Echo Boards
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
Normal male LVIDD?
Normal female LVIDD?
50 +/- 4 mm for male
45+/- 4 mm for female
How can you tell if an LV or LA measurement is foreshortened when doing biplane method of discs
4C and 2C lengths should be within 10% of each other
If apical views have poor imaging definition, how should you measure LV size instead of biplane method of discs?
area-length method from PSAX (area) and apical 4c (length)
Where should the LV borders be traced
between compacted and non-compacted myocardium
Normal LVEDVI male?
Normal LVEDVI female?
up to 75 ml/m2 for male
up to 62 ml/m2 for female
Formula to calculate LV mass (g)
0.8 × 1.04 x [(IVS + LVID + PWT)³ - LVID³]+0.6
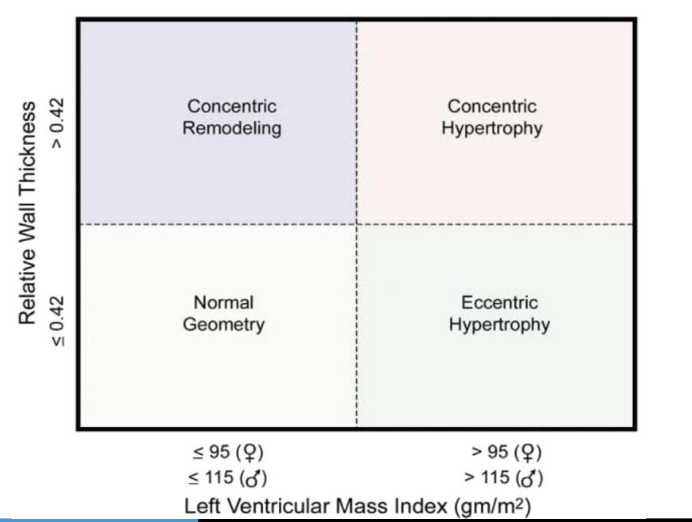
Formula for relative wall thickness and normal value
Relative wall thickness (RWT) = 2 x PWT / LVIDD, normal value is <0.42. If > 0.42, this is concentric hypertrophy or remodeling
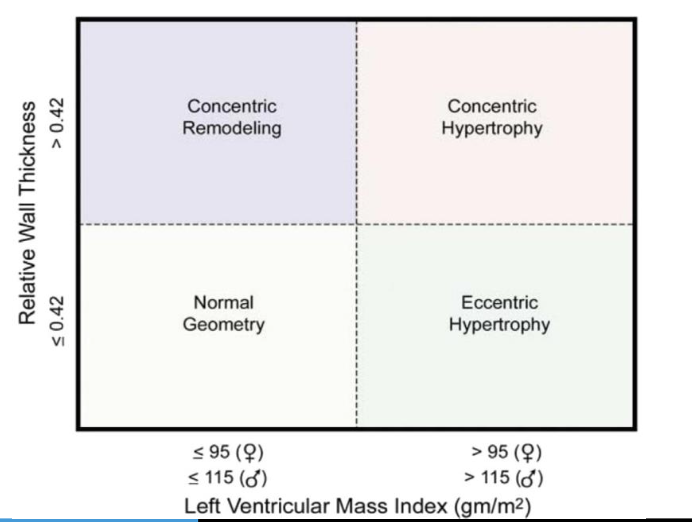
Normal cutpoints for LV mass index (gm/m2)
<= 95 gm/m2 for female
<= 115 gm/m2 for male
Formula for ejection fraction
100 x (EDV-ESV)/EDV
Upper limit of normal for indexed LA size (ml/m2)? mild, moderate, severe enlargement sizes?
up to 34 ml/m2 is normal
up to 41 - mildly enlarged
up to 48 - moderately enlarged
more than 48 - severely enlarged
RA volume indexed normal limits for male and female
(lower yield)
25 ± 7 ml/m² (male)
21 ± 6 ml/m² (female)
Normal RV basal and mid diameter (mm)
bonus: RV length
basal < 41 mm (not at annulus, widest portion in basal 3rd)
mid < 35 mm
length: 83 mm (annulus to apex)
What is RIMP (RV index of myocardial performance)? When should you use this and what are the limitations
RIMP = (IVCT+IVRT)/RV Ejection Time
This is really not used because it underestimates severity of disease (especially if RAP is high). If right atrial pressure is high, the isovolumetric contraction time (IVCT) of the RV is decreased.
