IB Biology HL Topic 11 - Animal Physiology
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:38 AM on 9/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
1
New cards
Osmoregulation
the control of solute concentrations and water balance
2
New cards
Osmoconformers
An organism that allows its internal salt concentration to change with the salinity of the surrounding water; always matches external conditions
3
New cards
Nitrogenous waste
Waste products of metabolism that must be excreted; ammonia (fish), urea (mammals) or uric acid (birds and insect)
4
New cards
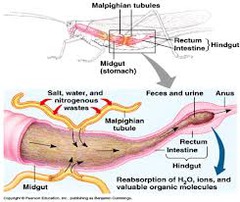
Malpighian tubules
An organ that is unique to insects, empties into digestive tract and removes nitrogenous wastes from the hemolymph
5
New cards
Hemoplymph
Circulating system of fluids in insects, akin to the blood system in humans; contains uric acid, amino acids, water etc
6
New cards
Hindgut
Selective reabsorption of useful substances in insects; uric acid and some water passes through to the rectum for excretion
7
New cards
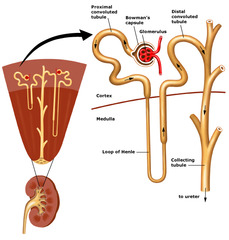
Cortex (kidney)
outer, dark layer of the kidney containing the majority of the nephron
8
New cards
Medulla (kidney)
inner portion of kidney, lighter colour where the loop of henle and collecting duct leads to
9
New cards
Renal artery
artery that carries blood to the kidney; higher glucose, oxygen, urea, toxins, drugs, salts; less CO2; variable concentrations
10
New cards
Renal vein
vein that carries blood out of the kidney; higher CO2; lower glucose, oxygen, urea; constant concentrations; equal blood cell count to artery
11
New cards
Ureter
tube that carries urine (urea dissolved in water) from the kidney to the urinary bladder
12
New cards
Nephron
functional unit of the kidney, dips into the medulla; bowman's capsule + proximal tubule + loop of henle + distal tubule + collectin duct
13
New cards
Ultrafiltration
a high pressure, nonspecific filtration through a the selectively permeable basement membrane, seperating the filtrate from the blood
14
New cards
Filtrate
contains water, amino acids, urea, glucose, small proteins, toxins, drugs, oxygen etc
15
New cards
ADH
antidiuretic hormone, increased levels cause the collecting duct to be more permeable to water, allowing more to be retained in case of dehydration; release by pituitary gland
16
New cards
Hemodialysis
the process by which waste products are filtered directly from the patient's blood using a dialyzer when the kidneys fail
17
New cards
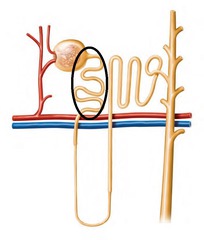
Proximal tubule
80% water reabsorbed by osmosis as well as many other nutrients, ions, minerals; equal concentration to distal tubule
18
New cards
Distial tubule
Follows the loop of Henle; equal concentration to proximal tubule although volume is much lower due to water reabsorbed in the loop of Henle.
19
New cards
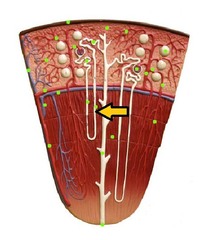
Loop of Henle
maintains hypertonic environment in medulla; descending limb impermeable to sodium ions and alows water to exit; ascending limb opposite
20
New cards
Urinary tests
test for blood, glucose, hormones (pregnancy), drugs
21
New cards
Antigen
a toxin or other foreign substance that induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies.
22
New cards
MHC I
found on all body cells with a nucleus; allows immune system to distinguish "self" from "foreign"; not found on blood cells (no nucleus) so blood can be transferred between patients
23
New cards
Specific immunity
specific immunity involves the production of antibodies against a specific antigens by the immune system
24
New cards
Clonal selection
The process by with an specific antigen will activate a specific helper T and B cell, causing the B cell to clone itself many times to produce plasma cells that all produce one type of antibody
25
New cards
Plasma cell
many rough ER and mitochondria to produce lots of antibodies (proteins); short lived cells
26
New cards
Aggulination
clumping caused by antibodies binding to multiple antigens at once
27
New cards
P.A.N.I.C acronym
Precipitation, aggulination, neturalisation (of toxic antigens), inflamation (thorugh histines), complement (system activation)
28
New cards
Passive artificial immunity
injection of monoclonal antibodies like in antivenom
29
New cards
Passive natural immunity
antibodies in breastmilk from mother to baby
30
New cards
Active artificial immunity
vaccination and deliberate exposure to antigen
31
New cards
Active natural immunity
natural exposure to antigen (infection)
32
New cards
Primary immune response
first immune response, generally slow with limited antibodies produced
33
New cards
Secondary immune response
usually much faster, with a large amount of antibodies produced, due to presence of memory B and helper T cells
34
New cards
Exoskeletons
External skeletons that are non-living; cannot "grow" with an organism and must be shed and replaced (e.g shells)
