CHEM1111 Periodic Trends and Molecular Orbitals
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
BE-ABE/2
Formula for bond order.
Bond length decreases
As bond order increases, so does stability, meaning…
Bonding MO
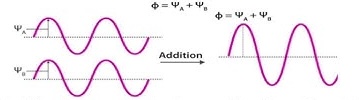
What is created from the addition of in-phase orbitals, as shown. (Constructive interference)
Antibonding MO
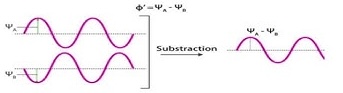
What is created from the addition of out-of-phase orbitals, as shown. (Deconstructive interference).
Between nuclei
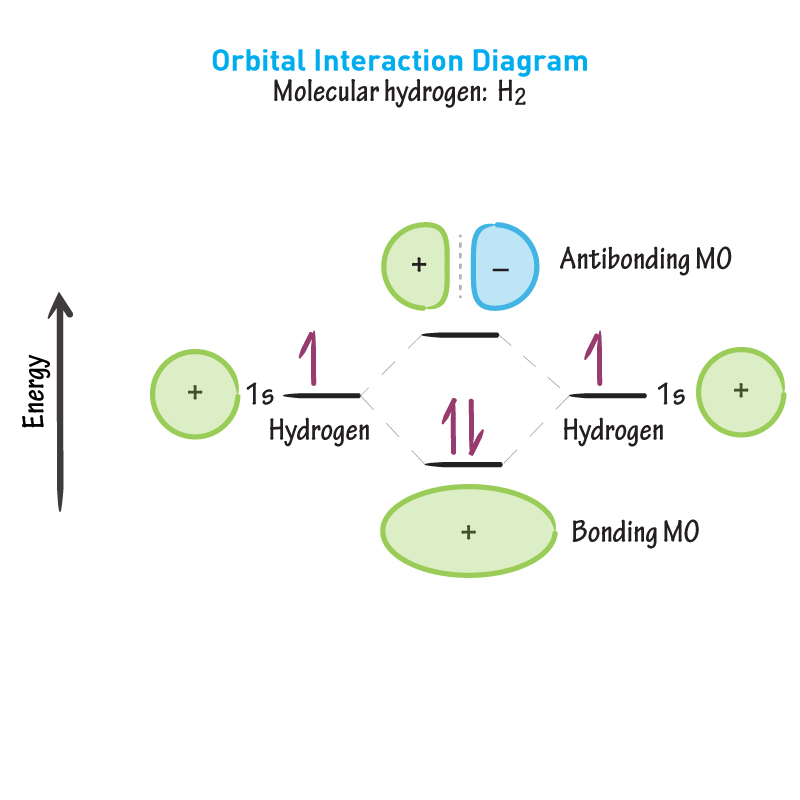
In the bonding MO shown, where are the electrons likely to be? Meaning bond formation is favoured.
Essentially 0
In the antibonding MO shown, what is the probability the electrons are between the nuclei? Meaning bond formation is NOT favoured.
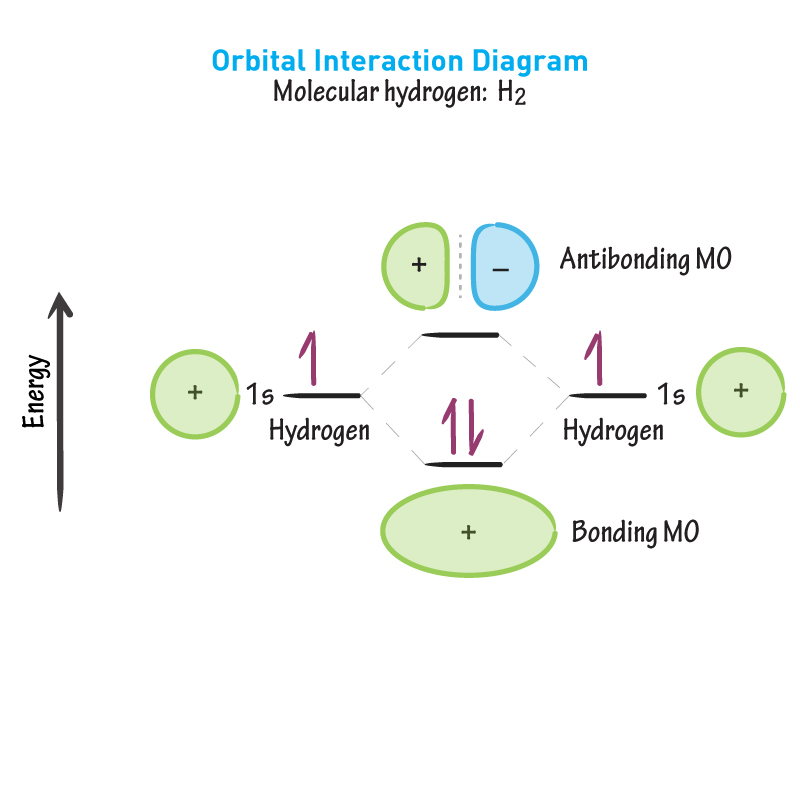
Energy level diagram
What is this image called?
