Chapter 6 and Interlude B
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Sediment
Loose fragments of rocks or minerals, shell and shell fragments, or mineral crystals that precipitate out of water
Weathering
processes that break down rocks into small pieces by chemical or physical/mechanicals means
What controls weathering?
Properties of parent rock
mineralogy anf crystal structure - Are the minerals soluble in water? Is the structure susceptible to breaking down?
Climate : rainfall and temp
Presence or Absence of Soil : soil formation promotes more soil formation
Length of Exposure: the longer exposed, the more altered a rock becomes
Physical weathering
Breaking larger rocks into smaller rocks without changing the minerals
along natural zones of weakness
Sedimentary rocks: along bedding planes
Foliated metamorphic rocks: along foliation/cleavage planes
Non foliated rocks: along fractures formed by deformation and cooling/contraction
Jointing
natural cracks formed in rocks due to the expansion of a rock undergoing exhumation and cooling contraction (ex: pressure expansion)
Exfoliation
when the outer layers of rock, approximately parallel to the surface, fracture off
Frost Wedging
breakage caused by freezing water
most effective in locations with frewuent freeze thaw cycles
Root Wedging
plant roots work into cracks in the surrounding rock ,forcing it apart
Salt Wedging
when saltwaters get into cracks in the rock and evaporates, salt crystals form and exert a force on the surrounding rock (occurs in arid climates and coastal areas)
Thermal expansion
some minerals expand more than others for any given temperature change
most effective in environments where there are large day night temp differences
the rock expands during the warm day then contracts at night, causing cracks to form
Chemical Weather
chemical reactions that cause some minerals to break down or form new minerals
Dissolution
when minerals dissolve in water
mostly effects carbonate rocks and salts
exL acid rain dissolution or marble statues
Hydrolysis
Carbonic acid reacts with some silicate minerals in rock to form clay minerals (which then get eroded away)
More resistant minerals do not weather and persist
Oxidation
Reactions during which an element loses electrons
Usually occurs when elements combine with oxygen
Common in iron bearing minerals (mafic minerals)
Weathering vs Erosion
weathering: breaking and transforming rock into sediments
erosion: removal of rock or sediment
Different types of erosion
waves
glaciers
wind
rivers
landslides
Depositional Environments
where sediments accumulate
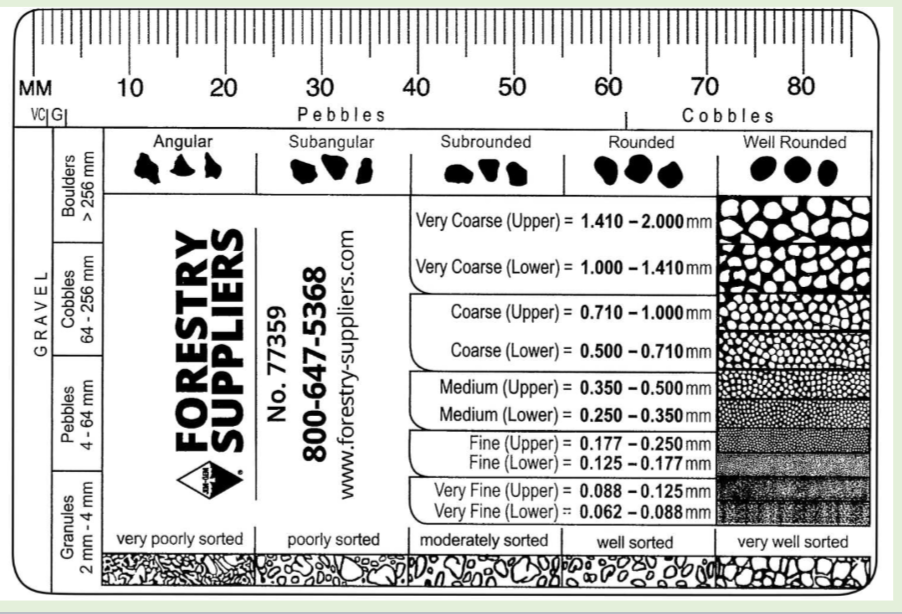
Properties of Sediments
texture
grain size
grain shape
grain sorting
composition
categories:
clastic
chemical/biochemical
organic
individual minerals
Texture
angular
subangular
subrounded
rounded
well rounded
Composition: clastic
made of weathered sediment (small pieces or minerals from pre existing rocks
Composition: biochemical/chemical
not made from sediment that was physically weathered
examples: a rock precipitated from a solution or a rock formed from pieces of shells
Based on the texture and composition you can interpret:
the energy of deposition
high energy: river
low energy: lake
sediment source
clastic sediment: weathered pieces of rock and minerlas
biochemical: shells of marine organisms