Critique review PET/CT
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
True or false: do positrons have short half lives
true
how can you tell the difference between a malignant and benign single pulmonary nodule
malignant will have more uptake on a F-18 FDG scan
what is the half live of C11
20 min
what is the half live of N13
9 min
what is the half live of O15
2.1 min
what is the half live of F18
110 min
what is the half live of Rb82
75 sec
what is the half live of Ga 68
68 min
what is the half live of Cu-64
12 hours
Numerous malignant tumors have an affinity for what
glucose
What happens to F-18 FDG when it is trapped in a cell
dose not re-cross the cell membrane = no redistribution
what is the name of F-18 FDG
Flurodeoxyglucose
FDG is tagged to what
F-18
what is the half life of F-18
109 minutes
F-18 emits what
two 511keV 180 degrees apart
what happens to F-18 when it decays
emits positron that annihilate and release photon energy
what is a true coincidence
simultaneous detection of two emissions resulting form a single decay event
what is scatter coincidence
one or both photons from a dingle event are scattered and both are detected
what is random coincidence
simultaneous detection of emission from more than one decay event
what is 2d acquisition mode for PET
with septa (collimated)
Still a 3D image
what is 3D acquisition
no septa (non-collimated)
what doee no septa lead to
increase in sensitivity and photons from a larger number of incident angles are accepted
what do newer PET scanner have
septa can be retracted and placed in the detector in 3D mode
What is the patient prep
NPO 4 hours
What is involved in the patient interview
identify the patient
patient height/weight
NPO 4 hours
Diabetic status
measure glucose
allergies if using CT contrast
What is the glucose range for PET/CT
< 160 > assess continuing
what is the adult dose for FDG
5-20mCi
most institution give 10mCi or 12mCi
what is the pediatric dose range
0.1-0.14mCi/kg
when is imaging performed for FDG after injection
60-90 minutes
True or false: FDG dose can be weight based
true
what is the patient procedure for FDG
patient voids
imaging starts 60-90 minutes after injection
select appropriate PET/CT procedure
place patient on imaging pallet/table
