Week 10: Urine Crystals, Cells, Casts
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Amorphus Urates
NORMAL
- acidic
- formed from salts after refrigeration
- acidic or neutral urine
- yellowy, brown, pink
- can change to uric acid crystals in the presence of HCL
- re-dissolves when heated to 60 degrees
What crystal is associated with gout?
Uric acid
what are the 4 shapes of uric acid crystals?
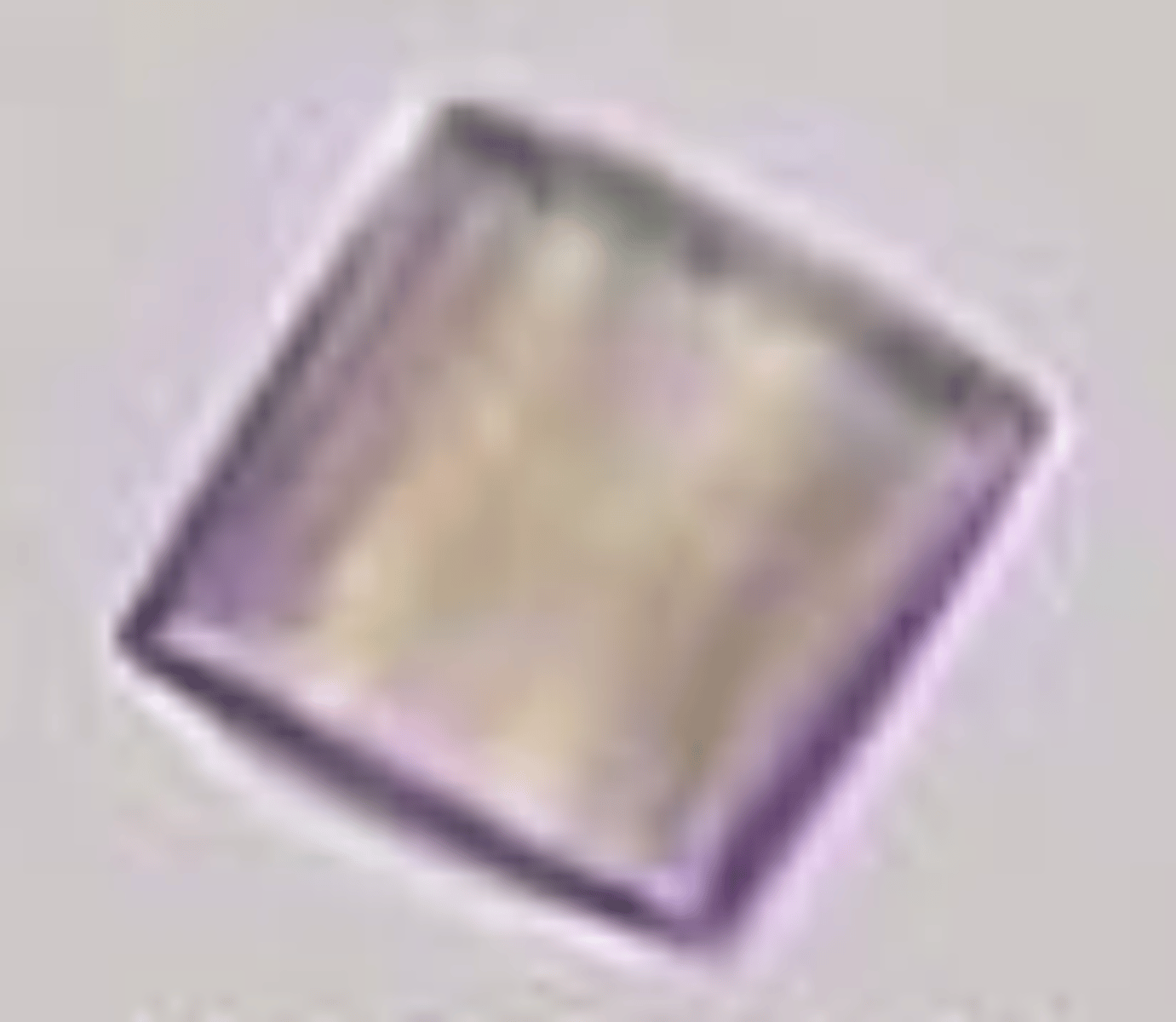
