🧬AP BIO Unit 1 Review - Chemistry of Life
Polymers and Macromolecules
Carbs
CHO
monosaccharide
glucose, fructose
fuel
convert/combine to other molecules/polymers
disaccharides
lactose, sucrose
fuel
convert/combine to other molecules/polymers
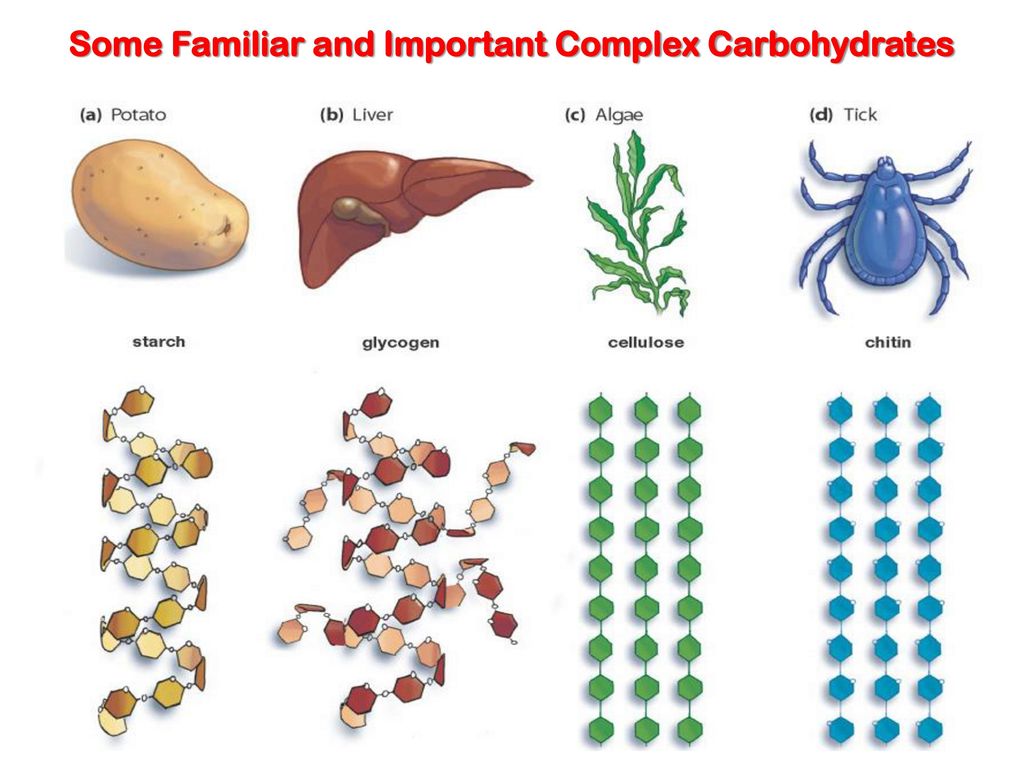
polysaccharides
Cellulose: plants, strengthen cell walls
starch: plants, stores glucose for energy
glycogen: animals, stores glucose for energy
chitin: animals/fungi, strengthen exoskeletons and fungal cell walls
Lipids
CHO sometimes P
-hydrophobic
-triacylglycerol: fats and oils, glycerol + 3 fatty acids, energy, butter, oil
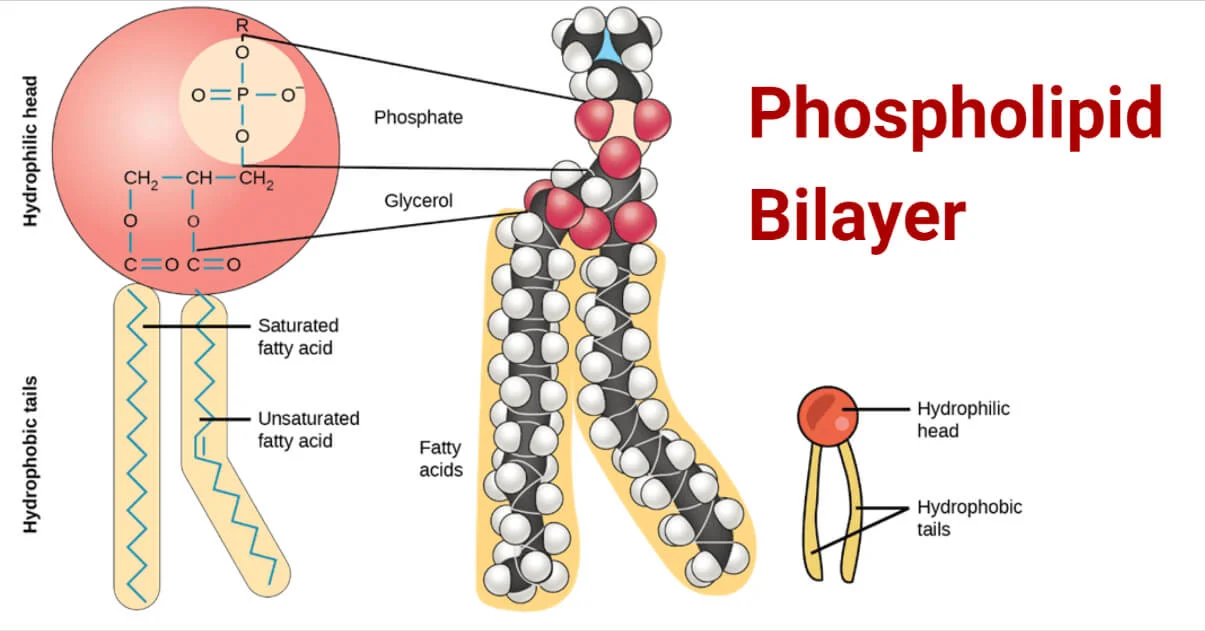
-Phospholipids: head with P + two fatty acids + glycerol,
bilayers: hydrophilic head towards water, tails on the inside
