Unit 4 - Business Management SL
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Marketing
A management process involved in identifying, anticipating, and satisfying consumer requirements profitably.
Four Main/Generic Objectives of Marketing Departments
Right products to fulfill needs
Correct prices
Distribute products conveniently for purchase
Adequate + Effective promotion
Importance of Marketing
Understanding Customer Needs - Meeting customers needs with affordable, valuable products that ensure satisfaction for both the business and customer.
How is Marketing an Ongoing Process?
Changing Customer Needs
Business Environment Changes
Competitive Pressure
Internal Development
Outcomes of Effective Marketing
Customer Satisfaction
Repeated Purchases, recommendation, customer loyalty.
Other obvious outcomes → more profit, stay competitive, can gain more market share with favor.
Aspects of Marketing
Exchange process - two-way process where business provides product and receive something (payment)
Mutual benefit - both customers and business benefit
Consumer Trends - understanding current and future needs.
Delighting Customers - exceed expectations → build customers loyalty.
Purpose of Marketing
To align business strengths with market needs through market research, product development, packaging, promotion, and pricing. Effective marketing creates value for customers and drives business profitability.
Key Areas Influence On Marketing
Product Nature (design, quality)
Quantity Produced (guide production)
Product Variety
Pricing
Marketing Collaboration with other Functions
Operations - discuss production capacity, product benefit, managing cost.
Finance - Negotiate budget for development, launch, production
HR - staffing needs and skill requirement.
Success in Coordination
Effective marketing requires collaborating with other functions to ensure resource availability and meet demand, leading to business success.
Product Orientation
A marketing approach that is inward-looking, focusing on creating an innovation that creates needs for it rather than looking at existing needs.
Market Orientation
A marketing approach that is outward-looking. Market orientation uses market research to focus on the customer in order to identify, design, develop, and supply products that meet their needs and wants.
Factors to Choose Market vs. Product Orientation
The market - Hi-tech products (smartphones) tend to start off as product oriented. Mass consumer markets typically have more market oriented.
Organizational structure - Business that puts customer as key stakeholders are more market oriented.
Barriers to entry - Less competition → less customer-focused. Such firms has market power in pricing, distribution, so more product oriented.
Market
A place or process where customers and supplies trade. A market exists where there is a demand for a particular product.
Market Characteristics that are researched
Market size
Customer base
Barriers to entry
Competition
Market Share
Percentage of 1 firm’s share of the total sales in the market. Can be measured in the volume of goods sold or the value of those goods.
Market Leader
An individual or company that owns the largest market share or highest profitability margin in a given market for goods and services.
Market Concentration
Measures the degree of competition that exists within a market by calculating the market share of the largest few firms in the industry.
Market Size
The magnitude of industry, usually measured in terms of the value of sales revenue from all the businesses in a particular market, per time period.
Marketing Strategy
Medium to long-term plan to achieve a firm's marketing objectives. Combines all marketing goals into a comprehensive plan. A good marketing strategy comes from market research, maximizing profitability and business sustainability.
Marketing Objective
The specific marketing goals of an organization.
Marketing Objectives of Profit Seeking Organizations
Increase sales revenue
Higher market share
Increased market leadership
Improved product/brand awareness
Marketing Objectives of NPO
Build membership + support
Generate awareness for NPO cause
Improve brand recognition of NPO
Positive attention to NPO operations
Why do market strategies change?
Changing consumer tastes
Shorter product life cycles
Internet and mobile technologies
Competitive Rivalry
Globalization
Needs
The essential necessities that humans must have for survival
Wants
Human desires that are not essential for survival
Marketing Plan
A document that includes marketing strategies, strategy, budget to achieve marketing objectives (7Ps). Planning allows for efficiency, organization, streamline business activities, maximize cost.
Marketing Audit
Inspection of existing marketing. This is to identify current weakness in marketing mix to make improvements.
Process of Marketing Planning
Marketing Audit
Marketing Objectives
Marketing Strategies
Marketing Mix
Key Insights from Market Research
Market size (sales volume or value)
Market growth potential
Competitor positioning and customer perceptions
Customer views on the brand
Marketing Planning
The systematic process of assessing marketing opportunities, resources, defining marketing objectives, marketing strategies, and establishing guidelines for implementation and control of the marketing program.
4Ps
Product
Price
Place (channels of distribution)
Promotion
7Ps
Product
Price
Place (channels of distribution)
Promotion
People
Process
Physical evidence
People (in Marketing Mix)
Individuals involved in the sales process such as shop assistants.
Process
The process that involves when customer buy the product (contracts, forms to make a purchase)
Physical Evidence
Refers to anything the customer can perceive when encountering the business. (e.g environment of stores where product is purchased).
Marketing Mix
The combination of various elements is needed to successfully market a product. E.g. The 7Ps.
Differentiation
The act of distinguishing a business or its products from rivals in the industry. Basically, you’re trying really hard to be different.