scout CT (FOV)
non diagnostic CT decrease dose ( transmission scan and attenuation values
PET scan (emission scan)
analyze study
where are we scanning from for a whole-body PET scan
base of brain to pelvis (mid thigh)
90cm scan length
what is scanned first for a whole-body PET scan
pelvis to head
how many bed positions are there for a whole-body scan
5-7 bed positions
how long dose a whole body scan take
30-1hour
what are we scanning form for a total body PET
head to legs
how long does a total body PET scan take
30mins-1 hour
what is the indication for a total body PET scan
malignant melanomas
how many bed positions are there for a total body PET
10
what should be done if there is cancer in the pelvis
catheterize to reduce bladder activity and saline flushes
what can be used to promote FDG excretion for patients that have cancer in the pelvis
diuretic
what is normal distribution of FDG (most common and constant sites of intense uptake)
brain
liver (moderate)
Kidneys (calyces and pelvis)
bladder
what is variable activity of normal distribution of FDG
salivary glands
thyroid
heart and vessels
spleen
stomach
bowel
bone marrow
muscles
testicles
muscle uptake can result from
exercise or weight lifting the day before a PET exam
how can muscle uptake be avoid
patient should be instructed to refrain form strenuous activity the day before the scan
how many scans must a radiologists have under their belt in order to become familiar with normal variations for FDG
100
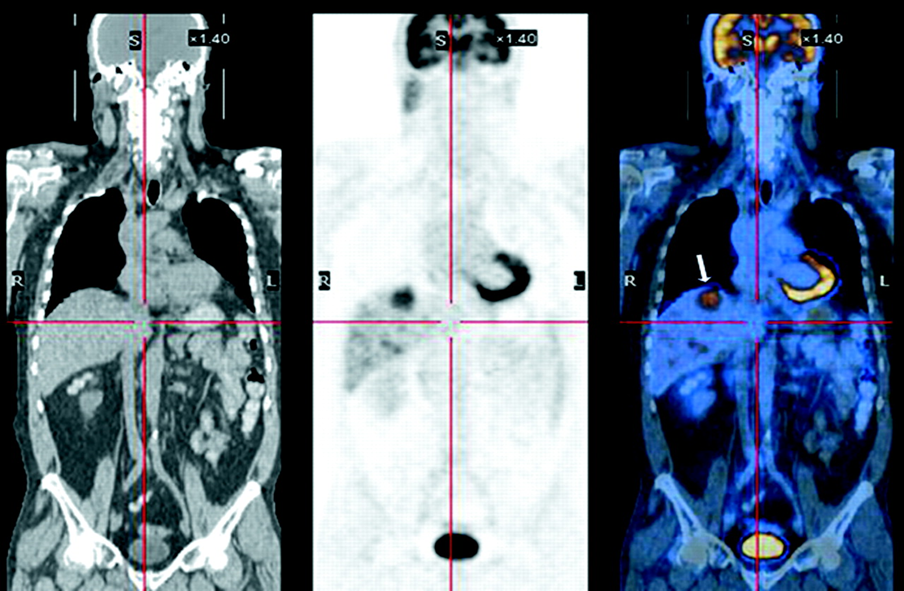
CT-PET-fused
is the normal PET/CT scan
yes
what view is the left image
transverse
what view is the middle image
sagittal
what view is the right image
coronal
what is CT used for in a PET scan
anatomy overlay and attenuation correction
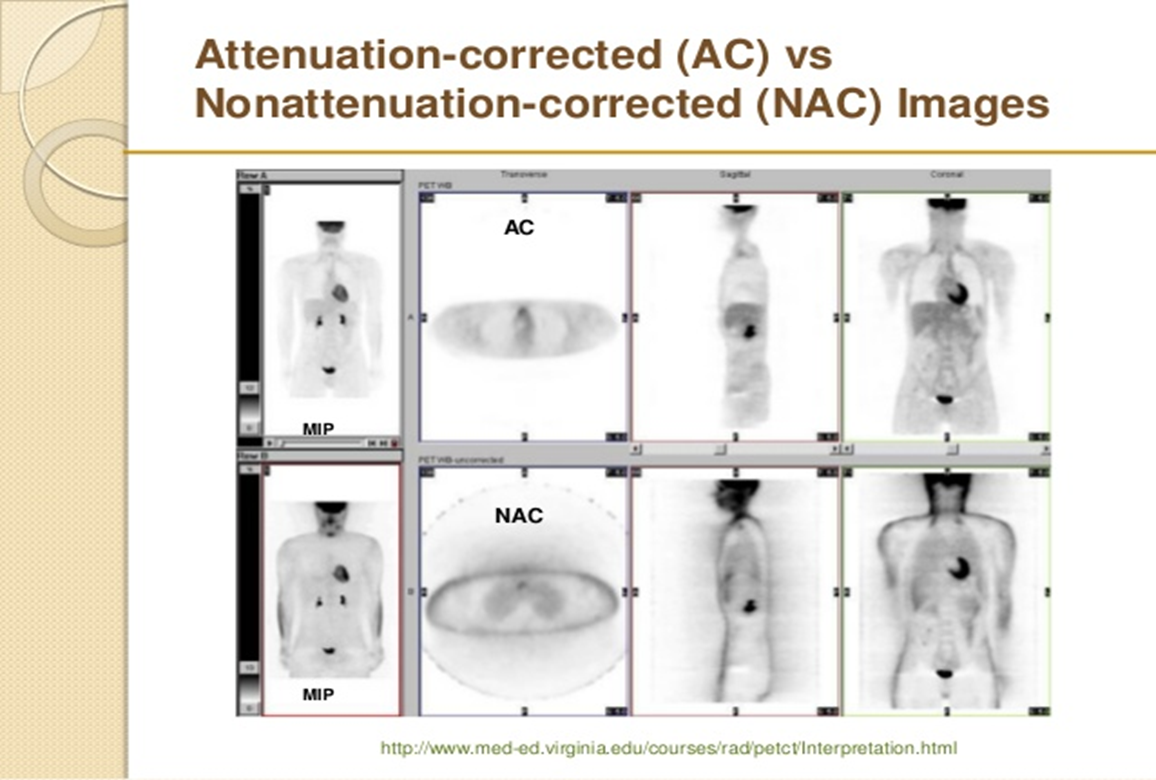
is the top row attenuation corrected (AC) or nonattenuation corrected (NAC)
attenuation corrected (AC)
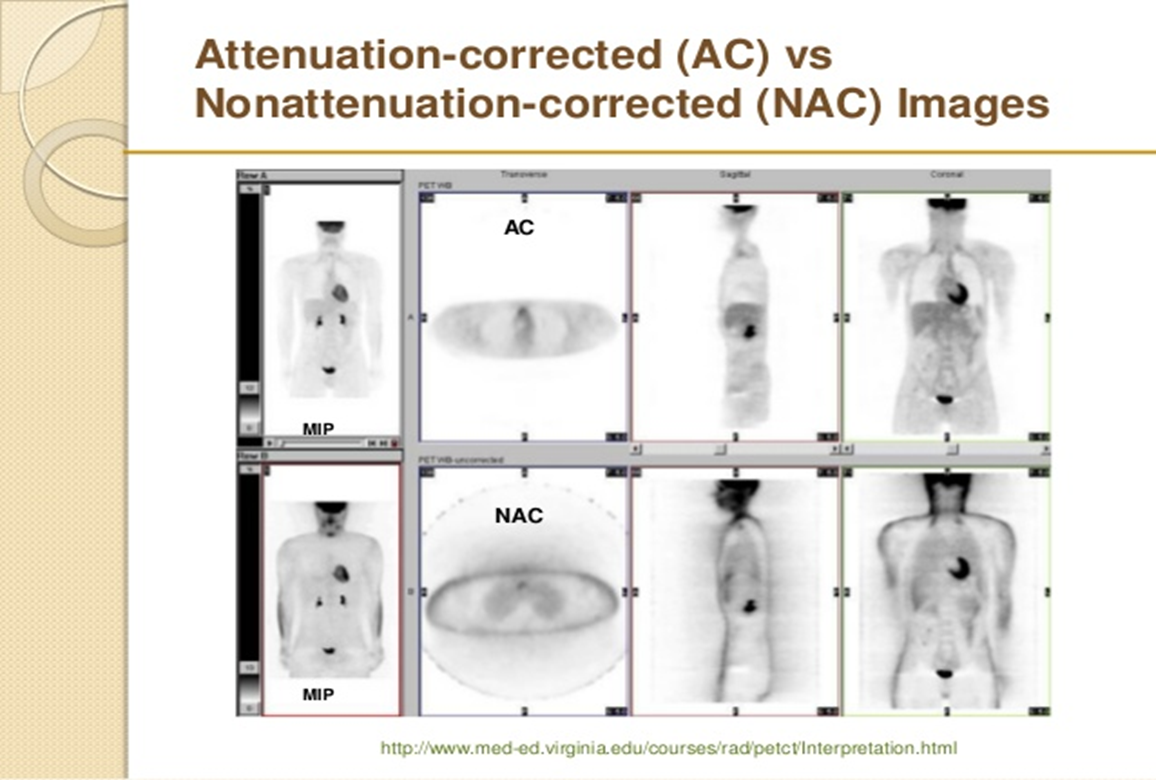
is the bottom row attenuation corrected AC or nonattenuation corrected NAC
nonattenuation corrected
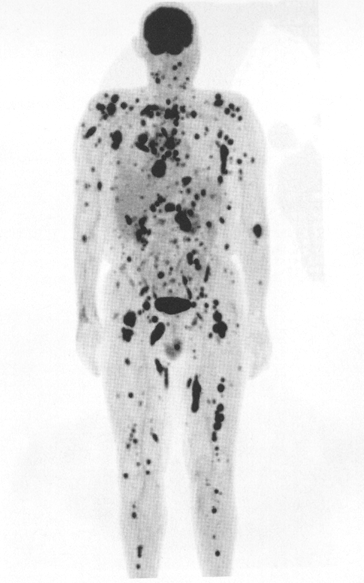
what does this image show
melanoma (diffuse) whole body
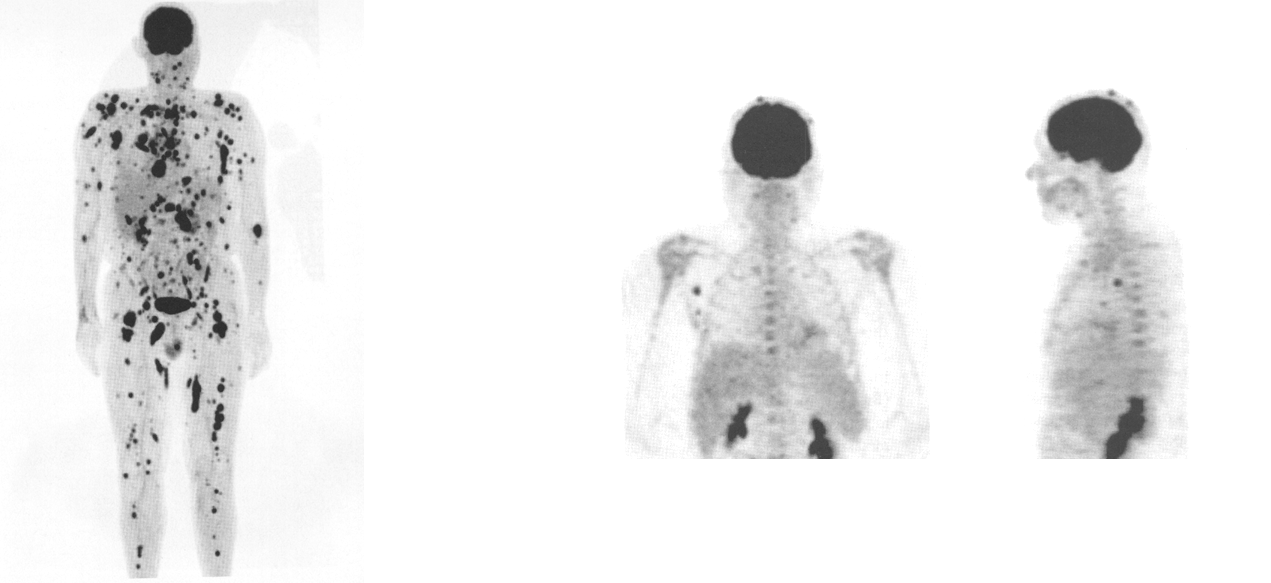
what does this image show
melanoma (scale area)
