Biology-Cell diversity and diffrentiation
1/346
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
347 Terms
Put these in order of smallest to largest
Chromatin
Chromosome
Atom
Neuclotide
DNA helix
Histone
Gene
Neucleosome
Atoms
Nucleotides
Histone
Neucleosome
Gene
DNA helix
Chromatin
Chromosome
At what phase does the replication of DNA occur
EQ
S
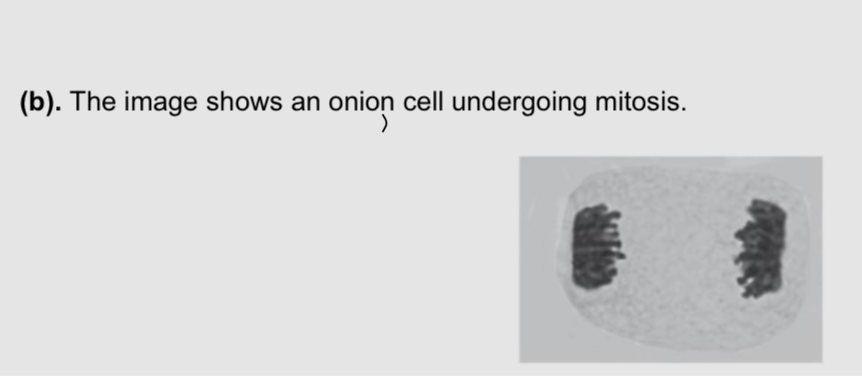
.describe how this cell would look different if it was in interphase
Not as dark
Single dark area in the middle
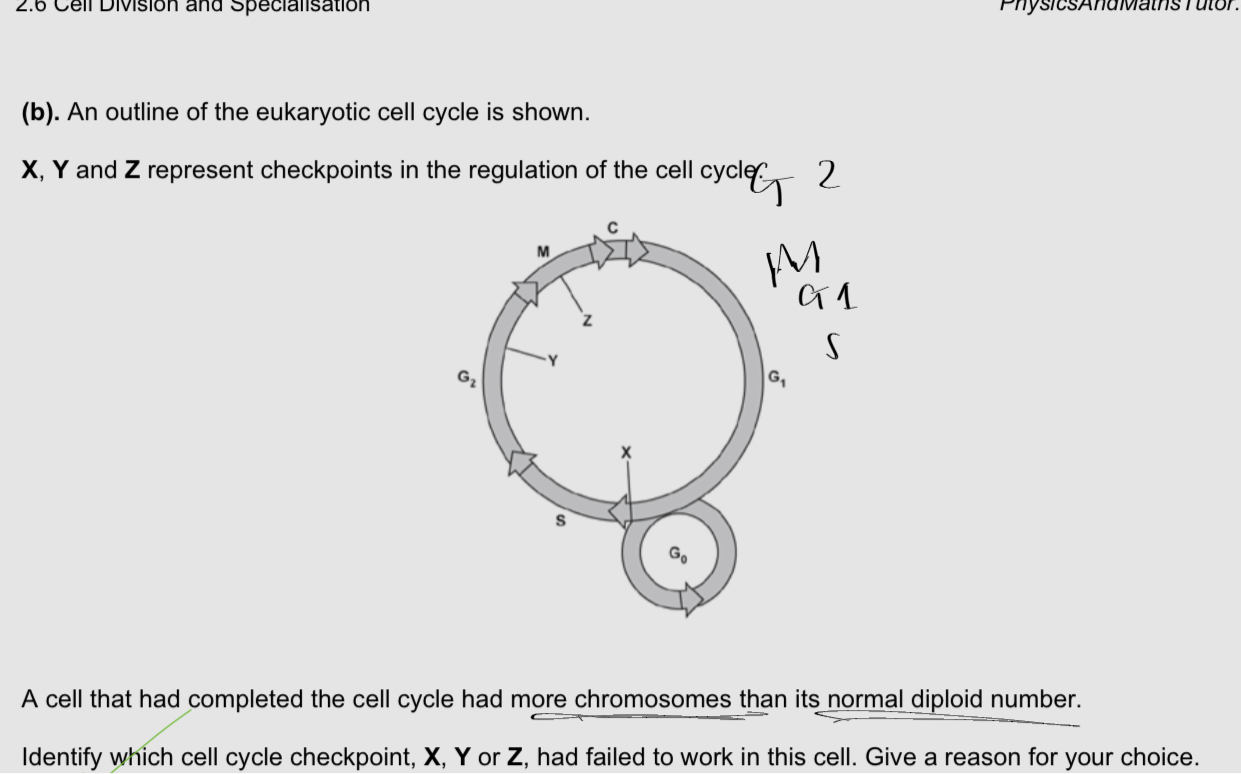
EQ
Z
As didn’t get enough chromosomes
State 2 roles of mitosis in organisms
EQ
Repair
Growth

EQ
To produce many genetically identical offspring
What condenses chromosomes or chromatin?
