Skin pathology 3
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What causes hypersensitivity dermatoses?
Exogenous antigens (drugs, pollen, food, arthropod)
(More important in dogs, cats, horses)
What are the most common types of cutaneous hypersensitivity?
Cutaneous mostly, type I, type IV or combination
Describe the pathogenesis of hypersensitivity dermatoses
Multifocal, pruritic
What are the clinical forms of hypersensitivity dermatoses?
Atopy, urticaria, angioedema, adverse food reaction, insect hypersens & contact dermatitis
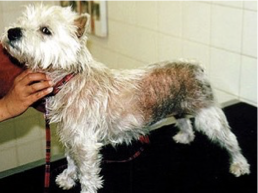
How does hypersensitivity present grossly?
Very variable. It might include erythema, oedematous plaques, papulae, alopecia, scaling, self-inflicted abrasions.

How does hypersensitivity dermatoses present histologically?
Very variable and non-specific.
Usually include an eosinophilic dermatitis which ,with chronicity, might turn to more lymphoplasmacytic one.
How is atopy diagnosed?
Cannot be diagnosed on pathology alone
What is the pathogenesis of autoimmune dermatoses? What can trigger it?
Immune system targets self antigens
Causes —> multiple ,including drugs, neoplasia, infectious agent, tissue injury, genetic phenotype or idiopathic.
Examples of autoimmune skin conditions
Hypersensitivity dermatoses
Autoimmune dermatoses
Pemphigus complex
Lupus erythematous
What is pemphigus complex?
Group of autoimmune skin disease characterise by pustules, crusts, erosions and acantholysis
Mostly idiopathic, can also be caused by drug admin or neoplasia (rare)
What is the pathogenesis of pemphigus complex?
Production of auto-antibodies targeting desmosomal proteins
Leads to loosening of keratinocytes and intra-epidermal accumulation of inflammatory cells (pustules)
Different types of pemphigus according to protein targeted by immune system
What is the most common type of pemphigus in animals? Which animals does it affect?
Pemphigus foliaceus
Dog, cat, horse and small ruminants.
What do autoantibodies target in pemphigus foliaces?
Desmocollin-1 (in epidermis layer of skin) in dogs
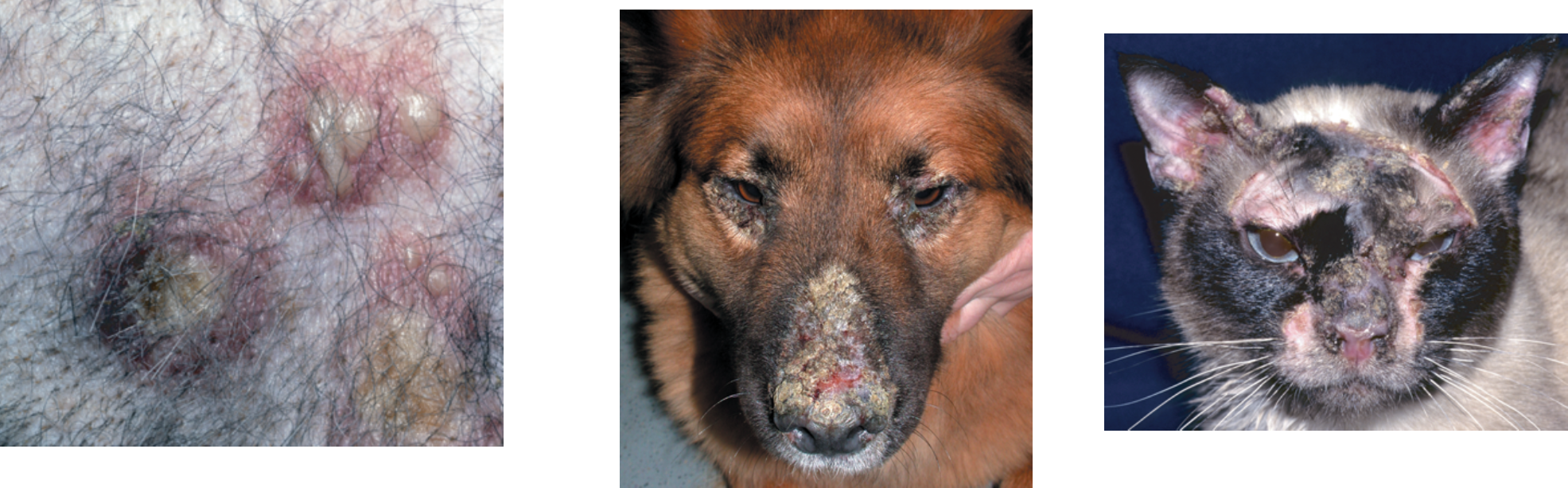
How does pemphigus foliaceus present grossly?
