Unit 2: Climate Change
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
State the ‘Spheres’ of the Earth
There are four major subsystems
"lithosphere" (land)
"hydrosphere" (water)
"biosphere" (living things)
"atmosphere (air)
Explain the importance of Atmosphere in agriculture
The atmosphere consists of gases and tiny water particles that are helf in place by Earth’s gravitational force.
Without gravity, gases would escape into space. Therefore, planets with weaker gravity cannot hold onto their atmospheric gases as effectively, resulting in thinner or less dense atmospheres.
Identify the compositon of the atmosphere
Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and trace gases
Explain Shortwave radiation
Can be known as: Incoming Solar Radiation or ‘insolation’
These are powerful energy emitted by the sun, in the form of visible light and UV light.
Distribution: Unevenly spread. The equator receives more radiation than the poles, due to the relative distance from the sun and the surface area.
This incoming radiation is then absorbed and circulated by the atmosphere and oceans, powering the planet’s weather and climate.
Absorption: Some incoming shortwave radiation is absorbed by atmospheric gases.
Reflection: Some incoming shortwave radiation is reflected by clouds.
Explain Longwave radiation
Relatively weaker energy emitted by the earth, in a form of infrared rays
How does this work: Powerful high-frequency shortwave radiation from the sun is absorbed and then re-emitted from both particles in the atmosphere and the surface of the earth at a lower, less powerful frequency (i.e. longer waves).
Absorption: Clouds in the troposphere absorb and prevent longwave radiation from escaping into space. If no clouds, 80% of emitted longwave radiation is lost to space. This is why clear days and nights in winter are so cold.
Greenhouse Gases: Water vapour, carbon dioxide and ozone absorb long-wave radiation very well, heating the earth. This is why they are known as ‘greenhouse’ gases.
What is the Greenhouse Effect?
A natural process that warms the earth’s surface.
Greenhouse gases absorb and reradiate longwave radiation that was initially shortwave, entering Earth’s atmosphere.
The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and surface, maintaining the average global temperature at around 33°c
State all the GREENHOUSE GASES (GHGs)
A gas that absorbs and emits longwave radiation
Note: they do not absorb/emit shortwave radiation, it passes through them on their way to the earth’s surface.
GHG by concentration
Water vapour
Carbon Dioxide
Methane
Nitrous Oxide
Ozone
CFCs
What is Global Warming Potential?
A GHG potency in terms of how much heat it can re-radiate varies, as does its concentration in the atmosphere and the period it remains there. This is called ‘Global Warming Potential’
CO2 absorbs less heat than methane but remains in the atmosphere for a lot longer.
Which GHG has the biggest impact in the atmosphere?
Water vapour and carbon dioxide have the largest overall warming effect within the atmosphere.
Methane and nitrogen oxides have a lesser overall warming effect
What is meant by feedback loops?
All systems need to be balanced, to achieve this they need to self-regulate through feedback loops
Explain positive loops and provide 2 examples
A positive feedback loop increases the amount of change with each loop. This leads to an imbalance with the system spiralling out of control. (Less common in nature) = Unstable
Melting ice
As the planet warms, ice melts, revealing darker land or water that absorbs more heat. This causes more ice to melt, which leads to more warming, and so on.
Permafrost melting
As the planet warms, more permafrost melts, releasing methane, a greenhouse gas that traps heat in the atmosphere
Explain negative loops and provide 2 examples
A negative feedback loop decreases the amount of change by reducing some of the inputs with ‘checks’, returning the system to stability. Keeping it in a dynamic equilibrium = Stable
Coastal erosion:
If a storm erodes a large portion of a beach, the newly exposed cliff face can protect the base from further erosion, stabilizing the coastline
Predator-prey dynamics:
When a predator population increases, it puts pressure on the prey population, causing it to decline, which then leads to a decrease in the predator population.