EQ
Chromosomes condense
What should you mention in evaluate questions?
EQ
Larger sample size
Explain the role of meristem tissue in a stem
EQ
Source of unspecialised stem cells that can differentiate into other cells
Which checkpoint checks for DNA damage first?
EQ
G1 bc cells should be stopped from entering the s phase
Brm
What happens when xylem vessels are formed
Lignin impregnates the cell walls making them impermeable to water
All cytoplasm is lost
What happens when phloem is formed
Sieve tube elements become elongated and lose most of their cytoplasm
How can stem cells be used to treat a disease mark scheme answer structure
Stem cells differentiate into (cells required) so (what the cells produce) levels increase
True or false
Neutrophils undergo mutation during differentiation
False
Tue or false
Erythrocytes develop large numbers of ribosomes early in their differentiation
True
True or false
Majorit of organelles in red blood cells are broken down by hydrolysis
True
True or false
Adult stem cells are totipotent
False
Is meiosis 2 reduction division
Yes
Is mitosis reduction division
Yes
Is meiosis 1 reduction division
No
Why is blood described as a tissue not an organ
Blood is a collection of different cells that work together to perform a function not a collection of different tissues
True or false
Adult stem cells can be used as a renewing source of undifferentiated cells
True
Pluripotent definition
Cells that can differentiate into any type of cell but cannot form whole organisms
Advantage of IPSCs
No risk of rejection
Disadvantages of IPSCs
Greater risk of cancer
Explain the role of meristem tissue in a stem
Source of undifferentiated cells for growth
Name on neurological disease that can treated by stem cells
Parkinson’s
What do you call chromosomes in meiosis 1
Homologous chromosomes
What do you call chromosomes in meiosis 2
Sister chromatids separate in anaphase
Chromosomes
Chiasmata
Parts where chromatids are joining
