ca 1 orgo lab
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Erlenmeyer flask

seperatory funnel

Lab support stand

Buchner funnel

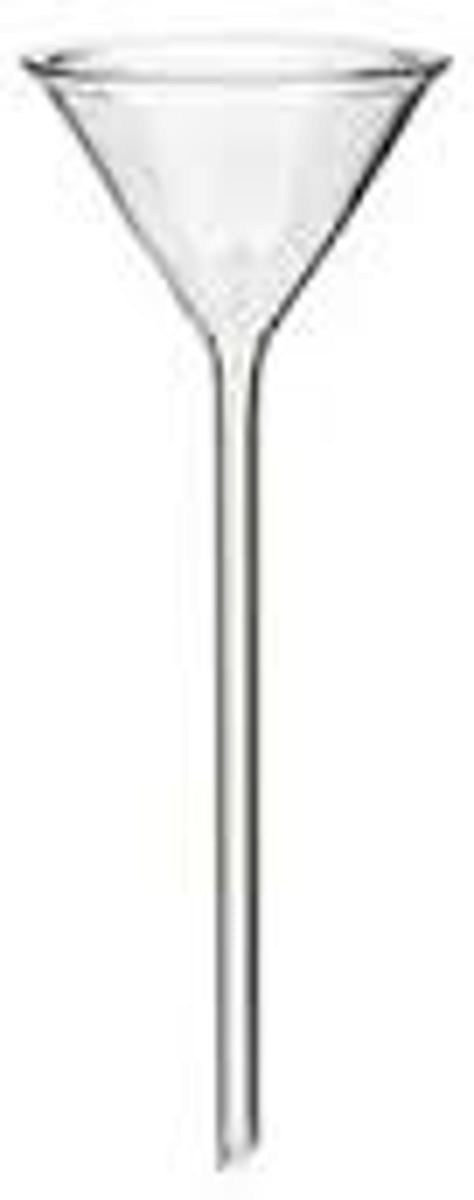
stemmed conical funnel

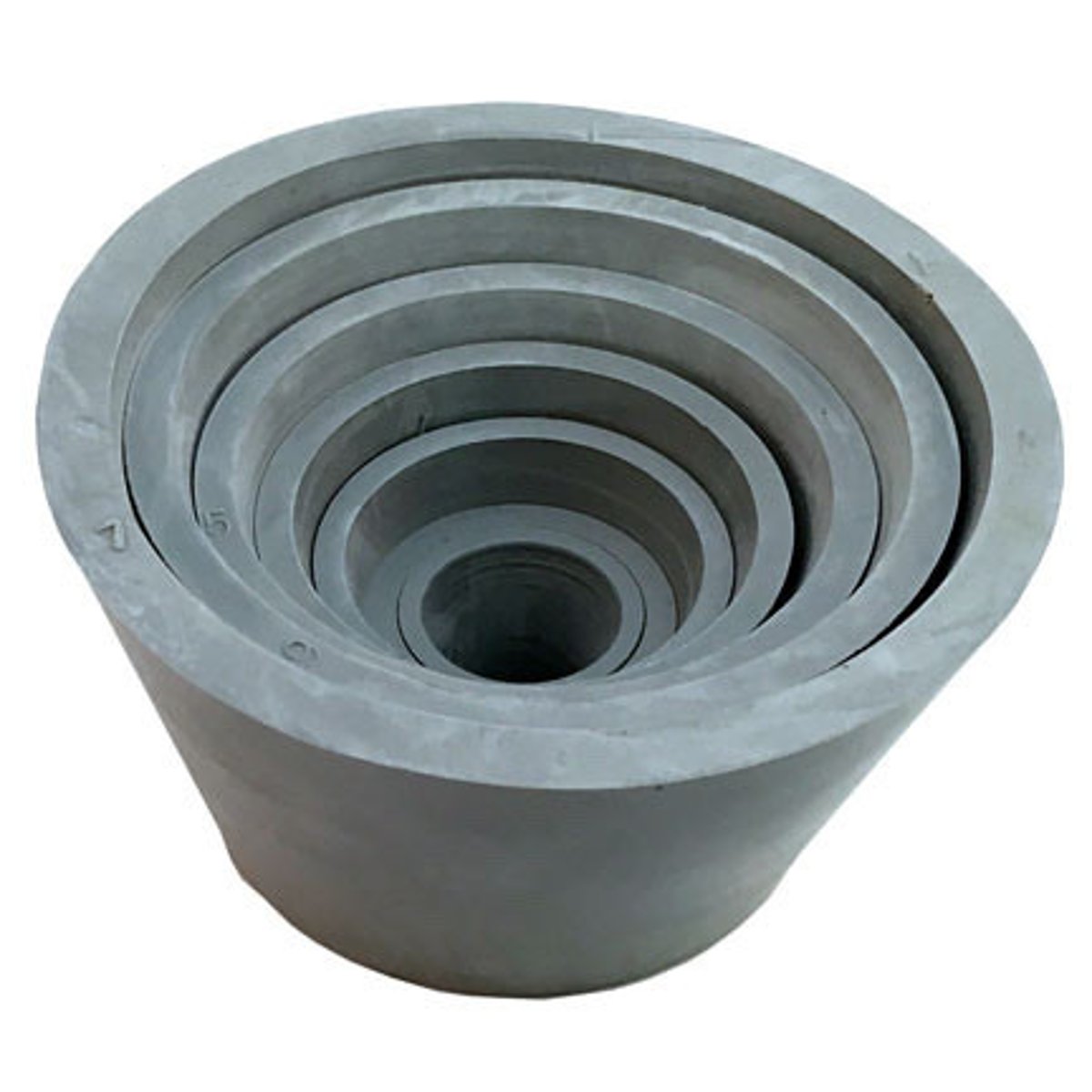