1. barrel
2. rosette
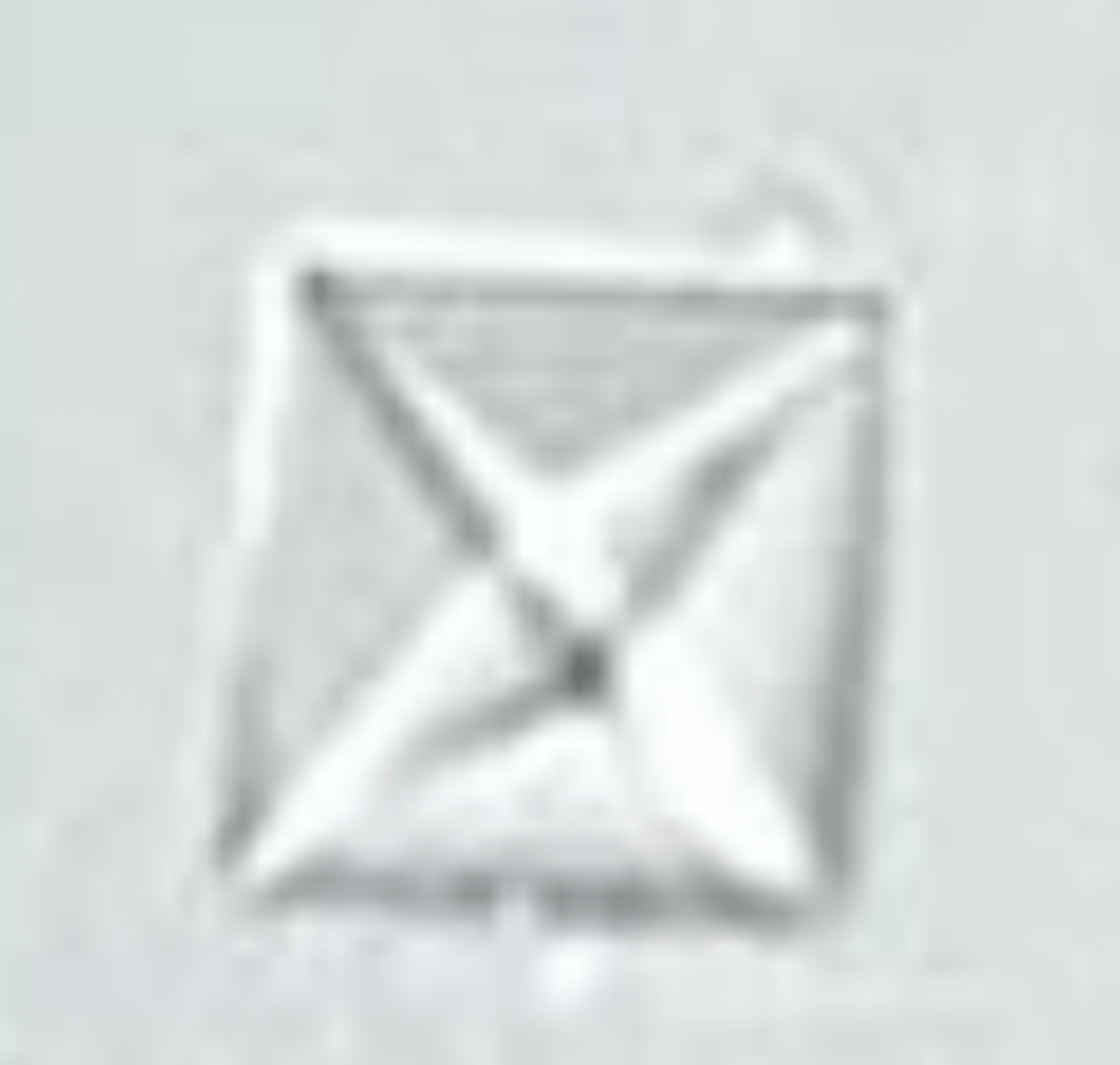
3. six-sided
4. diamond
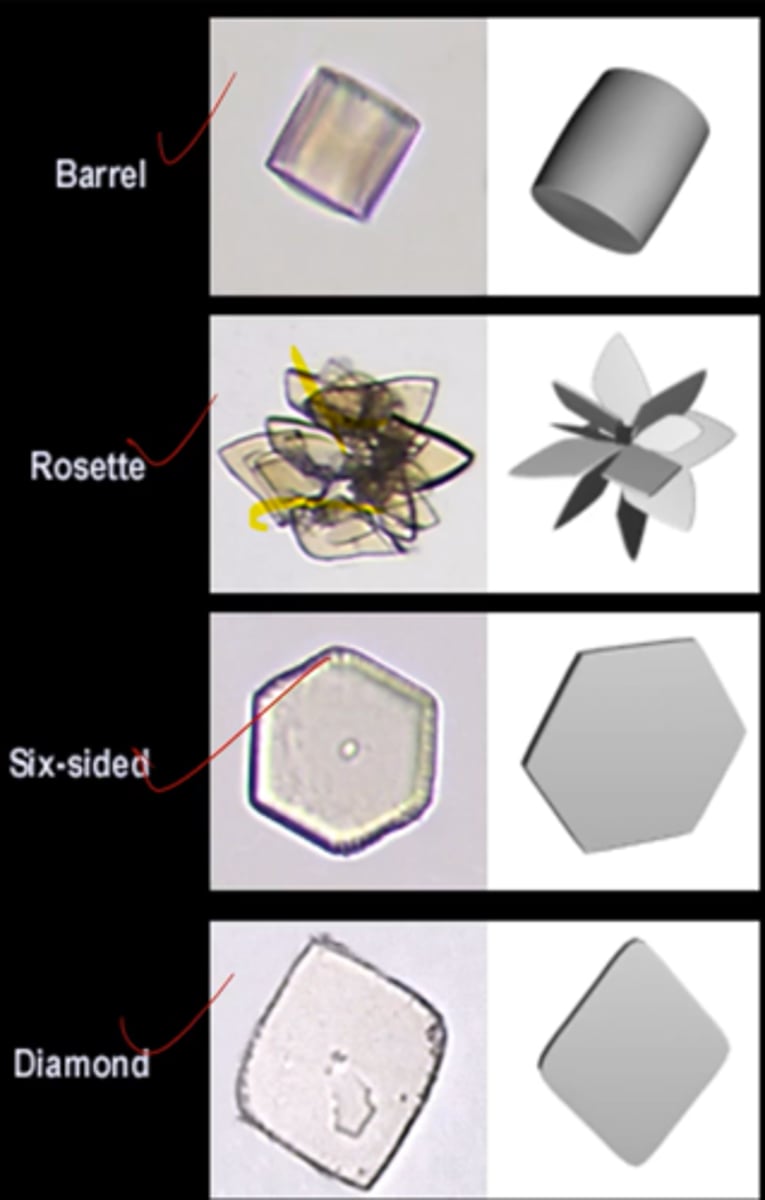
Uric acid crystals
NORMAL (mostly)
- acidic
- pleomorphic
- yellow/brown or colourless
- seen in NORMAL and in diseases
- GOUT MARKER
- could be from kidney stones
- Lesch-Nyhan
- chemo
- leukemia

Gout marker?
Uric acid crystals
Calcium oxalate
NORMAL (mostly)
- acidic
- forms from oxalic acid in food (tomatoes, asparagus, spin, berries, oranges)
- pleomorphic
- dihydrate (octahedral envelope)
- monohydrate (dumbbell, ovoid, rectangle)
- insoluble in acetic acid
- ovoid forms look like RBC

What crystal might you see if a patient is undergoing chemo?
Uric acid
What are the 2 categories of calcium oxalate crystals?
- dihydrate (octahedral envelope)
- monohydrate (dumbbell, ovoid, rectangle)
What type of calcium oxalate crystal is most common?
