Intro to Comp Networks Exam 2 (Ch 3 - Ch 4)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
1
New cards
rdt2.2
____________ has the same functionality as rdt2.1 but only uses ACKs, making it a NAK-free protocol.
2
New cards
rdt2.2
Duplicating ACK at sender results in the same action as NAK: it retransmits the current packet. Which protocol is sends ACK for last packet received OK instead of NAK?
- rdt2.1
- rdt2.2
- rdt3.0
- rdt2.3
- rdt2.1
- rdt2.2
- rdt3.0
- rdt2.3
3
New cards
both A and B
Underlying channels can also lose packets (data, ACKs). How does rdt3.0 handle lost sender-to-receiver data?
- sender waits "reasonable" amount of time for ACK
- both A and B
- retransmits if no ACK is received after waiting a certain amount of time
- restarts the entire channel and retransmits data for each ACK
- sender waits "reasonable" amount of time for ACK
- both A and B
- retransmits if no ACK is received after waiting a certain amount of time
- restarts the entire channel and retransmits data for each ACK
4
New cards
01100101 10101110
Compute the Internet checksum value for these two 16-bit words:
11101011 01011111
01111010 01001110
What is the sum of these two 16 bit numbers?
5
New cards
10011010 01010001
Compute the Internet checksum value for these two 16-bit words:
11101011 01011111
01111010 01001110
What is the checksum of these two 16 bit numbers?
11101011 01011111
01111010 01001110
What is the checksum of these two 16 bit numbers?
6
New cards
false
(TCP socket is identified by 4-tuple)
(TCP socket is identified by 4-tuple)
(T/F) UDP socket is identified by 4-tuple.
7
New cards
file transfer
Which of the following applications are not potential candidates to use UDP:
- File transfer
- Streaming multimedia apps
- DNS
- SNMP
- File transfer
- Streaming multimedia apps
- DNS
- SNMP
8
New cards
logical communication
Transport services and protocols provide _________________ between application process running on different hosts
9
New cards
sender
Which transport protocol actions breaks the application messages into segments and passes it to the network layer?
- sender
- receiver
- hosts
- none of the above
- sender
- receiver
- hosts
- none of the above
10
New cards
receiver
Which transport protocol actions reassembles segments into messages and passes it to the application layer?
- end systems
- sender
- none of the above
- receiver
- end systems
- sender
- none of the above
- receiver
11
New cards
network
The ___________ layer is the logical communication between hosts.
12
New cards
hosts
The network layer is the logical communication between what?
- end systems
- hosts
- processes
- segments
- end systems
- hosts
- processes
- segments
13
New cards
transport
The ____________ layer is the logical communication between processes.
14
New cards
transport
Which layer is the logical communication between processes?
- network
- application
- link
- transport
- network
- application
- link
- transport
15
New cards
handles data from multiple sockets, add transport layer
Multiplexing at sender...
- handles data from multiple sockets, add transport layer
- handles data from multiple headers, add transport layer
- handles segments from multiple sockets, add transport layer
- handles data from multiple sockets, add network layer
- handles data from multiple sockets, add transport layer
- handles data from multiple headers, add transport layer
- handles segments from multiple sockets, add transport layer
- handles data from multiple sockets, add network layer
16
New cards
uses header info to deliver received segments to correct socket
Demultiplexing at receiver...
- uses socket info to deliver received segments to correct socket
- uses header info to deliver received segments to correct socket
- uses header info to deliver received messages to correct socket
- uses socket info to deliver received messages to correct address
- uses socket info to deliver received segments to correct socket
- uses header info to deliver received segments to correct socket
- uses header info to deliver received messages to correct socket
- uses socket info to deliver received messages to correct address
17
New cards
to know where to send it back
Why does demultiplexing need the source port number?
- to carry one transport-layer segment
- to create a datagram
- to receive messages
- to know where to send it back
- to carry one transport-layer segment
- to create a datagram
- to receive messages
- to know where to send it back
18
New cards
multiplexing
_______________ at sender handles data from multiple sockets and adds transport header.
19
New cards
demultiplexing
______________ at receiver uses header info to deliver received segments to correct socket.
20
New cards
both a and b
In order for demultiplexing to work, the host uses port numbers & IP address to direct segment to appropriate socket.
- IP address
- port numbers
- segment number
- both a and b
- IP address
- port numbers
- segment number
- both a and b
21
New cards
host-local
In connectionless demultiplexing, when creating a socket it must specify what kind of port number?