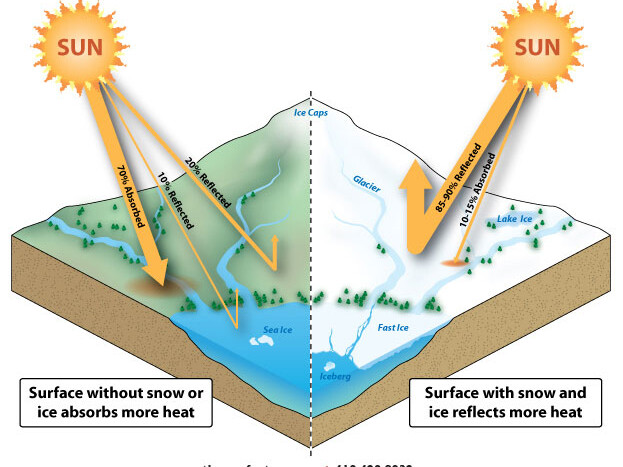
Explain the Albedo Effect
In the context of climate change, it’s a measure of how much shortwave radiation from the sun is reflected back into space.
‘Bright white reflects light”
Lighter = High Reflectivity = High Albedo
Darker = Low Reflectivity = Low Albedo
What does Permafrost contain?
Permafrost contains vast quantities of frozen, undecomposed, organic material (vegetation, bacteria, organisms, etc.) from when these regions were warmer - this is almost 50% of total global organic soil matter.
What is permafrost?
Any ground that remains completely frozen -0*C or colder for two consecutive years
A combination of soil, rock, and sand are held together by ice
There doesn’t need to be snow on the ground for the earth below the surface to be frozen.
What is the Solar Cycle?
The solar cycle is the cycle that the Sun’s magnetic field goes through approximately every 11 years.
How does the solar cycle alter climate?
Solar Minimum: The cycle where the sun has least sunspots
Solar Maximum: Middle of the cycle where the sun has the most sunspots
Variation in solar irradiance:
During a solar cycle, the Sun's overall brightness fluctuates slightly, with more energy emitted during solar maximum and less during solar minimum.
Impact on temperature:
This variation in solar radiation can cause a small change in Earth's average temperature, usually less than 0.1 degrees Celsius.
What is global dimming?
When incoming shortwave radiation is reflected back into space, preventing it from reaching the earth’s surface due to visible air pollution, such as soot, ash, sulphur compounds and other pollutants.
What are the issues caused by global dimming?
Changing Cloud Albedo: More shortwave radiation is reflected back into space due to polluted particles ‘seeding’ clouds, making the clouds denser and therefore changing their albedo.
Ocean Currents: Oceans absorb and release heat, driving the global climate system and making earth habitable. These clouds shield the oceans from shortwave radiation thus disrupting weather systems.
Regional Drought: This changing of weather patterns is suspected to have been responsible for many of the world’s droughts over the last 50 years.
Global Dimming Paradox: The big one - due to the dimming effect reducing temperatures we may well be underestimating the effects of manmade climate change.
What does Globlal Warming Potential mean?
Global warming potential is the calculation of the amount and time of gas that remains in the atmosphere.
CO2 is the benchmark gas for comparing GWP as it is the most abundant GHG in the atmosphere
The higher the GWP number, the greater potential warming impact it has.
What does anthropogenic climate change mean?
Anthropogenic means ‘man-made’ climate change
A theory that explains the long term increase in the average temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere as an effect of human industry and agriculture. AKA ‘the enhanced greenhouse effect’.
though industry, agriculture and transportation
What is the Hydrosphere?
The hydrophere is the total amount of water on the planet. This includes liquid, vapor, ice, ice sheets, glaciers, clouds, etc.
What are ‘Continental Glaciers’
This is also known as ‘ice sheets’, these are glacial land ice that extends more than 50,000km2
It is presently found on Greenland and Antarctic - due to these being the coldest regions of Earth
Contains 70% of all freshwater on Earth
Sea level rise, it will increase greatly if ice sheet completely melted
Ice sheets regulate temperatures that affect global climate patterns (due to albedo effect)
What is an ‘‘Ice Cap'“
A mass of glacial land ice that extends less than 50,000km2
Commonly in regions with cold temperatures
Melting ice caps provide essential water for many of the world’s densely populated regions, especially from the Himalayas to India, Bangladesh, China, and SE Asia.
Energy: Many glacially fed rivers are dammed for hydroelectric power, providing energy for industry.
