Week 2 - Job Performance & Organizational Commitment
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
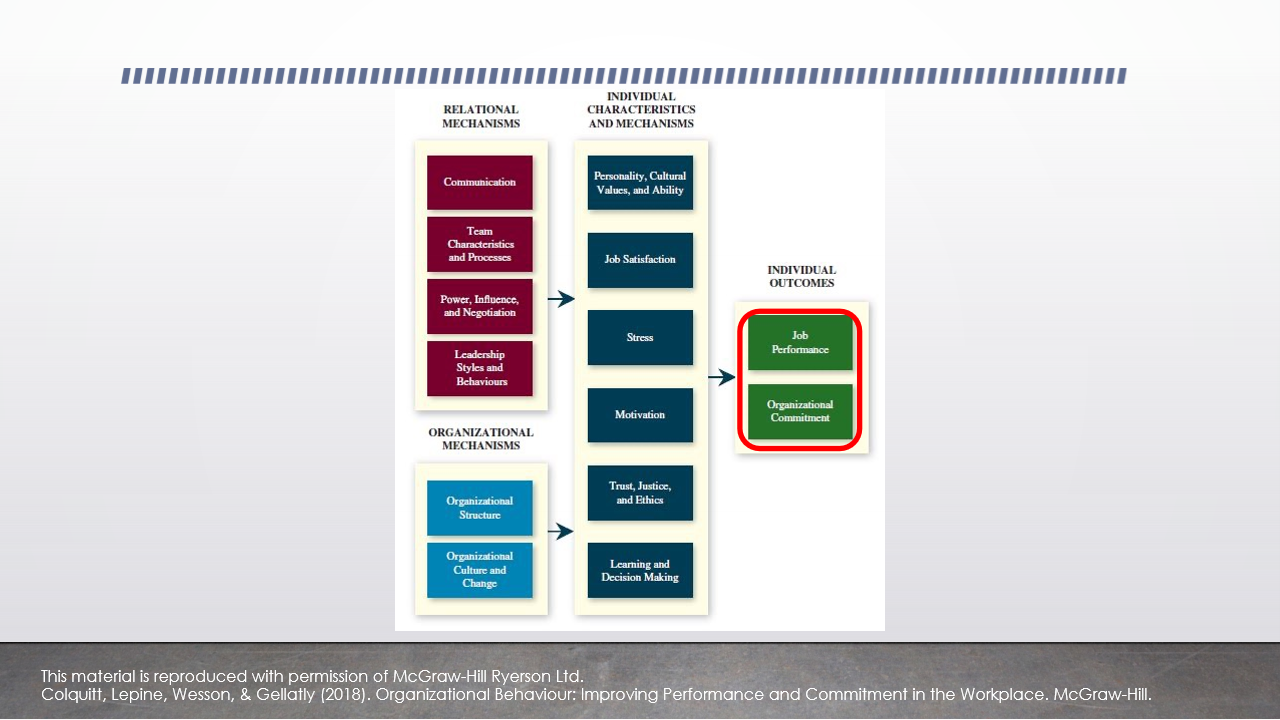
Integrative model of OB
In individual outcomes (job performance + organizational commitment)
Job performance
Employee behaviour that contribute either positively or negatively to the accomplishment of organizational goals
Assessment in behaviours over results.
Using results as the primary indicator of job performance can create problems
Flaws of result-based measurement
Employees may do activities that cannot be captured in results-based measure.
Results can lead to a competitive environment and sabotaging other people’s reputations.
Results are impacted by a lot of outside factors beyond our control, such as economy.
Does not tell us ways to improve
3 job performance segments
Task performance: routine, adaptive, creative
Citizenship behaviour: interpersonal, organizational
Counterproductive behaviour: property deviance, production deviance, political deviance, personal aggression
Task performance
Employee behaviours involved in converting organizational resources into goods/services
e.g. a restaurant server providing menus and bringing food.
Within the job description, required to keep job.
3 categories of task performance
Routine task performance
Adaptive task performance
Creative task performance
Routine task performance
well-known habitual responses by employees.
Things done repetitively, such as flight attendant explaining flight safety.
Adaptive task performance
thoughtful responses by an employee to unique or unusual task demands.
Things still trained for but are unique experiences, such as flight attendant dealing with a medical problem on flight.
Creative task performance
Degree to which individuals develop ideas or outcomes that are both novel and useful.
Sometimes no training with overlap between adaptive and creative. Following 9/11, many feared flying and flight attendants handed out crayons to draw on placemats and stick them around the plane.
Citizenship behaviour
Voluntary employee behaviours that contribute to organizational goals by improving the context in which work takes place.
e.g. a restaurant server might assist other servers with their tables and offer constructive suggestions for improving the restaurant.
Keyword, voluntary. Not part of the job description to help other coworkers or finding ways to increase efficiency.
Although voluntary, may not be considered so in nature when overlooking performance by some supervisors.
Interpersonal citizenship behaviour (3-kinds)
Going beyond expectations to assist, support, and develop colleagues
Helping: assisting coworkers with heavy workloads, aiding coworkers with personal matters, showing new employees the ropes. (assistance)
Courtesy: keeping coworkers informed about matters that are relevant to them. (informing)
Sportsmanship: maintaining a positive attitude with coworkers, even in tough times. (attitude)
Organizational citizenship behaviour (3-kinds)
Going beyond expectations to improve the organization, defend it, and be loyal to it.
