Net+, Chapter 3, Networking Connectors and Wiring Standards
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
coaxial
cable type, contains a center conductor made of copper that's surrounded by a plastic jacket with a braided shield over it
plenum-rated coating
a coating that allows a cable to be installed in plenum, essentially fire retardant, expensive
BNC
connector for thinnets
plenum
space between floors
thinnet
thin ethernet, 10Base2, same as thick coax but only 5mm
relevant coax cables
RG-59 and RG-6
RG-59
Cable television, low cost, short distance
RG-6
Cable television, cable modems, longer distances than RG-59; some power implementations
F-type connector
form of coaxial connector used for cable TV, screws to tighten to the interface, resembles RG-58
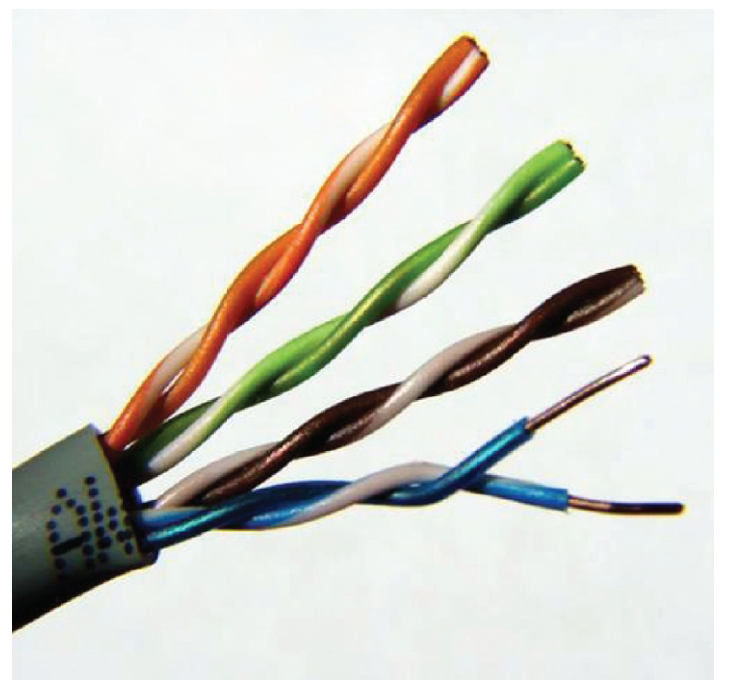
twisted pair
cable type, consists of multiple individually insulated wires that are twisted together in pairs
shielded twisted pair
STP, a metallic shield is placed around the pairs
unshielded twisted pair
UTP, does not have outer shielding, supports 10BaseT, 100BaseTX, 1000BaseTX, 10GBaseT, and 40GBaseT
fiber optic
cable type, transmits digital signals using light impulses rather than electricity, carried on glass or plastic core, immune to EMI and RFI
twinaxial
used for short-distance high-speed connections such as 10 and 40G Ethernet in data centers, bulkier, always shielded
direct attach copper
DAC, twinaxial child, has connectors at either end of a fixed-length ~26-28 AWG copper cable for direct device communication