In what condition are chromosomes visible
When they are condensed into chromosomes
Yes chromosomes
Helicase function
Unzips dna helix
Breaks hydrogen bonds between the two strands
The enzyme microtubules depolymerase breaks down spindle fibers in mitosis/Which phase of mitosis will have the highest number of active microtubules deplymerase enzymes
Telophase-spindle fibers are broken down/depolymerased during telophase
How is mitosis significant in the development of the whole organism
Mitosis can be controlled at certain points in development which will change body plans
Can microtubules be prevented form functioning and why
Yes
By a respiratory inhibitor
Which letter shows a homologous pair of chromosomes in metaphase2
A because these both have similar shapes and length
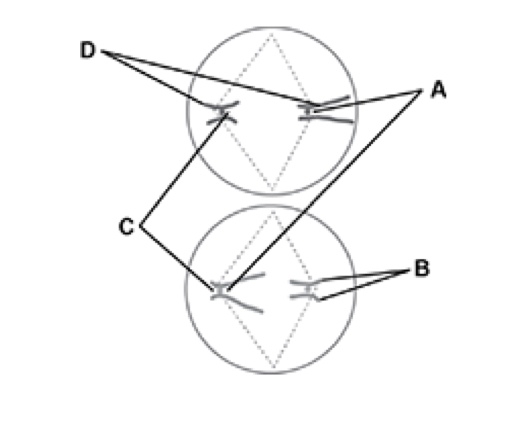
Suggest one abnormality in the cells of a tissue that has a genetic mutation stopping the metaphase checkpoint
Some cells contain an incorrect number of chromosomes
What will happen if there is a mutation in the G2
Cells should be stopped from entering the S phase and DNA damage is checked here
List all the phases of interphase in order
G1,S,G2
Don’t include G0
What is checked at G2 checkpoint
If DNA has replicated correctly
Which stage of interphase has the highest number of cells
G1
What observations would have proved that a cell had stopped dividing in the G2 checkpoint
More DNA
No visible chromosomes

How would you do this
Measure radius of the other cell adn substitute that value into the formula for the volume of a sphere
Roles of mitosis in multicellular organisms
Gametes from haploid cells
Asexual reproduction
Draw a biological drawing of the cell in metaphase
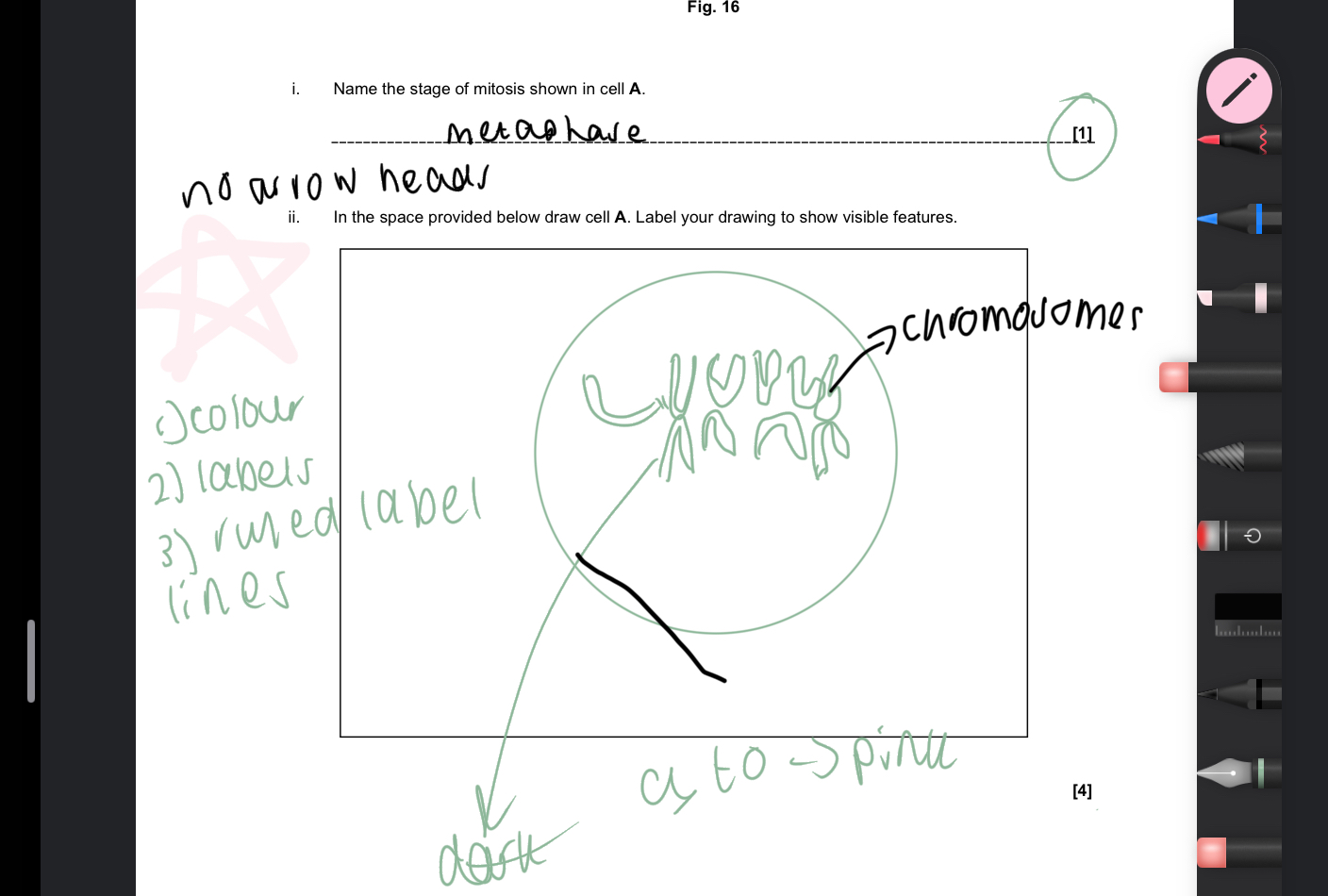
Draw a biological drawing of a cell in anaphase
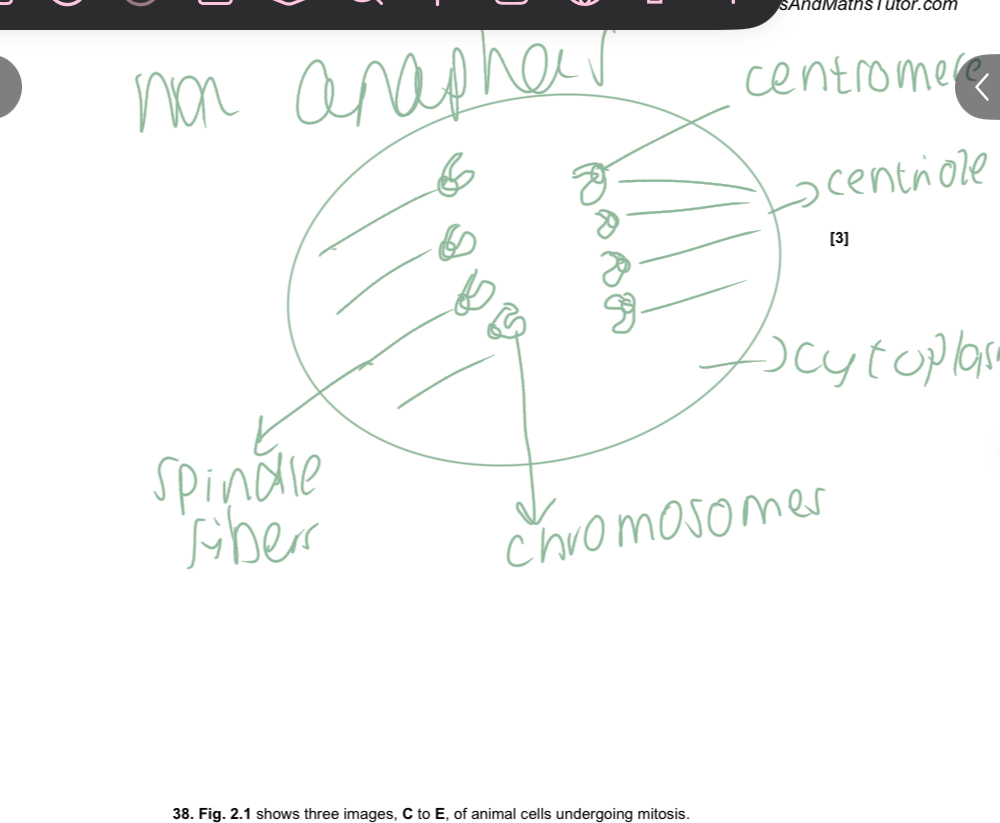
Prophase-mitosis
Mark scheme answer
Chromosomes condense and become visible
Membrane breaks down
Telophase mitosis
Spindles break down
Chromatids pulled to opposite poles of cell
