CHEM: LEC 1 Atoms & Bonds
DISREGARD THIS NOTE
Chemistry 1 Study Guide
Basic Chemistry
Basic Atomic Model Element Notation |
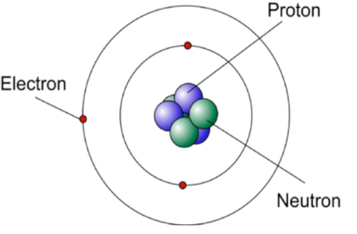 Rings = Energy Levels (can be labeled 1, 2, … or K, L, …) Outermost Electron = Valence Electron Outermost Ring = Valence Shell X = C = Element Symbol A = 12 = Mass Number = # of protons + # of neutrons Z = 6 = # of protons = # of electrons |
Electron Configuration
Sublevels Orbitals Number of Electrons |
s 1 2 |
p 3 6 |
d 5 10 |
f 7 14 |
Oxidation Numbers
Description Rules Examples | |
Knowing the oxidation number and the charge of one of the elements in the compound allows us to solve for the charge of the other element, Charge of H = +1 Charge of O = -2 (except for in hydrogen peroxide)
|
Isotopes vs. Ions
Isotopes Ions | ||
Same element but with a different number of neutrons Same element but with a different number of valence electrons | ||
|
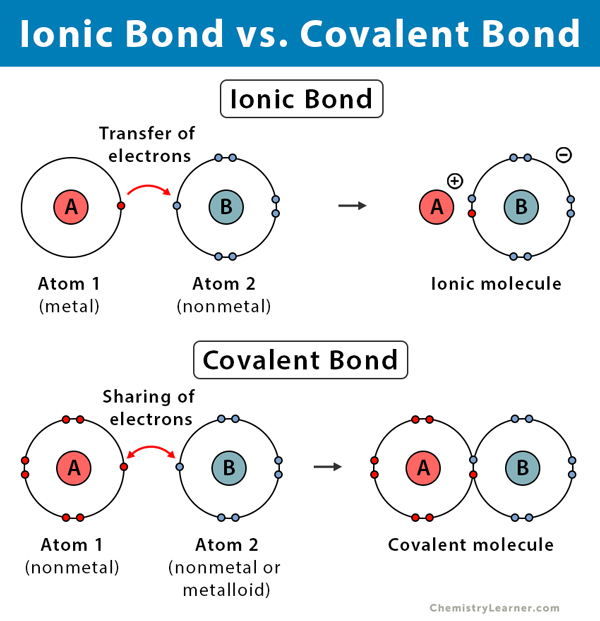
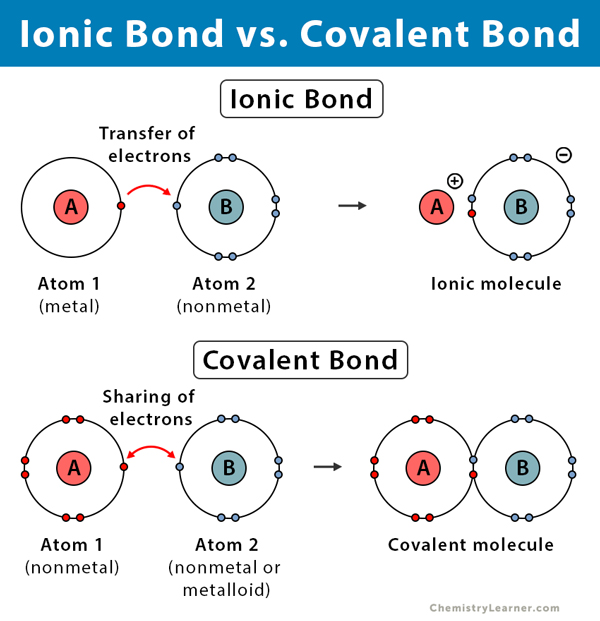
