Bio 101 exam 3 chapter 13
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
1
New cards
Chromosome
Structure made up of DNA and proteins; carries the cell’s hereditary information (genes).
2
New cards
Sex Chromosome
Chromosome associated with an individual’s sex
3
New cards
Autosome
Any chromosome other than a sex chromosome
4
New cards
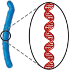
Unreplicated Chromosome
A chromosome that consists of one double-helical molecule of DNA packaged with proteins
5
New cards
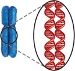
Replicated Chromosome
A chromosome after DNA replication. Consists of two identical chromatids, each containing one double-helical DNA molecule packaged with proteins
6
New cards

Sister Chromatids
The two identical chromatids in a replicated chromosome
7
New cards

homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that have the same genes in the same position and are the same size and shape but not always same allele so not identical.
8
New cards

Non-sister chromatids
Chromatids on different members of a homologous chromosome pair.
9
New cards
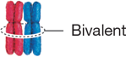
Bivalent
Paired, replicated homologous chromosomes
10
New cards
Haploid Number
The number of different types of chromosomes in a cell; symbolized *n. Humans have 23 different types of chromosomes (n=23).*
11
New cards
Diploid Number
The number of chromosomes present in a diploid cell (see below); symbolized 2*n.* All human cells except gametes are diploid and contain 46 chromosomes (2*n*= 46)
12
New cards
Ploidy
The number of each type of chromosome.The number of haploid chromosome sets present; shown by the number in front of *n* (for example, 2*n*)
13
New cards
Haploid
Having one of each type of chromosome (*n*).Bacteria and archaea are haploid, as are many algae; most plant and animal gametes are haploid
14
New cards
Diploid
Having two of each type of chromosome (2*n*). Most familiar plants and animals are diploid.
15
New cards
Polyploidy
Having more than two of each type of chromosome; may be triploid (3*n*), tetraploid (4*n*), hexaploid (6*n*), and so on.Seedless bananas are triploid; many ferns are tetraploid; bread wheat is hexaploid
16
New cards
What are sister and non-sister chromatids? Why is the latter important?
Sister chromatids are the two identical chromatids on the replicated chromosome. Non-sister chromatids are chromatids on different members of a homologous chromosome pair. Non-sister chromatids are important because they swap genetic information in crossing over.
17
New cards
At which stage of Meiosis do cells go from diploid to haploid?
After Meiosis 1
18
New cards
Describe events of Meiosis I, focusing on the events of Prophase I.
Interphase- DNA is duplicated
Prophase 1- little bits of information are swapped between non-sister chromatids called crossing over.
Metaphase 1, Anaphase 1, and Telophase 1 are identical to mitosis but with non-identical chromosomes. They separate homologous pairs instead of chromatids.
Prophase 1- little bits of information are swapped between non-sister chromatids called crossing over.
Metaphase 1, Anaphase 1, and Telophase 1 are identical to mitosis but with non-identical chromosomes. They separate homologous pairs instead of chromatids.
19
New cards
Explain crossing over and how it relates to genetic diversity.
Crossing over is when little bits of genetic information is swapped between non sister chromatids in prophase 1. This is creates genetic variability it is why we are not identical to our parents.
20
New cards
Describe events of Meiosis II and compare it to the events in Mitosis.
The events of meiosis II and mitosis are very similar except in meiosis II they are non identical daughter cells and you end up with 4 haploid cells instead of 2 diploid cells in mitosis.
21
New cards
What is non-disjunction?
Non-disjunction is a meiotic error where both homologs or both sister chromatids more to the same daughter cell.