What is the Cryosphere?
Locations on the planet where liquid water is turned into soil form
It can be found in extreme latitudes like the arctic/antarctic
Permafrost
Sea ice
Snow
Land cover
Ice sheets
Cryospheres include glaciers, ice, snow, icebergs, permafrost, mountains, etc.
Define the ‘Carbon Cycle’
The process in which carbon atoms continually move from the atmosphere to the earth and back again. There are two types of carbon cycles: Slow and Fast
Explain the slow carbon cycle
Over years, carbon moves between the atmosphere, lithosphere and oceans. Rocks are weathered and enter the atmosphere, and rivers. This solid matter: rocks (sediment) reaches the ocean floor and absorbed into the earth’s crust, then reentering the atmosphere and lithosphere through volcanic eruptions.
Explain the fast carbon cycle
Absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide through photosynthesis, as it is moved through the good chain and released through respiration. Prior to this, organisms use carbon to build cells, proteins and and DNA molecules. Fast carbon moves 1000 times more carbon per year than slow carbon cycle
What are extreme weather events?
Weather that is significantly different from the usual weather pattern in a given place over a period of day or longer.
Including unexpected, unusual, severe or unseasonal weather.
E.g. heatwaves, cold waves, droughts, temperate cyclones, tropical cyclones /8typhoons, hurricanes & cyclones)
CAUTION: Floods(caused by extreme weather), tsunamis, and earthquakes are not extreme weather, but are natural disasters
What are droughts and its different categories
Metrological drought Occurs when there is a prolonged period of time below average precipitation, it comes before the following
Agricultural drought: initially can be caused below average precipitation, but exacerbated by poorly planned irrigation systems and farming practices.
Hydrological drought: Caused by below average rainfall, followed decreases in quivers, lakes and reservoirs falling below replenish-able levels .
What are economical impacts of droughts?
Food insecurity
Energy insecurity
High food production costs
Reduction or loss of industrial production
Loss of tourism revenue
What are environmental impacts of droughts?
Lower water levels
Increased concentration of pollutants in water
Drying out of ecologically essential wetlands
More intense bushfires
Loss of biodiversity
What are the social impacts of droughts?
Direct effect of heat waves
Reduced access to drinking water
High food prices in supermarkets
Stress caused by failed harvests
Increase inequalities between HIC & LICs
What are biomes?
A community of plants & animals (flora & fauna) that have common characteristics for the climate or landscape that they live in
Different types of flora and fauna in each biome depends on the following:
Temperature range
Precipitation levels
Soil fertility
What are habitats?
A type of natural environment in which a particular species or organism lives. it provides food, shelter, protection and potential reproduction.
What is The Energy Balance?
The balance between incoming energy from the Sun and outgoing energy from the Earth. It explains how the Earth maintains an average temperature
Extreme Weather Events
Are short-term atmospheric events that are significantly more intense and frequent, or prolonged than average weather conditions for a given place
What are the different types of Extreme Weather Events?
Heatwaves: heat stress, wildfires, crop failure, excess mortality
Droughts: water shortages, food insecurity, desertification
Tropical Cyclones: storm surges, flooding, infrastructure damage
Floods: displacement, disease, damage to homes and farmland
Cold waves / Extreme snowstorms: hypothermia, transport distruption, crop damage
What are Droughts
A drought is a prolonged period of abnormally low precipitation that results in water scarcity and negatively affects ecosystems, agriculture, and human activities.
What are the different types of Droughts
Meteorological drought
Rainfall is significantly below average
Agricultural droughts
Soil moisure is insufficient for crops
Hydrological droughts
Caused by reduced river flow, reservoir levels, and groundwater
Socio-economic drought
Water demand exceeds supply, affecting people and economies
Migration patterns
Climate change–related animal migration is the movement of animal species to new locations or along altered routes in order to survive changing environmental conditions caused by climate change.
Why do animals migrate?
Temperature
Food Avaliability
water avaliability
breeding conditons
Habitat loss
What are Crop Yields?
Crop yield is the quantity of a crop produced per unit area of farmland, and it is strongly influenced by climatic and environmental conditions.
How does climate change affect crop yields?
