Anatomy and Physiology Nervous System Exam
5.0(2)Studied by 75 people
Card Sorting
1/245
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:15 AM on 1/24/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
246 Terms
1
New cards
communication: sends and recieves info as well as integration and decision making
What does the nervous system do?
2
New cards
sensory/ afferent, integration, and motor/efferent
What are the 3 functions of the nervous system?
3
New cards
sensory
What function brings sensory info into the CNS
4
New cards
integration
What function processes info and makes decisions
5
New cards
motor
what function gives outgoing information to effector tissues?
6
New cards
the brain and spinal cord
The central nervous system consists of
7
New cards
nerves and receptors
the peripheral nervous system consists of
8
New cards
special senses and somatic
What are the 2 sections of the sensory/ afferent pathway?
9
New cards
detect pain, tactile info, temperature, proprioception
what does the somatic system do in the afferent pathway
10
New cards
somatic and autonomic
What are the 2 sections of the motor efferent pathway?
11
New cards
outgoing information to skeletal muscle
the somatic efferent pathway gives what?
12
New cards
involuntary
What autonomic nervous system is
13
New cards
sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric
The autonomic nervous system can be divided into what 3 sections
14
New cards
sympathetic
Fight or flight system, increases heart rate and blood pressure
15
New cards
parasympathetic
rest or digest system, decreases heart rate and blood pressure
16
New cards
enteric
system that innervates smooth muscle and glands in the GI
17
New cards
neurons
What is the functional unit of the nervous system?
18
New cards
astrocytes, microglia, ependymal, oligiodendrocytes
What are the 4 glial cells of the CNS
19
New cards
astrocytes