Types of Bonds
Ionic Bond Covalent Bond |
Electron donating; between one nonmetal and metal Electron sharing; between two nonmetals |
  |
Naming Compounds
Description Rule Example |
Binary Compounds (Compounds with two elements) Cation + Anion in ide ending K+ = Potassium (Cation) O2- = Oxygen (Anion) K2O = Potassium Oxide |
Ternary/Tertiary Compounds (Compounds with three elements) Cation + Anion Na+ = Sodium (Cation) PO43- = Phosphate (Anion) Na3PO4 = Sodium Phosphate |
Binary Acids (Anion is NOT a compound) Hydro + Anion in ic ending + Acid H+ = Hydrogen (Cation) Cl- = Chlorine (Anion) HCl = Hydrochloric Acid |
Acids with Anion in ate Ending Anion in ic ending + Acid H+ = Hydrogen (Cation) SO42- = Sulfate (Anion) H2SO4 = Sulfuric Acid |
Acids with Anion in ite Ending Anion in ous ending + Acid H+ = Hydrogen (Cation) NO2- = Nitrite (Anion) HNO2 = Nitrous Acid |
Covalent Compounds (Compounds Composed of Only Nonmetals) Use mono, di, tri, etc. C = Carbon O = Oxygen CO = Carbon Monoxide CO2 = Carbon Dioxide |