-Steroids: 4 fused rings + chem groups, cell membrane (cholesterol), signal travel molecules(hormones)
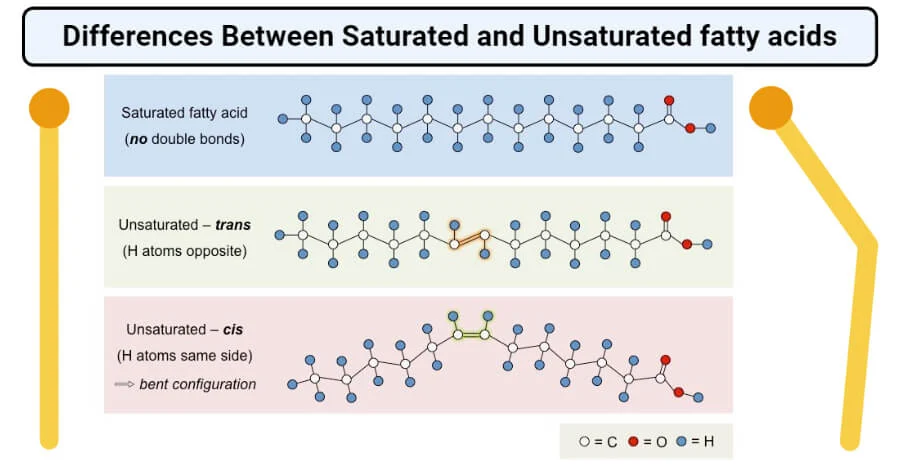
-fatty acid hydrocarbon chain + carboxyl group
-saturated more hydrogen, solid, unhealthy because they can stack close together
-unsaturated double bonds fewer hydrogen, kinks(cis), liquid
-trans fat add hydrogen
-fatty acid: long hydrocarbon chain + carboxyl group
Proteins
CHONS
-divers structures and functions
-amino acid monomers
-enzymes, structural, storage, transport, hormones, receptor, motor, defensive
-enzyme catalyst
-20 types: nonpolar+hydrophobic, polar+hydrophilic, acidic/- charge, basic/+ charge
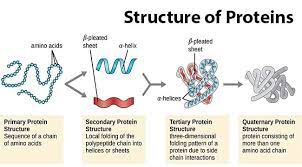
-primary linear sequence