35
New cards
Endoskeletons
Internal skeletons that provide support and framework for muscles and tissue; grow with organism
36
New cards
Antagonistic pairs
Pair of muscles arranged around a joint that produce opposite actions; bicep and tricep in the upper arm produce opposing effects
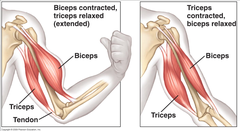
37
New cards
Grasshopper Leg Muscles
Antagonistic pair of the flexor (pull up, tensing) and extensor (pull out, propelling out) muscle in leg
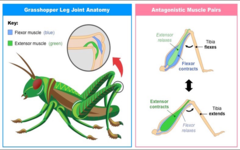
38
New cards
Synovial joint
A moveable joint in the area where two bones meet; composed of the cartilage, synovial fluid and joint capsule
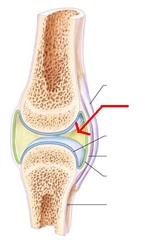
39
New cards
Joint capsule
seals the joint space and restricts movement to avoid dislocation
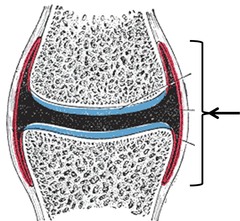
40
New cards
Synovial fluid
Fluid in space between bone ends that nourishes cartilage tissue and provides lubrication
41
New cards
Cartilage
Hard tissue that covers the end of bones, providing shock absorption and smoother movement
42
New cards
Skeletal muscle
A muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones (NOT cardiac or smooth muscle)
43
New cards
Myofibrils
Microscopic protein "myofilaments" that make up muscle fibre cells
44
New cards
Myofilaments
Contractile proteins forming myofibrils; myosin and actin
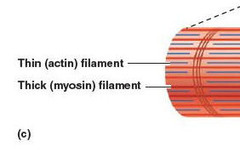
45
New cards
Sarcomere
Smallest contractile unit of a muscle; a section of a myofibril between two adjacent Z lines
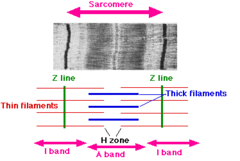
46
New cards
Sacroplasmic reticulum
Specialized endoplasmic reticulum in muscle fibre cells; stores and releases calcium ions used to trigger contraction
47
New cards
Tropomyosin
Rod-like protein found on actin that covers myosin binding sites; also bound to troponin
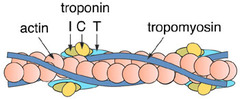
48
New cards
Troponin
A protein bound to tropomyosin with calcium ion receptors; when calcium ions bind to troponin, it causes tropomyosin to move away from myosin binding sites
49
New cards
Cross bridge formation
Occurs when myosin heads bind to actin at binding sites
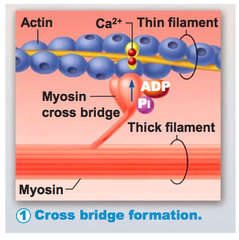
50
New cards
Spermatogensis
The production of sperm cells in the seminiflerous tubules of the testes
51
New cards
Oogenesis
The production of egg cells in the ovaries
52
New cards
Spermatogenesis Progression
Spermatogonia > 1 Spermatocytes > 2 Spermatocytes > Spermatid Cells > Spermatozoa
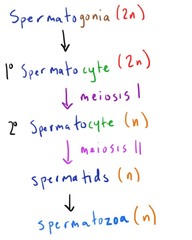
53
New cards
Nurse Cells
Assist differentiation of spermatid cells into spermatozoa, the final form of sperm cells
54
New cards
Semen
A thick fluid containing sperm and other secretions from the male reproductive system
55
New cards
Oogenesis Progression
Oogonia > 1 Oocytes > (meiosis I) 2 Oocytes > (meiosis II) Ovum

56
New cards
Acrosome
A vesicle at the tip of a sperm cell that helps the sperm penetrate the egg, contains enzymes
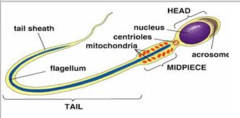
57
New cards
Acrosome reaction
First step of fertilization, in which sperm binds to zona pellucida and enzymes dissolve the zona
58
New cards
Zona pellucida
A thick, transpartent coating rich in glycoproteins that surrounds an oocyte.
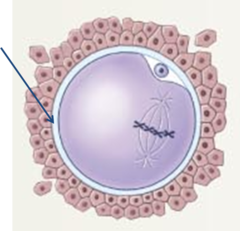
59
New cards
Penetration
Sperm binds to docking proteins on egg; sperm DNA and centrioles enter egg cell
60
New cards
Cortical reaction
cortical granules in egg fuse with plasma membrane; release of enzymes to destory sperm binding sites and prevent polyspermy
61
New cards
Polyspermy
The fertilization of an oocyte by more than one sperm. Prevented in humans through the cortical reaction
62
New cards
Blastocyst implantation
Blastocyst releases digestive enzymes to break down endometrium layer and implant into lining, allowing it to receive nutrients from mother
63
New cards
hCG
human chorionic gonadotropin hormone, secreted by the embyro and stimulates the maintainence of the corpus luteum, which in turn secretes progesterone to maintain thick lining of uterus
64
New cards
Placenta
A structure that allows an embryo to be nourished with the mother's blood supply; chorionic villi from fetus lie in the intervillus space, allowing for exchange of nutrients and waste with mother's blood
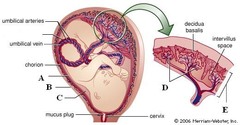
65
New cards
Estrogen (Pregnancy)
Stimulate growth of uterine linging, inhibit secretion of FSH and LH
66
New cards
Progesterone (Pregnancy)
Reduce uterine contractions through inhibition of oxytocin, develops breast tissue, maintain endometrium lining; secreted by corpus luteum, then placenta itself
67
New cards
Oxytocin
A hormone released by the posterior pituitary that stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth in a positive feedback loop (more contractions signals release of more oxytocin)
68
New cards
Prostoglandin
Hormone produced by fetus which encourage cervix to dialate and uterine contractions