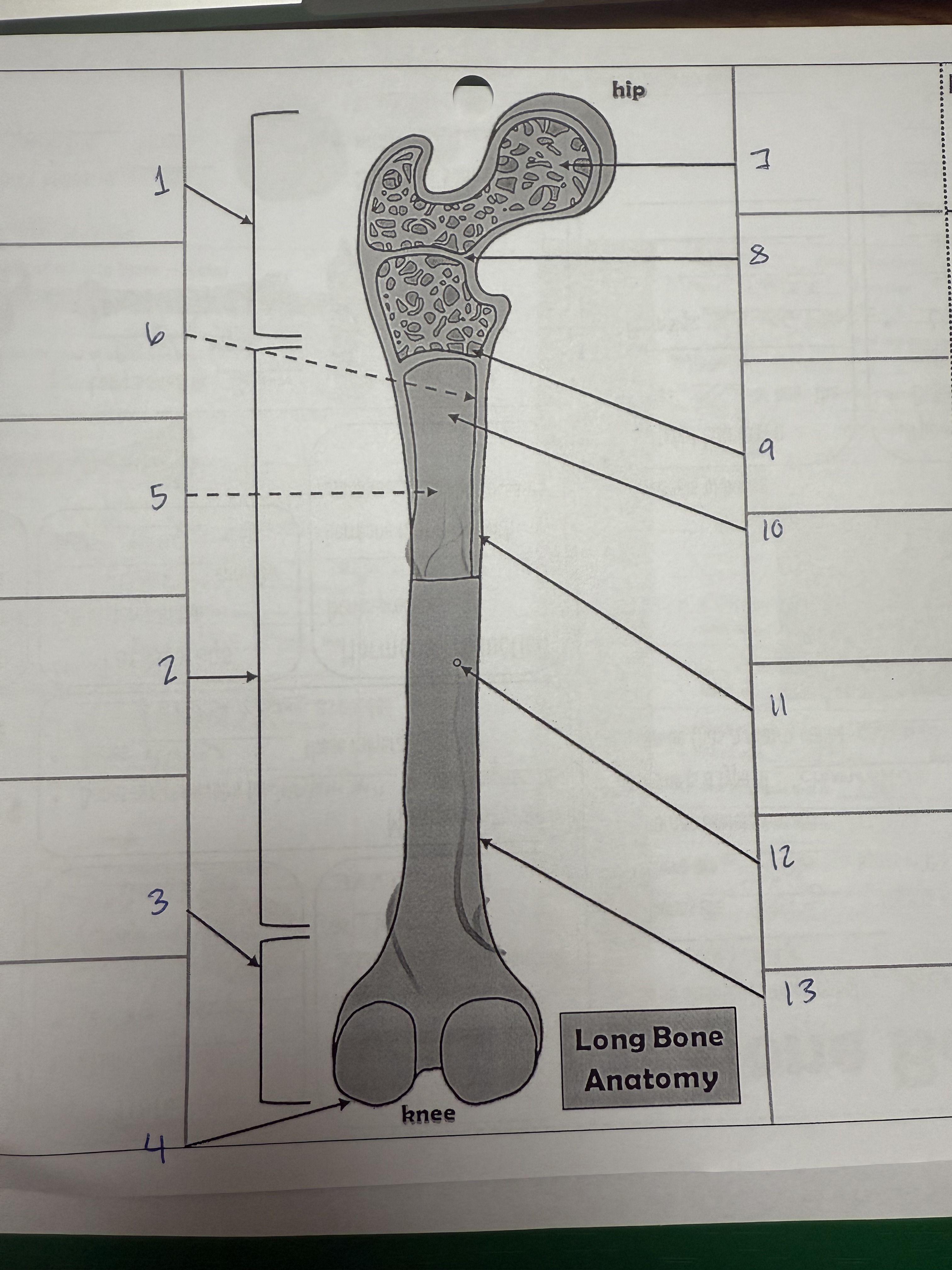
6
endosteum
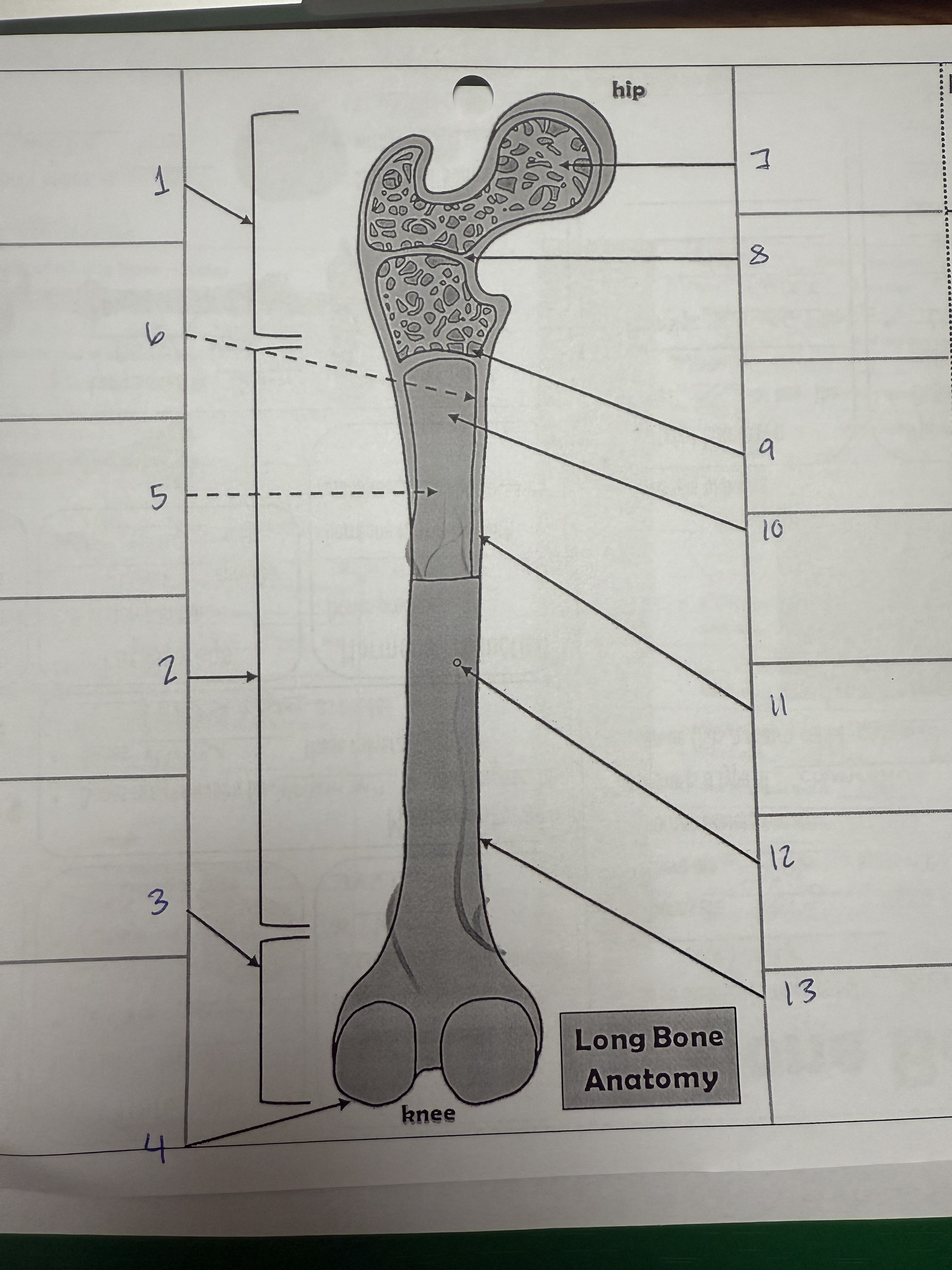
7
spongy bone