Normal TAPSE?
17 mm
Normal RV S’?
10 cm/s
Normal RV vs LV strain?
normal RV strain -25%
nromal LV strain -20%
Normal RVEF?
42%
what is the gold standard for MS gradient assessment?
CW across MV (better than invasive)
formula for MV area based on PHT?
MVA = 220/PHT
limitations for MVA by PHT?
affected by pressure in the LV and LA - if the LV pressure is high, the PHT will be short and you will underestimate the degree of stenosis. Same if LA compliance is messed up.
Also not as good for calcific/degenerative MV disease. ONLY for rheumatic!! cannot use on prosthetic valves
how do you calculate MVA by continuity for mitral stenosis?
(LVOT area x LVOT VTI)/MV VTI (at annulus)
which is stroke volume/MV TVI
what is severe MV stenosis criteria for rheumatic MV disease
not defined by gradient. MVA < 1.5cm.
time from S2 to diastolic opening snap indicates what
shorter esp less than 80ms = severe MS (opens early due to high LA pressure)
how do you calculate PHT from decel time
Decel time x 0.29 = PHT
how do you calculate MV EROA by PISA
2*pi*r² * aliasing velocity / peak mitral valve velocity. Then multiple by the theta/180 correction.
what are the absolute contraindications to TEE (4)
known esophageal stricture or obstruction
active upper GI bleeding
esophageal perforation
esophageal diverticulum
what causes methemoglobinia in TEE? how do you treat?
the benzocaine spray causes it, treat with methylene blue, peripheral sat is not helpful for this
what are your reversal agents and doses for moderate sedation?
naloxone (0.4mg IV) and flumazenil (0.2-0.4mg.
might have to redose the flumazenil since half life is shorter than that of the benzos
If ultrasound were to travel through a medium that is 2x a fast as blood, what would happen to the velocity detected?
the velocity is doubled
velocity = c (speed of US in blood)/2 x deltaf/fo
what is the relationship between pulse repititon frequency and nyquist limit?
proportional -
Nyquist limit = PRF /2
if you want to increase your NyQuist limit, what are 2 things you could do?
decrease the depth of ultrasound —> increased PRF —> increased Nyquist Limit
select a transducer with a lower frequency to reduce the amount of doppler shift
what PHT corresponds to SEVERE for acute aortic regurgitation
< 200 ms
what mechanical index do you usually image at?
less than 0.3. often less than 0.2.
what mechanical index would you use for suspected LVNC
0.3-0.4 to help deliniate the endocardial border
how do you perfusion imaging with contrast/UEA
can transiently go high (0.8-1) to destroy microbubbles and deplete the myocardium and watch to see how long it takes to replenish - normal is within 5 seconds at rest, within 2 seconds at stress
how to correct swirling of contrast at apex
use a very low MI imaging, or increase the UEA infusion rate, move focus to nearfield
how ot deal with contrast attenuation artifact
can FLASH high MI briefly, or can decrease the contrast infusion rate
how do you calculate the wavelength from a frequency of 3MHz of an ultrasound probe transducer
in soft tissue, the velocity is 1540 m/sec
velocity = frequency * wavelength
so wavelength = 1540 m/s divided by 3MHz = 0.5 mm
what is a duty factor
percentage of time that hte ultrasound system is transmitting a pulse.