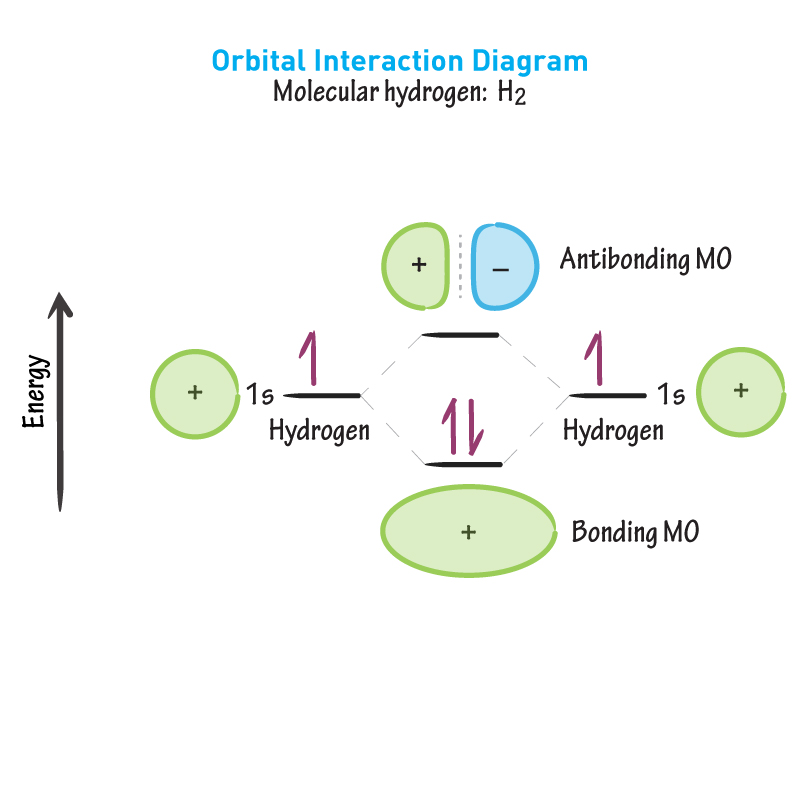
Bond formation is exothermic
What is the thermodynamic outcome of electrons falling to a lower level in molecular orbitals, thus releasing energy when molecules form?
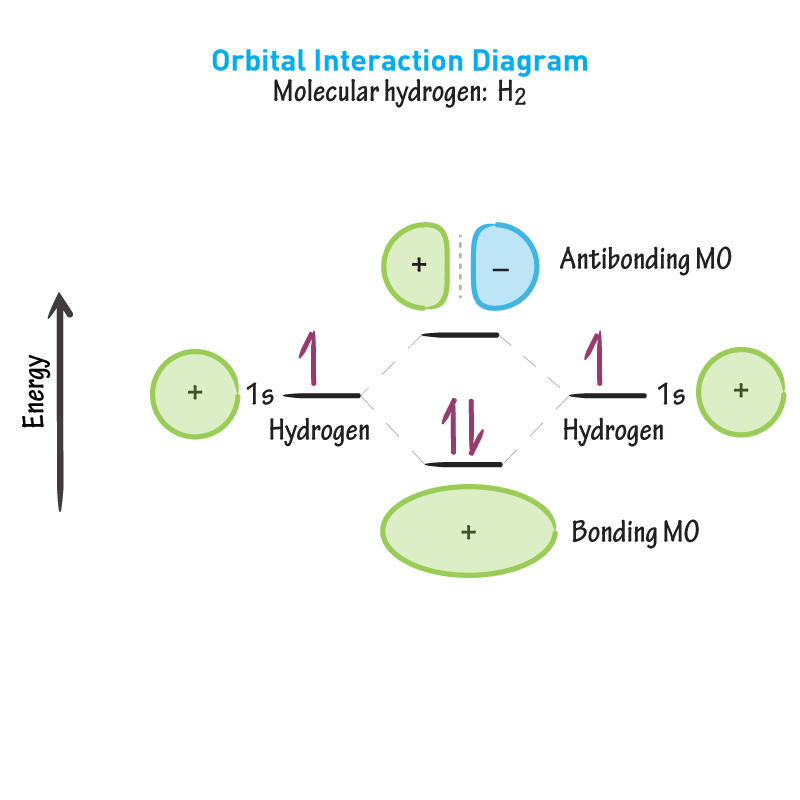
Paramagnetic
molecules with unpaired electrons and a net magnetic moment.