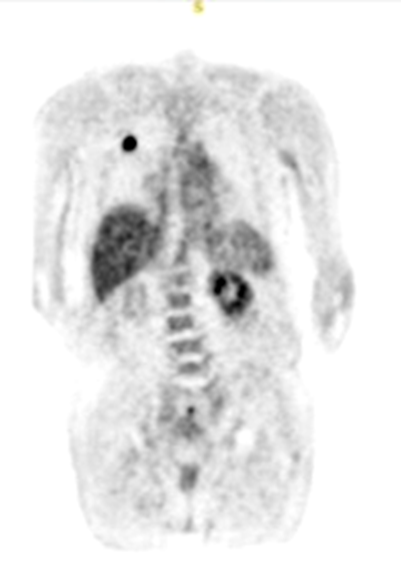
what does this image show
malignant single pulmonary nodule
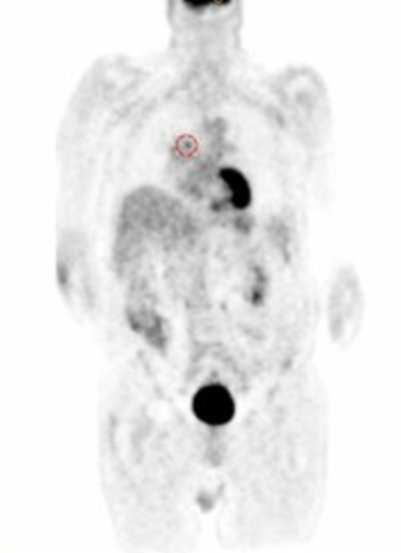
what does this image show
benign single pulmonary nodule
what are standard uptake values used for
measure tumor metabolic function
uptake on a scan (ROI) can be converted to what for a SUV
number or ratio
what are the parameter needed for a SUV
dose injected
imaging time post injection
absolute activity calibration QC
reconstruction algorithms used

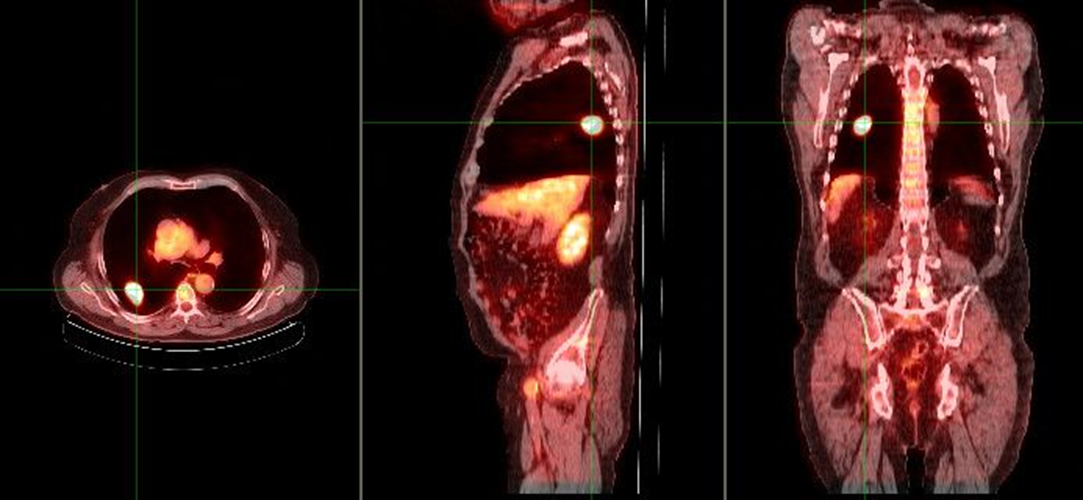
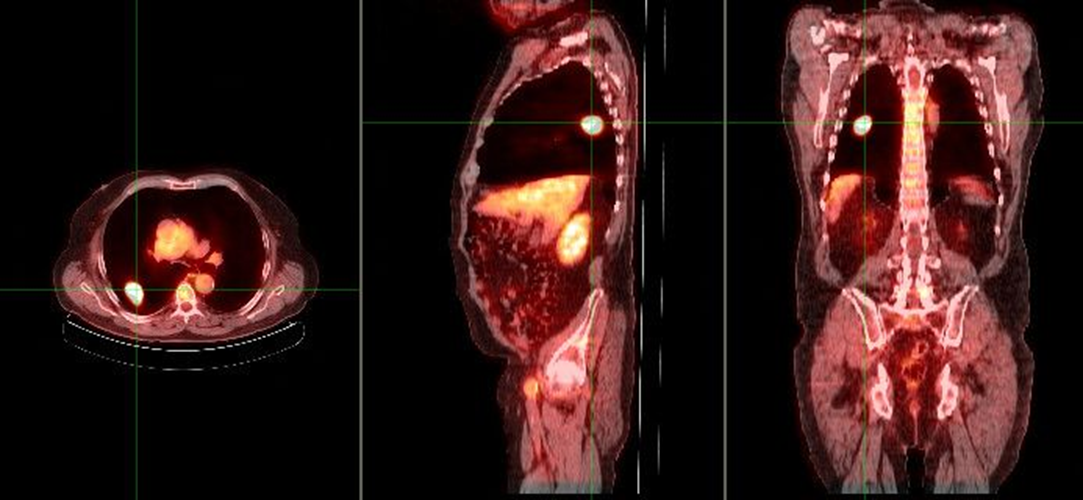
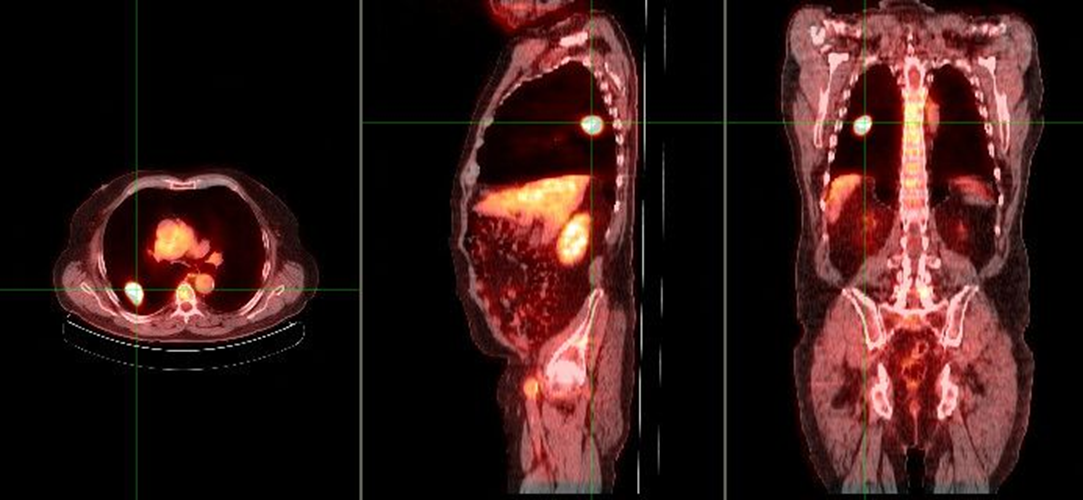
what does this image show if the chest x-ray demonstrated a nodule in the right lung
increased metabolic activity indicative of malignancy
single pulmonary nodule (SPN)
what are the two different lymphoma
Hodgkin’s (HL) and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas (NHL
how can PET be used for lymphoma
staging of the disease
how are pre and post therapy scan helpful for lymphoma
evaluating response to therapy
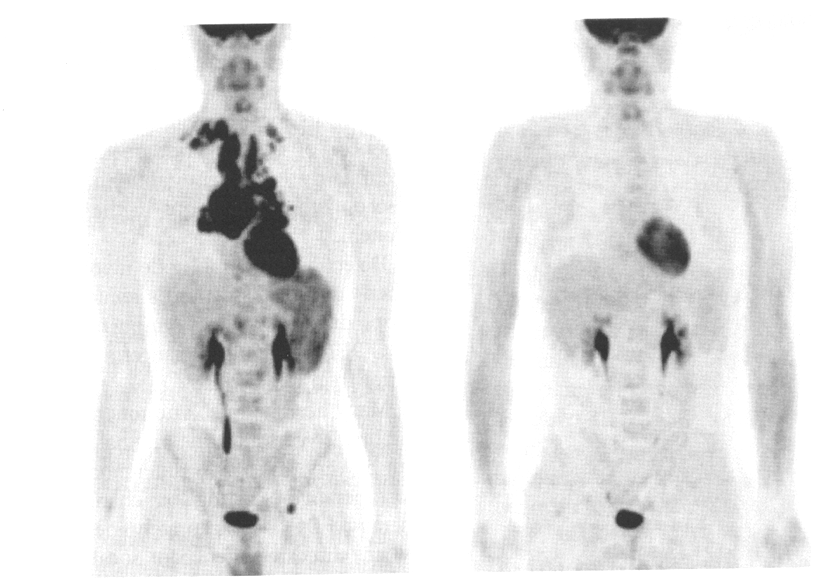
the image on the left is pre or post therapy for lymphoma