AWG
the smaller the number, the thicker the wire
N<Sig>X
N=signal in megabits per sec, Sig=sig type (base or broad), X=unique identifier for cable scheme
crosstalk
when electromagnetic signals conducted on copper wires in close proximity cause interference
CAT1
Two twisted wire pairs (four wires), limited to 1 MHz frequency, voice grade only, not rated for data communication
CAT2
Four twisted wire pairs (eight wires), handles up to 4 Mbps with 10 MHz frequency limitation, now obsolete
CAT3
Four twisted wire pairs (eight wires) with three twists per foot, up to 16 MHz and 10 Mbps, obsolete for networks
CAT4
Four twisted wire pairs (eight wires), rated for 20 MHz, obsolete
CAT5
Four twisted wire pairs (eight wires), used for 100BaseTX (two pair wiring), rated for 100 MHz
CAT5e
Four twisted wire pairs (eight wires), recommended for 1000BaseT (four pair wiring), rated for 100 MHz, handles disturbance on each pair
CAT6
Four twisted wire pairs (eight wires), used for 1000BaseTX (two pair wiring), rated for 250 MHz
CAT6a
Rated to 500 MHz with improved crosstalk, allows 10GBaseT for up to 100 meters
CAT7
Allows 10 Gigabit Ethernet over 100 meters of copper, contains four twisted copper wire pairs
CAT8
Supports 25G and 40G Ethernet with a 30-meter distance, ideal for data center deployments
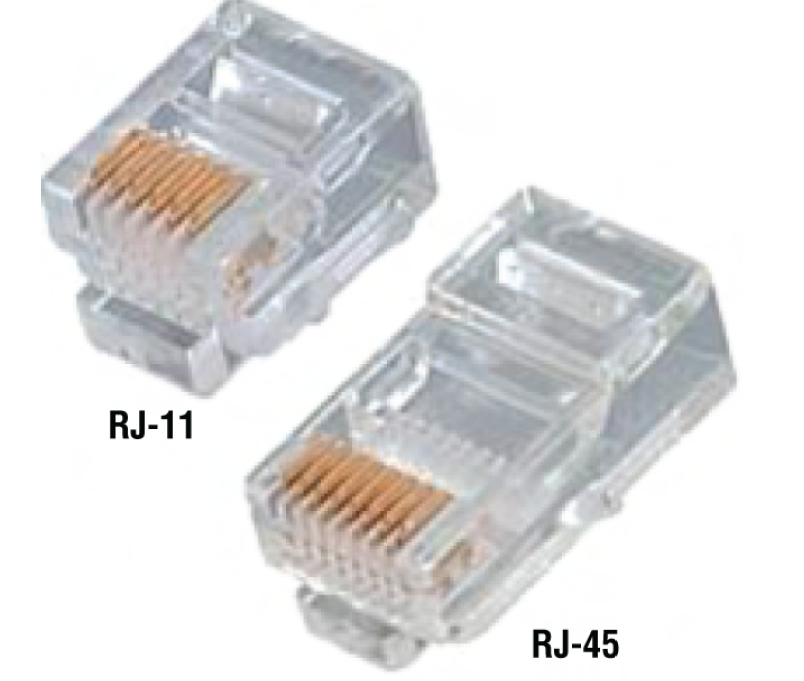
registered jack
RJ connector used with UTP; RJ-11 for phones (four wires), RJ-45 for LAN (four pairs, eight wires), RJ-48c used with T1, shielded (obsolete)