pulse duration / pulse repetition period
decreasing imaging depth will do what to the PRF
will increase the PRF — inverse relationship
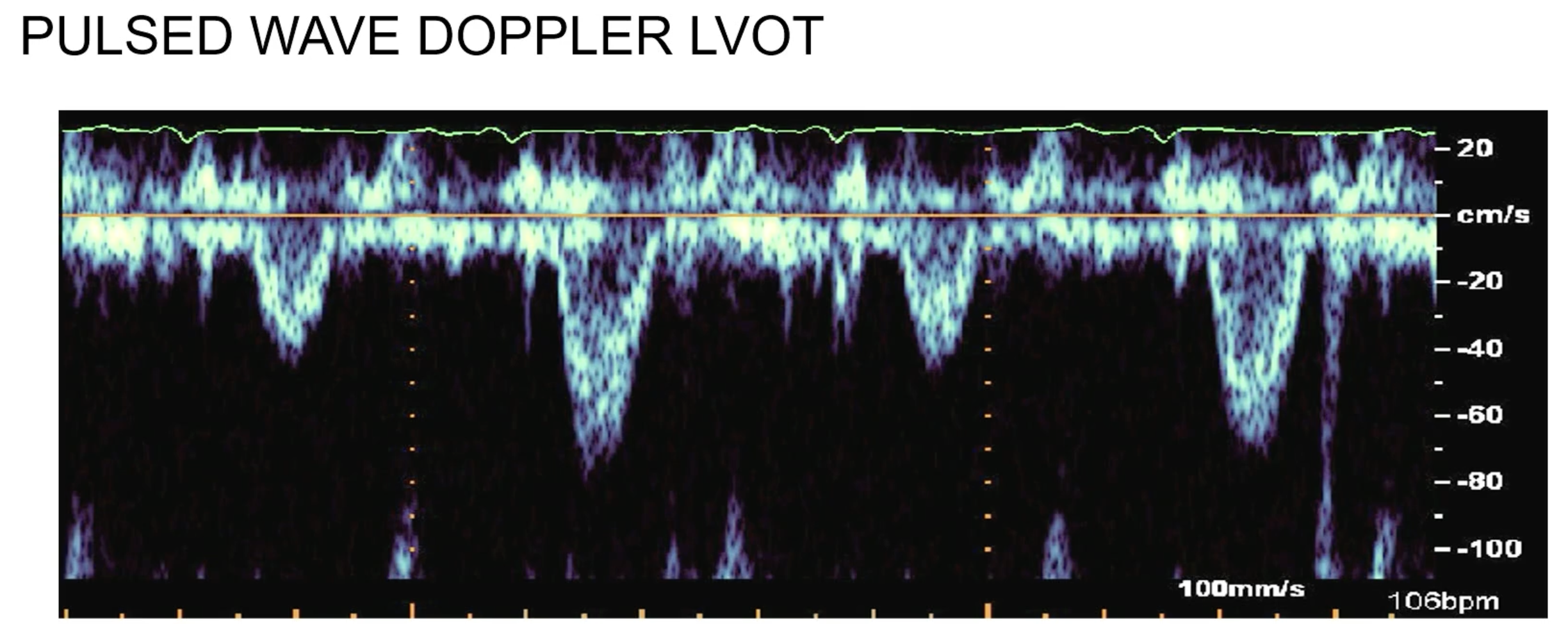
what is this finding indicative of?
pulsus alternans at LVOT — VERY sick left ventricle, can be seen in end stage DCM
which leaflet of the tricuspid valve is the longest
anterior
what kind of ASD causes LVOT obstruction
primum ASD
what EKG finding can be seen with primum ASD
left axis deviation
what is most common type of ASD
secundum
what type of ASD is associated with anomolous pulmonary veins
sinus venosus ASD — kind of a misnomer - due to abnormal pulmonary vein drainage into SVC (or rarely IVC)
what chamber gets enlarged with a VSD
systole pushes extra blood flow across the VSD into the pulmonary vasculature, and then all that extra volume goes back into the left side causing LA/LV dilation
what is most common type of VSD
membranous — at level of AV/TV
what kind of VSD is between the MV/TV
inlet VSD
syndrome with secundum ASD and skeletal abnormalities
Holt-Oram Syndrome
congeinital defect associated with Downs
total AV canal defect (primum ASD + inlet VSD) or inlet VSDs
what chamber enlargement would you expect with a PDA
LV - volume overload from aorta to PA to LA and LV
cleft mitral valve is associated with what kind of defect
primum ASD
ebstein anomoly is associated with what EKG finding
accessory pathway
WPW syndrome/pre-excitation may be present in 20% of Ebstein’s patients
coronary sinus ASD is associated with what other finding
persistent L.SVC
outlet type VSDs cause what valvular issue
aortic regurgitation
what kind of VSD is most common in kids
muscular (aka trebecular)
what is the mustard/senning operation and what conenital disease is it often used for
D-TGA — it re-routes the atrial flows into opposite ventricle via 2 baffles (atrial switch procedure). This is an old surgery not done anymore - now we do arterial switch. problem with this repair is RV remains systemic ventircle
if a patient had a mustard for D-TGA, and their LV ends up dilating over time, what may be cause?