-secondary pleated sheets alpha helix (from backbone molecule interactions)
-tertiary shape from side chain interactions
-quaternary multiple polypeptide chains
DNA/RNA
CHONP
-Transmit genetic info and allow protein synthesis (DNA→ Proteins)
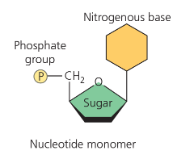
-Nuceotide monomers
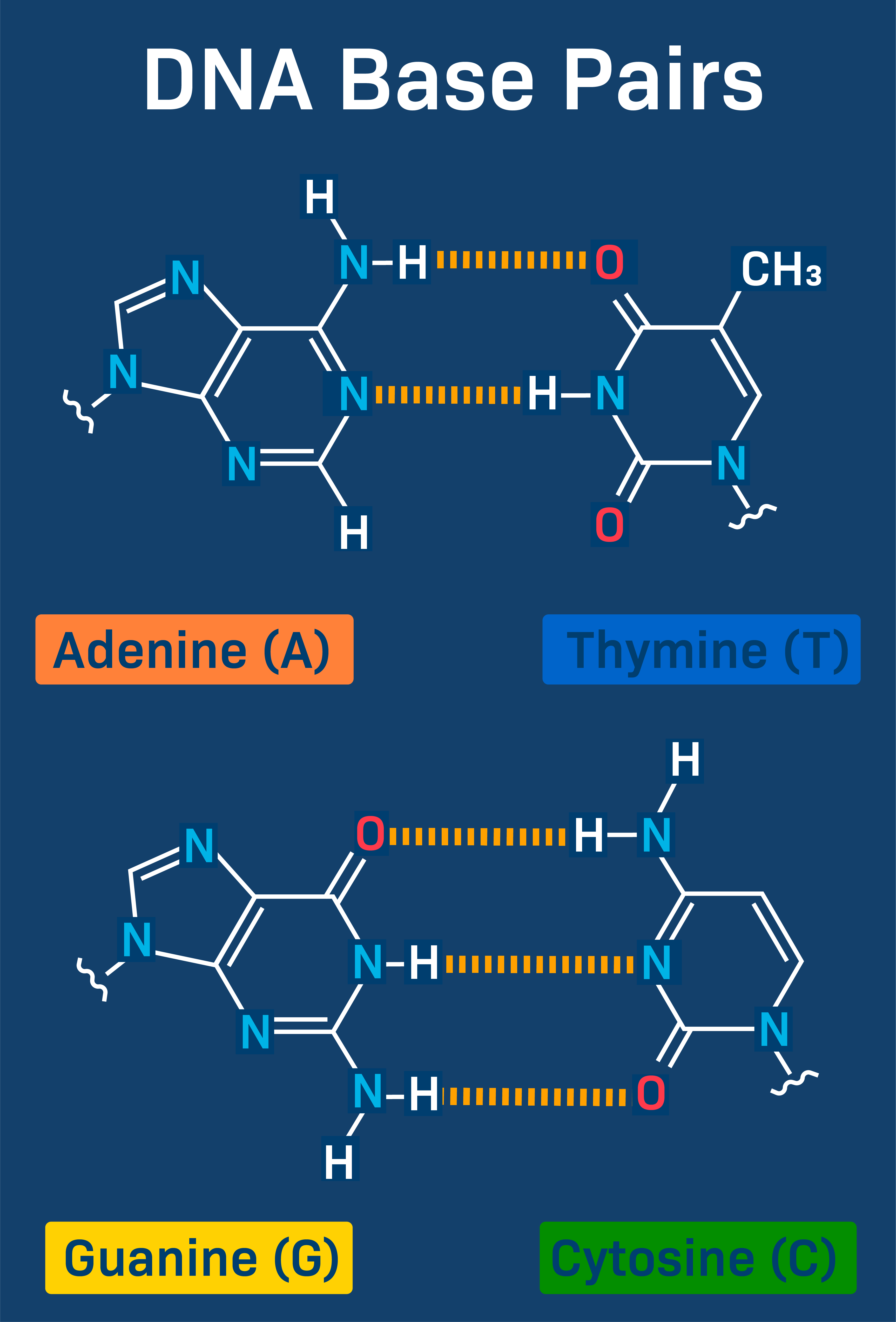
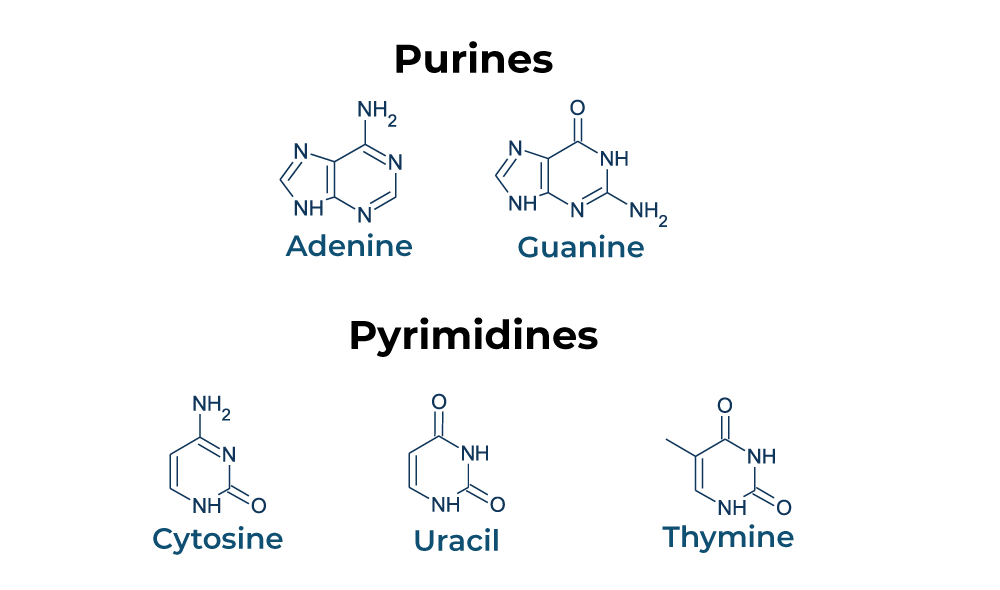
nitogenous bases
pyrimidines: cytosine, thymine, uracil
puines: adenine and guanine, double ring
DNA:
cytosine pairs iht gunaine
adenine pairs with thymine
has thymine no uracil
RNA:
adenine pairs with uracil
cytosines pairs with guanine
has uracil not thymine
phosphate group
sugar
-bonds
C and G have 3 hydrogen bonds, A and T have 2 (more bonds = stronger hold)