- IP
- host-global
- host-local
- destination
- IP
- host-global
- host-local
- destination
22
New cards
destination IP address and destination port number
In connectionless demultiplexing, when creating a datagram to send into the UDP socket, it must specify
- destination IP address and destination port number
- source IP address and source port number
- destination IP address and source port number
- source IP address and destination port number
- destination IP address and destination port number
- source IP address and source port number
- destination IP address and source port number
- source IP address and destination port number
23
New cards
true
(T/F) IP/UDP datagrams with the same destination port number but different source IP and/or source port numbers will be directed to the same socket at the receiving host.
24
New cards
4-tuple
In connection-oriented demultiplexing, the TCP socket is identified by ________________.
25
New cards
source IP address and port number, destination IP address and port number
The 4-tuple that is used to help identify a TCP consists of
26
New cards
false
(each socket is associated with a different connecting client)
(each socket is associated with a different connecting client)
(T/F) A server may support many simultaneous TCP sockets where each socket is identified by its own 4-tuple and each socket is associated with its own connecting client.
27
New cards
header field
Multiplexing and demultiplexing are based on segment and datagram ________________ values
28
New cards
destination port number
UDP demultiplexes using
- 4-tuple
- destination port number
- destination IP address
- none of the above
- 4-tuple
- destination port number
- destination IP address
- none of the above
29
New cards
4-tuple
TCP demultiplexes using
- 4-tuple
- destination port number
- destination IP address
- none of the above
- 4-tuple
- destination port number
- destination IP address
- none of the above
30
New cards
true
(T/F) Multiplexing/demultiplexing happens at all layers.
31
New cards
true
(T/F) UDP is connectionless and TCP is connection-oriented.
32
New cards
there's no connection establishment and therefore is faster, it's simple, can function in the face of congestion, it has no congestion control
Why is there a UDP? (Select multiple)
- there's no connection establishment and therefore is faster
- it's simple
- can function in the face of congestion
- it has no congestion control
- handshaking is used between the sender and receiver
- there's no connection establishment and therefore is faster
- it's simple
- can function in the face of congestion
- it has no congestion control
- handshaking is used between the sender and receiver
33
New cards
true
(T/F) UDP is good to use with DNS because DNS wants the query result as fast as possible.
34
New cards
false
(complexity of reliable data transfer protocol DOES depend on characteristics of unreliable channel)
(complexity of reliable data transfer protocol DOES depend on characteristics of unreliable channel)
(T/F) Complexity of reliable data transfer protocol will not depend strongly on characteristics of unreliable channel.
35
New cards
all of the others
When a TCP segment arrives to a host, the socket to which the segment is directed depends on
- all of the others
- the source IP address of the datagram that encapsulated the segment
- the destination port number
- the source port number
- all of the others
- the source IP address of the datagram that encapsulated the segment
- the destination port number
- the source port number
36
New cards
none of the others
UDP has which of the following characteristics?
- connection state at the server
- three-way hand shake for connection establishment
- regulated send rate
- none of the others
- connection state at the server
- three-way hand shake for connection establishment
- regulated send rate
- none of the others
37
New cards
Host A will retransmit neither segments
Over a TCP connection, suppose host A sends two segments to host B. Host B sends an acknowledgement for each segment, the first acknowledgement is lost, but the second acknowledgement arrives before the timer for the first segment expires.
- Host A will retransmit both segments
- Host A will retransmit the second segment
- Host A will retransmit the first segment
- Host A will retransmit neither segments
- Host A will retransmit both segments
- Host A will retransmit the second segment
- Host A will retransmit the first segment
- Host A will retransmit neither segments
38
New cards
all of the others
Pipelining requires which of the following?
- transmitting many packets before receiving acknowledgements
- sender-side buffering of unacknowledged packets
- unique sequence numbers for each in-transit packet
- all of the others
- transmitting many packets before receiving acknowledgements
- sender-side buffering of unacknowledged packets
- unique sequence numbers for each in-transit packet
- all of the others
39
New cards
true
(T/F) In the End-End congestion control approach, congestion is inferred from observed loss or delay.
40
New cards
false
(the size of the receiver's buffer never changes)
(the size of the receiver's buffer never changes)
(T/F) The size of the TCP RcvWindow never changes throughout the duration of the connection.
