Political Science - Aurele's Courses
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Is it really possible to define politics?
impossible to have well-defined politics, particularly impossible to define politics through their object
Objects are by definition
fluid
Politics, policy, polity
can be used to describe all human relationships/power dynamics/etc
The personal/private is political
Slogan/argument of 2nd wave feminism (60s)
Geneviève Pruvost
eco-feminist researcher
Every day life and politics are not supposed to be together
Pruvost: Question Everything
Why in urban societies do we never see food in its natural state anymore? Gardens, fruit trees, etc
Epistemology
science that looks at science method (not history, more philosophical)
Weber’s theory on political science
the analysis of the exercise of physical creation through an organization in a defined territory
a lot of theories from anarchists said that politics cant be defined through
territory
ECONOMIC definition of social classes
the place that people occupy in the productive apparatus
not a question of money
CULTURAL definition of social classes
A way of life (according to your position in the society)
Diet and love relation
love = you generally fall in love with someone of your same class (shared way of life)
How can we explain how people dress
not individual/free choice
economic constraints
anticipation of professional benefits (“respectability”)
employees/factory workers
Choices w/in social classes: Bourdieu
social classes as a game of opposition, of distinction between tastes/distastes
tastes/disgusts expressed according to social class, but also w/in classes
3 capitals
economic
cultural
social
Choices: Distinction through
detachement
Intersectionality
cross-analysis of diff. social characteristics (gender/race/disability/etc) » gives rise to specific social reality
US 2024 election: gender division
54% of men voted republican
54% of women voted democrat
US 2024 election: Age
18-29 = 55% dem
20-44 = 51% dem
45-64 = 53% rep
65+ = 50/50
US 2024 election: education
w/degree = 57% dem
no degree = 54% rep
Sate Sovereignty": The king’s 2 bodies
“the king is dead long live the king”
even after his death the state still lives on
14th-16th century concept > before legitimacy came from religion
Sovereignty according to Jean Bodin
sovereignty is the power to make and break laws
Sovereignty’s 3 parts (Bodin)
absolute
perpetual
one and indivisible
Exclusivity (Sovereignty)
monopolization of power - ability to exert absolute power
Contract Theories - Hobbes ‘Leviathan’
“Men are wolves to men”
Pact of Submission
we accept someone’s power to stop the war of all against all
3.5 main elements of a state
permanent population
defined territory
government
+ capacity to enter into relations with other states
Is a state w/out a territory possible?: Stateless territories
oceans and arctics
Is a state w/out a territory possible?: Territoriless states
ukraine, palestine, etc
Population made from
nationals and residents
The state: a special form
“There is no king in the tribe, but a chief who is not a head of state…Simply the chief has no authority, no power of coercion, no means of giving orders. The chief is not a commander, the people of the tribe have no power to obey - the chiefdom is not a place of power”
Anarchism POV of the state
order w/out power/authority (Foucault)
Anarchist focus
not only on opposition and critiquing the state but also on situations of communal living against the state
example of successful anarchist state
Chiapas in mexico
Europe particularly post fall of Roman empire
stateless - many degrees of small entities controlling diff areas
Historical explanations for creation of states:
creation of monopoly (internal and external)
Uniformisation and monopolization of taxation - by central power
creation of monopoly (internal and external)
through war
territory
Uniformisation and monopolization of taxation - by central power
Taxing everything (incl church etc)
Less random system, more regularized/institutionalized
Local taxes abolished
Taxes justified today not to pay for war (as in past) but for social spending
Administration
Becomes dedicated to the actions of the state as an institution
When people in power change, the administration stays the same/endures
Extremely recent modern form (2-3 centuries max)
4 waves of war/states
Fall of empires
wwi/ii
Decolonization
Fall of USSR
Welfare state
State intervention not really the case before - state not solely focused on the army/justice
Public services
Distribution
Neo-Liberal
Economy regulates (market independence) itself without intervention of state
Proliferated in the 80s throughout western countries, particularly france
Believes in slimming down of state
New public management (modern dev of state in terms of relations w/non-profit sector)
Transposition of private sector work organization into public sector
pursuit of cost reductions, performance improvement (by any means), implies a better spending culture and reduction of unnecessary spending
3 types of association
de facto
declared
association recognized as being of public interest
Contractualization logic
private sector engaged to take on what the state cannot/doesnt want to handle anymore
Privatization of the public sphere
Cheaper to use association contracts for public service > not always always the case but often
You stand to lose everything as a protestor when you
depend on the state’s money
Maud Simonet > NY public park
60s-70s: only civil servants who cleaned public parks in NY, associations started to come in and do those jobs, less and less civil employees then
Easier to use association > if you need budget you can stop the contract, rather than the impossible task of firing actual employees
Now volunteers are even doing it > VOLUNTARIZATION of work place
Contractualization is not onyl at state level
instead of doing research you can ask McKinsey (or other consulting firms) to do it
Political regime is different from a State
Regimes change (even from democracy to other types) but the state endures
Why do we need definitions of non-democratic regimes?
Plato said that we had tyrannical regimes, french revolutionaries talked about autocracy
constructed in opposition
No perfect definition of “democracy” or “totalitarianism” - why do we need definitions anyway?