Elements with Different Ions/Different Oxidation Numbers Lower Oxidation Number = ous ending Higher Oxidation Number = ic ending Fe2+ = Ferrous Fe3+ = Ferric Pb2+ = Plumbous Pb4+ = Plumbic |
Compounds with a Different Number of Oxygen Lower Oxygen Number = ite ending Higher Oxygen Number = ate ending PO33- = Phosphite PO43- = Phosphate |
Types of Reactions
Type Description Example |
Single Displacement Reaction Only one element in the compound is replaced by another 2 Al (s) + 6 HCl (g) → 2 AlCl3 (aq) + 3 H2 (g) |
Double Displacement Reaction Reactants and products switch their ions 3 NaOH (aq) + FeCl3 (aq) → 3 NaCl (aq) + Fe(OH)3 (s) |
Combination Reaction/Synthesis Two reactants result in one product Na2O + H2 → 2 NaOH |
Decomposition Reaction/Analysis One reactant results in two products 2KClO3 (s) → 2 KCl (s) + 3 O2 (g) |
EXP 2: SOLUTIONS, ACIDS, AND BASES
Chemical Formulas
Chemical Name Chemical Formula Chemical Name Chemical Formula |
Iodine I2 Ferric Chloride FeCl3 |
Sodium Thiosulfate Na2S2O3 Chromic Sulfate Cr2(SO4)3 |
Carbon Tetrachloride CCl4 Calcium Chloride CaCl2 |
Chloroform CHCl3 Zinc Nitrate Zn(NO3)2 |
Ethyl Alcohol CH3CH2OH Aluminum Sulfate Al2(SO4)3 |
Glycerin C3H8O3 Ammonium Hydroxide NH4OH |
Blue Vitriol (or Cupric Sulfate) CuSO4 Acetic Acid CH3COOH |
Sodium Hydroxide NaOH Hydrochloric Acid HCl |
Ammonium Chloride NH4Cl Aluminum Shavings Al |
Marble Chips CaCO3 |
A: Solubility of Solids in Liquids
Substance Iodine Sand Table Salt Sugar |
Solubility in Water Slightly Soluble (Dissolved faster in chloroform) Insoluble Soluble Soluble |
B: Solubility of Liquids in Liquids
Substance Ethyl Alcohol (CH3CH2OH) Glycerine Oil |
Solubility in Water Mixes with water meaning it is a miscible liquid Does not mix with water, sinks to the bottom Does not mix with water, remains at the top |
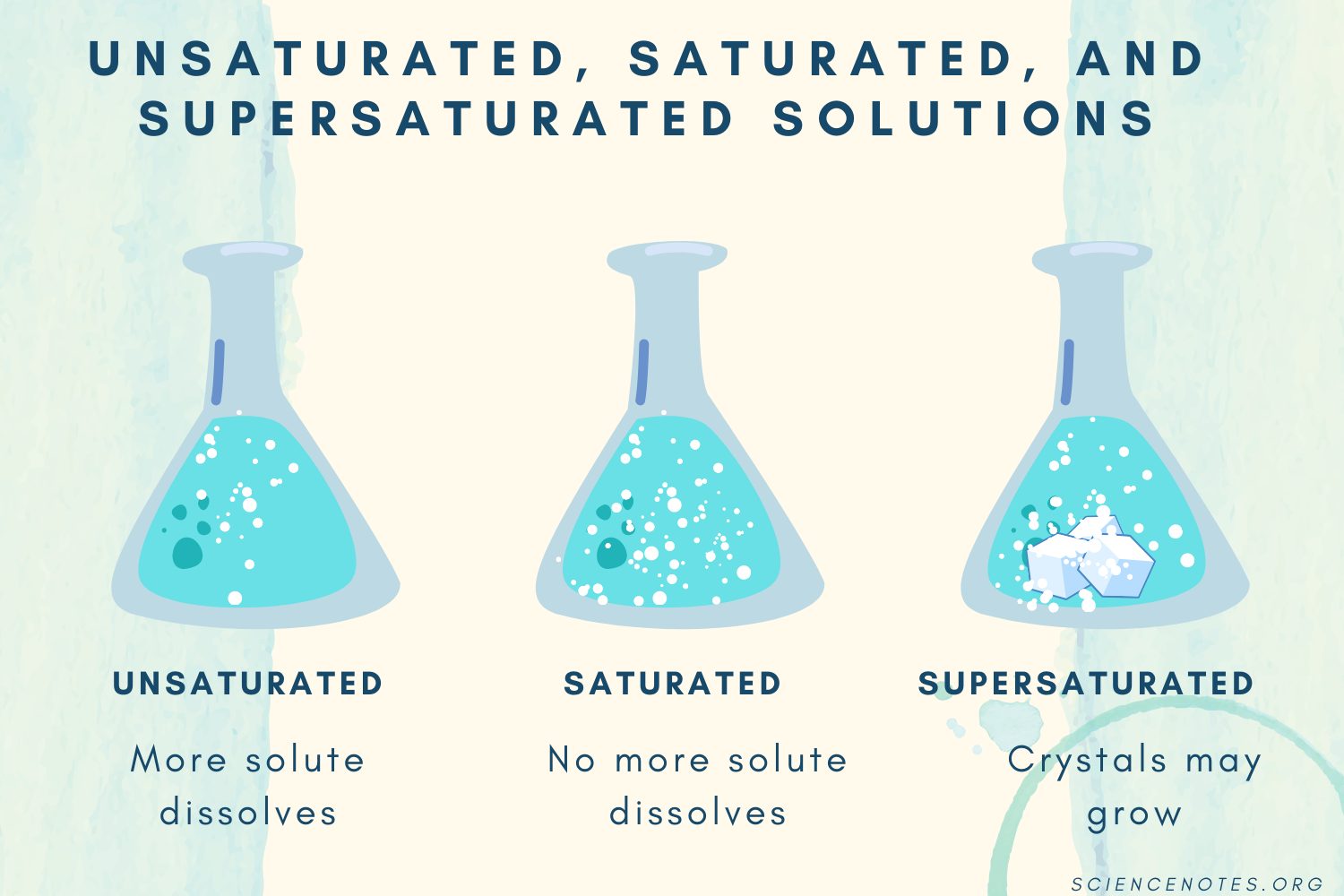
C: Unsaturated, Saturated, & Supersaturated Solutions
Unsaturated Saturated Supersaturated |