41
New cards
false
(the sequence number of the subsequent segment depends on the number of 8-byte characters in the current segment)
(the sequence number of the subsequent segment depends on the number of 8-byte characters in the current segment)
(T/F) Host A is sending a large file to host B over a TCP connection. If the sequence number for a segment of this connection is m, then the sequence number for the subsequent segment will necessarily be m+1.
42
New cards
increases utilization
TCP uses pipelining to:
- none of the others
- increases utilization
- establish connections
- control congestion
- none of the others
- increases utilization
- establish connections
- control congestion
43
New cards
segments
On the sending side, the transport layer converts the application-layer messages it receives from a sending application process into transport-layer packets, known as transport-layer ___________.
44
New cards
0010010100000110
What is the sum of these two 16 bit numbers?
10001011 01001110
10011001 10110111
10001011 01001110
10011001 10110111
45
New cards
1101101011111001
What is the checksum of these two 16 bit numbers?
10001011 01001110
10011001 10110111
10001011 01001110
10011001 10110111
46
New cards
183, 1118, 2053, 2988
1118, 2053, 2988, x
1118, 2053, 2988, x
Consider the figure below in which a TCP sender and receiver communicate over a connection in which the sender->receiver segments may be lost. The TCP sender sends an initial window of 4 segments. Suppose the initial value of the sender->receiver sequence number is 183 and the first 4 segments each contain 935 bytes. The delay between the sender and receiver is 7 time units, and so the first segment arrives at the receiver at t=8. As shown in the figure below, 1 of the 4 segment(s) are lost between the segment and receiver.
What is the sequence numbers associated with each of the 4 segments sent by the sender?
Give the ACK numbers the receiver sends in response to each of the segments. If a segment never arrives, use 'x' to denote it.
What is the sequence numbers associated with each of the 4 segments sent by the sender?
Give the ACK numbers the receiver sends in response to each of the segments. If a segment never arrives, use 'x' to denote it.
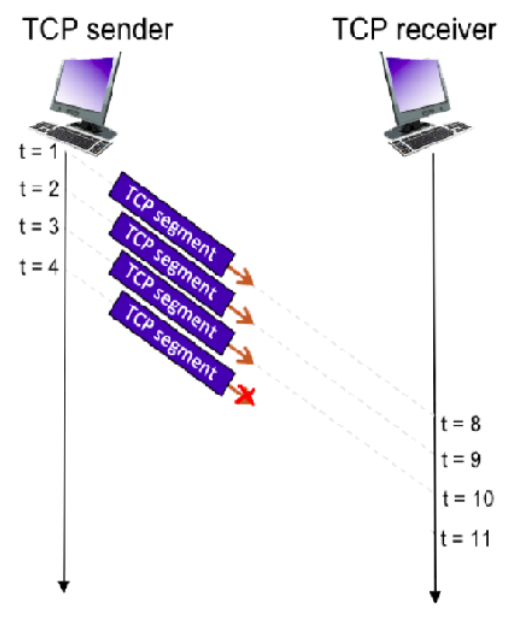
47
New cards
5840
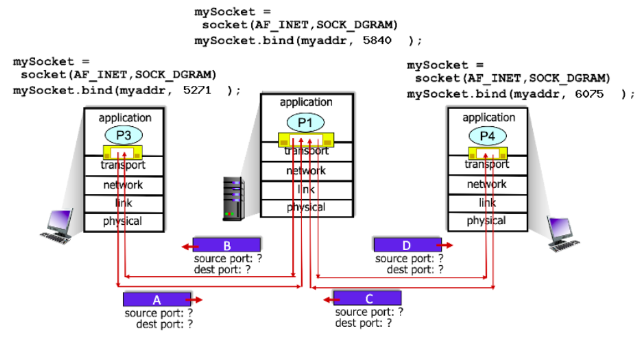
In the scenario below, the left and right clients communicate with a server using UDP sockets.
What is the source port # for packet D?
What is the source port # for packet D?
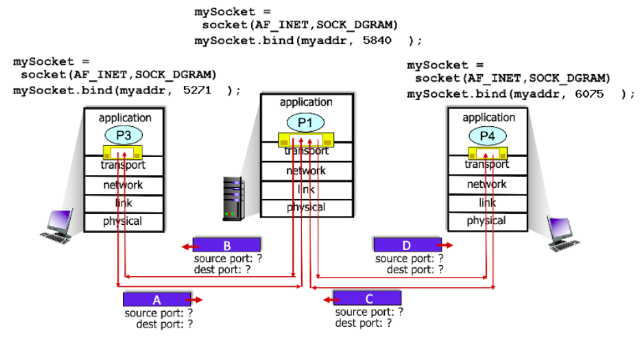
48
New cards
6075
In the scenario below, the left and right clients communicate with a server using UDP sockets.