New cell membrane visible down center of cell
Why does a zygote undergo mitosis and not meiosis
Cell growth
Genetically identical gametes produced
Observations of a cell in prophase1
Dark area of chromosomes visible in the center
Nuclear envelope present
No nucleolus
Explain how the organisation of homologous chromosomes during metaphase 1 increases genetic variation
Independent assortment
Homologous chromosomes line up across the equator of the cell
Maternal and paternal chromosomes face either pole in either cell
What is genetic variation
Variety of alleles
How does crossover in prophase 1 produce genetic variation
Alleles swapped
Base sequence of chromosomes altered
How do haploid gametes produce genetic variation
Sperm form one cell can fertilise an egg form any other cell in the population
Hydra can have different alleles
Why does sexual reproduction occur in some organisms only in the winter
Offspring need genetic variation to survive unfavourable condition
In what phase of interphase is the enzyme helical present
S phase
What happens at one of the checkpoints if damages DNA is present
If detected at G2 checkpoint then cell cycle is halted adn cell tries to repair damage
Which stage of the cell cycle would DNA polymerase be most active
S phase
As polymerase synthesises strands of DNA
Do erythrocytes undergo mitosis
No
At which stage does the p53 gene interrupt the cell cycle to prevent the copying of damaged DNA
G1 checkpoints
Pauses cell cycle before DNA replication occurs in the S phase
Reduction division
The first stage of meiosis where a diploid parent cell divides to produce two haploid cells,
How is the second division of meiosis different from mitosis
Separating chromatids of a pair are not the same
No homologous in second division—>cross over and genetic variation
What leads to variation within a species
Independent assortment of homologous chromosomes
What happens if DNA damage is discovered at the G2 checkpoint?