Baffle leak or pHTN
main long-term complication of tetrology of fallot in adulthood?
pulmonary regurgitation
what is a BT shunt - what does it do, and for what disease
conduit between subclavian artery and PA to allow some more blood to get to the lungs due to the pulmonary artery obstruction in tetrology of falllot. done before the definitive surgical repair
What is as Fontan
single ventricle palliation (hypoplastic left heart most common reason) - allows blood from the ICV to go directly to the PAs. usually follows a Glenn (same thing except SVC to PA) and a Norwood (which makes the RV pump to the aorta in addition to the PAs since the LV is underdeveloped, often done in conjunction with a BT shunt)
what is the typical strain pattern for Fabry’s disease
reduced strain in the posterior and lateral walls
dimensionless index - how to calculate and what is considered severe?
LVOT VTI/AV VTI — if < 0.25, severe
what is the calcium score cutoff for CT aortic valve for men and women
> 2000 in men
> 1200 in women
use in those who have a valve area < 1, are symptomatic, do not have high gradients, have a low stroke volume index but normal EF
asymptomatic chronic severe AR — what are the class 1 indications for surgery? (2)
ESD 50 MM or
EF < 50%
(EDD 65 MM is class IIa)
aortic regurgitation - what vena contracta is mild and what is severe
< 0.3 is mild
> 0.6 is severe
what is the regurgitant volume cutoff for AR and MR?
BOTH are > 60 cc per beat
what is the EROA cutoff for severe for AR and MR?
for AR is 0.3 cm2
for MR is 0.4 cm2
how to calculate EROA?
regurgitant flow (cm³/s) / regurgitant velocity (cm/s)
how to calculate regurgitant flow from PISA
pisa radius² * 2pi * aliasing velocity = cm³/s
what systemic disease should you think about in a patient with basal septal thinning and subecpicardial LGE
sarcoid
how do you diagnose HCQ toxicity
gold standard is electron microscopy on biopsy. PYP scans often are false positive
what is Fabry’s disease manifestations?
angiokeratomas, neuropathy, renal failure, GI symptoms and LVH
hypereosinophilic syndrome manifestation on echo?
LV apical thrombus with normal apical wall motion. sometimes can also get in RV or underneath the MV or TV. over time becomes endomyocardial scar in these areas
how does hemachromatosis present on echo
LV dilated cardiomyopathy
On MRI, you got T2* mapping with < 20ms
what % respirophasic variation is significant for tamponade in MV and TV
MV - 30%
TV - 60%
always put the bigger # in the denominator when calculating %
formula for near zone length of a transducer based on the diameter and frequency of transducer?
NZL = D2f/4c where D = diameter of the transducer, f = frequency of the probe, c = the velocity of ultrasound in soft tissue (1.54 mm/μsec)
calculate tricuspid valve area from PHT
190/PHT
cutoffs for severe mitral stenosis?
PHT
valve area
mean gradient
1. Pressure halftime ≥150 ms
2. Valve area ≤1.5 cm2
3. Mean gradient >5 mmHg at
HR 60-80
criteria for severe AR?
Regurg vol
Regurg fraction
EROA
PHT
Vena Contracta
• Regurgitant volume >60 mL
• Regurgitant fraction >50%
• ERO >0.3 cm2
• AR PHT <250 ms
• Vena contracta >0.6 cm
criteria for severe Mitral Regurgitation
Regurg Volume
Regurg Fraction
EROA
Regurg Volume > 60
Regurg Fraction 50%
EROA > 0.4
name 5 ways to resolve aliasing - this occurs at the Nyquist limit
hints:
transducer type
transducer frequency?
what do you do to PRF?