What is the destination port # for packet D?
What is the destination port # for packet D?
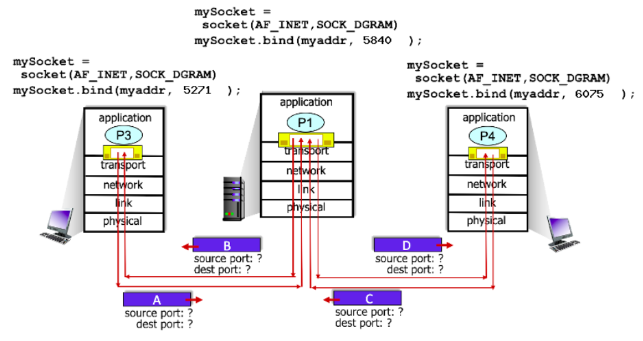
49
New cards
6075
In the scenario below, the left and right clients communicate with a server using UDP sockets.
What is the source port # for packet C?
What is the source port # for packet C?
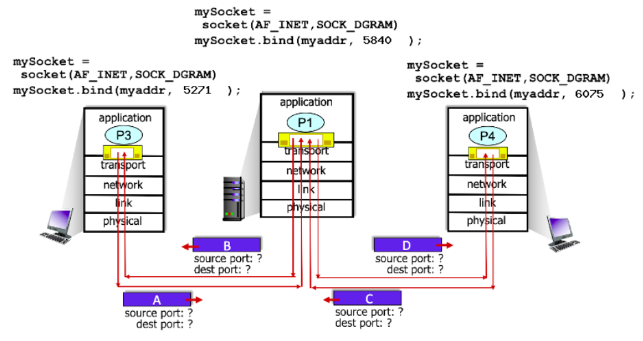
50
New cards
5271
In the scenario below, the left and right clients communicate with a server using UDP sockets.
What is the destination port # for packet B?
What is the destination port # for packet B?
51
New cards
forwarding, routing
Network-layer functions
___________: move packets from router's input link to appropriate router output link
____________: determine route taken by packets from source to destination
___________: move packets from router's input link to appropriate router output link
____________: determine route taken by packets from source to destination
52
New cards
false
(forwarding moves packets from router's input link to appropriate router output link)
(forwarding moves packets from router's input link to appropriate router output link)
(T/F) One of the two network-layer functions of forwarding determines the route taken by packets from source to destination.
53
New cards
b) determines the route taken by packets from source to destination
One of the two network-layer functions of routing...
a) moves packets from router's input link to appropriate router output link
b) determines the route taken by packets from source to destination
c) determines the router's appropriate input link
d) none of the above
a) moves packets from router's input link to appropriate router output link
b) determines the route taken by packets from source to destination
c) determines the router's appropriate input link
d) none of the above
54
New cards
a) data plane and control plane
What are the two planes of the network layer?
a) data plane and control plane
b) local plane and network-wide plane
c) arrival plane and router plane
d) none of the above
a) data plane and control plane
b) local plane and network-wide plane
c) arrival plane and router plane
d) none of the above
55
New cards
local
The data plane of the network layer is ________, per-router function. It determines how the datagram arriving on router input port is forwarded to router output port.
56
New cards
True
(T/F) The data plane of the network layer determines how the datagram arriving on router input port is forwarded to router output port.
57
New cards
network-wide
The control plane of the network layer uses _____________ logic. It determines how datagrams are routed among routers along end-end path from source host to destination host.
58
New cards
False
(it determines how datagrams are routed among routers along end-end path from source host to destination host)
(it determines how datagrams are routed among routers along end-end path from source host to destination host)
(T/F) The control plane of the network layer controls the flow of datagrams among routers along end-end path from source host to destination host.
59
New cards
c) traditional routing algorithms and software-defined networking (SDN)
What are the two control-plane approaches?
a) end-end routing algorithms and software development systems (SNS)
b) modern routing algorithms and domain name system (DNS)
c) traditional routing algorithms and software-defined networking (SDN)
d) none of the above
a) end-end routing algorithms and software development systems (SNS)
b) modern routing algorithms and domain name system (DNS)
c) traditional routing algorithms and software-defined networking (SDN)
d) none of the above
60
New cards
routers
One of the two control-plane approaches, traditional routing algorithms, is implemented in ___________.