Helps form blood brain barrier and regulates ion concentrations
20
New cards
microglia
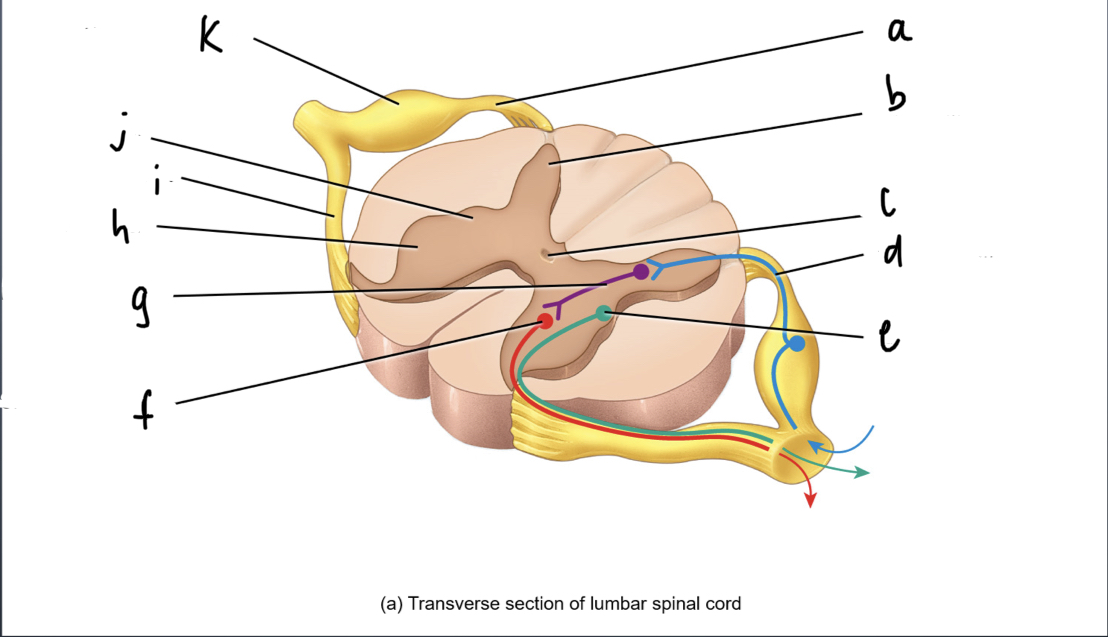
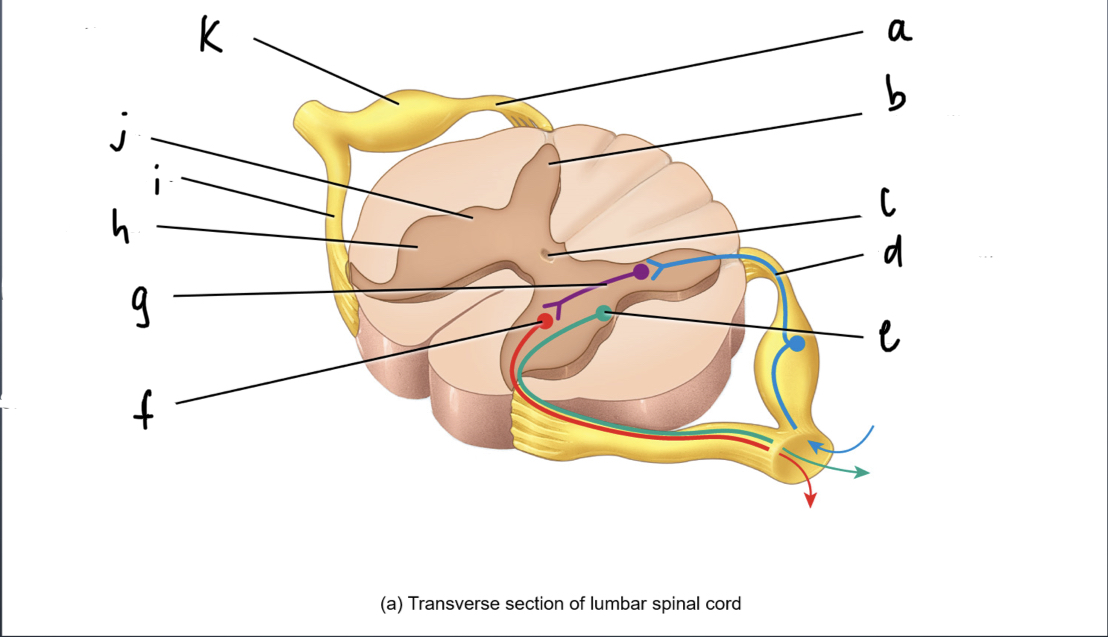
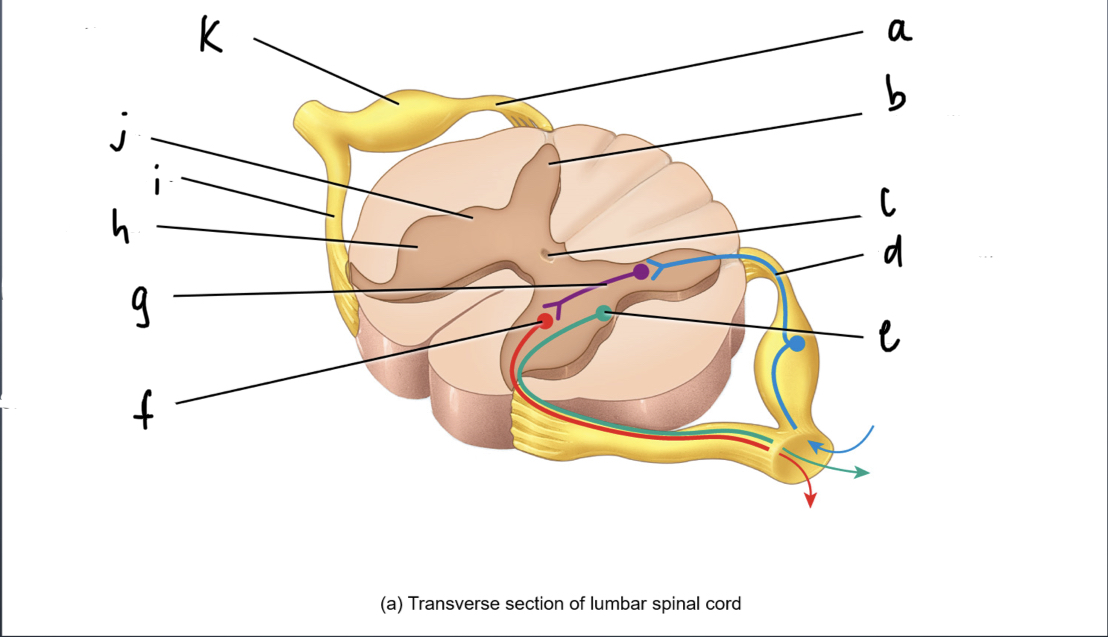
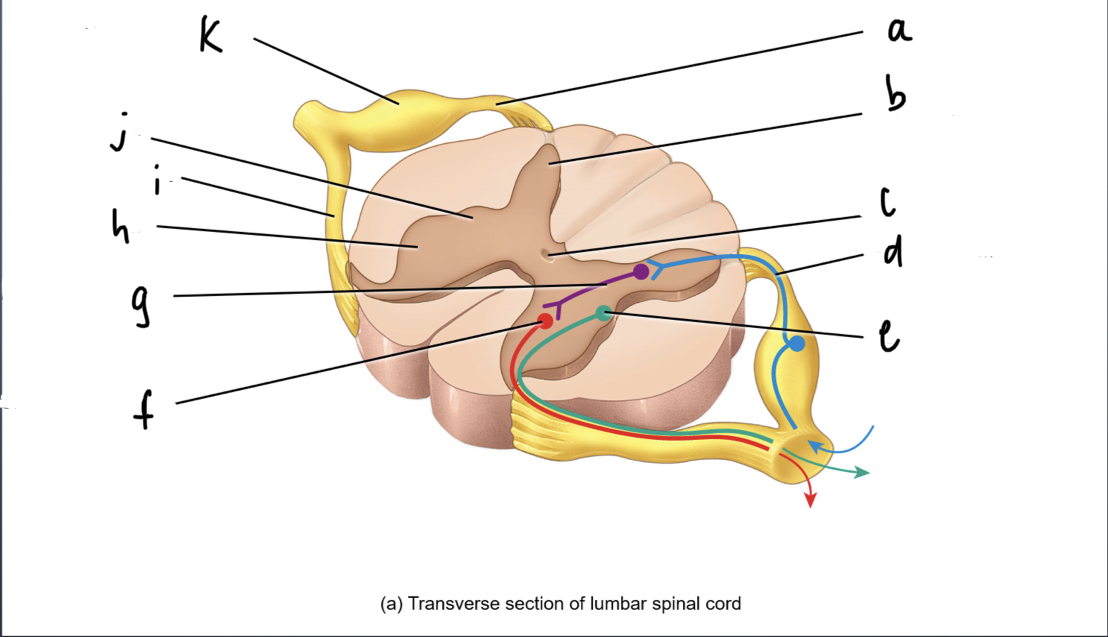
phagocytes that get rid of debri and microbes
21
New cards
ependymal cells
simple ciliated cuboidal cells that line ventricles and central canal of the CNS
-circulates and secretes cerebrospinalal fluid
-circulates and secretes cerebrospinalal fluid
22
New cards
oligodendrocytes
wraps around and insulates the neurons of the CNS
23
New cards
Schwann Cells
responsible for myelination in the PNS
24
New cards
satellite cell
provides structural support and regulates fluid exchange in the PNS
25
New cards
nerve fibers
What are extensions from cell body of neurons
26
New cards
synapse
Where neuron meets another neuron or connective tissue
27
New cards
propogates
the axon _____ electrical signal
28
New cards
the axon hillock
Where is action potentials generated
29
New cards
dendrites
Branches off the cell body of neurons
30
New cards
to recieve signals
What are the functions of dendrites
31
New cards
microtubule track
What is the pathway for protiens to carry down track
32
New cards
physical
Axonal transport transports _____ substances
33
New cards
slow and fast
What are the 2 types of axonal transport
34
New cards
cell body to axon terminal
Slow axonal transport goes in what direction
35
New cards
bidirectional
fast axonal transport is ___-
36
New cards
retrograde
what is the type of transport that goes from axon terminal to the cell body
37
New cards
multipolar, bipolar, and psuedounipolar
What are the 3 structural classifications of neurons
38
New cards
multipolar
Neuron structure that has several dendrties and one axon
39
New cards
bipolar
neuron structure that has one main dendrite and one axon
40
New cards
pseudounipolar