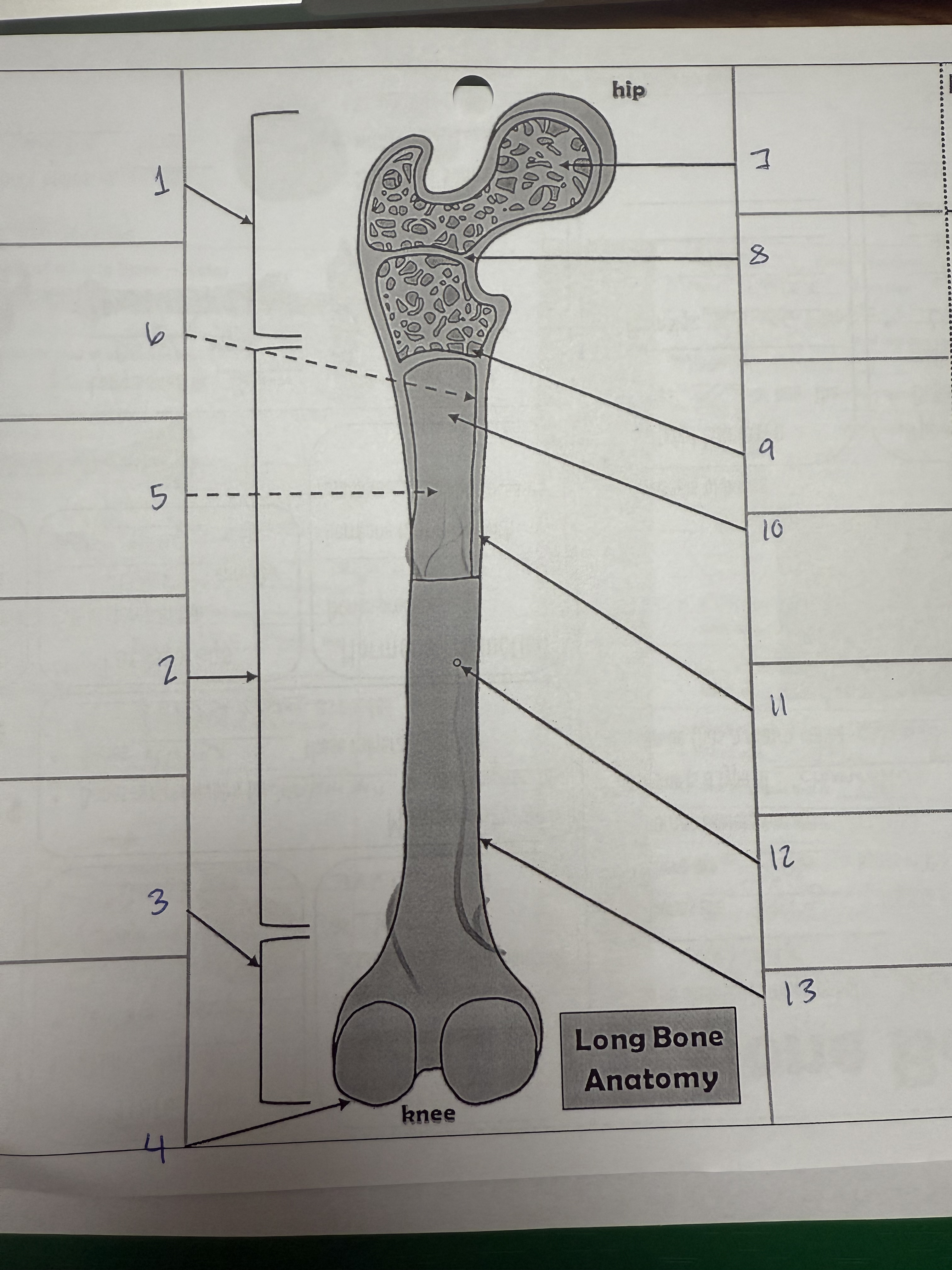
8
epiphyseal line
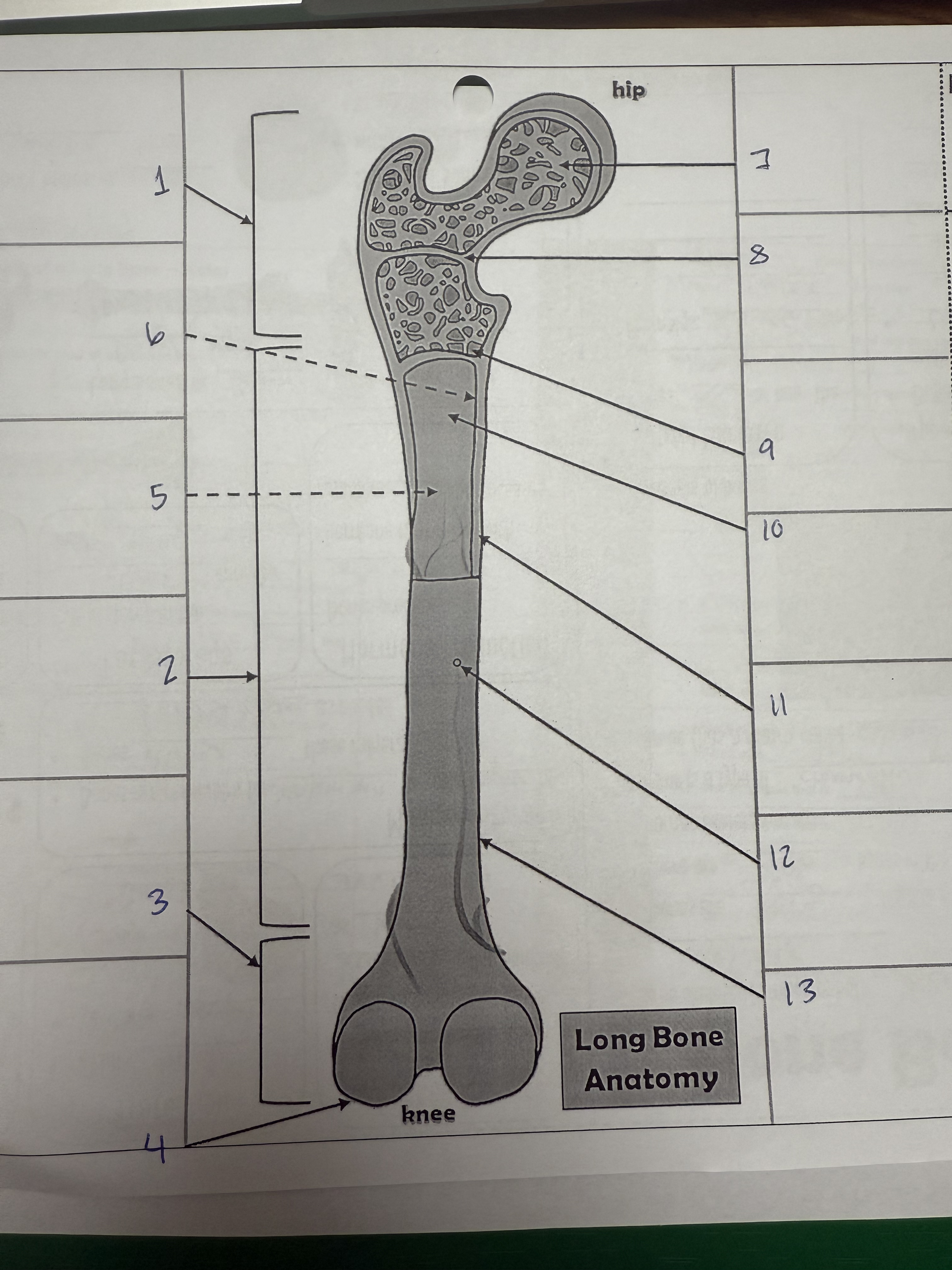
9
red bone marrow