neoprene adapters

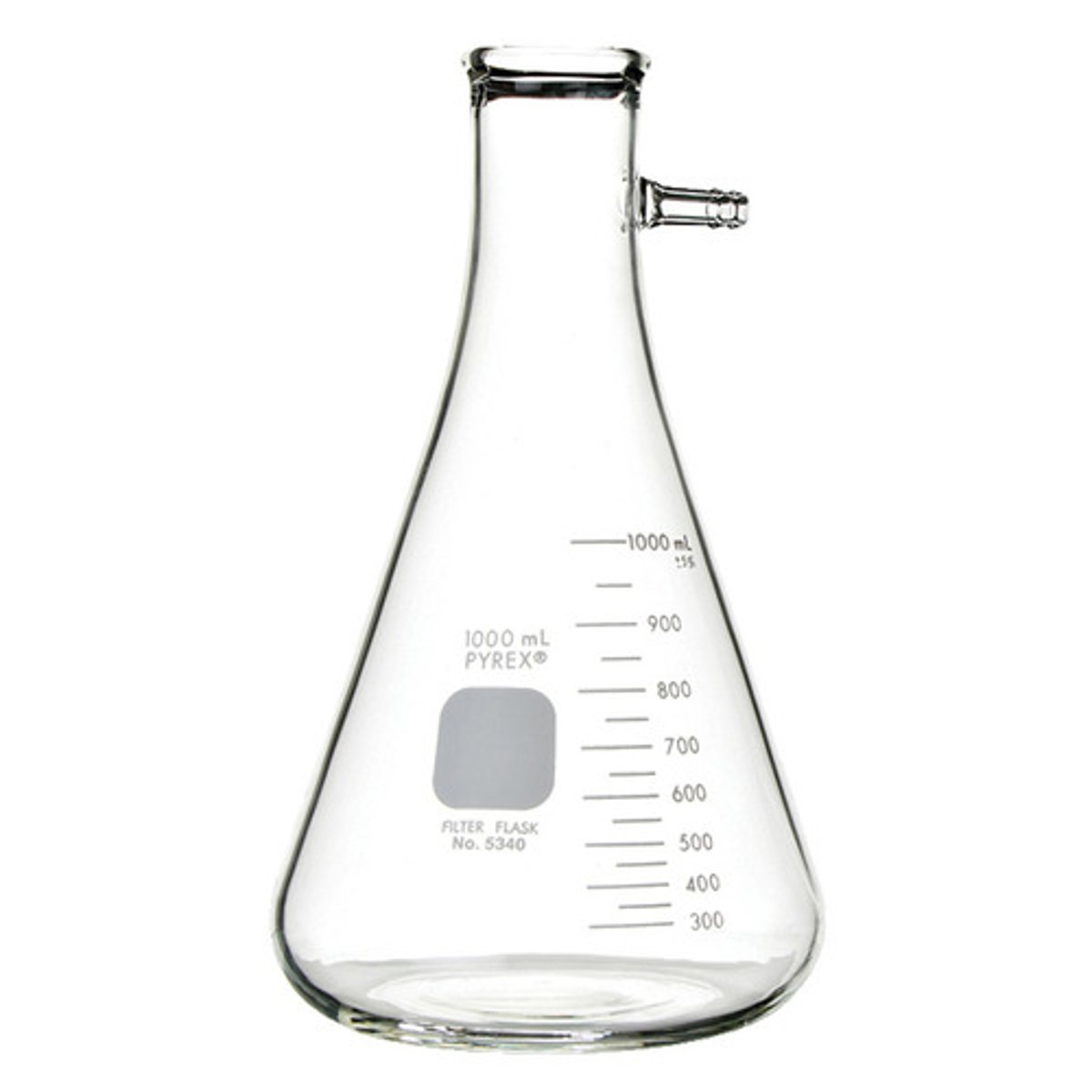
filter flask

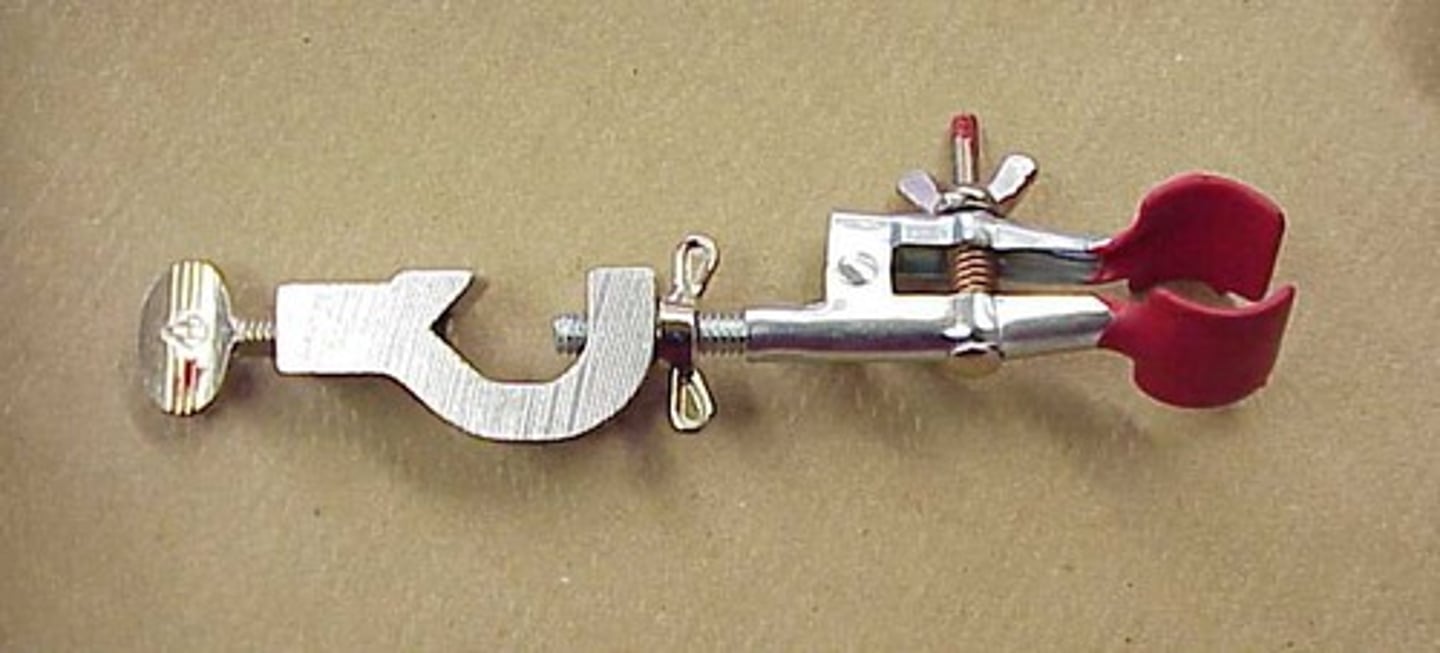
support clamp