Market Segmentation
The process of categorizing customers into distinct groups of people with similar characteristics (such as age or gender), and similar wants or needs for research and targeting purposes.
Three Main Category of Marketing Segmentation
Demographic
Geographic
Psychographic
Demographic Factors - Segmentation
Age
Gender
Race
Religion
Income
Geographic Factors - Segmentation
Demographics is largely influenced by geographic location (culture, language, social attitude)
Climate → weather’s condition can impact business activity.
Psychological Factors
Hobbies and Interest
Values (companies can ethically appeal to customers)
Religion
Culture
Targeting
Aiming your product at a specific segment and making sure it’s built based on that segment’s needs. After segmenting its market, the business now decides on a target market.
Mass Marketing
Refers to marketing to all people. Basically, a strategy that ignores targeting individual market segments. (Coca Cola)
Differentiated Marketing
Market to many segments (Toyota)
Niche Marketing
Marketing that targets a specific and well-defined market.
Positioning Map
A product position map (or perception map) is a two-dimensional visual tool that reveals customer perceptions of a product or brand in relation to others in the market.
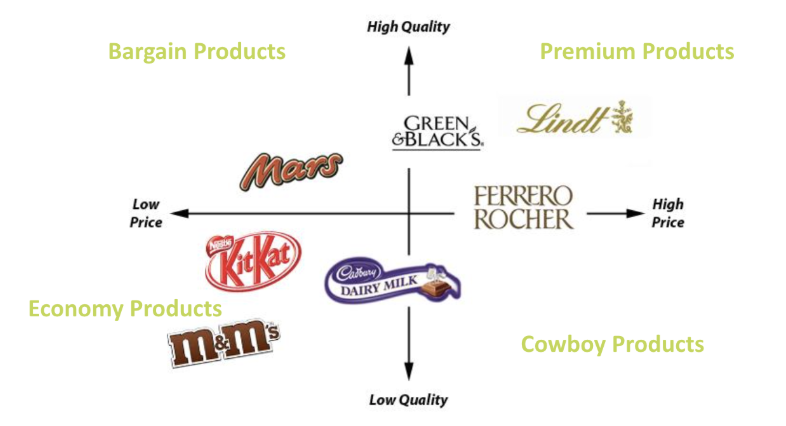
Repositioning
A marketing strategy that involves changing the customer’s perception of a firm's product or brand in comparison to rival firms.
Unique Selling Point (USP)
Refers to any aspect of a product that differentiates it from its competitors.
e.g pioneer of a product, reputation for being superior, only firm to provide it (monopoly)
Product Differentiation
The act of distinguishing a product or service from rivals in the industry, creating a perception among consumers that they are different and unique.
Purpose of Market Research
Successful business conduct market research continuously to keep up with trends and stay competitive. Market research is vital in maximizing sales and understanding your target market.
Primary Research
New and original data is collected for a specific purpose (also known as field research or bespoke research).
Secondary Research
Using a collection of second-hand data and information that already exists (also known as desk research).
Ethics in Market Research
Deceptive Practices
Invasion of Privacy
Breaches of Confidentiality
Objectivity
5Ds of Unethical Market Research
Damage
Deceitful
Deceptive
Disclosure
Detachment
Sampling
The practice of taking a small group of people or a particular market and estimating the results for the rest of the population.
Types of Sampling (Examples)
Quota sampling
Convenient sampling
Random Sampling
Snowball Sampling
Cluster Sampling
Product
Any good or service that serves to satisfy the needs or wants of customer.
Product Lifecycle
Stages a product goes through from its introduction to the market until it is removed from sale. It starts from development, introduction, growth, maturity, and then decline.
Market Research
A systematic process that involves gathering, organizing, and interpreting information and data about the market and current trends.
Extension Strategies
Refer to strategies that lengthen the maturity phase of the product life cycle, still creating demand for the product to be purchased, reducing decline.
Extension Strategies Examples
Introducing the product to new markets
New uses for the product
Change packaging
Target different market segments
Promotions
Differentiation Strategies
Changing parts of the product to create demand.
Size
Color
Design
Packaging
Boston Matrix
A tool/framework that helps companies decide the prioritization of their different products/businesses by how profitable they are.