1. Rising Temperatures
Heat stress reduces photosynthesis
Shortens growing seasons for some crops
Can reduce yields of wheat, maize, and rice
2. Changes in Rainfall Patterns
Droughts reduce soil moisture and crop growth
Intense rainfall and floods damage crops and cause soil erosion
3. Increased Frequency of Extreme Weather
Heatwaves, storms, and floods cause crop failure
Greater year-to-year yield variability
4. Increased Pests and Diseases
Warmer temperatures allow pests to survive longer
Crops face higher losses without adaptation
5. Elevated CO₂ (Mixed Effects)
Can increase photosynthesis in some crops (CO₂ fertilisation)
Benefits are often offset by heat stress and water shortages
What are ‘Limits of Cultivation’
The limits of cultivation are the physical and human factors that prevent or reduce agricultural production, making it difficult or impossible to grow crops in certain areas.
Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is the wearing away and removal of topsoil by natural agents such as water, wind, and ice, often accelerated by human activities.
What are Supply Chains?
A supply chain is the sequence of stages involved in the production, processing, distribution, and sale of goods, linking producers to consumers.
How does climate change disrupt supply chains?
Extreme Weather Events
Floods damage transport infrastructure
Droughts reduce agricultural output
Storms disrupt ports and shipping
Environmental Stress
Reduced crop yields affect food supply chains
Water shortages disrupt industrial production
Increased Risk and Uncertainty
Delays, shortages, and rising prices
Greater vulnerability in global supply chains compared to local ones
Arctic Shipping Lanes
Arctic shipping lanes are marine transport routes through the Arctic region that are opening for longer periods each year as rising temperatures reduce sea ice cover.
Vector Brone diseases
A vector-borne disease is an infectious disease spread through vectors, rather than by direct human-to-human contact.
Risk
Risk is the probability of a hazardous event occurring combined with the severity of its potential impacts on people, environments, and economies.
Vulnerability
The susceptibility of exposed populations to harm, Influenced by poverty, health, age, and preparedness
Risk perception
Risk perception is the subjective judgement people make about the severity and likelihood of a risk, shaped by social, cultural, economic, and psychological factors.
Resilience
Resilience is the ability of people, communities, or environments to withstand, adapt to, and recover from hazards or stresses.
“A community rebuilding and adapting after a flood or drought”
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
The IPCC is a United Nations body that assesses scientific research on climate change and reports its impacts, risks, and possible responses.
Governments use IPCC findings to plan climate mitigation and adaptation strategies
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
The UNFCCC is an international agreement that brings countries together to limit climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
E.g. Paris Agreement 2015, COP conferences
Carbon offsetting
Carbon offsetting is when emissions produced in one place are balanced by reducing or removing carbon dioxide elsewhere.
A company invests in renewable energy projects (e.g. wind or solar) in LICs
Carbon Trading
Carbon trading is a system where countries or companies buy and sell permits that allow them to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide.
Geo-engineering
Geo-engineering refers to large-scale technological interventions designed to deliberately alter the Earth’s climate in order to reduce the impacts of climate change.
Climate mitigation
Climate mitigation refers to actions taken to reduce the causes of climate change, mainly by lowering greenhouse gas emissions or increasing carbon sinks.
Reduce causes
Climate adaptation
Climate adaptation refers to actions taken to adjust to the impacts of climate change in order to reduce harm and increase resilience.
Cope with impact
Triple bottom line
The triple bottom line is a way of measuring success by considering economic, social, and environmental impacts, not just profit.
Economic – is it financially viable?
Social – does it benefit people and communities?
Environmental – does it protect the environment?
Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in climate change refers to actions taken by companies to reduce their environmental impact and address climate change beyond legal requirements.
Low carbon Economy
A low-carbon economy is an economy that produces low levels of greenhouse gas emissions by reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Countries investing in wind, solar, and hydroelectric power
Electrification of transport (electric cars, trains)
Aarhus Convention
The Aarhus Convention is an international agreement that gives the public rights to access environmental information, participate in decision-making, and seek justice in environmental matters.
Access to information – governments must share environmental data
Public participation – people can take part in environmental decision-making
Access to justice – people can challenge environmental decisions in court