neuron structure that has dendrites and one axon that are fused togehter to form a continuous process that emerges from the cell body
41
New cards
ganglia
clusters of cell bodies in the PNS
42
New cards
nuclei
clusters of cell bodies in the CNS
43
New cards
nerve
bundles of axons in the PNS
44
New cards
tract
bundles of axons in the CNS
45
New cards
white
matter that contains myelinated axons of neurons
46
New cards
gray
matter that has no myelination of axons
47
New cards
dura mater, skull cap, blood brain barrier, cerebrospinal fluid
What are the protective coverings of the CNS
48
New cards
dura mater
What is the most superficial meninge
49
New cards
dense irregular CT
what is the dura mater made of
50
New cards
arachnoid mater
what is the web-like appearance mater made of collagen and elastic fibers
51
New cards
the pia mater
What is the deepest meninge
52
New cards
epithelial and simple squamous
what type of tissue and cells is the pia mater
53
New cards
interstital fluid
What is the subdural space filled with
54
New cards
CSF
what is the subarachnoid space filled with?
55
New cards
shock absorption
What do the fluids in space between meninges help
56
New cards
to regulate what passes from the blood to the brain
What is the function of the blood brain barrier
57
New cards
tight junctions, astrocytes, and thick basement membranes
What three things help secure capillarys in the blood brain barrier
58
New cards
mostly water, with some ions that are highly regulated
What is CSF made of
59
New cards
mechanical protection, chemical protection, and circulation
What are the 3 major functions of CSF
60
New cards
lateral ventricle> 3rd ventricle> cerebral aqueduct> 4th ventricle> either subarachnoid space or central canal of spinal cord> reabsorbed into venous circulation
Describe the flow of CSF
61
New cards
equal
Rate of formation of CSF is ____ to rate of absorption of CSF
62
New cards
Brainstem, diencephalon, cerebellum, and cerebrum