RJ-45 usage
mainly LANs up to 100 meters, unshielded
RJ-11 usage
home DSL connections, not LAN
multimode fiber
MMF, high speeds over medium distances (~3,000 feet), cladding focuses light back onto core
single mode fiber
SMF, used for longer distances (40–80 km depending on transceiver)
straight tip
ST, fiber connector, commonly used with SMF, positive locking mechanism
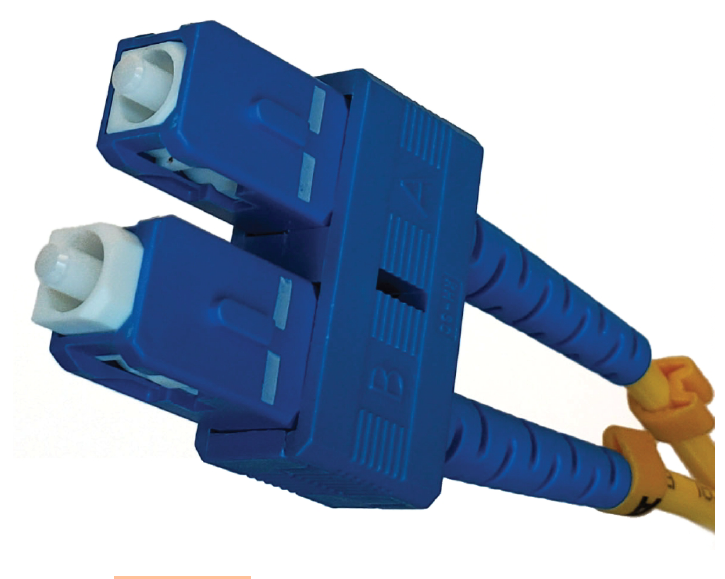
subscriber connector
SC, square fiber connector with a floating ferrule
ferrule
small, rigid tube (ceramic, stainless steel, or plastic) used to align and protect stripped fiber core or conductor
small form factor
connector style allowing more fiber optic terminations
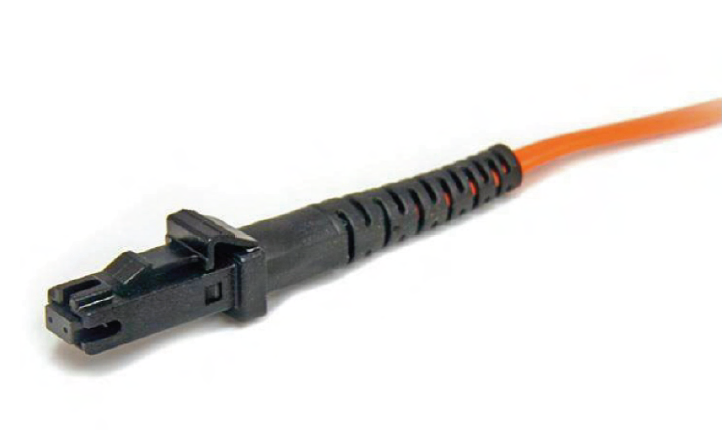
mechanical transfer registered jack (MT-RJ/MTRJ)
one-third size of SC/ST, TX and RX strands in one connector, keyed for single polarity, pre-terminated, easy to use
local connector (LC)
resembles RJ-style connector, popular for Fibre Channel adapters, easier to terminate, cable cannot be disassembled like SC
multi-fiber push on (MPO)
provides 2, 8, 12, or 24 fiber connections in a single connector, fans out to multiple LC connectors, 10–100 Gbps per connection
transmit strand
TX
receiver strand
RX
fibre channel
FC, very high-speed data transfer protocol (2–32 Gbps), delivers raw block data in order and lossless, often connects SANs, switches operate as one large switch
APC
connector end finish, green, angled physical contact, reduces decibel loss
UPC