61
New cards
(remote) servers
One of the two control-plane approaches, software-defined networking (SDN), is implemented in ___________.
62
New cards
a) in each and every router
In the per-router control plane, individual routing algorithm components _______________ interact in the control plane.
a) in each and every router
b) in a singular router
c) in a large database
d) none of the above
a) in each and every router
b) in a singular router
c) in a large database
d) none of the above
63
New cards
True
(T/F) In the software-defined networking (SDN) control plane, a remote controller computes and installs forwarding tables in routers.
64
New cards
a) successful datagram delivery to destination; c) timing or order of delivery; d) bandwidth available to end-end flow
Select what the Internet "best effort" service model has NO guarantees on: (select multiple)
a) successful datagram delivery to destination
b) guaranteed minimum of available bit rate
c) timing or order of delivery
d) bandwidth available to end-end flow
e) constant bit rate
a) successful datagram delivery to destination
b) guaranteed minimum of available bit rate
c) timing or order of delivery
d) bandwidth available to end-end flow
e) constant bit rate
65
New cards
routing, management control plane
_____________________ (software) operates in millisecond time frame.
66
New cards
forwarding data plane
_______________ (hardware) operates in nanosecond time frame.
67
New cards
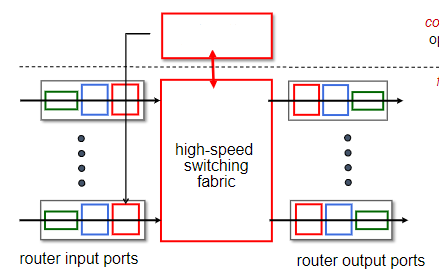
routing processor
What is the missing part of this router architecture?
68
New cards
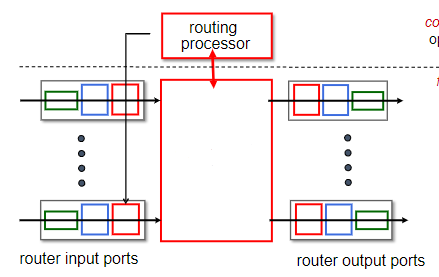
high-speed switching fabric
What is the missing part of this router architecture?
69
New cards
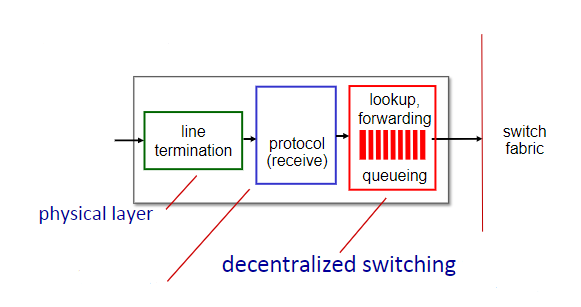
link layer
What is the missing function of these input port functions?
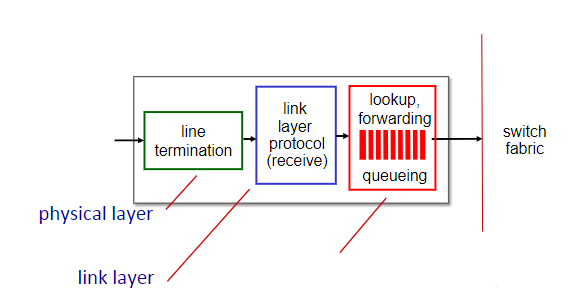
70
New cards
physical layer
What is the missing function of these input port functions?
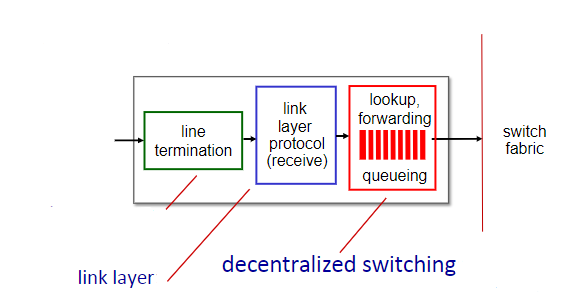
71
New cards
decentralized switching
What is the missing function of these input port functions?