weak hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous base pairs of complementary strands
strong polar covalent bonds on nucleotides of sugar phosphate backbone
-rna
ribose sugar
A ribose sugar has an −OH group linked to the 2′ carbon that a deoxyribose sugar does not
single stranded
gene expression
instructions from DNA to ribosomes
folds in on self sometimes from bonds between N bases
-dna
deoyribose sugar
double sranded
antiparallel
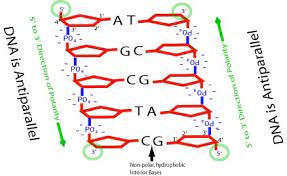
contains hereditary information
-3’ = OH (hydroxyl) 5’ = Carbon, nucleotides added to 3’
ADP/ATP
-adenine base, ribose sugar, 3 or 2 P groups
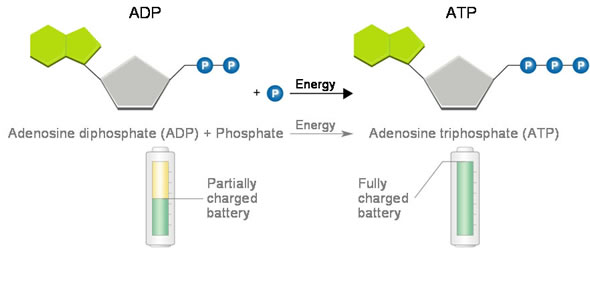
-ADP
diphosphate
energy from carbs synthesizes ADP back into ATP
-ATP
triphosphate
stores energy
2nd and 3rd bonds like a spring, hold potential chemical energy