Because Nazi and Soviet regimes were so different but both so violent - we were in need of new notions, old ones weren't sufficient
When was the concept of totalitarianism created
1950s-60s
Hannah Arrendt & totalitarianism
Didnt try to only define through police, hitler, etc she tried to find the NATURE of totalitarianism
Ideology = a major role in Arrendt’s totalitarianism
need to define an enemy
For nazis it was non aryans and the jews
For the soviets it was a fantastic bourgeois
Fragmentation of society (Arrendt/totalitarianism)
Atomization of society
Not to block unity but they fragment to create unity
No unions, religions, no neighborhood solidarity, nothing to get in way of mass
UNITY behind the ideology
Beyond ideology, what is essential in totalitarianism
repression
Hannah Arrendt definition of totalitarianism
the production of another humanity > the never ending search for a new humanity
Repression in Hannah Arrendt’s Totalitarianism
Repression becomes an end in itself, the regimes essence
Repression doesn't mean regime is in danger, but is trying to enter the regime into all parts of life
Proactive repression
Arrendt’s definition is useful but perhaps too rigid
Even nazi’s are not totalitarianism according to her definition
There was still independence in some parts > religion was still active and not totally under nazi control for example
Carl Freidrich - takes parts from Arendt’s work but defines 6 keys points in defining totalitarianism
totalist ideology
single party applying this ideology under one leader (dictator)
terroristic police control through secret police
power controlling mass comms
weapon monopoly owned by power
centrally directed econ by power
authoritarianism
more recent term than totalitarianism
from one part, those who govern dont rlly submit power to hazard of an open election
dissident public opinion is repressed
SIMILARITIES authoritarianism/totalitarianism (EXAM)
control over state apparatus
control over media system
restriction of public space and ban of dissident expressions
tight control of political life
DIFFERENCES authoritarianism vs totalitarianism (EXAM)
no search for new humanity, no totalist ideology > regime solely looks for control of political sphere
no fragmentation of society. standardization/absence of parties isnt necessary
essentially, the ideology and the monolithism are absent/less pronounced
Democracy Criterias
separation of powers
monitoring between the powers
rule of law
consent to taxation/representation
separation of public/private
Types of representative democracies
presidential regime
parliamentary regime
other (ex. france)
Presidential regimes
president does not respond to parliament and cannot dissolve it (ex. USA and Brazil)
Huge separation between the two
Not where the president is very very strong
Aside from Juridical tool of impeachment
Parliamentary regime
the executive power responds to the parliament and can dissolve it (ex. Italy and Germany)
Mobilization - Theory of Relative Frustration
Frustration arises from perceived inequality, not actual need
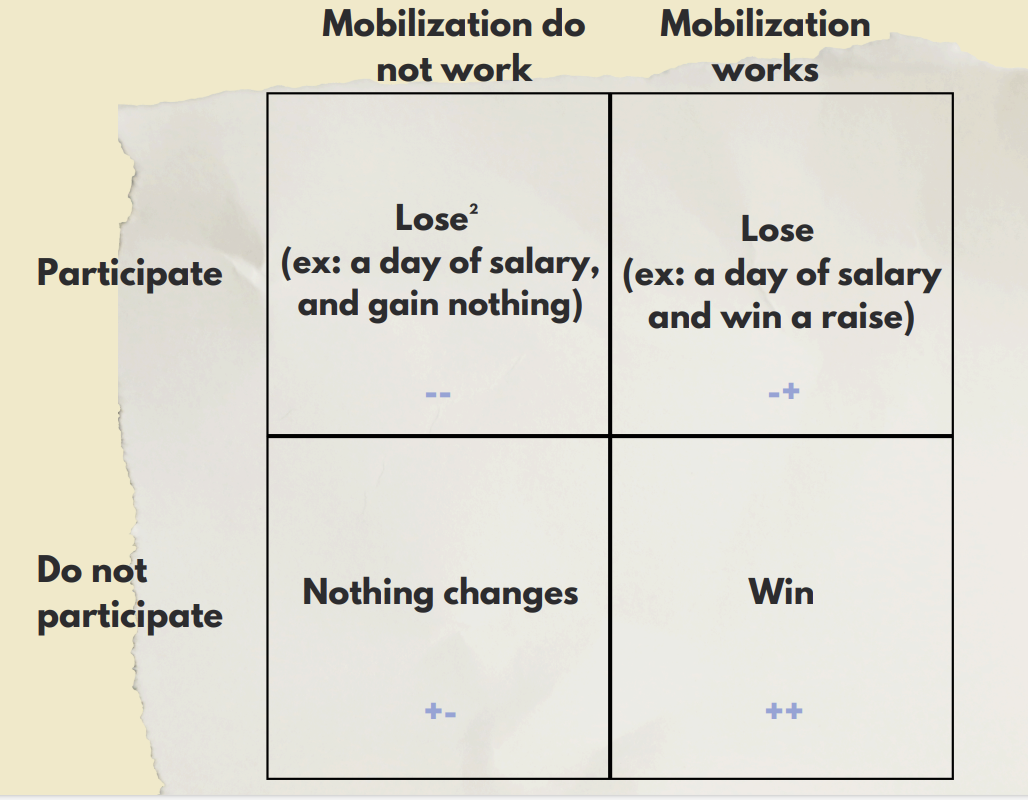
Prisoner’s Dilemma
rationally nobody should mobilize > peer pressure and material advantages
How to explain that people mobilize without anything to gain?
symbolic rewards of engagement
identity
Mobilizing - Who and for whom?
2 main distinctions:
interest groups/political parties
identity groups and cause-driven groups
separation can be unclear
How to mobilize based on Repertoire of Collective Action
est by Charles Tilly
means by which a group can act collectively on basis of shared interests
Other elements of “How to Mobilize”
not all means can be used by any group at any time
historical shift from local patronage (before 19th) to national autonomy
New Repertoire in mobilization
internationalization
expertise (use of cause lawyering)
new causes
Cause Lawyering
lawyers use their legal skills to advance a political, social, or moral cause, rather than focusing solely on traditional client service or commercial goals.
Mobilization Critics
focused on western world & around mobilization on groups w/large cultural capital
No mobilize or not to mobilize