72
New cards
a) datagrams arrive faster than forwarding rate into switch fabric
Decentralized switching uses input port queueing which is if
a) datagrams arrive faster than forwarding rate into switch fabric
b) datagrams arrive slower than forwarding rate into switch fabric
c) datagrams arrive at the same time as the forwarding rate into switch fabric
d) none of the above
a) datagrams arrive faster than forwarding rate into switch fabric
b) datagrams arrive slower than forwarding rate into switch fabric
c) datagrams arrive at the same time as the forwarding rate into switch fabric
d) none of the above
73
New cards
destination IP address
Destination-based forwarding is a forward based only on ______________________ (traditional).
74
New cards
header field values
Generalized forwarding is a forward based on any set of ___________________________.
75
New cards
longest address prefix
When looking for forwarding table entry for given destination address, use ___________________ that matches destination address.
76
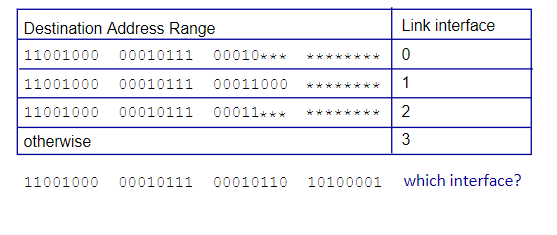
New cards
interface 0
Which link interface should be used for the given destination address?
77
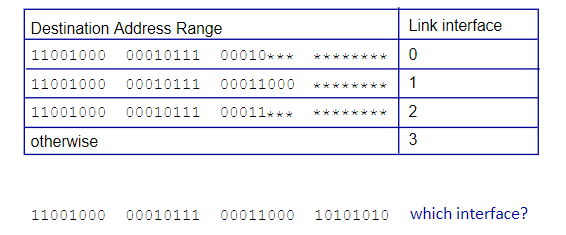
New cards
interface 1
Which link interface should be used for the given destination address?
78
New cards
content addressable
Retrieving an address in one clock cycle, regardless of table size, is known as ____________________.
79
New cards
True
(T/F) Longest prefix matching is often performed using ternary content addressable memories (TCAMs)
80
New cards
a) memory; c) bus; d) interconnection network
The tree major types of switching fabrics are: (select multiple)
a) memory
b) routers
c) bus
d) interconnection network
e) switcher
a) memory
b) routers
c) bus
d) interconnection network
e) switcher
81
New cards
bus contention
When switching via bus, ______________ is the switching speed limited by bus bandwidth.
82
New cards
c) switching via interconnection network
Which switching method uses multistage switch, an n x n switch from multiple stages of smaller switches?
a) switching via bus
b) switching via memory
c) switching via interconnection network
d) none of the above
a) switching via bus
b) switching via memory
c) switching via interconnection network
d) none of the above
83
New cards
d) there is no queueing delay in the router
Suppose a router has n input ports each with identical line speeds, n output ports each with identical line speeds, and the line speed of an output port is at least n times as that of an input port. Further suppose that the switching fabric speed is at least n times as fast as an input line speed. Then
a) queueing can occur in an output port
b) queueing can occur in an input port
c) queueing can occur in the switching fabric
d) there is no queueing delay in the router
a) queueing can occur in an output port
b) queueing can occur in an input port
c) queueing can occur in the switching fabric
d) there is no queueing delay in the router
84
New cards
b) in the input ports and in the output ports
In a router, queueing can occur
a) only in the output ports
b) in the input ports and in the output ports
c) none of the others
d) only in the input ports
a) only in the output ports
b) in the input ports and in the output ports
c) none of the others
d) only in the input ports
85
New cards
d) The sending IPv6 router creates an IPv6 datagram and puts it in the data field of an IPv4 datagram
Suppose one IPv6 routers wants to send a datagram to another IPv6 router, but are connected together by intervening IPv4 routers. If the two routers use tunneling, then
a) none of the others
b) The sending IPv6 router creates one or more IPv6 fragments, none of which is larger than the maximum size of an IPv4
c) The sending IPv6 router creates an IPv4 datagram and puts it in the data field of an IPv6 datagram
d) The sending IPv6 router creates an IPv6 datagram and puts it in the data field of an IPv4 datagram
a) none of the others
b) The sending IPv6 router creates one or more IPv6 fragments, none of which is larger than the maximum size of an IPv4
c) The sending IPv6 router creates an IPv4 datagram and puts it in the data field of an IPv6 datagram
d) The sending IPv6 router creates an IPv6 datagram and puts it in the data field of an IPv4 datagram
86
New cards
true
(T/F) With a datagram network layer, each packet carries the address of the destination host
87
New cards
true
(T/F) The network portion of an IP address is the same for all the hosts on the same IP network.