Things that one can do to resolve aliasing are 1) use a continuous-wave transducer, 2) increase the PRF (scale) to the maximum setting for the depth you are imaging at, 3) switch to a high pulse repetition frequency, 4) utilize a lower frequency transducer and 5) adjust the baseline to allow for imaging the maximum velocity.
which type of artifact is decribed:
create ghost images of high contrast structures off axis to the sound beam
grating lobes
what type of artifact is described:
occurs behind low attenuating structures (i.e. fluid filled structures) and results in a hyperintense signal.
enhancement
what type of artifact is described
the misplacement of a structure in an image due to a change in direction at non-perpendicular boundaries with a difference in tissue impedance.
refraction
what causes the S1 of pulmonary vein flow?
early systolic flow is due to left atrial relaxation. S1 is absent in patients with atrial fibrillation
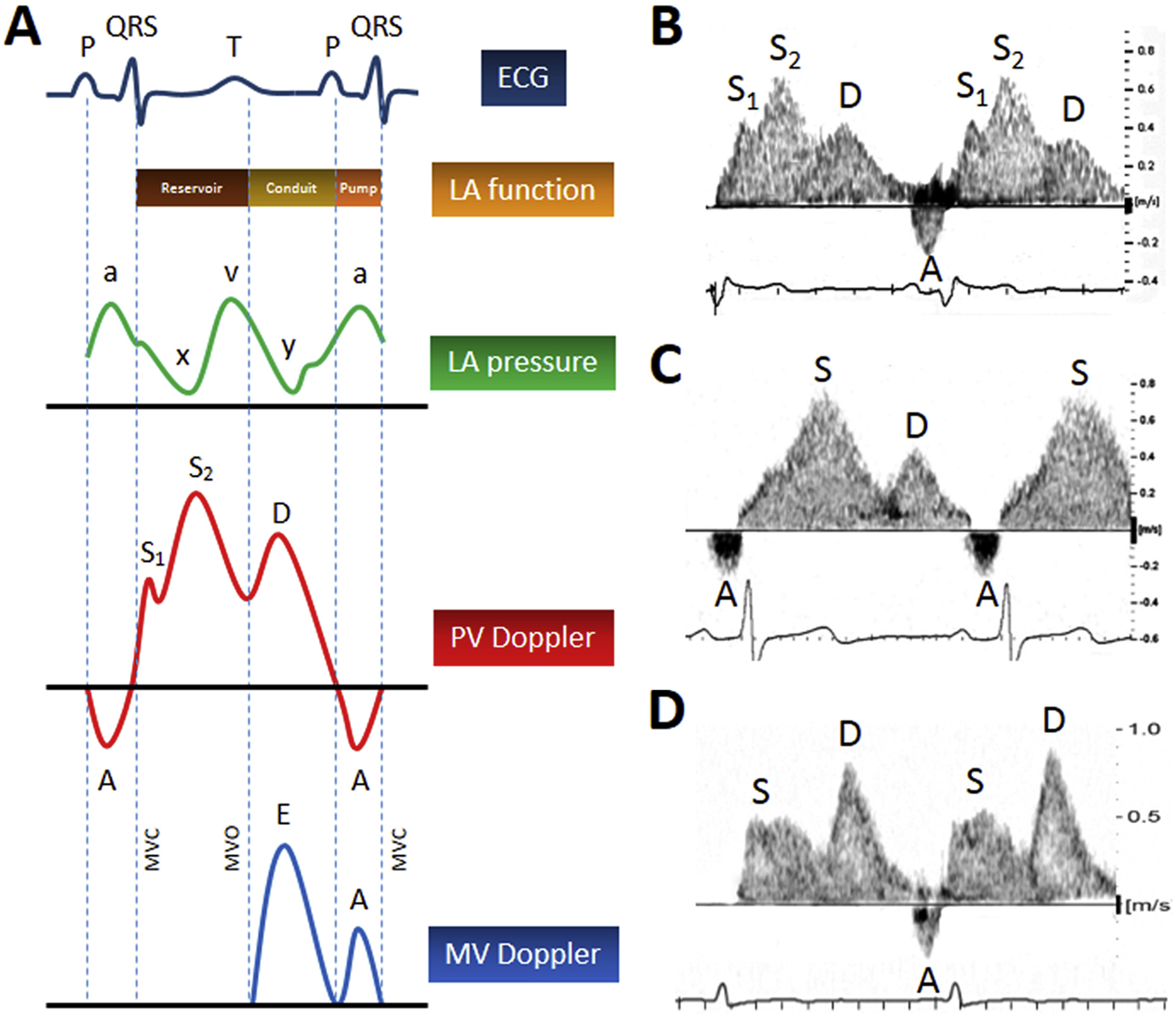
what would you see for E deceleration time in high LA pressure state?