Pustules leading to crusts and scaling —> more frequently in the face
Usually bilateral and symmetrical
How does pemphigus foliaceus present histologically?
Superficial micropustules, also extending to hair follicles
Acantholysis (acantholytic keratinocytes present)
Minor dermal inflammatory infiltrate
What is lupus erythematous?
Spectrum of inflammatory autoimmune conditions targeting the skin (Cutaneous LE) or/and the entire body (systemic LE).
CLE characterised by damage to the basal cell layer and basement membrane.
What is the pathogenesis of lupus erythematous?
Genetic predisposition, solar exposure, drugs and idiopathic causes might trigger the production of autoantibodies
Mostly affects dogs, very rarely cats
What is the most important antibody present in lupus erythematous?
Anti-nuclear antibodies.
What are the types of lupus erythematous?
Cutaneous LE
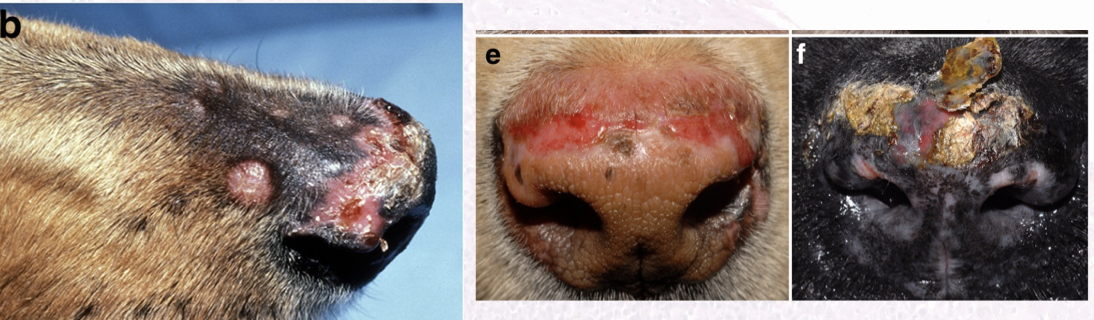
(Nasal planum) Discoid LE
Disseminated LE
Multiple Breed-specific Lupus conditions
How does discoid lupus erythematous present grossly?
Erythema, erosions/ulcers, depigmentation, hyperkeratosis, and crusting
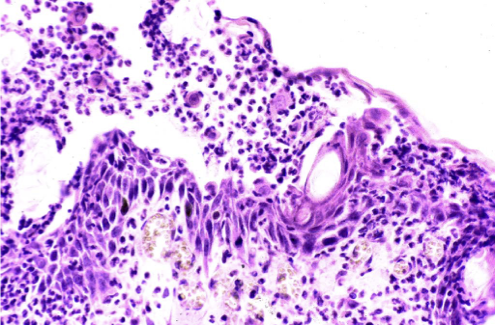
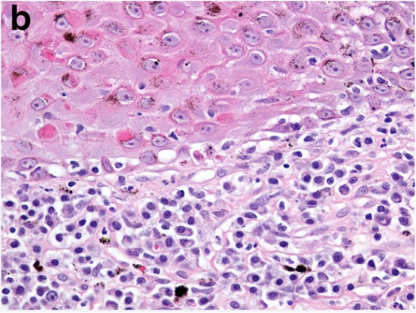
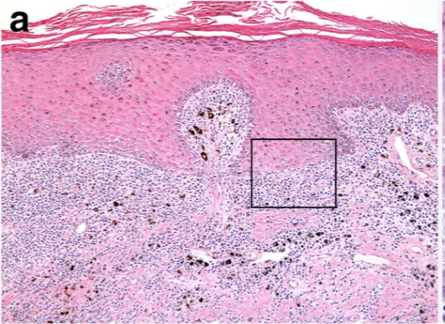
How does discoid lupus erythematous present histologically?