88
New cards
b) could increase the end-end delay
Increasing the amount of per-hop buffer
a) could decrease the end-end delay
b) could increase the end-end delay
c) will not decrease packet loss
d) none of the others
a) could decrease the end-end delay
b) could increase the end-end delay
c) will not decrease packet loss
d) none of the others
89
New cards
true
(T/F) Multiple packets can be transferred by the switch fabric in parallel, as long as their output ports are different.
90
New cards
b) the transmission of packet A will not be interrupted. So, packet B has to wait after fully transmitting packet A
Assume packet A has begun transmission. If packet B (a high-priority packet) arrives during the transmission of packet A (a low-priority packet), then
a) packet B will be transmitted immediately while packet A is still being transmitted
b) the transmission of packet A will not be interrupted. So, packet B has to wait after fully transmitting packet A
c) the transmission of packet A will be interrupted to allow the transmission of packet B
d) transmission cannot be based on priorities
a) packet B will be transmitted immediately while packet A is still being transmitted
b) the transmission of packet A will not be interrupted. So, packet B has to wait after fully transmitting packet A
c) the transmission of packet A will be interrupted to allow the transmission of packet B
d) transmission cannot be based on priorities
91
New cards
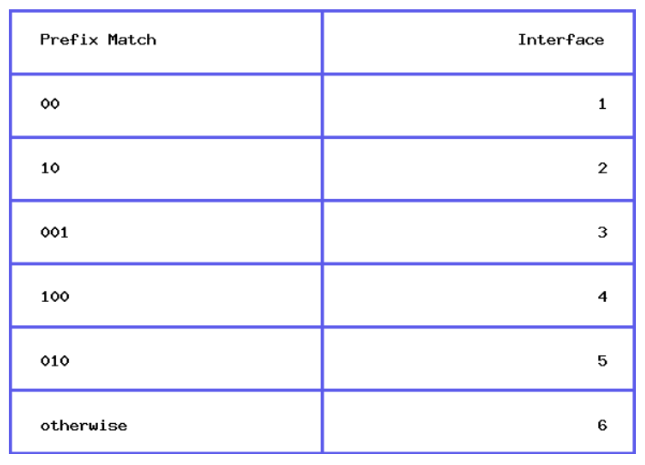
interface 6
Suppose a router uses longest-prefix matching, and has the following forwarding table:
Suppose a datagram arrives at the router, with destination address 01111111. To which interface will this datagram be forwarded?
Suppose a datagram arrives at the router, with destination address 01111111. To which interface will this datagram be forwarded?
92
New cards
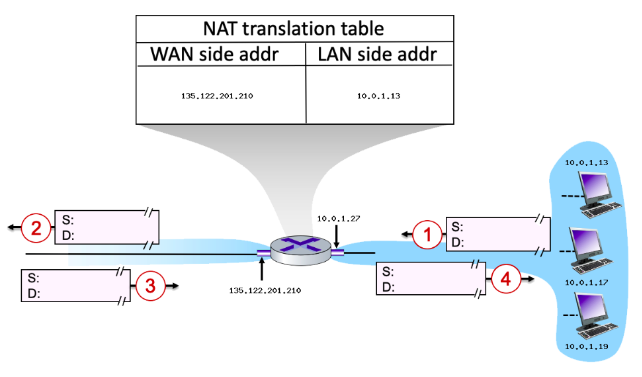
10.0.1.13
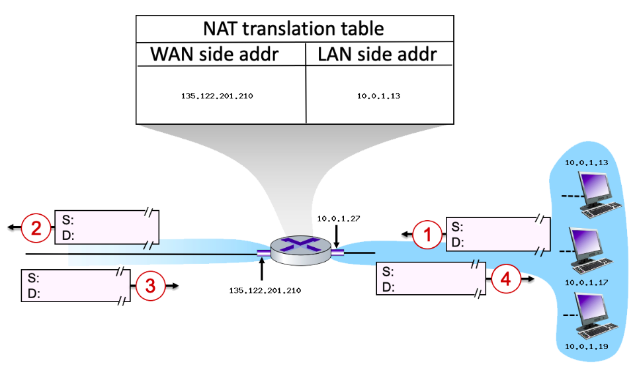
Consider the scenario below:
Suppose that the host with IP address 10.0.1.13 sends an IP datagram destined to host 128.119.173.181. The source port is 3461, and the destination port is 80.