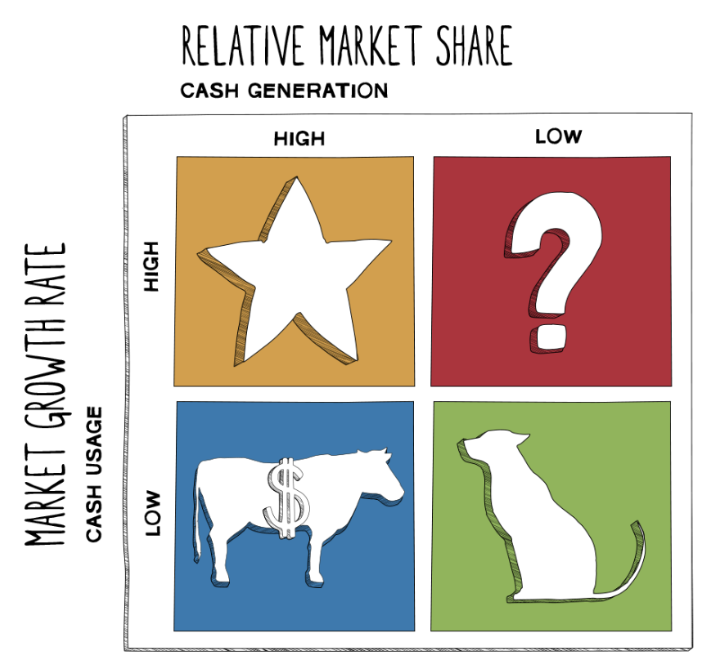
Branding
A form of differentiating the firm from competitors. A brand refers to a name that is identifiable with a product or a particular business. Things such as signs, symbols, and designs can create a brand.
Aspects of Branding
Brand Awareness
Brand Development
Brand Loyalty
Brand Value
Brand Awareness
Extent to which people can recognize a particular brand.
Brand Loyalty
When customers repeatedly buy the same brand of product again.
Brand Value
Refers to the ‘premium’ that customers are willing to pay for a brand name over and above the value of the product itself.
Importance of Branding
Legal Instrument (legal ownership)
Risk Reducer
Image Enhancer (charging premium prices for brand)
Revenue Earner
Importance of Packaging
Physical Protection
Convenience
Information
Security Risks
Aids promotion
Factors that affect pricing (some)
The type of product
The cost of producing a unit
The demand for a product
Competitors
Price Higher if the Product …
Has unique selling point
Perceived as exclusive
High in demand
Sold exclusively
Cost-Plus (Mark-Up) Pricing
A pricing method where a fixed percentage is added to the cost of production to determine the selling price.
Penetration Pricing
Setting a low initial price to attract customers and gain market share before gradually increasing the price.
Price Skimming
Setting high prices at first for the richest, then, after the demand dwindles, decreasing the price for the next layer of the customer (uniquely linked to technological innovation).
The Loss Leader
Selling a product at a price below cost to attract customers, with the expectation that they will buy the other profitable complementary products.
Predatory Pricing
Temporarily reducing price to attempt to force out rivals (destroyer pricing). This is a huge gamble.
Premium Pricing
It is easily perceived as more price meaning more quality, and based on the brand reputation, they can charge higher prices.
Objectives of Promotion
Inform
Persuade
Remind
Above the Line Promotion
Mass promotion and appeals to a large number of audiences rather than targeting specific customer groups.
Below the Line Promotion
The use of non-mass media promotional activities, with the business having more control. Involves promotional techniques which aim to reach consumers more directly that the organization can control.
Through the Line Promotion
Combining both below and above the line promotion.
The Promotional Mix
Direct Marketing
Advertising
Personal Selling
Public Relations
Sales Promotions
Direct Marketing
Involves communicating directly with targeted customers through channels like phone calls, social media, or direct mail to promote products or services rather than being face-to-face.
Personal Selling
Involves direct, face-to-face interaction between a salesperson and a potential customer to persuade them to purchase a product or service.
Public Relations
Marketing activities aimed at establishing and protecting the desired image of an organization. PR is about getting positive media coverage, usually without directly paying for it.
Sales Promotion
Short-term incentives designed to encourage the purchase of a product or service, such as discounts, coupons, or contests.
Guerilla Marketing
A marketing form that uses ‘untraditional’ activities to help companies weaken their rivals and stay successful on the market, even with limited resources.
Importance of Place
Location of Business + Customers
Effective distribution strategies
Make use of intermediaries
Online channels streamline distribution
Types of Distribution Channels
Zero Level Channel
One Level Channel
Two Level Channel
Zero Level Channel
Direct selling, no intermediaries. This means the business produce directly to the customers.
One Level Channel
There is only one intermediary between the producer and customer. Usually this is for consumer goods and the intermediary is the retailer.
Two Level Channel
Two intermediaries involved between manufacturer and consumer. This usually refers to a wholesaler and a retailer in the process.
Wholesalers
Businesses that purchase large quantities of products from a manufacturer and then separates or ‘break’ the bulk-purchases into smaller units for resale to mainly retailers
Distributors
Independent and specialist businesses that trade in the products of only a few manufacturers. For example, car distributors typically sell the products of one manufacturer, such as Honda or BMW, to the consumer.
Agents
Negotiators who act on behalf of buyers and sellers of a product. They are not usually employed by the producer but are used as an intermediary to help sell the vendor’s products.
Retailers
Sellers of products to the final customers e.g. shops, supermarkets, department stores.
Indirect Way to Distribute Products Without Retailers
Telemarketing
E-Commerce
Vending Machines
Mail and Direct mail