pre therapy
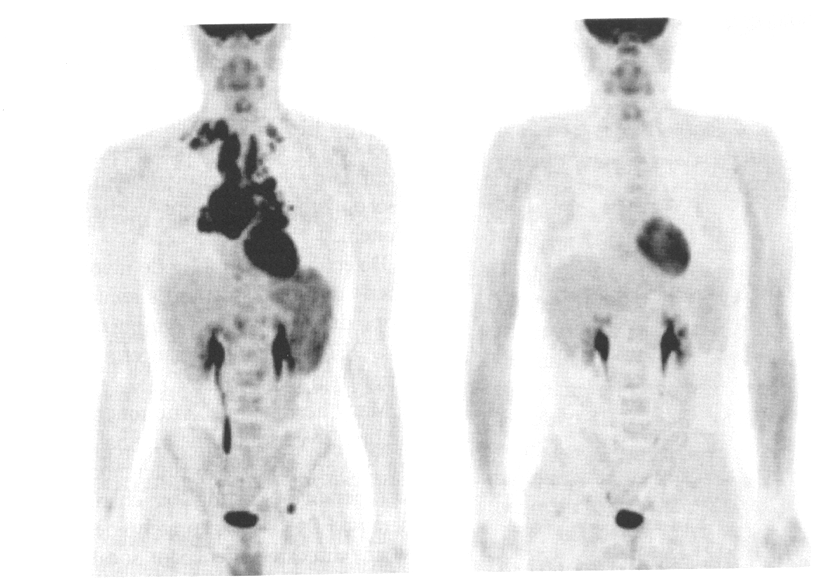
the image on the right is pre or post therapy for lymphoma
post therapy
colon cancer can lead to what
bowel cancer
multiple metastatic sites for colon cancer suggest what
widespread disease
where can colon cancer spread to
liver and lung
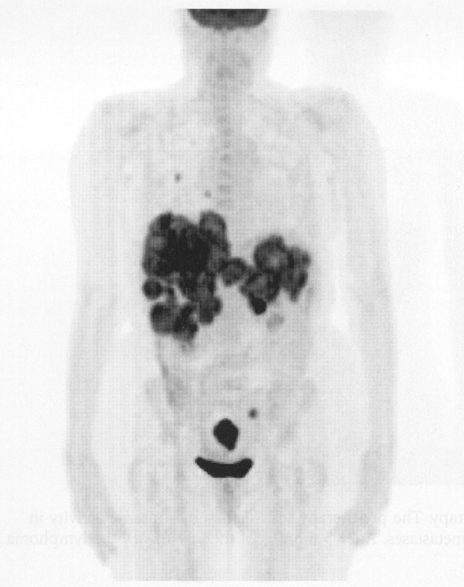
this image shows what
colon cancer
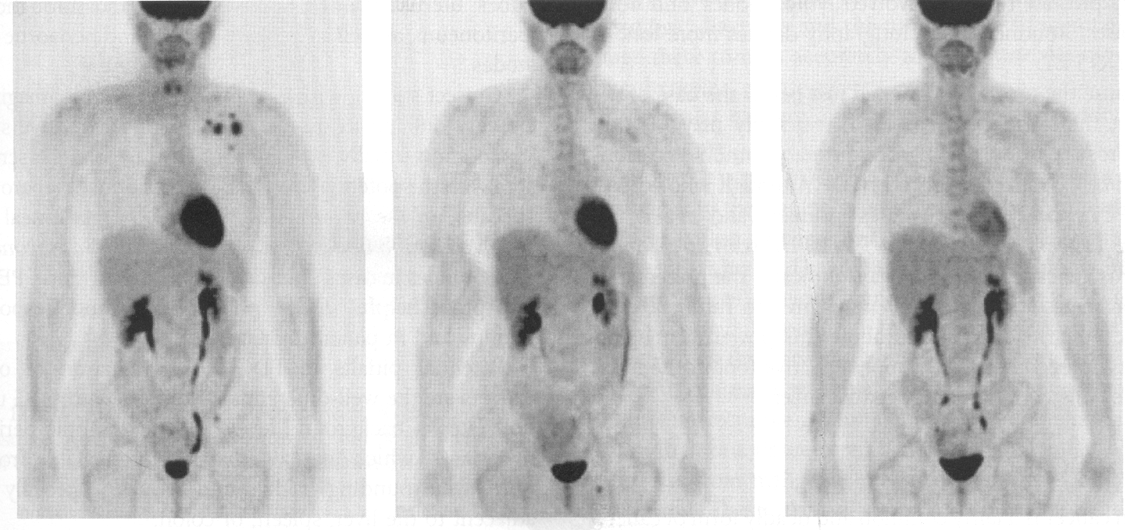
this image shows pre and post breast cancer monitoring (pre and post chemotherapy)
the image on the left is initial, 3 months or 5 months
initial
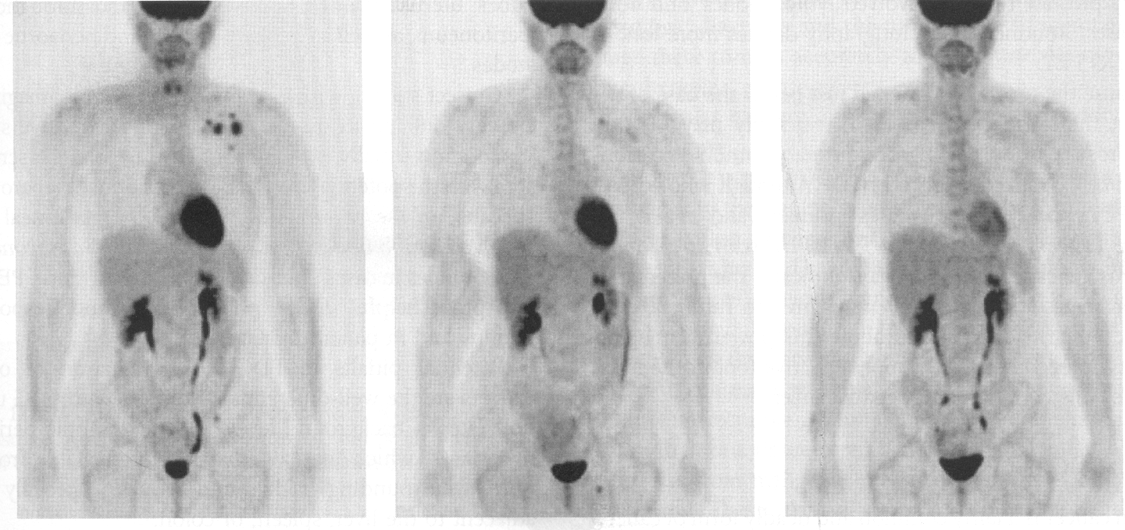
this image shows pre and post breast cancer monitoring (pre and post chemotherapy)
the image in the middle is initial, 3 months or 5 months
3 months
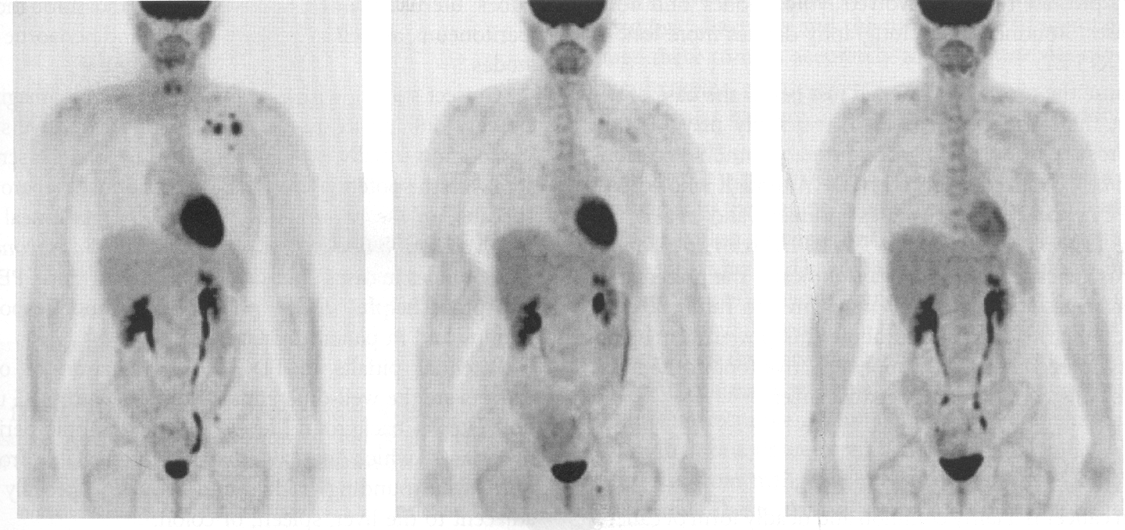
this image shows pre and post breast cancer monitoring (pre and post chemotherapy)
the image on the right is initial, 3 months or 5 months
5 months
ovarian cancer with extensive METS to where
peritoneal cavity
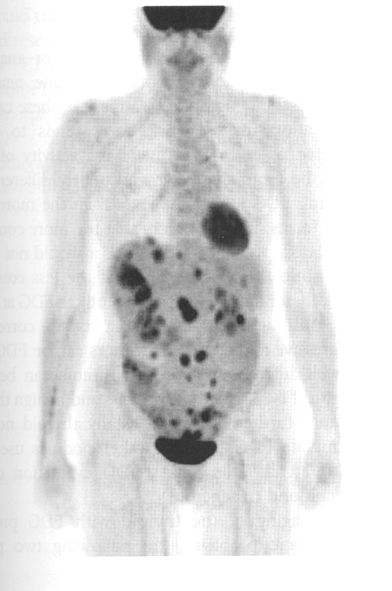
what does this image show
ovarian cancer
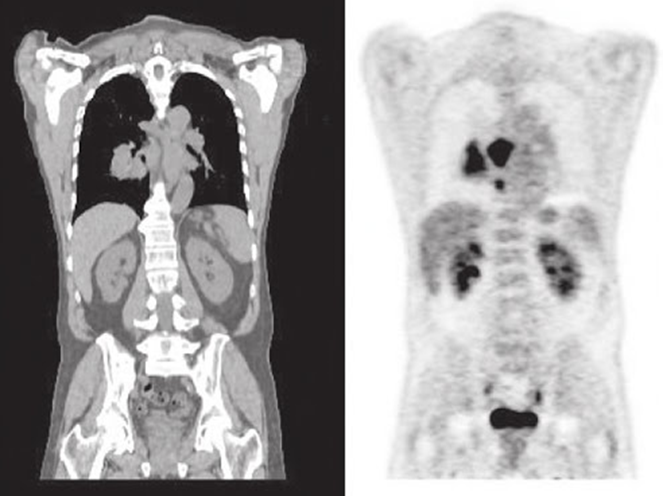