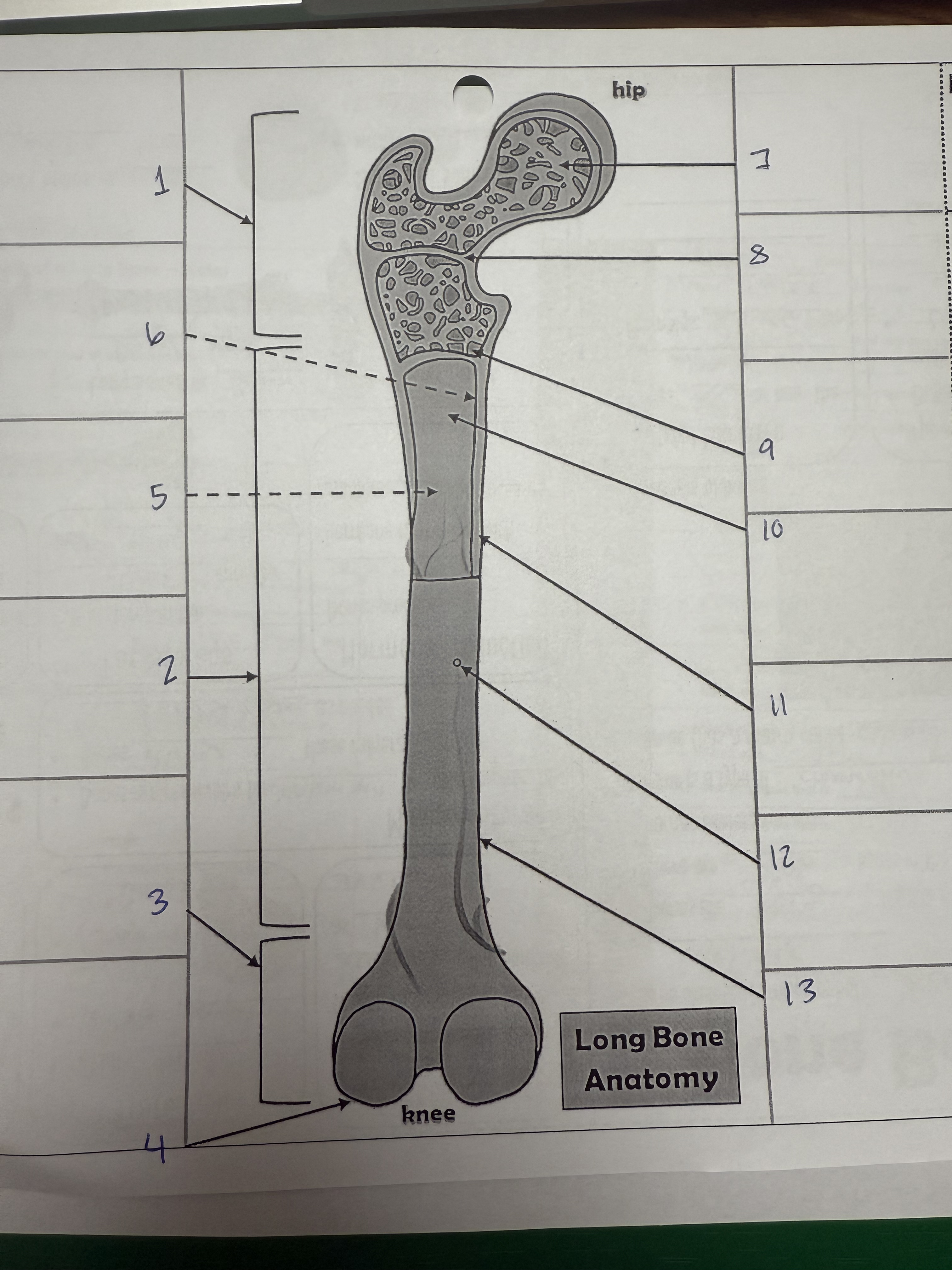
10
medullary cavity
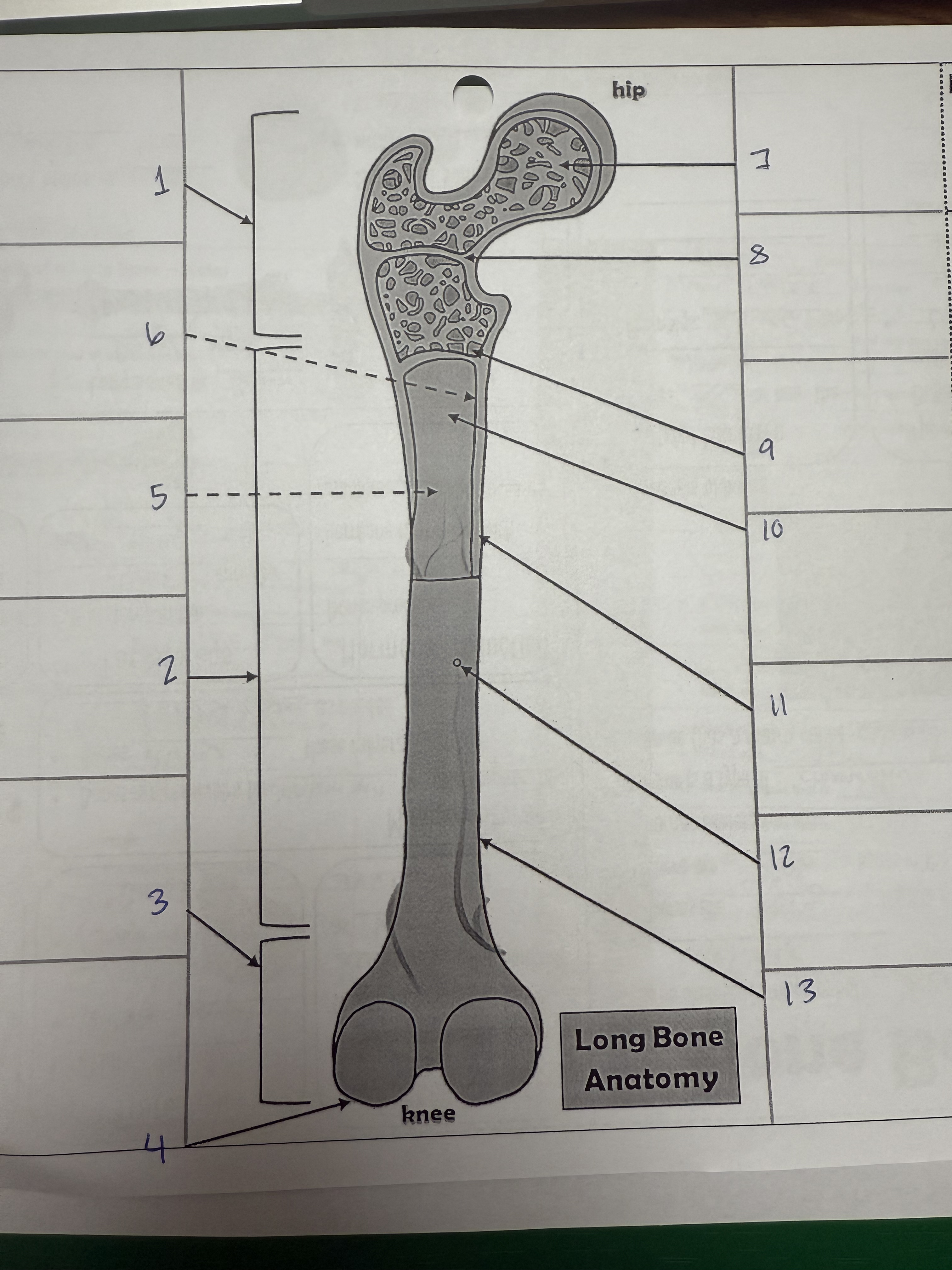