short < 150 ms
what do you see of pulmonary vein tracing in high LA pressure
the low peak s velocity and the low s/d ratio
what pulmonary vein pattern would you see in restrictive cardiomyopathy?
In the setting of restrictive filling, most filling of the LA from the pulmonary veins occurs in a brief period in early diastole, when the mitral valve opens. Hence, the pulmonary vein flow pattern would have a small S-wave and a large D-wave, or a ratio of S:D << 1.
In Freidrich’s ataxia, patients present with ataxia, cerebellar dysarthria, and areflexia. what is seen on echo?
Echocardiographic features mimic cardiac amyloidosis.
how do you approximate a mean gradient from a peak gradient?
0.7x the peak gradient = mean gradient
Normal prosthetic aortic valve vales
peak velocity
mean gradient
DVI
EOA
AT
shape of jet
Peak prosthetic AV velocity < 3.0 m/s
mean gradient < 20 mmHg
DVI ≥ 0.30
EOA > 1.2 cm2
Acceleration Time < 80 msec
contour of jet triangular and early peaking
severe prosthetic aortic valve stenosis?
peak velocity
mean gradient
DVI
AT
shape of jet
Significant AVA stenosis is suggested by the following:
Peak prosthetic AV velocity > 4.0 m/s
mean gradient > 35 mmHg
DVI < 0.25
acceleration time > 100 msec
contour of jet rounded/symmetric
is it more important to do tissue doppler mitral annular velocities in heart with normal or abnormal LV function?
The principal difference in the assessment of filling pressures between patients with preserved and reduced LV systolic function occurs because in normal hearts, mitral annular velocities tend to be more preload dependent. Therefore, inferring filling pressures in normals by solely relying on mitral inflow velocities can be misleading.
By contrast, in abnormal hearts, tissue Doppler velocities change very little with loading conditions. In such patients, if the mitral E/A ratio is ≥ 2 or < 1, an estimation of filling pressures can be made without knowledge of mitral annular velocities.
what type of cardiac tumor is rarest in children?
Myxoma- it is the most common primary tumor in adults, but rare in children. Typically they are associated with heart failure, systemic emboli, and neurologic symptoms. |
what kind of cardiac tumor has a median age of 13 years old at presentation, and often you will see calcifications
Fibroma- median age is 13 years old for presentation, and are singular, large, well-circumscribed, hyperechoic lesions associated with the ventricular free wall or septum.
Calcification can be seen and is an important diagnostic clue. Focal necrosis or cystic degeneration can also be present.
These tumors distort the ventricular myocardium and cause outflow obstruction
what kind of cardiac tumor usually presents as multiple masses
Rhabdomyoma- they are typically multiple lesions (2 or more), hyperechoic, and appear in the ventricular septum and free wall. |
what kind of cardiac tumor usually causes a pericardial effusion?
Teratoma- they most commonly originate in the pericardial cavity attached to the great vessels. They have both multicystic and solid areas. A pericardial effusion can also be seen and is large, hemodynamically important, and patients are typically symptomatic. It is the 3rd most common pediatric tumor.
what is the most common mutation causing aortic dilation in a non-syndromic patient?
ACTA2