CT left and PET right
this scan shows what
abnormal distribution in the right lung = lung cancer
what is the protocol for a brain scan with FDG
interview the patient
take glucose
place IV
make patient comfortable, dim the lights, allow them to rest with eyes closed
no talking/music
after 10 minutes inject
scan 30 minutes after injection
scan takes 10 min
for a brain FGD how long after injection does imaging begin
30 minutes
how long does a FDG brain scan take
10 min
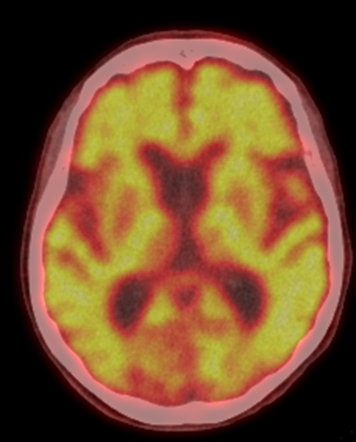
this image is an example of
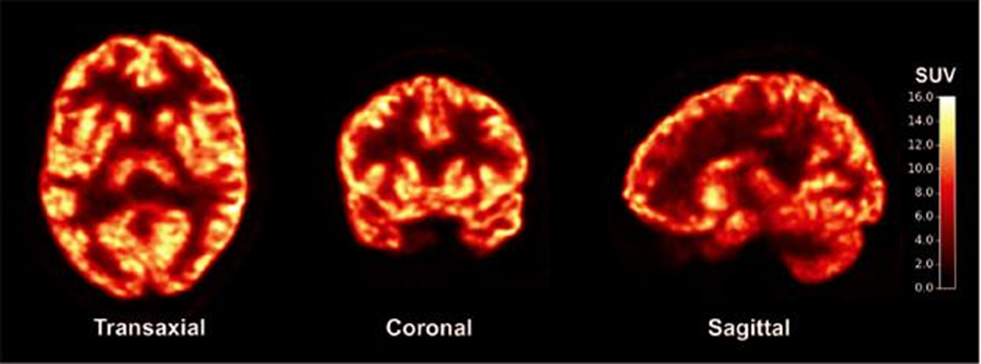
F-18 FDG brain
what view is this image
transverse or axial
top to bottom
what view is this image
coronal
front to back
what view is this image
sagittal side to side
this image is an example of axial PET, CT or fused
axial PET
this image is an example of axial PET, CT or fused
CT axial
this image is an example of axial PET, CT or fused
axial fused
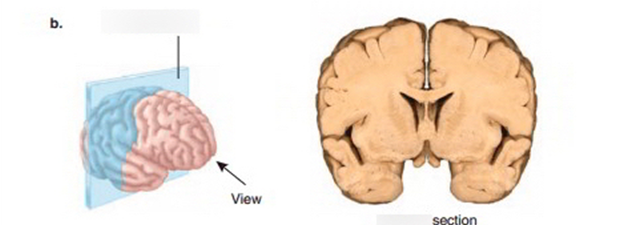
what view of the brain is this
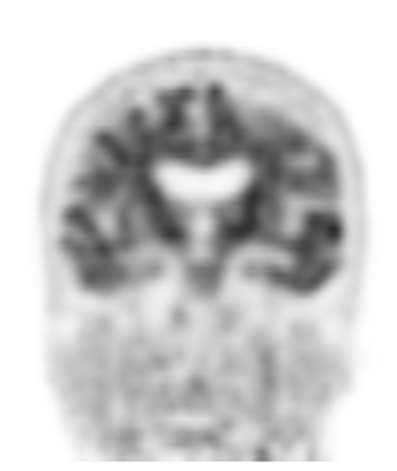
coronal
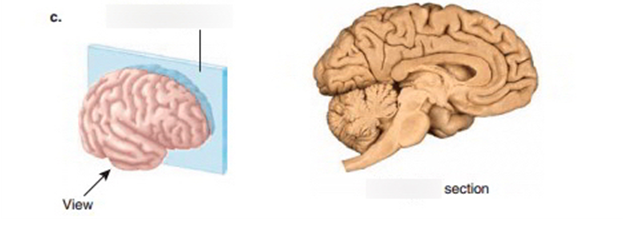