released as bond is broken by hydrolysis
- 
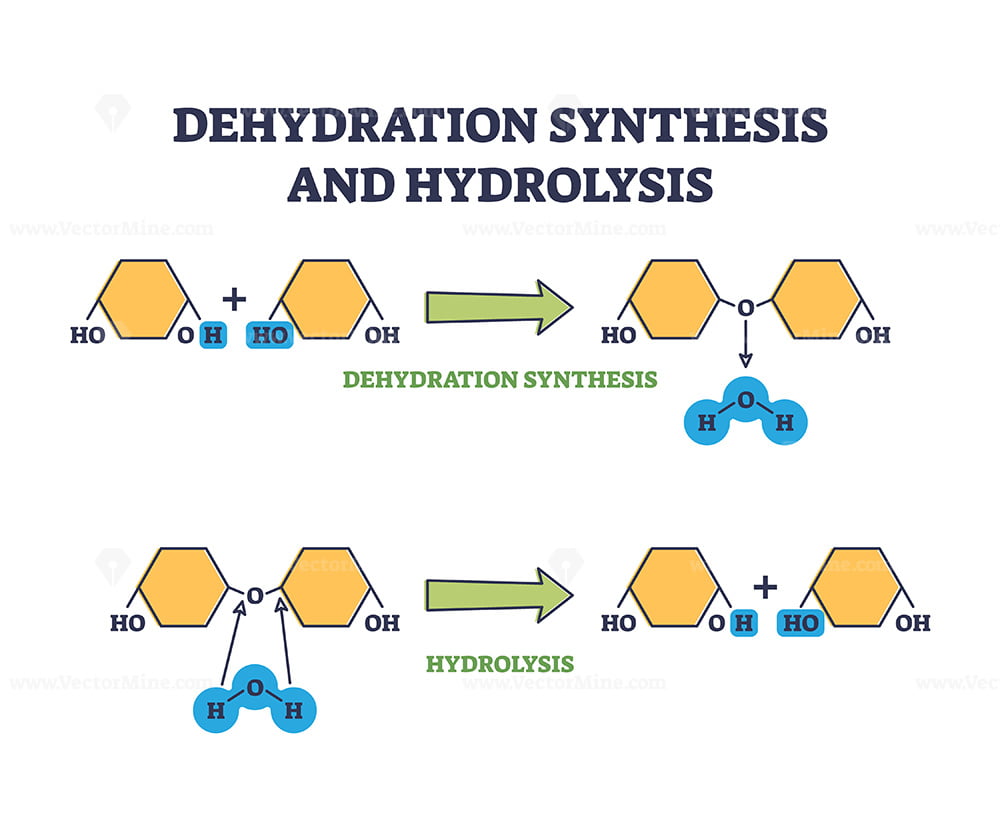
-hydrolysis
a water molecule is added
breaks bonds
-dehydration
a water molecule is removed
monomers are joined
-how would a monosaccharide be added to a polysaccharide?
A specific enzyme removes the hydrogen (HH) from the monosaccharide and the hydroxide (OHOH) from the polysaccharide, creating a bond between the two and creating a water (H2OH2O) molecule
This is a description of dehydration synthesis, which joins multiple monosaccharides to create a polysaccharide and produces water (H2OH2O) molecules
- 
Chemical Groups
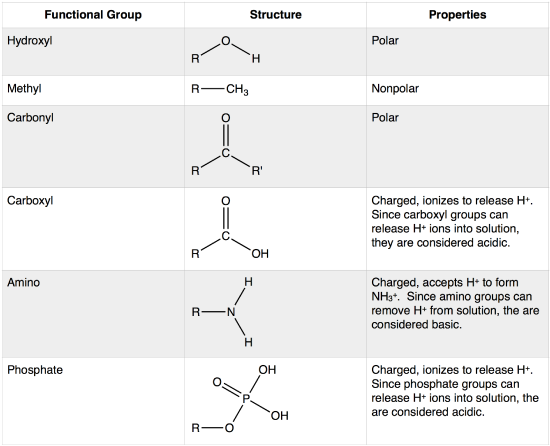
-HYDROXYL, -OH, alcohol
-CARBOXYL, -COOH, acid
-AMINO, base, -NH2
