ECG
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
How does an AP travel through the heart?
AP generated in the sino-atrial node - primary heart pacemaker
Atrial depolarisation (wave of depolarisation/contraction)
AP delayed at the atrioventricular node
AP travels down the septum, to the apex of the heart and around the ventricles
Wave of AP causes wave of contraction
Wave of repolarisation (relaxation) follows wave of depolarisation
What is the P wave?
Atrial depolarisation/contraction
Positive deflection, wave of depolarisation direction is parallel to lead II
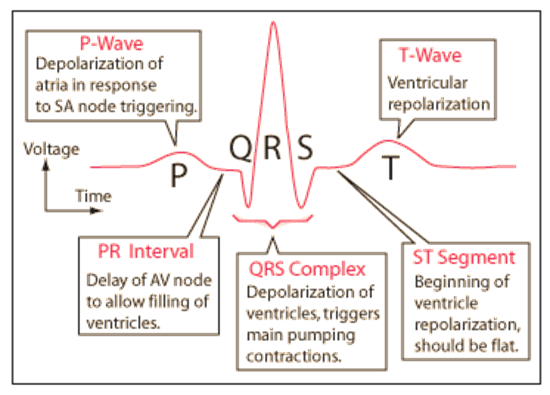
what is the PR interval?
AVN delay
No deflection, no net current flow
What is the QRS wave?
ventricular depolarisation/contraction
Why is the Q wave negative?
Septal depolarisation, occurs left to right in body, so vector away from lead II
But small magnitude
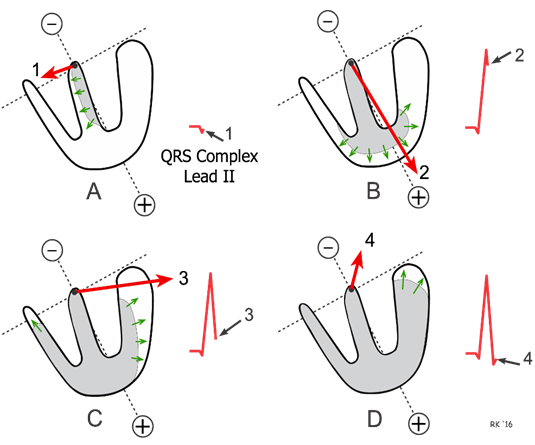
What is the R wave?
Ventricular depolarisation towards apex, parallel to lead II so positive deflection
depolarisation towards positive electrode
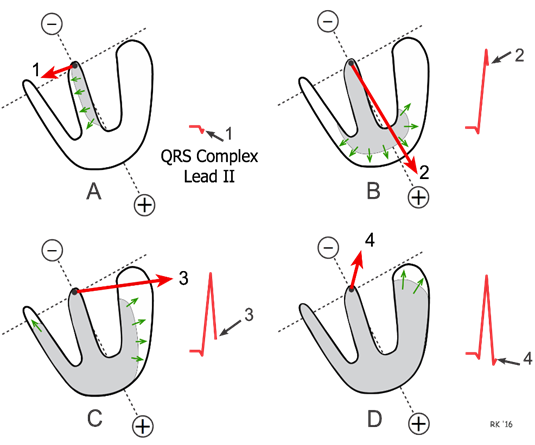
Why is the S wave negative?
Last ventricular region to depolarise: from endocardium to epicardium
Starts pointing more towards the left, away from lead II, so slight negative deflection
What is the ST segment?
beginning of ventricular relaxation, no net current flow so no deflection

What is the T wave?
Ventricular repolarisation
Direction of repolarisation is away from electrode of lead II so positive deflection
Starts at apex, epicardium, endocardium
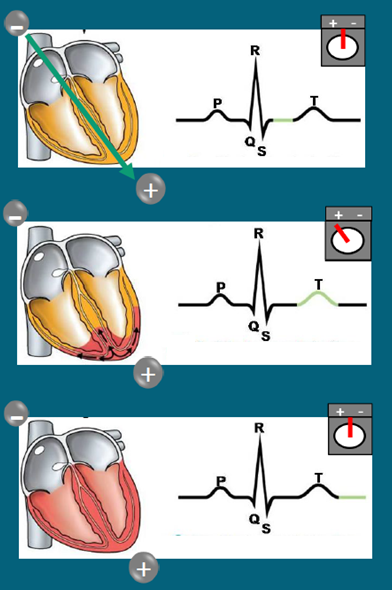
Describe T wave inversion in NSTEMI?
Normal T wave = repolarisation from epi to endo cardium = away from positive electrode = positive deflection
In NSTEMI, sub endocardium ischemia = open KATP channels = faster repolarisation
Repolarisation from endo to epi cardium = towards positive electrode = negative deflection