Sub-epidermal lymphoplasmacytic dermatitis (interface dermatitis)
Pigmentary incontinence (basal cell damage = melanin no longer held well)
What deficiency diseases exist in the skin?
Zinc responsive dermatoses
Superficial necrolytic dermatitis (aka Hepatocutaneous syndrome)
What causes zinc responsive dermatoses?
Zinc deficiency, other condition reducing zinc in food
(Reported in pigs, dogs (puppy and Nordic breeds), ruminants, including alpaca and llamas)
How does zinc responsive dermatoses present grossly?
Scales and crust that may reach mm in thickness.
Distribution varies but usually bilateral and symmetrical.
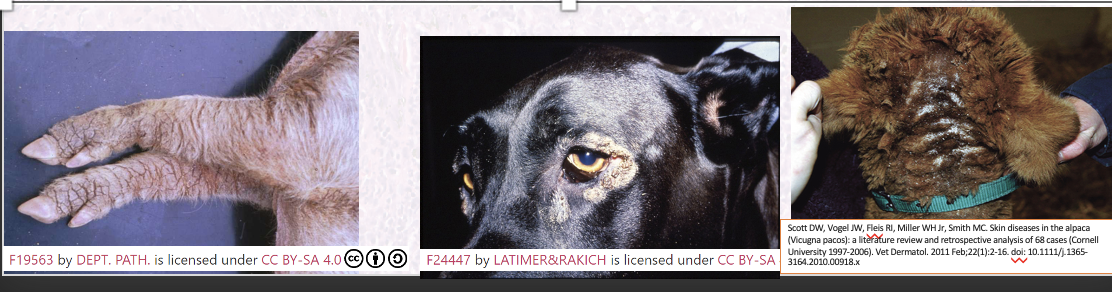
How does zinc responsive dermatoses present histologically?
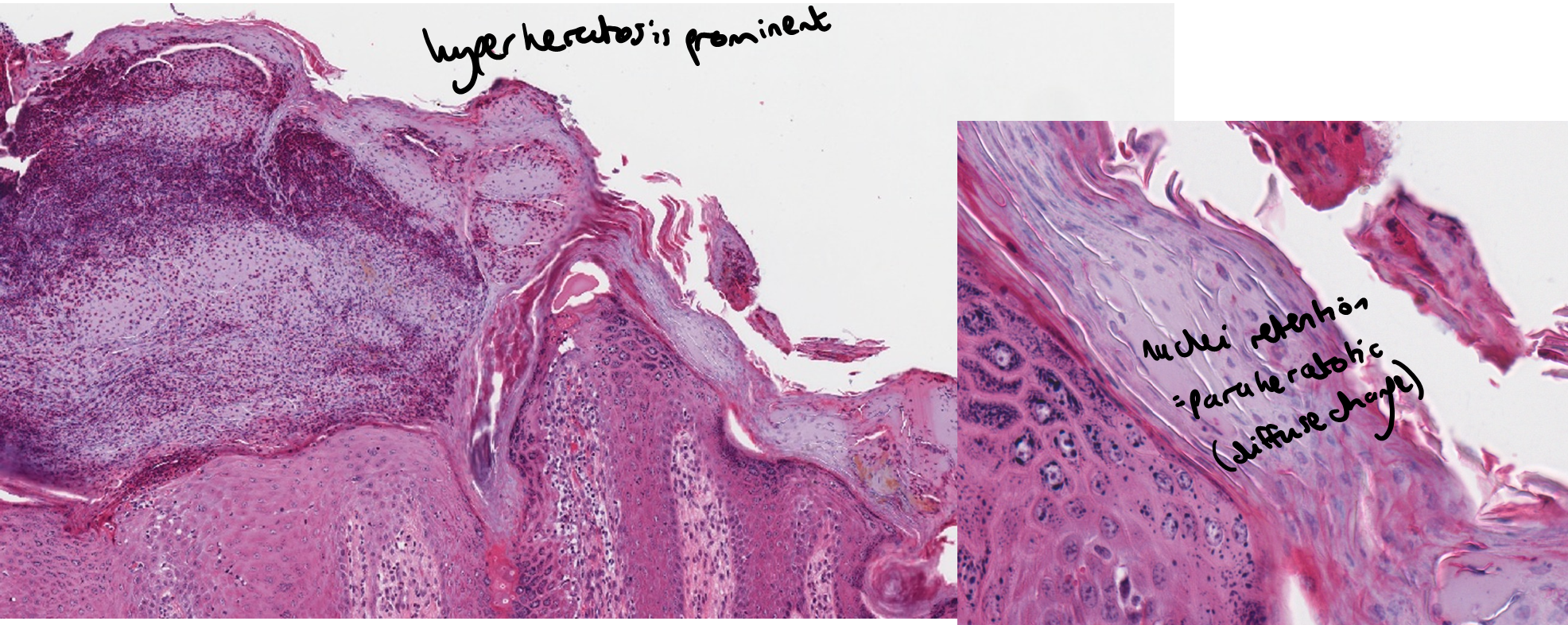
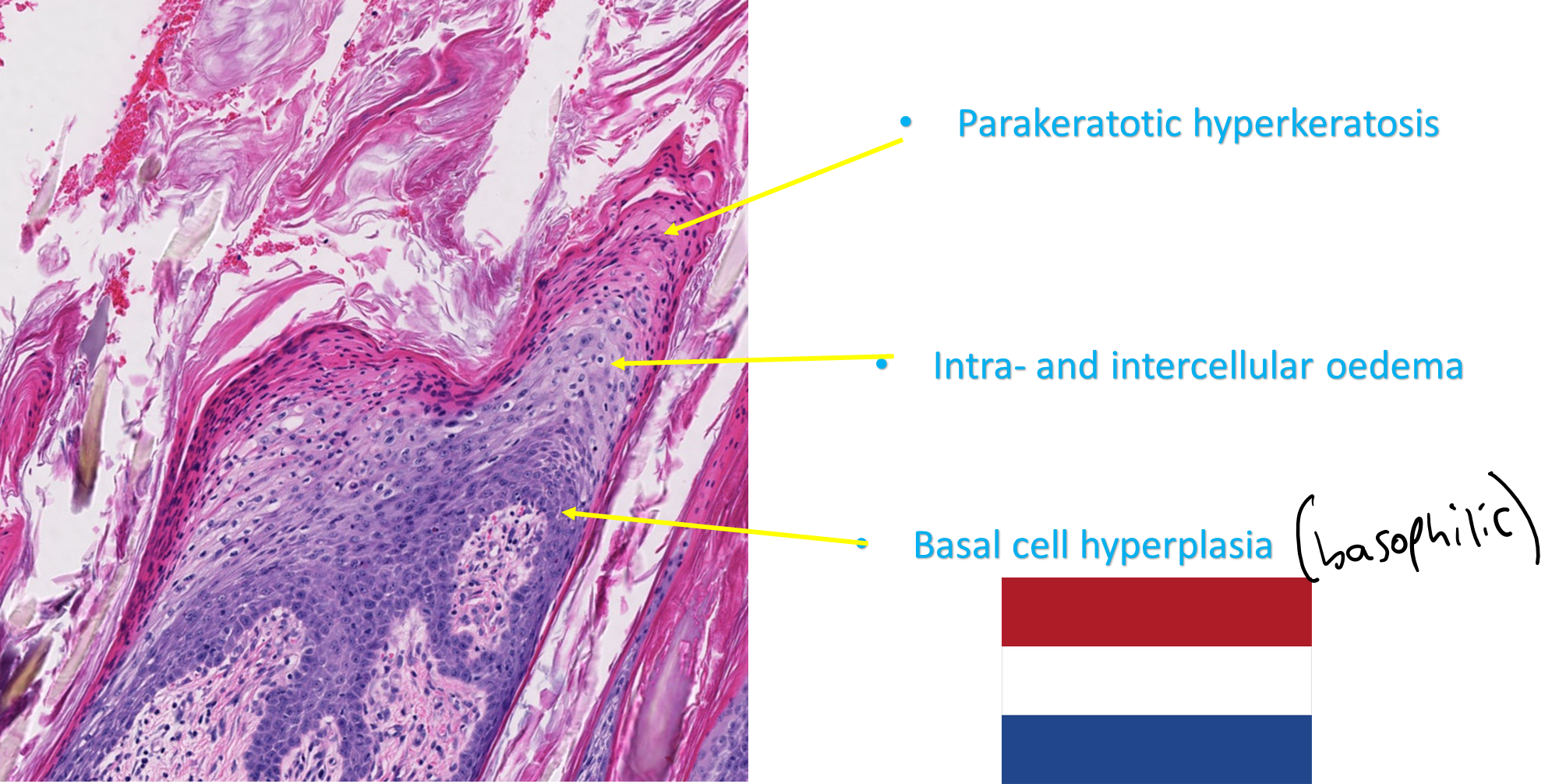
Diffuse parakeratotic hyperkeratosis
Epidermal hyperplasia
Dermatitis possible (non specific)
What causes superficial necrolytic dermatitis (Hepatocutaneous syndrome)?