Consider the datagram at step 1, after it has been sent by the host but before it has reached the router. What is the source IP address for this datagram?
Suppose that the host with IP address 10.0.1.13 sends an IP datagram destined to host 128.119.173.181. The source port is 3461, and the destination port is 80.
Consider the datagram at step 1, after it has been sent by the host but before it has reached the router. What is the source IP address for this datagram?
93
New cards
135.122.201.210
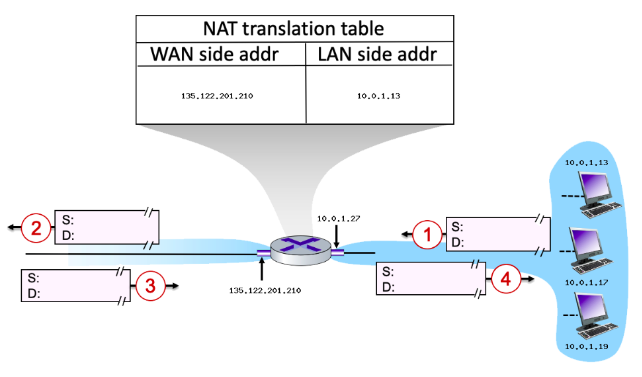
Consider the scenario below:
Suppose that the host with IP address 10.0.1.13 sends an IP datagram destined to host 128.119.173.181. The source port is 3461, and the destination port is 80.
Now consider the datagram at step 2, after it has been transmitted by the router. What is the source IP address for this datagram?
Suppose that the host with IP address 10.0.1.13 sends an IP datagram destined to host 128.119.173.181. The source port is 3461, and the destination port is 80.
Now consider the datagram at step 2, after it has been transmitted by the router. What is the source IP address for this datagram?
94
New cards
yes
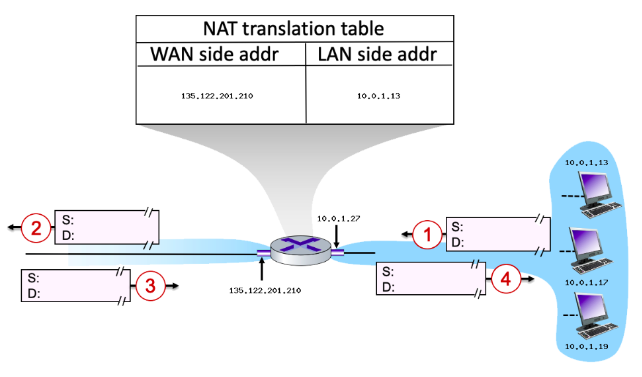
Consider the scenario below:
Suppose that the host with IP address 10.0.1.13 sends an IP datagram destined to host 128.119.173.181. The source port is 3461, and the destination port is 80.
Will the source port (at step 2) have changed (from step 1)? Y/N
Suppose that the host with IP address 10.0.1.13 sends an IP datagram destined to host 128.119.173.181. The source port is 3461, and the destination port is 80.
Will the source port (at step 2) have changed (from step 1)? Y/N
95
New cards
no
Consider the scenario below:
Suppose that the host with IP address 10.0.1.13 sends an IP datagram destined to host 128.119.173.181. The source port is 3461, and the destination port is 80.
Has a new entry been made in the router's NAT table (between step 3 and step 4)? Y/N
Suppose that the host with IP address 10.0.1.13 sends an IP datagram destined to host 128.119.173.181. The source port is 3461, and the destination port is 80.
Has a new entry been made in the router's NAT table (between step 3 and step 4)? Y/N
96
New cards
forwarding
Moving packets from a router's input link to appropriate router output link is called ______________.
97
New cards
32
In Internet protocol version 4, the IP address consists of ____________ bits.
98
New cards
128
In Internet protocol version 6, the IP address consists of ____________ bits.
99
New cards
b) none of the others
Network-layer service model provide guarantee(s) on:
a) bandwidth available to end-end flow
b) none of the others
c) delivery to destination
d) timing or order of delivery
a) bandwidth available to end-end flow
b) none of the others
c) delivery to destination
d) timing or order of delivery
100
New cards
buffering
Because datagrams might arrive from switch fabric faster than link transmission rate, ____________ is required at the output port.