what view of the brain is this
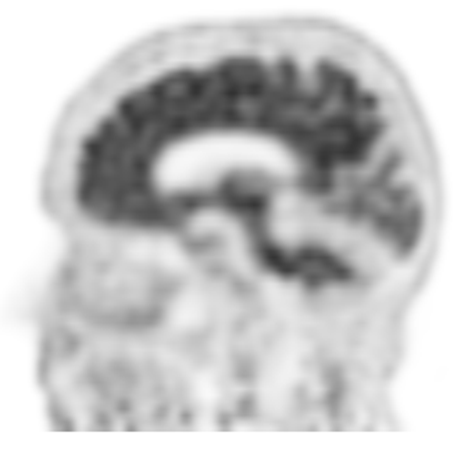
sagittal
what is the part of the brain called where the seizure starts
seizure focus
what is it called during or immediately a seizure
ictal
True or false: blood flow is increased to the seizure focus during a seizure
true
when the focus area is not causing a seizure is called
hypometabolic
when the focus area is hypometabolic that means
decreased blood flow and uses less glucose
when focus returns to the hypometabolic/hypoperfusion state it is called
interictal
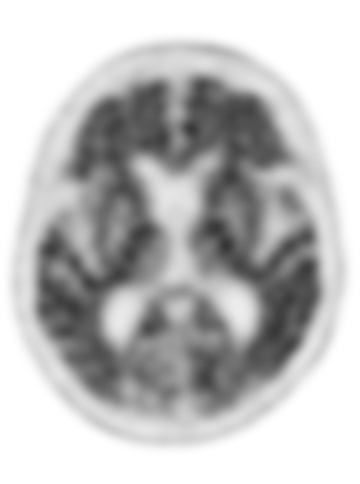
what is the organ of this image
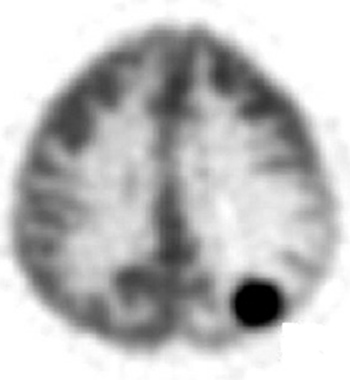
brain
what is view of this image
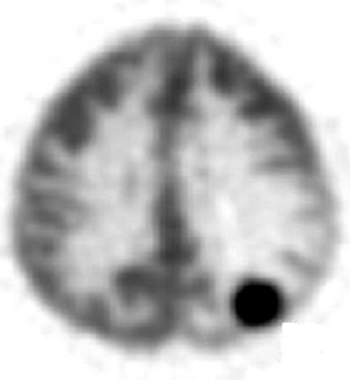
transaxial (transverse) slice
what are the results of the scan
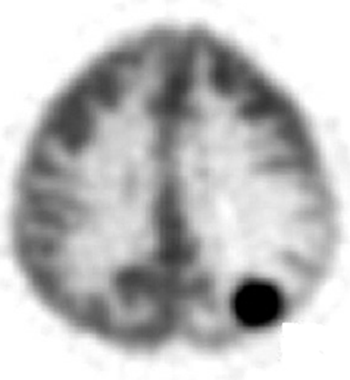
brain metastases
what are some symptoms Alzheimer disease
cognitive impairment
speech problems
confusion
aggression
impaired muscle coordination
what can plaques and tangles cause
neuron degeneration
what causes Alzheimer disease
build up of amyloid plaques in the brain and neurofibrillary tangles