CHEM: LEC 1 Atoms & Bonds
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Basic Atomic Model
A model that describes the structure of an atom, including energy levels and electron configuration.
Mass Number = number of protons + neutrons
what is the “A” equivalent to in the diagram
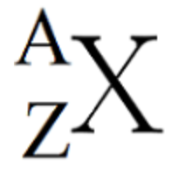
number of protons
what is the “Z” equivalent to in the diagram
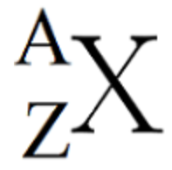
element symbol
what is the “X” equivalent to in the diagram
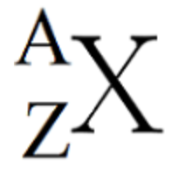
Valence Electron
The outermost electron of an atom that is involved in chemical bonding.
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons.
Ions
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of valence electrons, resulting in a charge.
Ionic Bond
A type of chemical bond formed through the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, typically between a metal and a nonmetal.
Covalent Bond
A type of chemical bond formed by the sharing of electrons between two nonmetals.
Binary Compounds (Potassium Oxide)
Compounds composed of two different elements, typically named with the cation first followed by the anion. (Name K2O)
Ternary/Tertiary Compounds (Sodium Phosphate)
Compounds composed of three different elements, named similarly to binary compounds. (Name Na3PO4)
Binary Acids (Hydrochloric Acid)
Acids that consist of hydrogen and a nonmetal, named with the prefix "hydro" and the suffix "ic." (HCl)
Acids with Anion in "ate" Ending (Sulfuric Acid)
Named by changing the "ate" to "ic" and adding "acid." (H2SO4)
Acids with Anion in "ite" Ending (Nitrous Acid)
Named by changing the "ite" to "ous" and adding "acid." (HNO2)
Covalent Compounds (Carbon dioxide)
Compounds formed between nonmetals, often using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms. (CO2)
Single Displacement Reaction
A reaction where one element replaces another in a compound.
Double Displacement Reaction
A reaction where the ions of two compounds exchange places.
Combination Reaction/Synthesis
A reaction where two or more reactants combine to form a single product.
Decomposition Reaction/Analysis
A reaction where a single reactant breaks down into two or more products.
Solubility
The ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent, such as water.