What are the 4 major regions of the brain
63
New cards
midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
What are the 3 sections of the brainstem?
64
New cards
midbrain
coordinates movement of the head, neck, and trunk after visual stimuli
65
New cards
pons
relays motor information to cerebellum
-"bridge"
-"bridge"
66
New cards
medulla oblongata
cardiovascular and respiratory control center
67
New cards
thalamus, hypothalamus, and pineal gland
What are the 3 sections of the Diencephalon
68
New cards
thalamus
relays almost all sensory information to the brain
69
New cards
hypothalamus
responsible for endocrine functions, thirst hunger, and temperature
70
New cards
pineal gland
makes and secretes melatonin for sleep regualtion
71
New cards
cerebellum
coordinates movement, balance and posture
72
New cards
arbor vitae
the cerebellum contains a tree like structure called
73
New cards
cerebral cortex
what is the outer gray matter of the cerebrum
74
New cards
deep
the cerebrum has ____ nuclei
75
New cards
corpus callosum
bridge between the right and left side of the brain
76
New cards
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, and insula
What are the lobes of the cerebrum
77
New cards
frontal lobe
has motor functions, contains the motor cortex
78
New cards
parietal lobe
contains the somatosensory cortex,
recieves nerve impulses for touch, pressure, vibration, itch, tickle, temp., pain and proprioception
recieves nerve impulses for touch, pressure, vibration, itch, tickle, temp., pain and proprioception
79
New cards
temporal
audio and olfactory processing lobe
80
New cards
occipital lobe
recieves visual information and is involved in visual perception
81
New cards
insula
recieves impulses for taste and is involved in gustatory perception and taste discrimination
82
New cards
medulla oblongata to 2nd lumbar vertebrae
The spinal cord runs from where to where?