11
compact bone
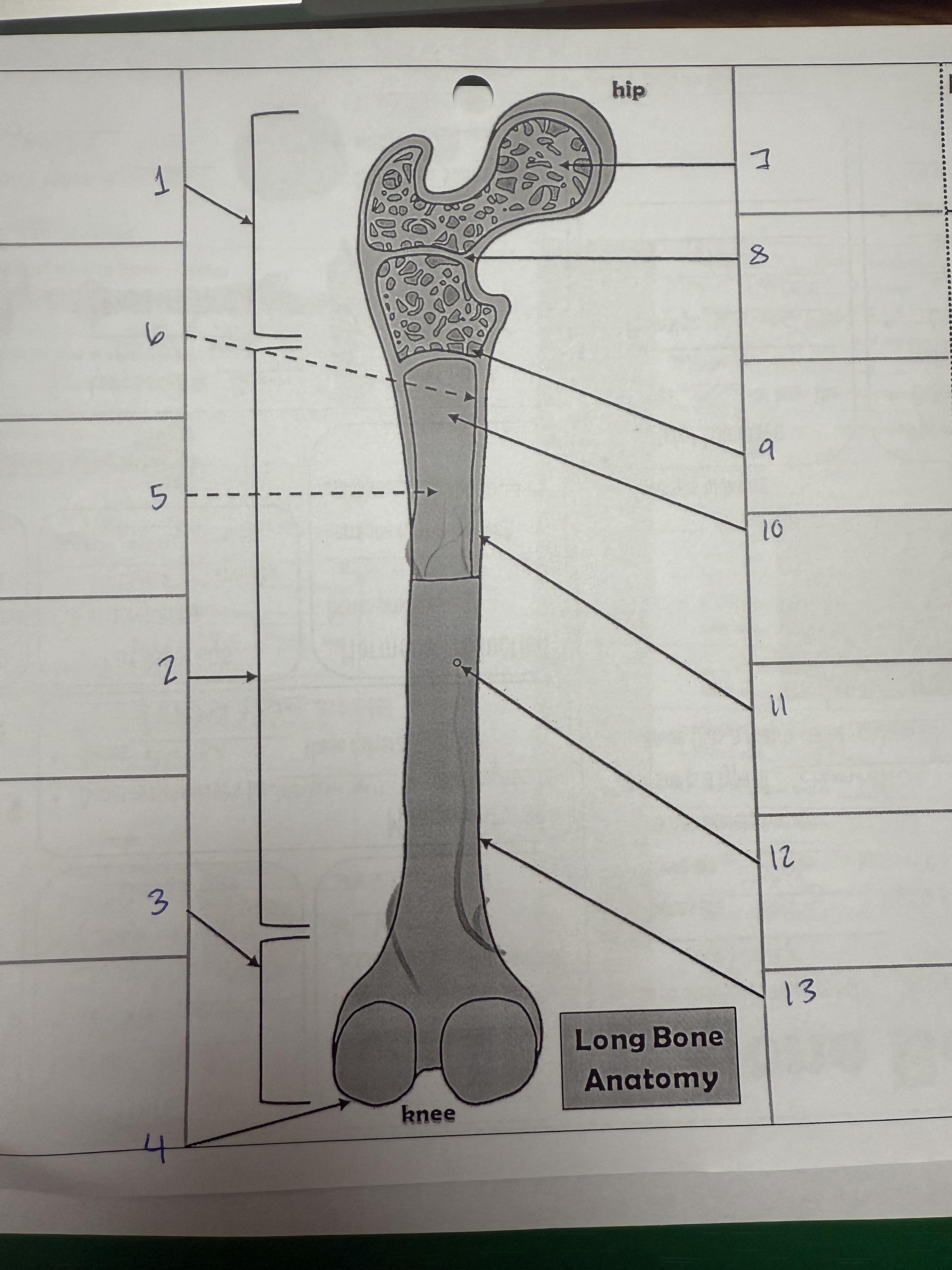
12
nutrient foramen/artery
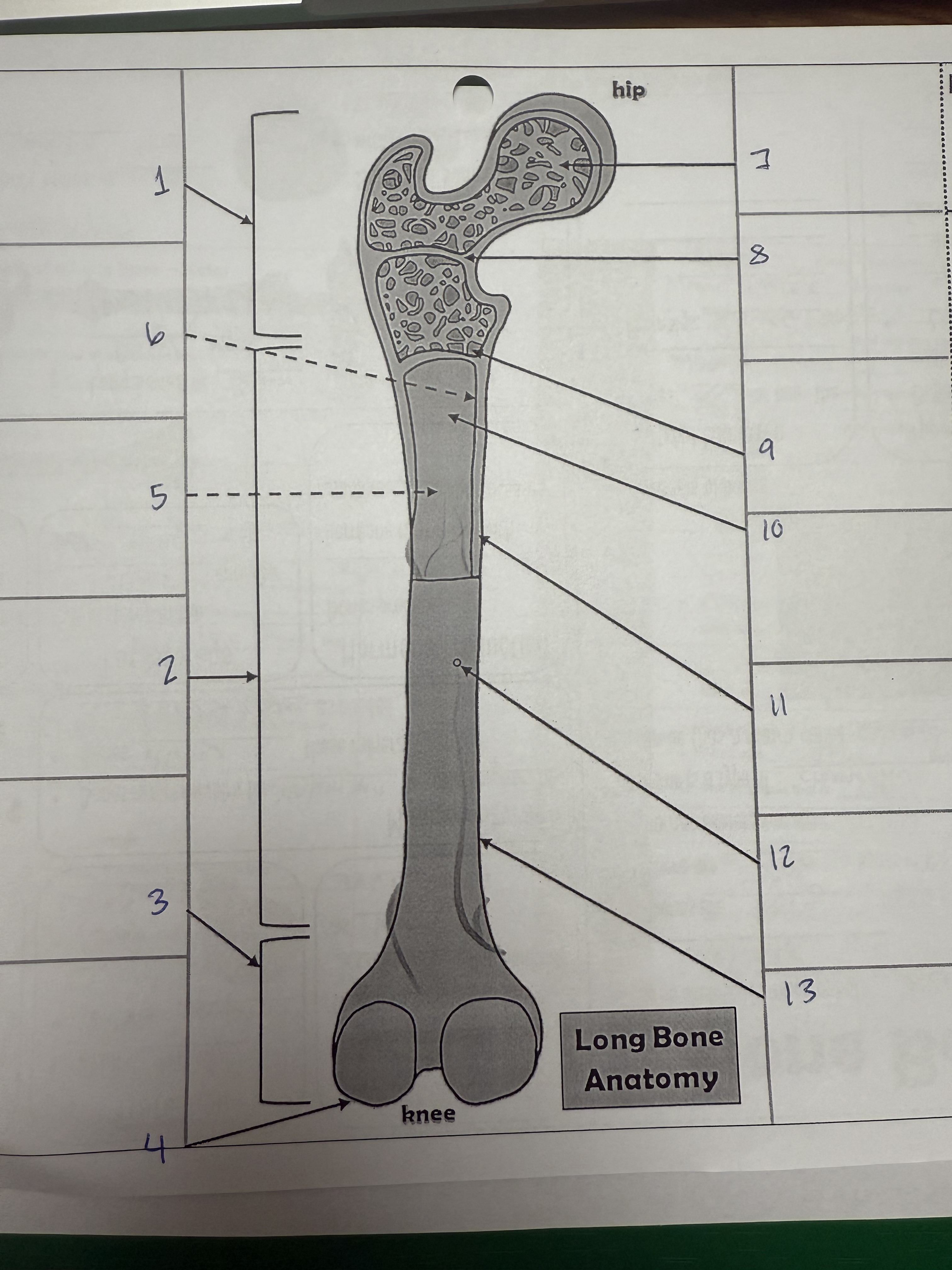
13
perosteum
Long bones
Support weight and facilitate movement; act as levers.
Short bones
Provide stability and some movement; cube-shaped.
Flat bones
Protect internal organs and provide broad surfaces for muscle attachment.
Irregular bones
Have complex shapes that protect organs or provide specialized support.
Sesamoid bones
Develop within tendons; protect tendons from stress and wear, and improve mechanical efficiency.