-Phosphate, OPO32-, head charged phospholipids
- 
Types of Bonds
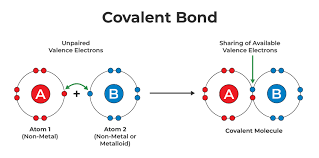
-covalent bond
pairs of electrons are shared
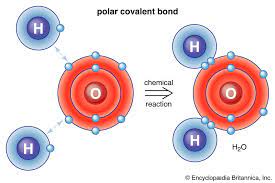
-polar covalent bond
atoms with different electronegativities share electrons in a covalent bond
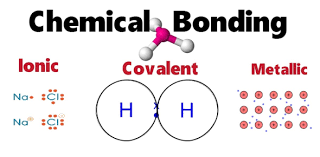
-chemical bond
atoms interact and complete their valence shells
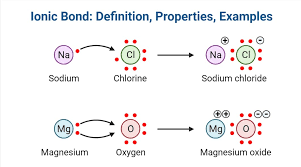
-ionic bond
the attraction between two oppositely charged ions, such as Na+ and Cl−
-van der waals interactions
adjacent atoms come close enough that their outer electron clouds just barely touch
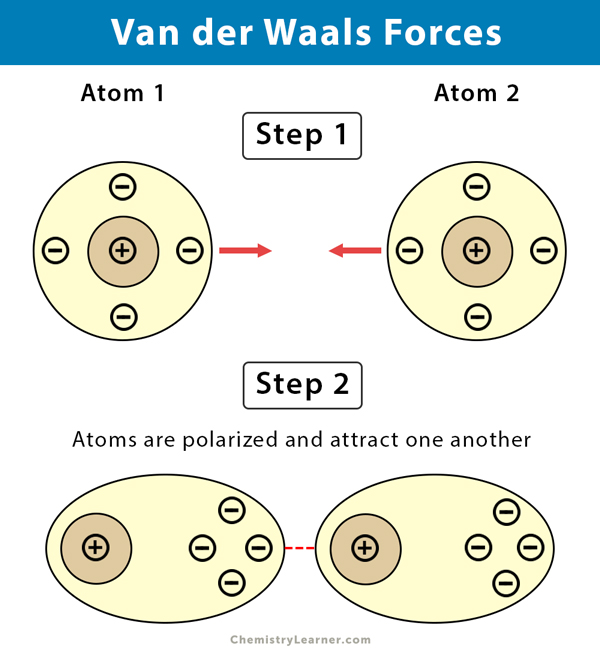
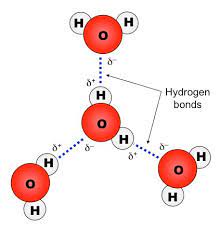
-hydrogen bond
