MAT187 midterm 1 things I keep forgetting!
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Simpson’s rule formula

Trapezoid rule vs midtpoint rule reinman sum formulas
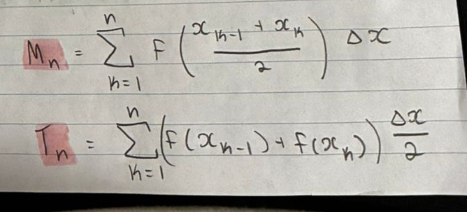
Its a numeric integration question. The x intervals on the table you get are not consistent. wyd?
literally just find the area of each “rectangle” or “trapezoid” individually with a different base length for each delta x and add them up!
integral of 1/x
ln|x| + C
integral of 1/(1+x²)
tan^(-1) (x) + C
improper integral where one of the bounds is infinity - when does it converge? (assume the form 1/x^p)
when p is greater than 1 (less or equal to one diverges!)
improper integral where one of the bounds is a vertical asymptote - when does it converge? (assume the form 1/x^p)
when p is less than one (greater or equal to one diverges!)
You have an indefinite integral from a to infinity and you write it as the sum of two indefinite integrals that are both also from a to infinity. One of those two converges and the other diverges. Does your original integral converge or diverge?
diverges
Strategies for bounding a function (4)
Always check critical points - start and end of the interval AND points where derivative is zero
|a+b|<=|a|+|b|, so you can break up a function like sinx + x² and bound each part individually
cosine and sine are easy. anything with 1/x^p on a given interval is easy.
if you KNOW a function is strictly increasing/strictly decreasing on the interval, then just find the value of the function at the endpoints
when is each approximation method an overestimate? (assume they are an underestimate otherwise)
L - any decreasing function
R - any increasing function
M - any concave down function
T - any concave up function
arclength formula
derive: make a mini triangle, pythagorean theoream, write f’(x) in terms of delta x and delta y, isolate delta y and write it in terms of f’(x) and delta x, factor out the delta x squared (easy!)
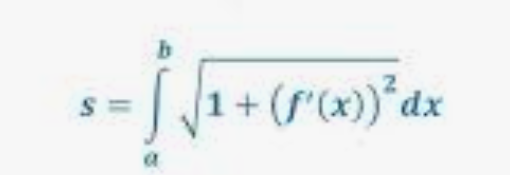
surface area rotating around an axis formula
somehow forgot the dx at the end when i wrote this but basically arc length formula times 2pi*f(x) which is basically the SA of a cylinder for each subinterval - 2pi*rh, where r is f(x) and h is the arclength. also consider that you can use this for VOLUME of solids rotating around an axis if you just squared f(x) to have pir² times the arclength for each subinterval
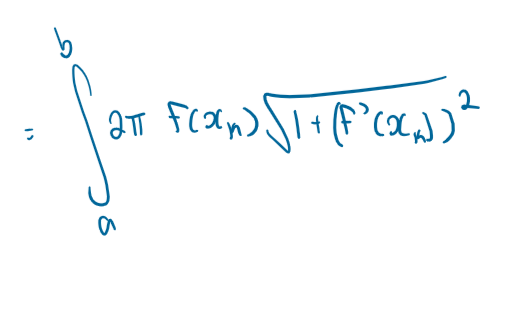
for determining if an improper integral diverges or converges: rank e^x, lnx, and x^p from slowest to fastest growing (as x goes to infinity)
slowest: lnx
middle: x^p
fastest: e^x (any function with e^x in the denominator will almost always converge!!!!)
integral of sec²x
tanx
how do you differentiate arcsin and arccos
arcsinx = y
siny=x
implicit diffentiation to solve for y’ in terms of x
derivative of a^x
(a^x)*ln(a)
integral of a^x
(a^x)/ln(a)
integral of 1/(x²+16)
(arctan(x/4)) / 4
how do you integrate sin²x or cos²x
formula booklet for the trig identities!!! and they become so easy to integrate
how do you integrate sec³x?
integration by parts, and you’ll get to a point where the integral you have left is sin²x. From there use the trig identity in the formula booklet!
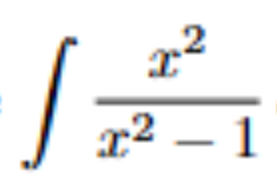
you see this wyd
turn the numerator into x²-1+1 and then split it into (1)+(1/(x²-1)) and then the first integral is x and the second integral can be solved by partial fraction-ing