83
New cards
shorter
The spinal cord is ____ than spinal column
84
New cards
conus medullaris
What is the end of the spinal cord called
85
New cards
31
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there
86
New cards
the cord is tissue the column is bony structure
What is the difference between the spinal cord and spinal column
87
New cards
ventral
motor nerves are always on the ____ side
88
New cards
dorsal
sensory nerves are always on the _____ side
89
New cards
brings information up to or down from the brain
White matter in the spinal cord does what?
90
New cards
epinerium
the dura mater fuses with waht around the spinal cord
91
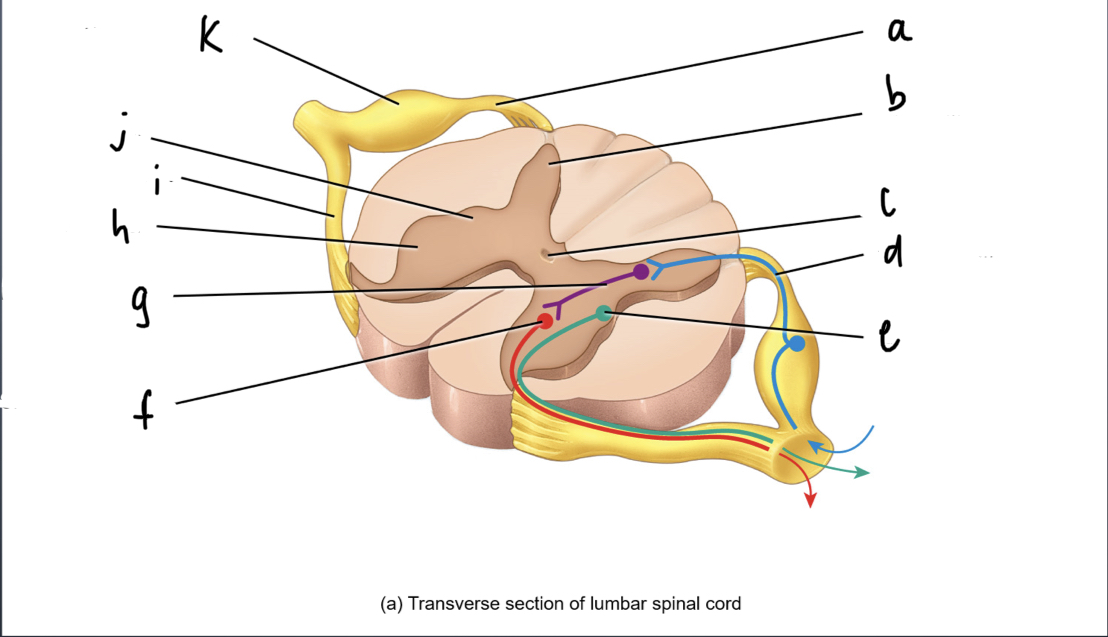
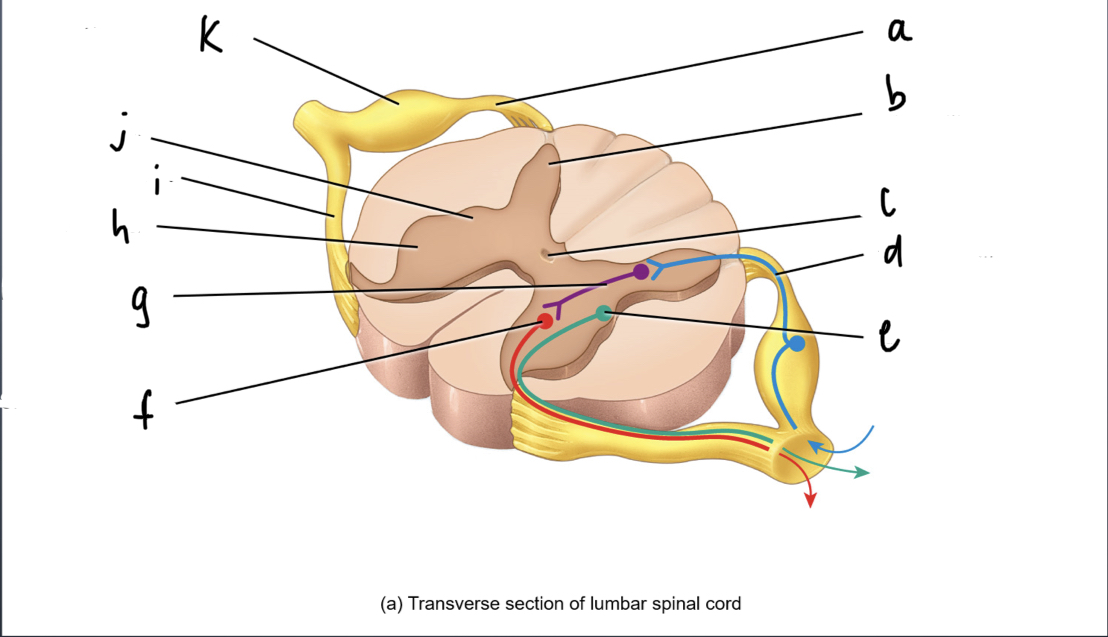
New cards
dorsal root
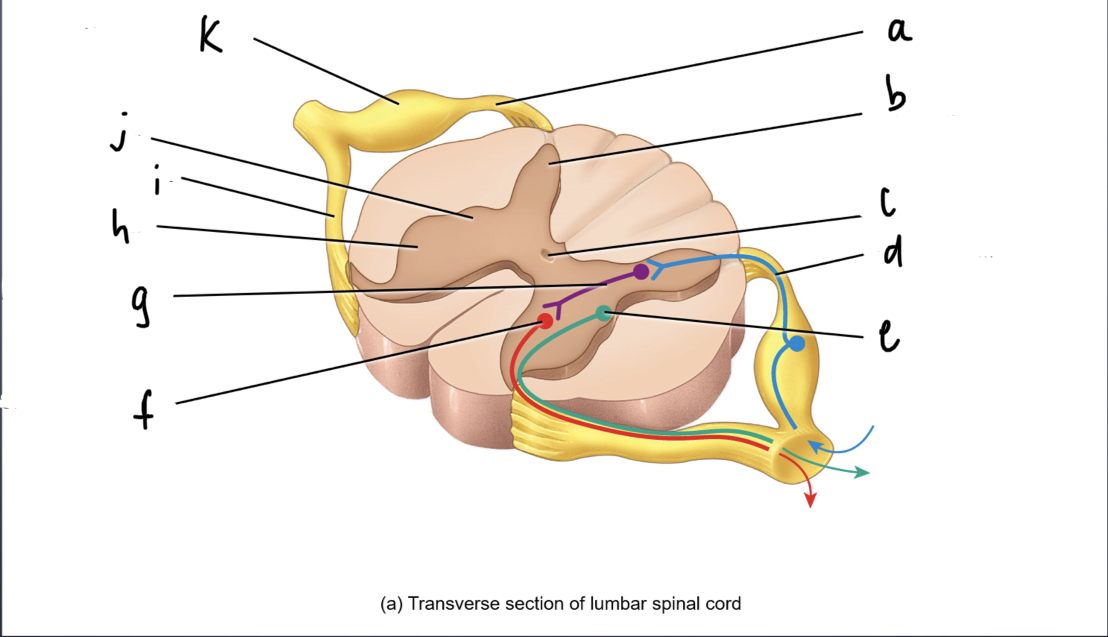
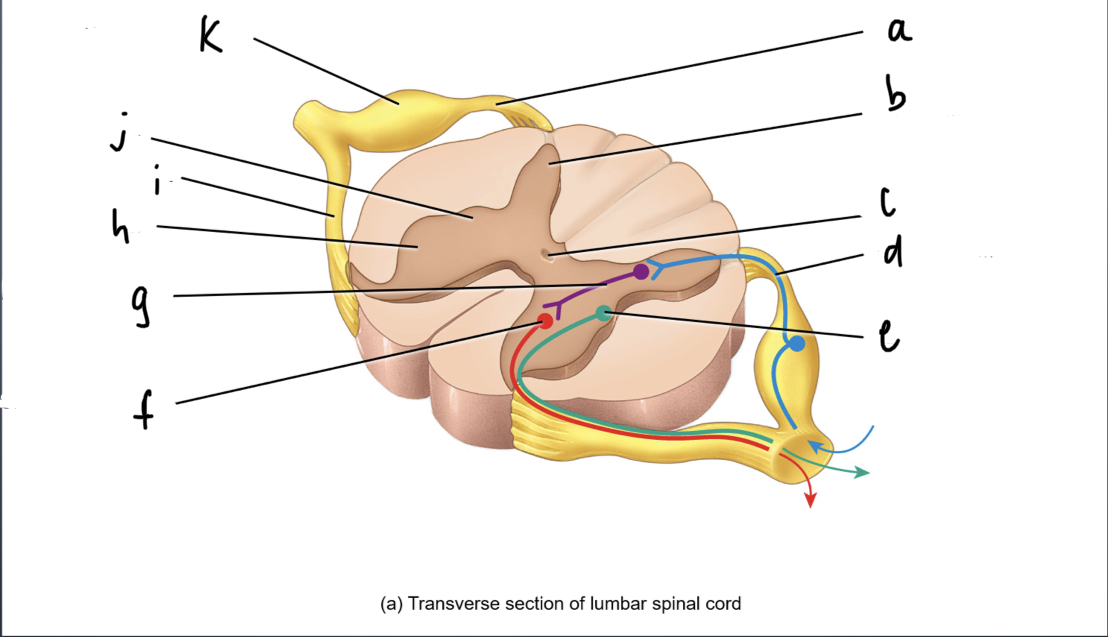
What is A
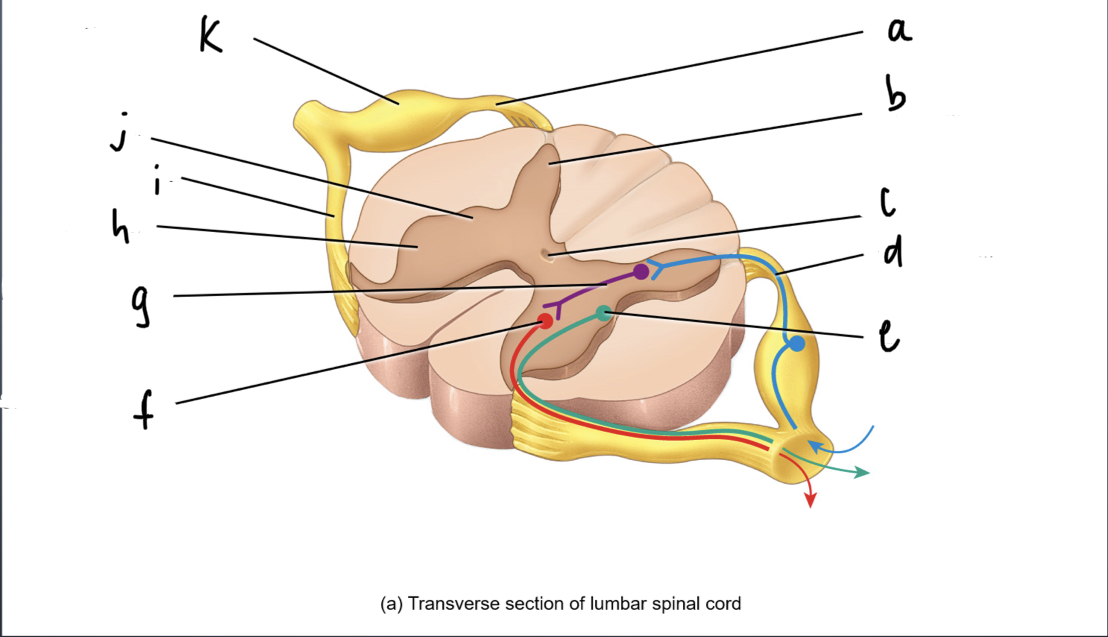
92
New cards
dorsal gray horn
What is B
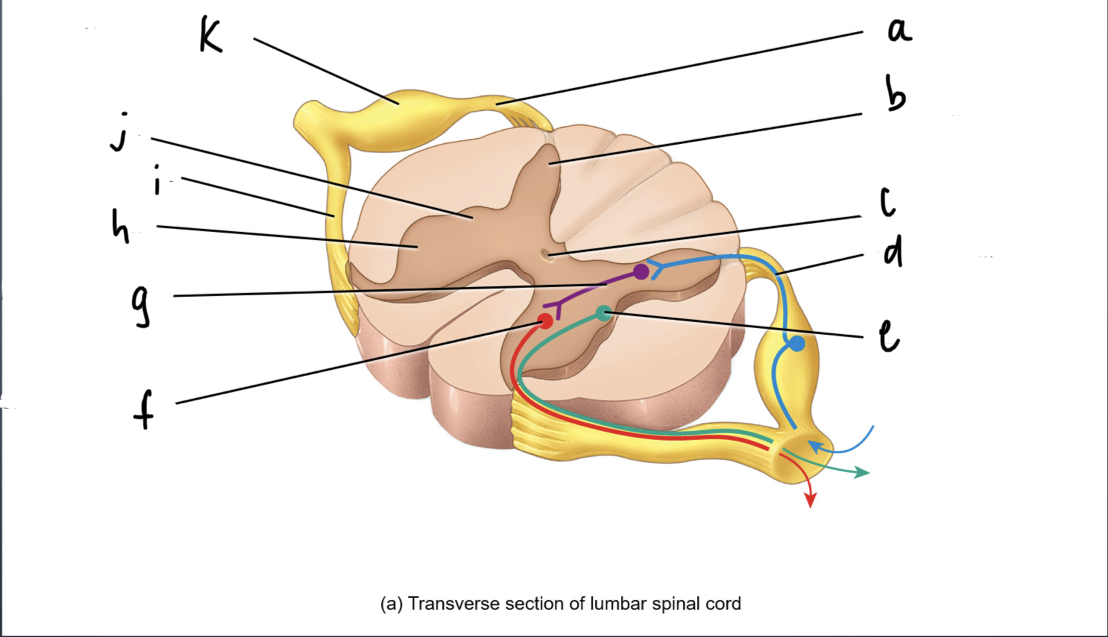
93
New cards
central canal
What is C
94
New cards
sensory neuron
What is d
95
New cards
autonomic motor neuron
what is e
96
New cards
sensory motor neuron
what is f
97
New cards
interneuron
what is g
98
New cards
ventral gray horn
what is h
99
New cards
ventral root
what is i
100
New cards
lateral gray horn
what is j