connector end finish, blue, ultra physical contact, causes return loss
Fiber distribution panels (FDPs)
termination and distribution systems for fiber-optic cable facilities
fiber optic transceivers
can be unidirectional or bidirectional, device with transmitter and receiver
small form factor pluggable
SFP/SFP+, compact pluggable optical module, supports up to 16 Gbps
quad small form factor pluggable
QSFP, interfaces networking hardware to fiber or copper, data rates from 4x1 Gbps to 4x28 Gbps (QSFP28)
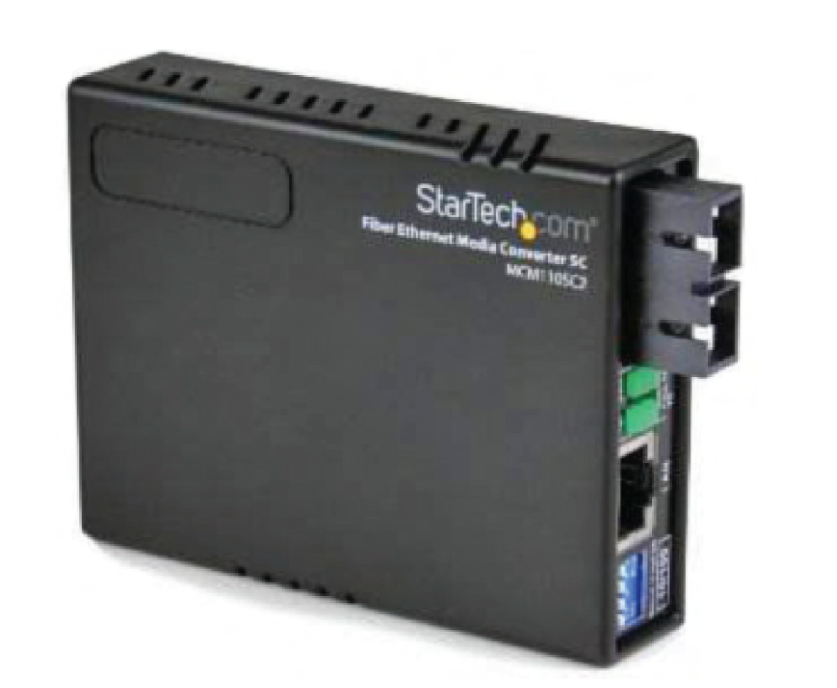
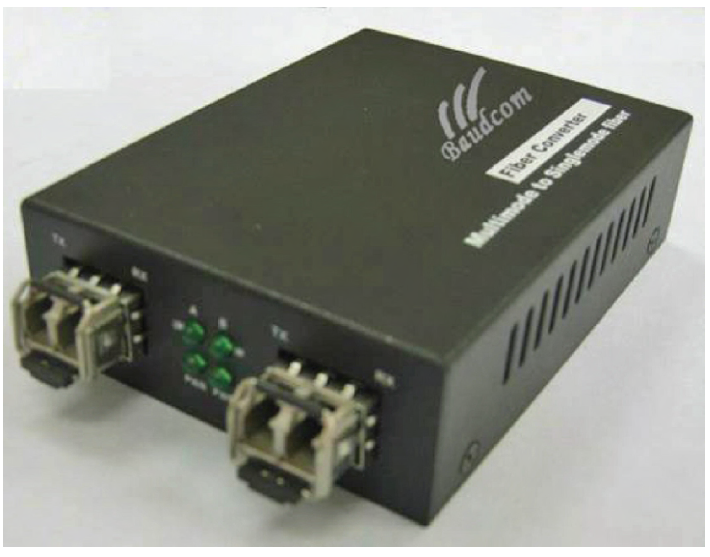
media converter
converts one media type to another (SMF to Ethernet, MMF to Ethernet, Fiber to Coaxial, SMF to MMF)
serial cables
RS-232, USB, DB-25
universal serial bus
USB
attenuation
degradation of a signal due to the medium and distance
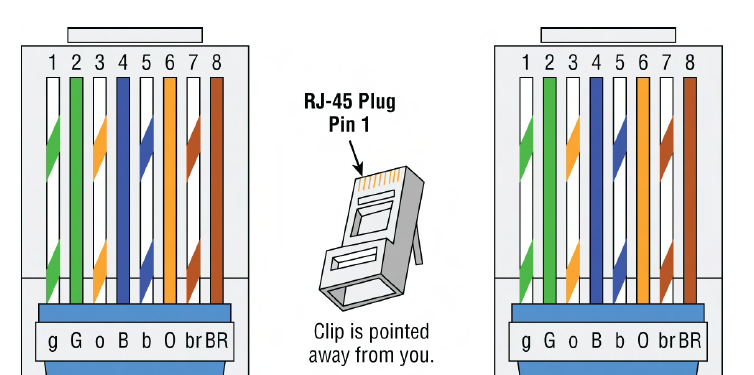
T568A
wiring standard (green/white, green, orange/white, blue, blue/white, orange, brown/white, brown) symmetrical
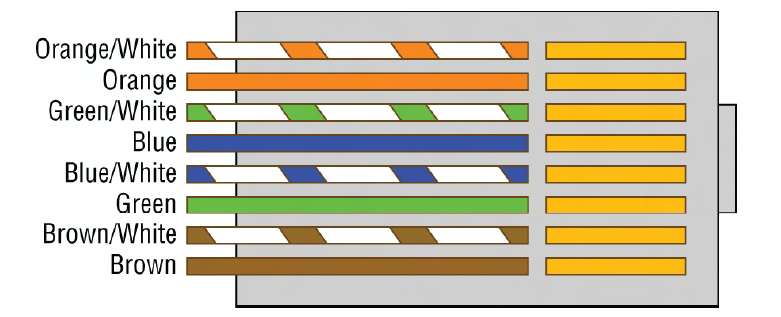
T568B
wiring standard (orange/white, orange, green/white, blue, blue/white, green, brown/white, brown) symmetrical
Straight-through
cable connects host/router to switch or hub
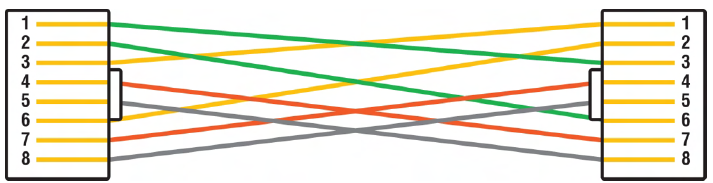
Crossover
cable connects switch to switch, hub to hub, host to host, hub to switch, router to host (T568A + T568B)
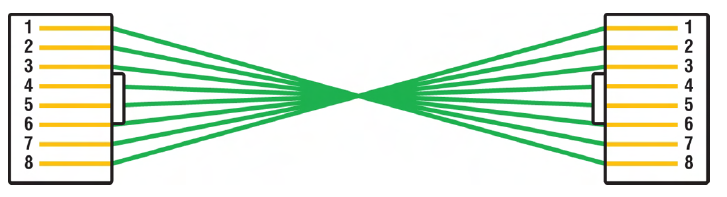
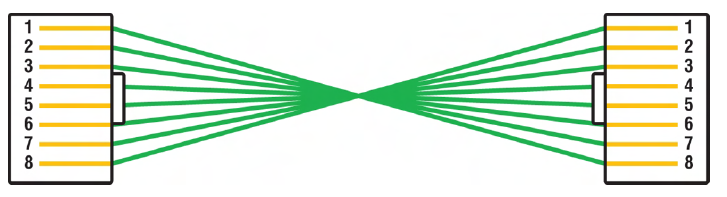
Rolled/rollover
1↔8, 2↔7, etc., used to connect host EIA-TIA 232 interface to router console serial COM port