Severe hepatopathy (in dogs, rare in cats)
Derangement of hepatic function and derangement of glucose and amino acid metabolism (hypoaminoacidaemia —> reduction of amino acids in blood)
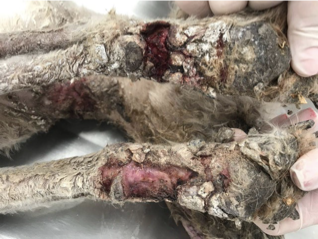
How does a superficial necrolytic dermatitis present grossly?
Bilateral and symmetrical erosions, ulcers and severe crusting; pawpads commonly affected (dog)

How does a superficial necrolytic dermatitis present histologically?
What gross and histology signs would cause you to suspect an endocrinopathy?
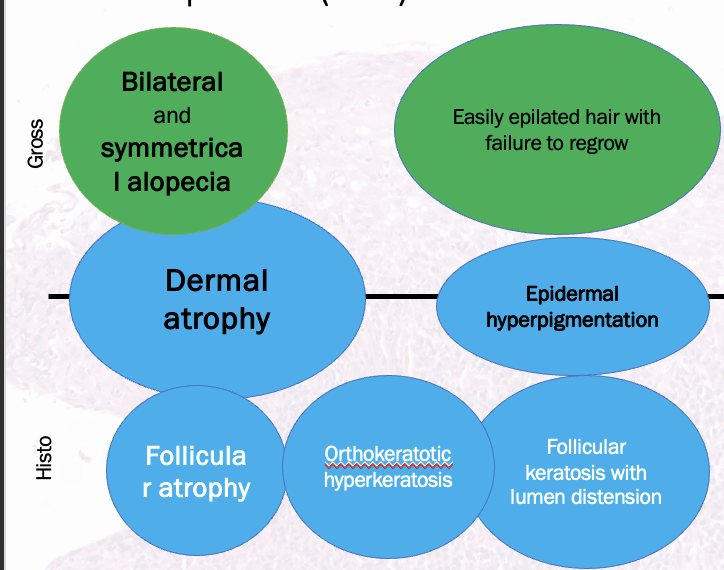
dermal atrophy = thin skin
alopecia of tail (rat tail)
diagnosis cannot be done on histo alone
What are the endocrinopathies of the skin?
Hypothyroidism
Hyperadrenocorticism (Cushing)
Hyperoestrogenism
Which species is eosinophilic disease common in?
Cats & horses
What is the histological presentation of eosniophilic disease?