Paramagnetic
Out of paramagnetism and diamagnetism, which molecule be be drawn strongly into magnetic fields?
Diamagnetic
molecules that do NOT have unpaired electrons, and have no magnetic moment.
Effective nuclear charge (Zeff)
positive charge ‘felt’ by an electron in a multi-electron atom.
Nuclear charge (Z)
number of protons in nucleus.
First ionisation energy
energy required to remove the first electron from a neutral atom.
Ionisation energy (Ei)
the amount of energy required to remove an electron completely from an atom in the gas phase.
Anion radii
when electrons are added more electronic repulsion occurs, causing an increase in atomic radii.
Cation radii
when electrons are removed, the valence orbitals becomes closer to the nucleus, causing a decrease in atomic radii.
Electron affinity (EA)
the energy change when an electron is added to an atom as a gas.
Noble gases
elements with NO electron affinity because the electrons added must occupy a higher orbital.
Half-filled p or d orbitals
What group of elements have NO electron affinity because all the electrons currently in their valence orbital have parallel spins?
Atomic orbitals
describe the electrons in an atom.
Molecular orbitals
describe the electrons in a molecule.
Bond length
the average distance between the nuclei of two atoms that are covalently bonded to each other within a molecule.
Equilibrium bond length
the average distance between two bonded atoms at the point of minimum potential energy, described using the unit, Ångström.
The Bohr radius
the most probable distance between a proton and an electron in a H atom, 0.53 Å.
Angstrom (Å)
unit of distance used for atomic distances, Å is 1 x 10−10 m (= 0.1 nm).
Sigma (σ) orbitals
appear as s orbitals (i.e. round) when looking along the bond axis.
Non-bonding orbital
an MO that does not change the bond order between atoms because the electrons in it do not increase or decrease the bond strength.
Conduction band
the band of electron orbitals that are typically unoccupied so electrons are free to move and carry an electric current.
Valence band
the band of electron orbitals that are typically occupied.
Band gap
the energy gap between the valence and conduction band.
Hole
the absence of an electron in the valence band where an electron is expected to be.
Acceptor level
energy levels in the band gap close to the valence band created by impurities.
Donor level
energy levels in the band gap close to the conduction band created by impurities which holds one electron that can be easily donated to the conduction band.
n-doping
adding impurity atoms with more valence electrons than the semiconductor, increasing electrical conductivity by adding essentially free electrons.
p-doping
adding impurity atoms with fewer valence electrons than the semiconductor, increasing electrical conductivity by creating holes energy levels.
Network solids
multi-atom structures with electronic bands (rather than molecular orbitals), e.g. diamond.
Insulator
large band gap, electrons cannot be promoted to conduction band.
Semiconductor
electrons can be promoted from valence to conduction band upon heating.
Intrinsic semiconductor
have a small band gap so electrons can be promoted to the conduction band at higher temperatures, leaving holes in the valence band, e.g. silicon, germanium.
Extrinsic semiconductor
semiconductors that are doped with specific impurities, allowing stable conductivity at all temperatures. n-type and p-type.
Metal
no band gap as valence/conduction bands overlap, so can conduct electricity.
Allotrope
different crystalline or molecular forms of the same substance.
Doping
adding certain chemicals to a semiconductor to change its conductivity.
Donor level
What type of level is added in n-type doping of semiconductors?
Acceptor level
What type of level is added in p-type doping of semiconductors?
Right
What direction on the Periodic table should added elements be found relative to the host semiconductor for n-type doping?
Left
What direction on the Periodic table should added elements be found relative to the host semiconductor for p-type doping?
Solar cells
can be generated by combining an intrinsic semiconductor with both p-type and n-type extrinsic semiconductors.
Temperature
What condition can be increased to improve the conductivity of semiconductors by providing electrons with more energy?
Electrical conductivity, colour
What 2 properties can be attributed to the band gap in network solids?
Horizontally (— + —)
How are p orbitals added together to create sigma orbitals?
Vertically ( | + | )
How are p orbitals added together to create pi orbitals?
Black
What optical property is associated with a small band gap, which absorbs light?
Transparent
What optical property if associated with a large band gap, which does not absorb light?
Effective nuclear charge, ionisation energy, electron affinity (somewhat).
Which periodic trend/s increase going up and to the right of the periodic table?
Atomic radii
Which periodic trend/s increase going down and to the left of the periodic table?