Voice: offering constructive suggestions for change. (feedback)
Civic virtue: participating in company operations at a deeper-than-normal level (e.g. voluntary meetings) (participation)
Boosterism: positively representing the organization in public (representation)
Counterproductive behaviour
Employee behaviours that intentionally hinder organizational goal accomplishment
e.g. a restaurant server might gossip about coworkers
Must have three of the following:
Relevant to every job.
Contagious
Employee engaging in one sector of behaviour are likely to engage in others.
Counterproductive behaviour have a weak negative correlation to task performance. Every now and then there will be high performers engaging in counterproductive behaviour.
4 categories of counterproductive behaviour
Property deviance
Production deviance
Political deviance
Personal aggression
Property deviance
Behaviours that harm the organization’s assets and possessions
Stealing equipment, damaging equipment, etc.
Production deviance
Intentionally reducing organizational efficiency of work output
Wasting resources such as time, material, substance abuse.
Political deviance
Behaviours that intentionally disadvantage other individuals
Gossiping
Personal aggression
Hostile verbal and physical actions directed toward other employees
Harassing, hurting coworkers
Prosocial counterproductive behaviour
Workplace behaviours that are intended to benefit others but are counterproductive because they violate norms, rules, policies, or laws.
e.g. hiding negative information about a coworker’s performance
4 kings of Performance management
Management by objectives (MBO)
Behaviourally-anchored rating scales (BARS)
360-degree feedback
Forced ranking
Management by objectives (MBO)
Management philosophy based on employee evaluations whether specific performance goals have been met.
e.g. improving efficiency by 25% within 6 months.
Specific measurable goals attached with a timeline.
Have a results component alongside the behaviour component. However results may be out of employee control.
Behaviourally-anchored rating scales (BARS)
Examples of critical incidents to evaluate an employee’s job performance behaviours directly.
Critical incidents: short descriptions of effective and ineffective behaviours
360-degree feedback
Performance evaluation system that uses ratings provided by supervisors, coworkers, subordinates, customers, and employee themselves.
Best use for developmental purposes than administrating bonuses.
Log-rolling issue.
Forced ranking
Performance management system that forces managers to rank each employee into one of multiple categories
Can be stressful way of assessing performances.
Focus in routine performances which hinders creative performances.
Creates competition.
3 kinds of organizational commitment
Employee’s desire to remain in an organization
Affective commitment
Continuance commitment
Normative commitment
Affective commitment
Desire: emotional attachment to and involvement in the organization.
Employee wants to remain in the organization
Comes from good work atmosphere, enjoying the work, connections with coworkers.
Erosion model
Employees with fewer bonds with coworkers are more likely to quit. The person with the fewest connections are most likely to leave.
Social influence model
Employees with direct linkages to coworkers who leave the organization will themselves be more likely to leave.
Continuance commitment
Desire: awareness of costs associated with leaving the organization
Employee has to remain with the organization.
Having no available alternatives, bills, major investment in company, sense of embeddedness in local community.
Will not go out and beyond to do tasks.
Embeddedness
Sense of fit to the organization or community.
A feeling of having to stay due to non-work related factors.
Connections to whom is important to understand if its continuance or affective.
Positively associated with continuance commitment.
Normative commitment
Desire: feeling of obligation to the organization.
Employees feels they ought to remain with the organization.
ex. an organization expecting you to stay at least a minimum of 6 months.
Arises when sense of indebtedness to organization’s debt such as tuition reimbursements.
Four primary responses to negative events
Destructive + Passive [Neglect]: declined interest and effort
Destructive + Active [Exit]: end/restrict involvement
Constructive + Passive [Loyalty]: maintain public support while private hope for improvement
Constructive + Active [Voice]: attempt to improve the situation
Withdrawal behaviour: 5 Psychological withdrawal
Daydreaming
Socializing
Looking busy
Moonlighting: misuse of company resources
Cyberloafing: using organization’s email/internet for personal use.
Withdrawal behaviours: 5 physical withdrawl
Tardiness: arriving late for work
Long breaks
Missing meetings
Absenteeism
Quitting
3 models of withdrawal behaviours: Independent forms model
Withdrawal behaviours are uncorrelated with one another.
Occurs for different reasons and fulfill different needs.
ex. a tardy employee does not correlate to their absence.
3 models of withdrawal behaviours: compensatory forms model
Withdrawal behaviours are negatively correlated with one another.
Any form of withdrawal compensates for a sense of dissatisfaction, making other forms unnecessary.
e.g. knowing an employee is tardy informs that they will not be absent.
3 models of withdrawal behaviours: progression model
Withdrawal behaviours are positively correlated with one another.
The model with the most scientific support.
e.g. knowing that an employee is tardy tells you that same employee is probably going to be absent.
Trends that affect commitment
Diversity of the workforce
Changing employee-employer relationship
Commitment initiatives
Creates a sense of perceived organizational support
Increase employee bonds
Provide good salary and benefits
Offer training and development opportunities.