forms when the slightly negatively charged oxygen of one water molecule is attracted to the slightly positively charged hydrogen of a nearby water molecule. Hydrogen bonding between water molecules is the basis for water’s properties
Properties of Water
4 main properties:
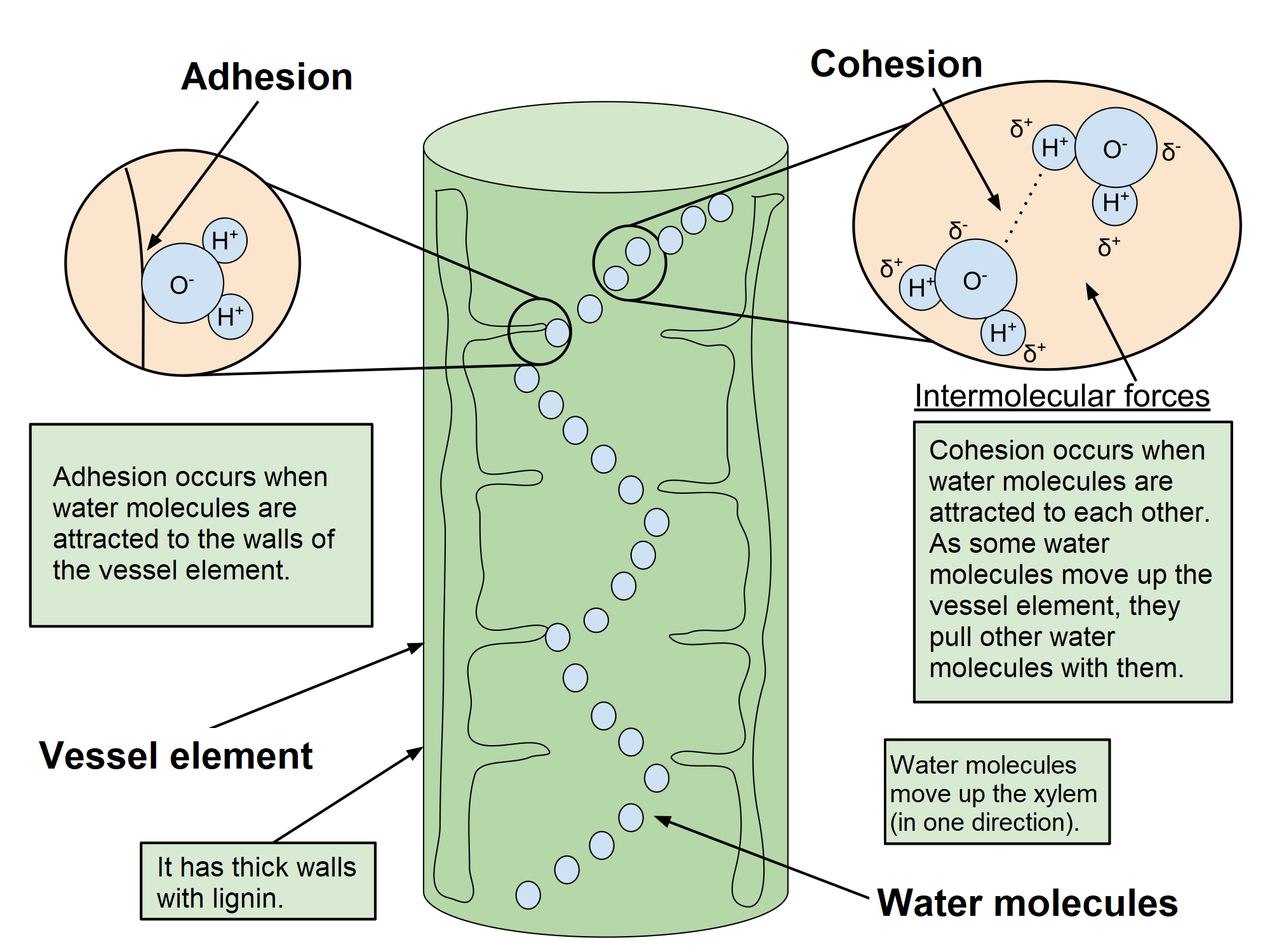
cohesion
moderation of temperature
high specific heat
moderation of coastal climates
evaporative cooling (sweat)
heat of vaporization
ice floats on liquid water
molecules expand as they get colder
solid water floats insulating water below for aquatic organisms
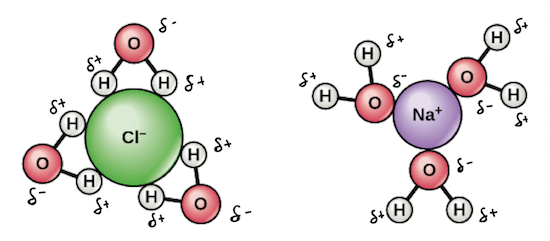
water as a solvent
its polarity helps break bonds
Vocab:
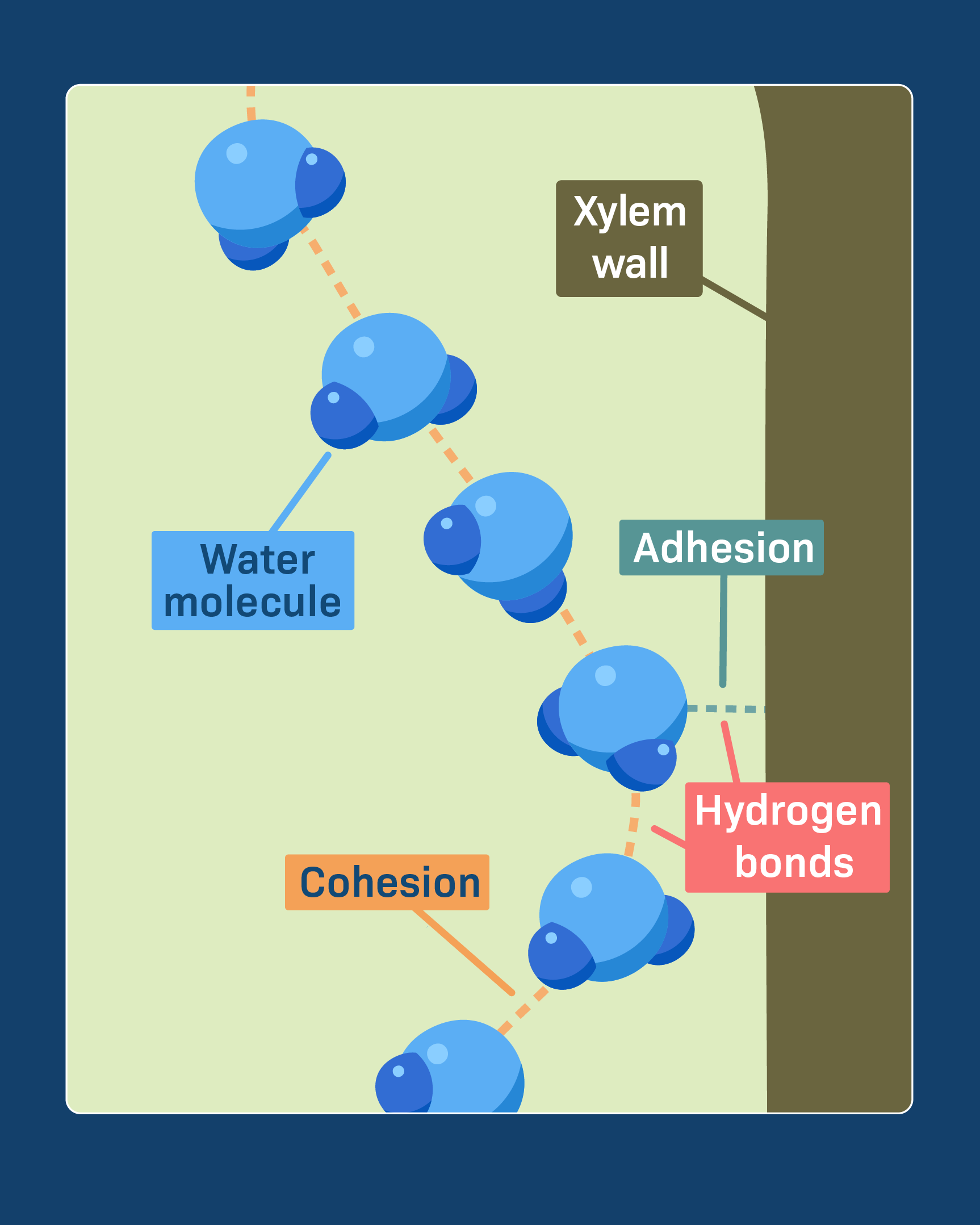
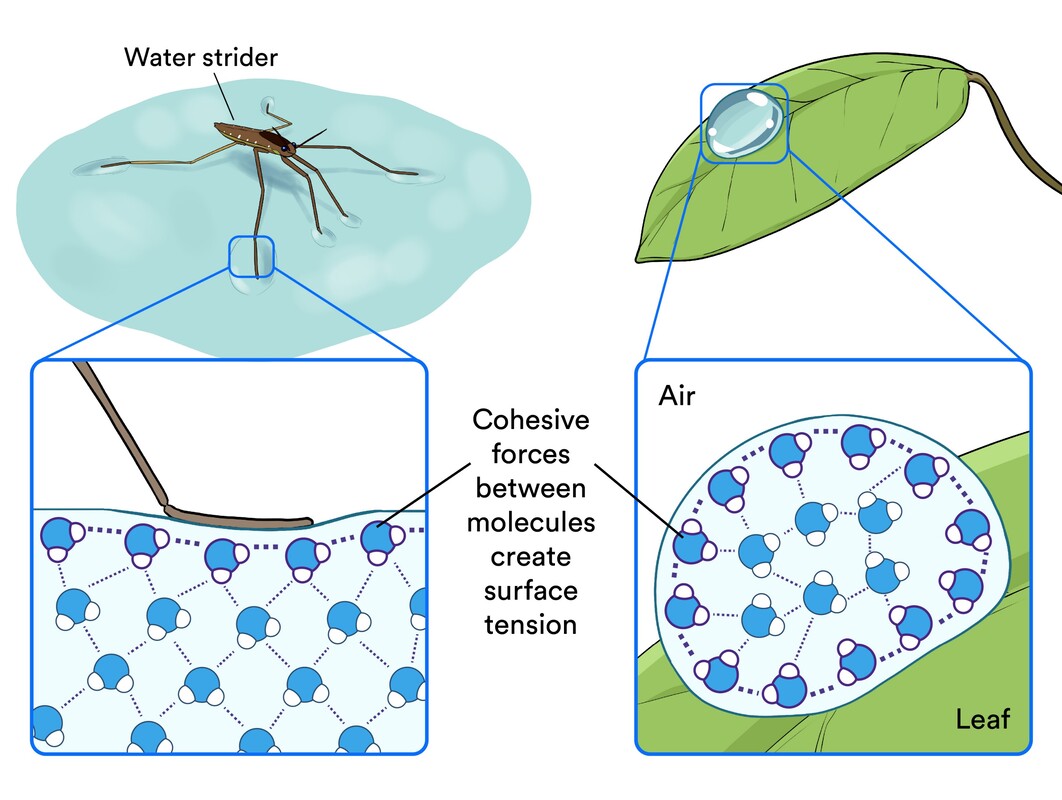
Cohesion: The linking together of like molecules, often by hydrogen bonds
Adhesion: The clinging of one substance to another, such as water to plant cell walls, by means of hydrogen bonds
Surface tension: A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
Specific heat: The amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1 g of a substance to change its temperature by 1°C
Evaporative cooling: The process in which the surface of an object becomes cooler during evaporation, a result of the molecules with the greatest kinetic energy changing from the liquid to the gaseous state
Heat of vaporization: The quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g of it to be converted from the liquid to the gaseous state
Solvent: The dissolving agent of a solution. Water is the most versatile solvent known