Dihydrate
How do we deal with ovoid calcium oxalate appearing like RBC?
Add acetic acid to lyse the RBC
What is the clinically significant calcium oxalate? Why?
- long form
- may indicate Ethelyne glycol poisoning
- anti-freeze
- component of renal calculi
Bilirubin crystal
- ABNORMAL
- acidic
- when urine bilirubin exceeds its solubility conc
- yellow-brown needles
- insoluble in alcohol
- POS BILI RESULT accompaniment
-seen in hepatic disorders
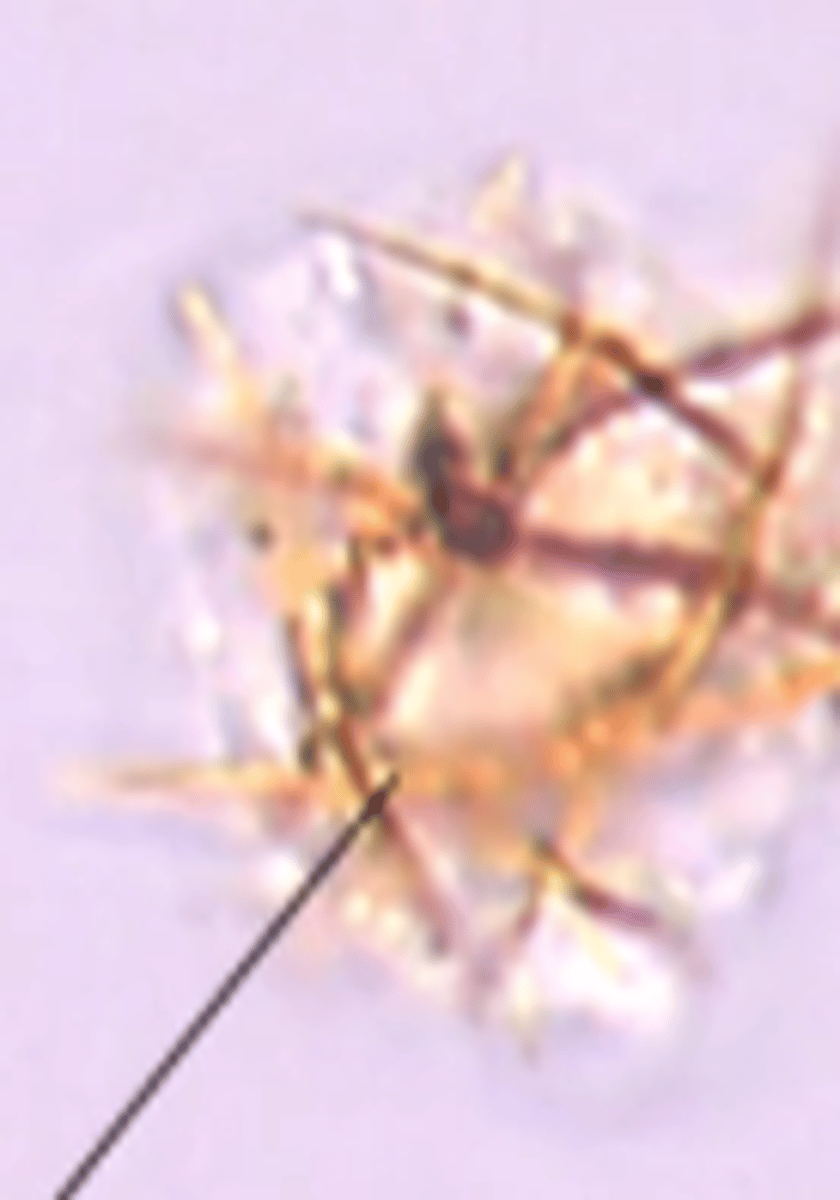
Cysteine crystals
ABNORMAL
- congenital disorder that inhibits renal reabsorption of cysteine (IEM)
- hexagon
- no birefringence
- POS CYANIDE NITROPRUSSIDE TEST
- cystinuria (calculi of children usually)