Infiltration of macrophages (granulomas) and eosinophils in different quantities
Presence of flame figures
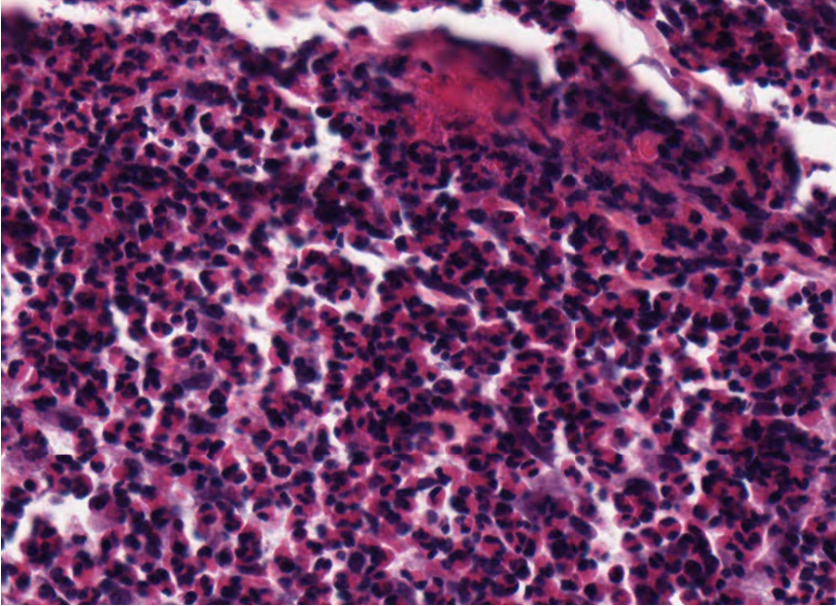
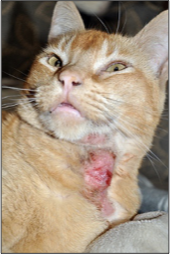
What are the components of the eosinophilic granuloma complex? What species does it occur in and where?
Cat
Eosinophilic plaque (always affects skin)
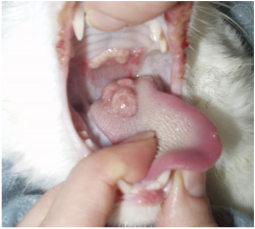
Eosinophilic granuloma (affects both skin & mouth)
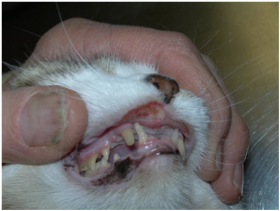
Indolent ulcer (upper lip of cat affected)
What eosinophilic diseaes occurs in horses?
Eosinophilic granuloma —> occurs in skin only

Axillary nodular necrosis (not in UK)
Unilateral papular dermatosis
What are the forms of calcinosis
Calcification of skin
Calcinosis cutis —> Dog
Calcinosis circumscripta —> dogs rarely horses and cats
What causes calcinosis cutis?
Hyperadrenocorticism (in dogs)
What causes calcinosis circumscripta?
Not known (localised mechanical pressure?)
In dogs, rarely horses & cats
How does calcinosis cutis present grossly?
Firm erythematous papules or plaques that frequently ulcerate
Usually in dorsal neck, groin or axilla
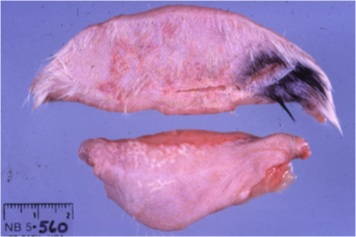
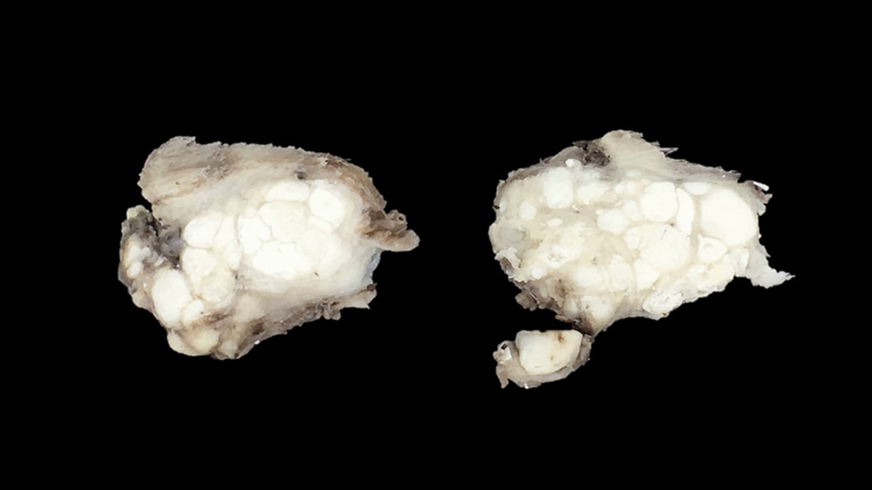
How does calcinosis circumscripta present grossly?
Occasionally ulcerated nodule with well demarcated chalky white material
Usually in skin over bony prominences (dog)