wiring standard tip
45 and 78 positions stay the same between standards (B/b and BR/br)
UTP Gigabit Wiring (1000BaseT)
1↔3, 2↔6, 4↔7, 5↔8 both ways
CSU/DSU connection
requires T1 crossover cable
main distribution frame (MDF)
wiring point used as reference for telephone lines, WAN termination point
intermediate distribution frame (IDF)
located in equipment/telecom room, connected to MDF, provides flexibility for distribution, sturdy metal rack holding bulk cables
25-pair cable
consists of 25 wire pairs inside one jacket, mainly for telephone cabling, backbone, and cross-connects, reduces cable clutter
feeder cable
supplies signal to many connected pairs
66 block
standard termination block using 25-pair cable, contains 50 rows, standard for voice cabling
110 block
newer wiring distribution point, wires punched down on one side, RJ-11/RJ-45 connections on the other, supports up to 1 Gbps with Cat6+
bix block
punch-down block, terminates up to 25 cable pairs, slip-in fitting, no pre-stripping required
demarc
last point of responsibility for service provider
smart jack
also called network interface device (NID) or network interface unit (NIU)
CAT 5e UTP cable
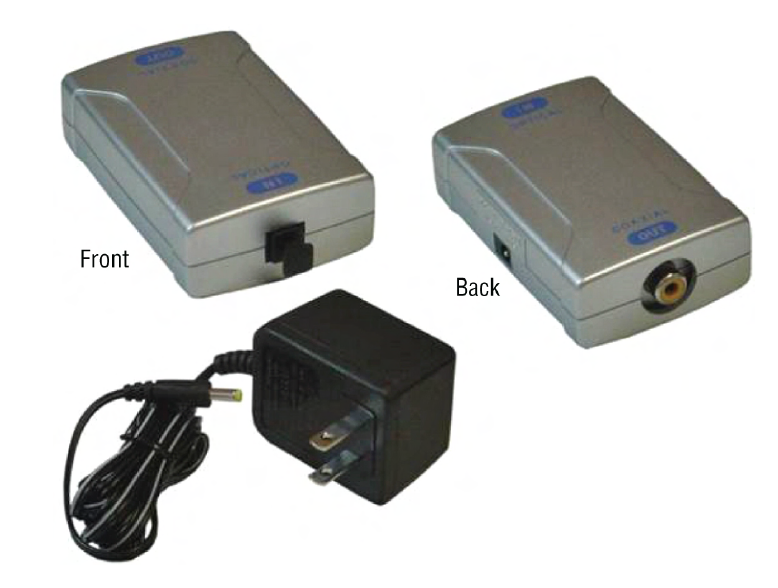
fiber to coaxial

MT-RJ connector

multimode fiber to ethernet

registered jack connectors

RJ-45 connector, T568B standard
rolled ethernet cable
SC connector

ST connector

single mode to multimode fiber

T568B
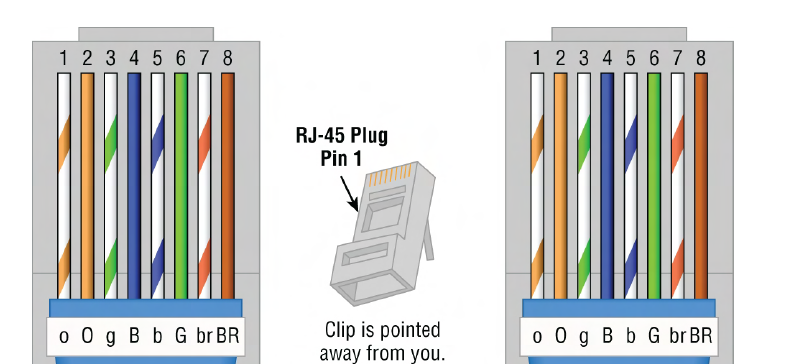
T568A
UTP gb crossover ethernet cable
rolled ethernet cable