   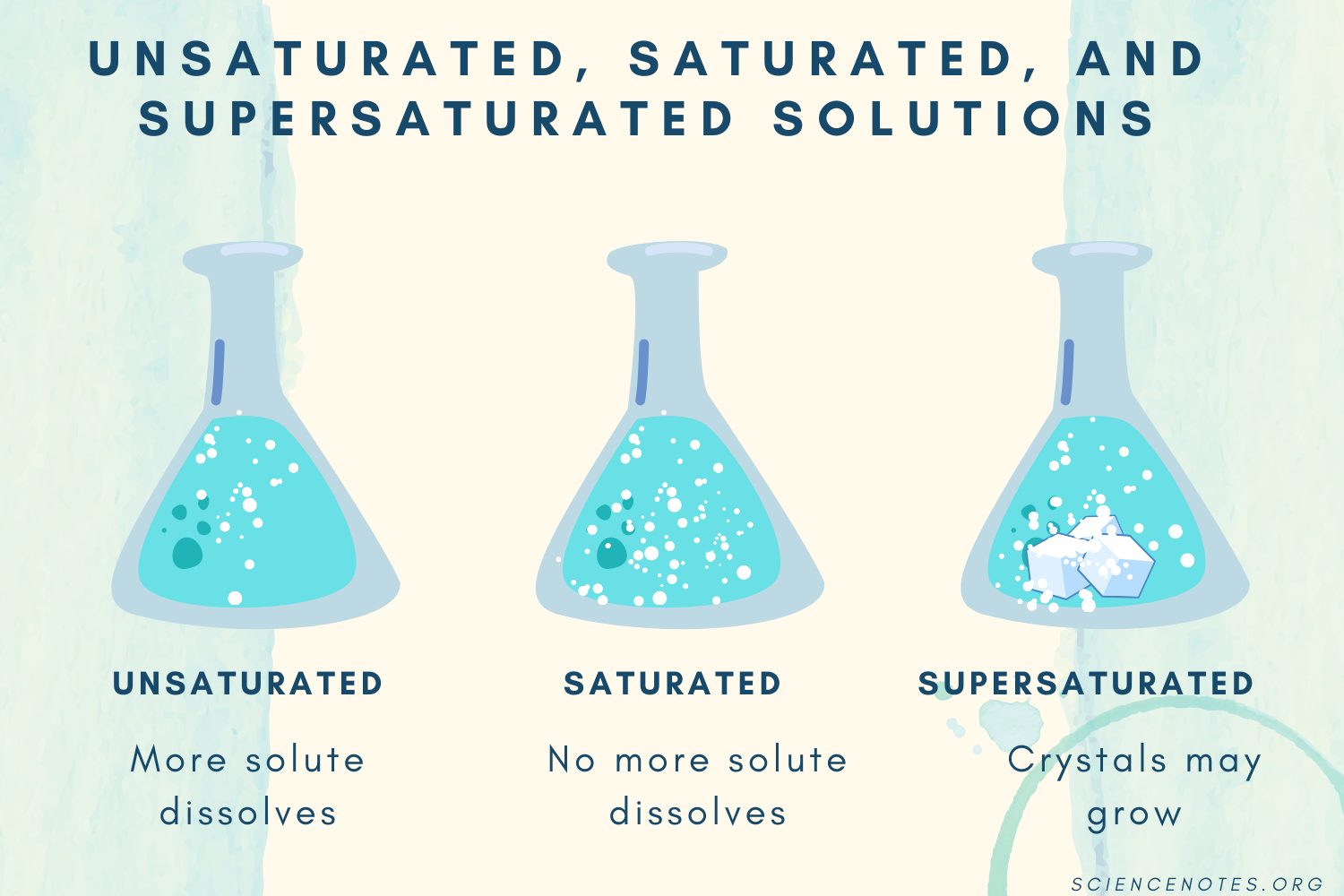  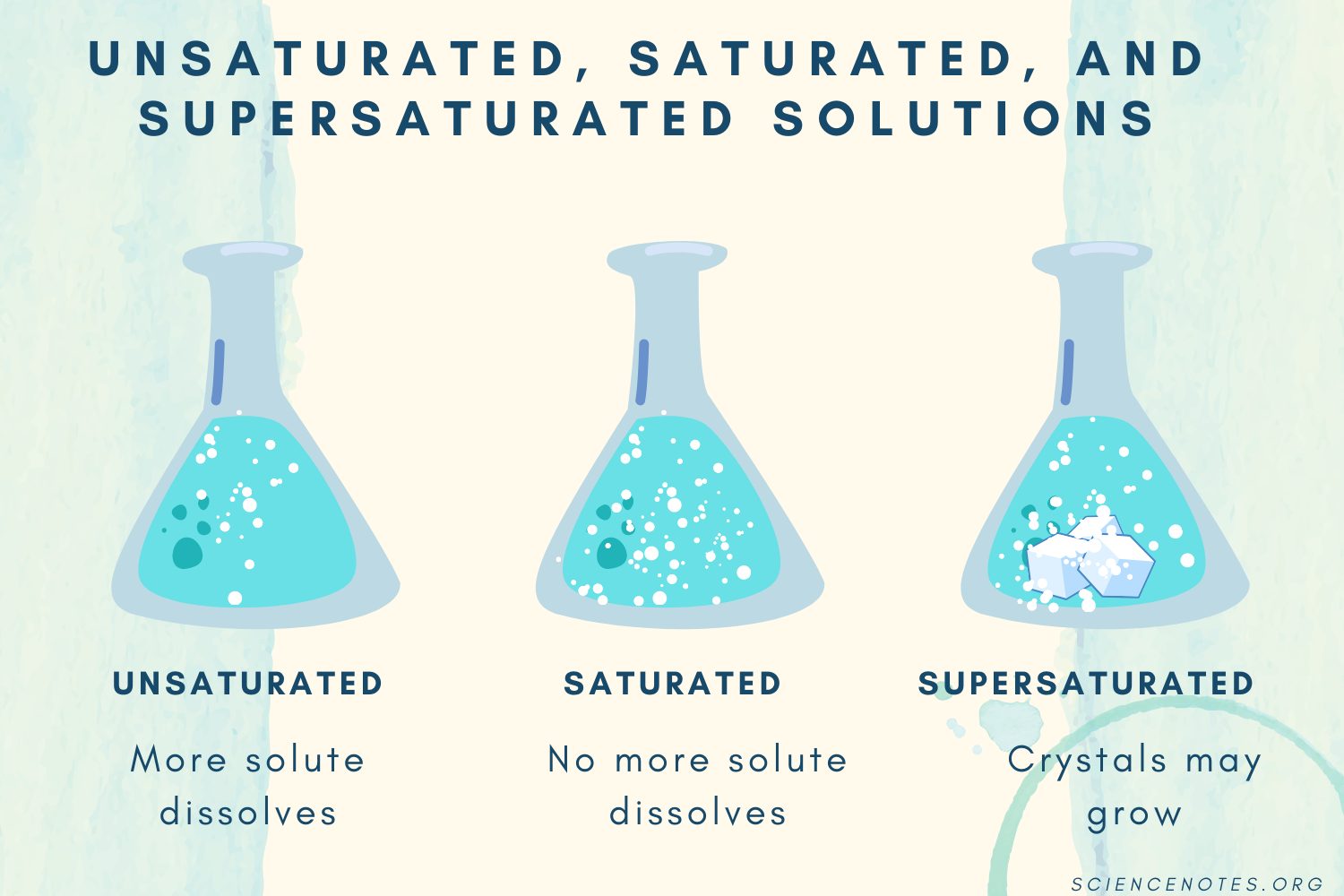 |
Occurred in steps…
Occurred in steps…
Occurred in steps…
|
D: Exothermic & Endothermic Reactions
Exothermic Endothermic |
Energy RELEASING reaction; solution becomes WARMER Energy ABSORBING reaction; solution becomes COLDER |
Occurred when 10mL H2O added to NaOH (s) Occurred when 10mL H2O added to NH4Cl (s) |
E.a: Properties of Acids & Bases
Taste Litmus Paper Indicator |
Acetic Acid (CH3COOH) Sour, vinegar-like Blue → Red Methyl Orange (Neon Pink) |
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) Astringent (dry), less sour Blue → Red Methyl Orange (Neon Pink) |
Ammonium Hydroxide (NH4OH) Bitter, acrid (strong & sharp) Red → Blue Phenolphthalein (Dark Pink) |
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) Bitter Red → Blue Phenolphthalein (Light, Clear Pink) |
E.b: Relative Activity of Acids
Reacts faster with Al? Reacts faster with CaCO3? |
CH3COOH NO |
HCl YES 6 HCl (aq) + 2 Al (s) → 2 AlCl3 (aq) + 3 H2 (g) |