Cell cycle is halted and the cell tries to repair the DNA
What divides during mitosis
Nucleus
When does the second checkpoints occur
At the end of the g2 phase
What do G1 and g2 checkpoints both check for
Damage to DNA
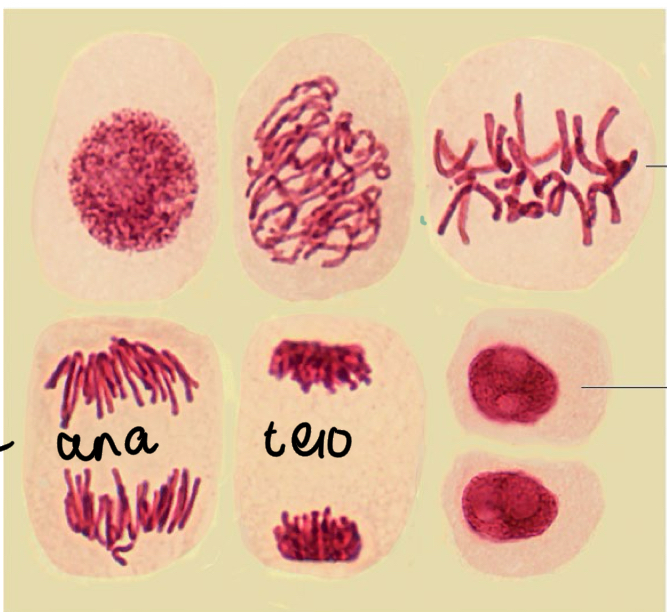
What stage of mitosis is shown in this image
Telophase
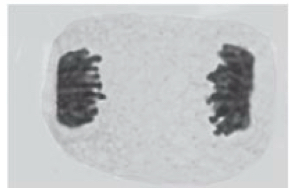
What would anaphase look like in mitosis in an image
V shaped chromosomes
Chromosomes would be shown separating
What would an image of a cell that was in interphase look like
Single dark area
Chromosomes wouldn’t be visible
Why are root tissues chosen to study mitosis
Cells undergo mitosis
Two similarities between prophase in mitosis and prophase 1 in meiosis
Spindle fibres appear
Chromosomes condense in prophase 1
Name two differences between prophase in mitosis and prophase 2 of meiosis
Meiosis:
Only one chromosome present form each homologous pair
-chromatids are not genetically identical
How can phloem cells be produced
Meristem tissues divide and differentiate
Difference between tissue and organ
Tissue is collection of cells
Organ is a collection of tissues
Helicase function
Unzips double helix
Breaks hydrogen bonds between two strands
Explain how errors may occur during DNA replication
Mutation so change in DNA sequence
Exposure to mutagen
What checkpoint has not worked properly as there are more chromosomes than the normal diploid number
Not all chromatids have been replicated
Chromosomes have not aligned correctly at th equator
Why is mitosis not meiosis used for asexual reproduction on plants
Produced genetically identical cells
Maintains chromosome number
Why can bacteria not reproduce asexually by mitosis
Mitosis is nuclear division and bacteria do not have a nucleus
Why do erythrocytes have to be replaces by bone marrow stem cells
Can’t undergo differentiation as have no dna
Sequence of events in cell cycle
G2
Mitosis
Cytokinesis
G1
S
Why does interphase sometimes stop
Few nucleotides
S phase stops
As less complementary bases
Role of mitosis in fragmentation
Produce many cells that are genetically identical
How does meiosis produce genetic variation in the offspring
Independent arrangement of chromosomes in metaphase 1 and 2
Crossover
When haploid cells fuse to form diploid cells are they genetically different or identical
Meiosis occurs even if haploid cells fuse to form diploid cells
Even if join still are Gentically different
Name cell x and y
X is a lymphocyte
Y is a neutrophil
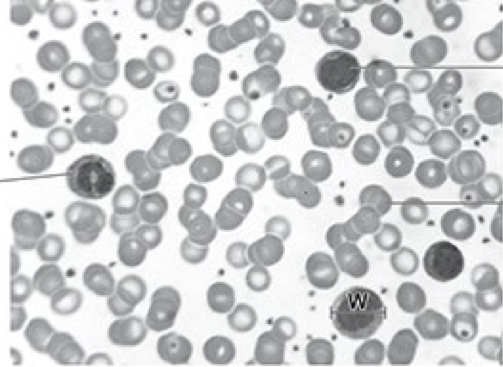
What occurs in g2 phase
Exam mark scheme
Mitochondria organelle replicates
Tubulin proteins synthesis
Are there homologous pair of chromosomes in mitosis
No
Meiotic index
number of cells in mitosis divided by the total number of cells observed
What can be deduced about a cell that remains in apoptosis
Not dividing
Spends all its time in G1
28×2=56
56×2=112
112×2=224
What is the role of guard cells in photosynthesis
Water enters guard cells from neighbouring epidermal cells By osmosis
Guard cells swell
Tips bulge and the gap between the stoma enlarges
Photosynthesis
Light energy used to make ATP
ATP actively transports potassium ions from epidermal cells into guard cells lowering their water potential
Guard cells bit -on another flashcard
Stomata opens air can enter the spaces within the layer of cells beneath the palisade cells
Gas exchange occurs-CO2 diffuses into the palisade cells -maintains steep concentration gradient
Oxygen produced can diffuse out of palisade cells into air spaces and out through the stomata