heating mantle

stemless conical funnel

beaker

filter paper

water tubing/hose

hot plate

graduated cylinder

clamp holder

striker

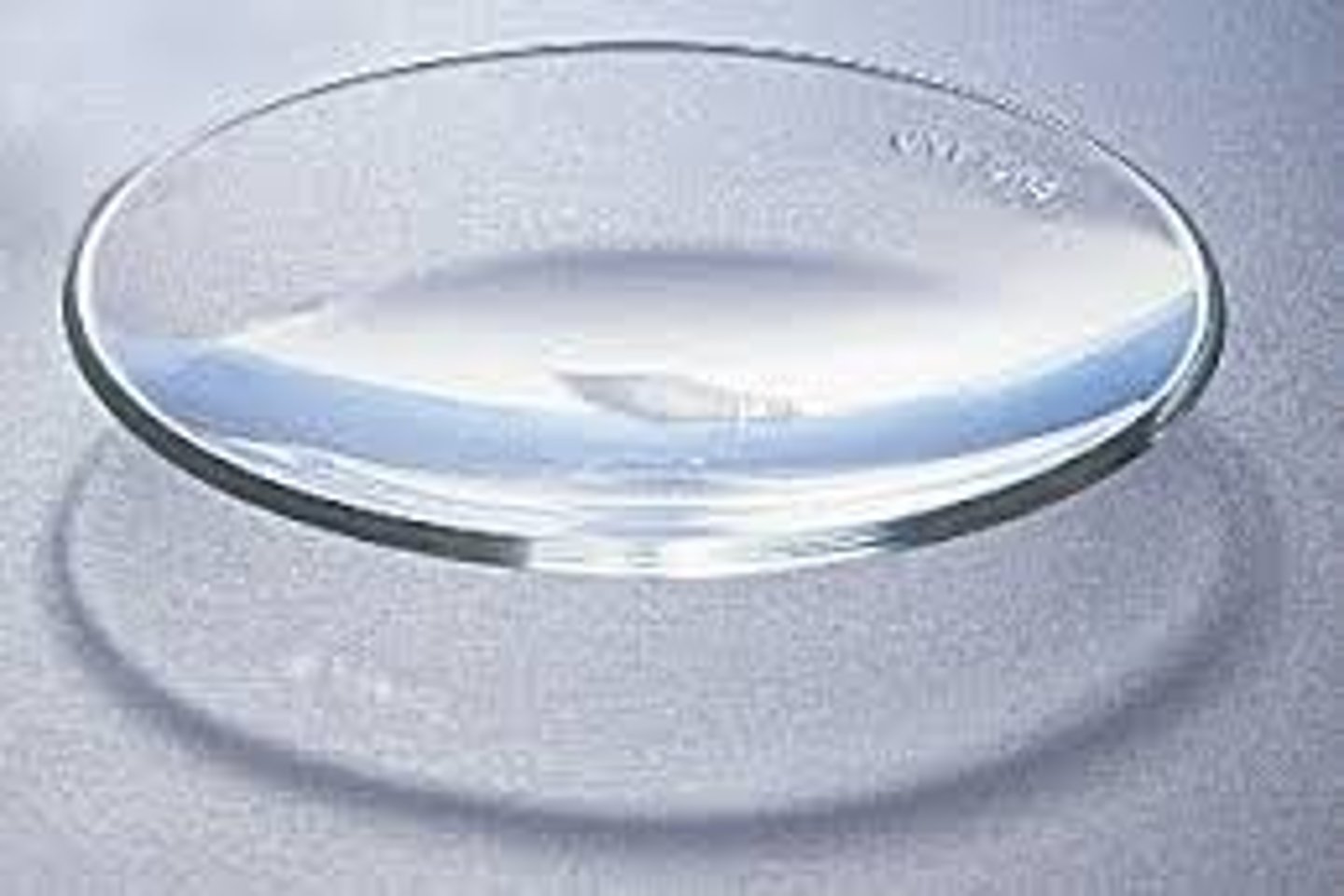
watch glass

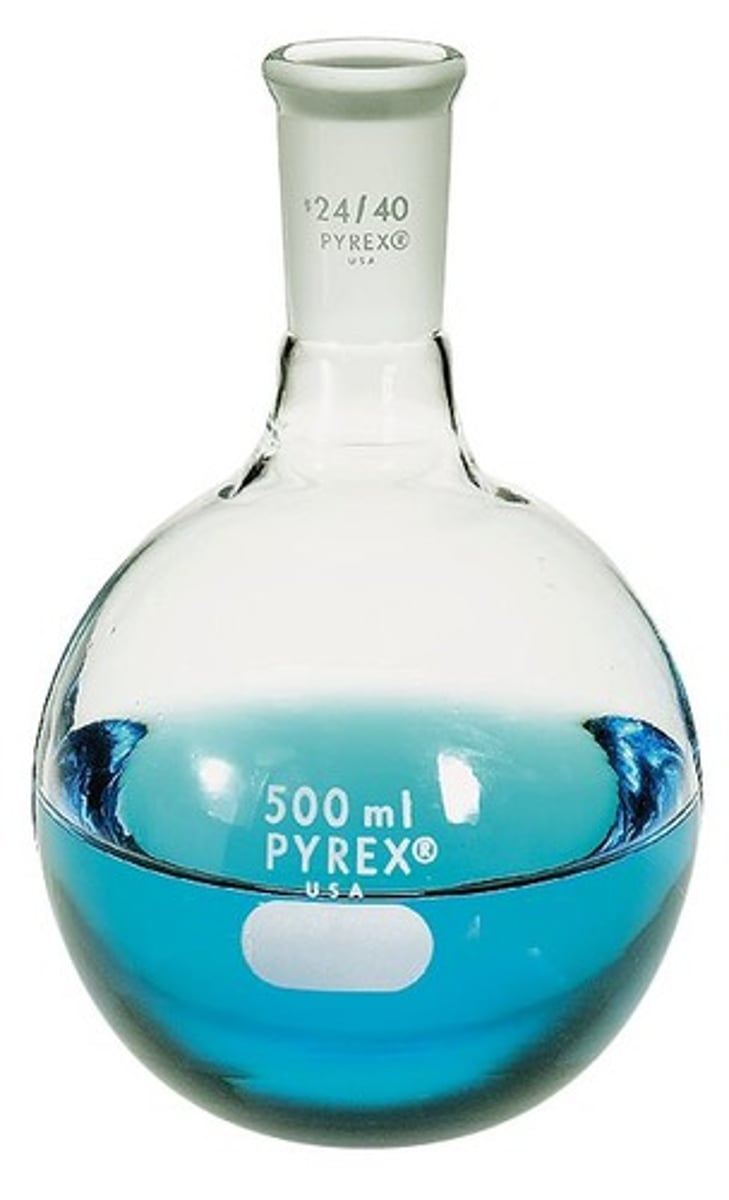
round bottomed flask

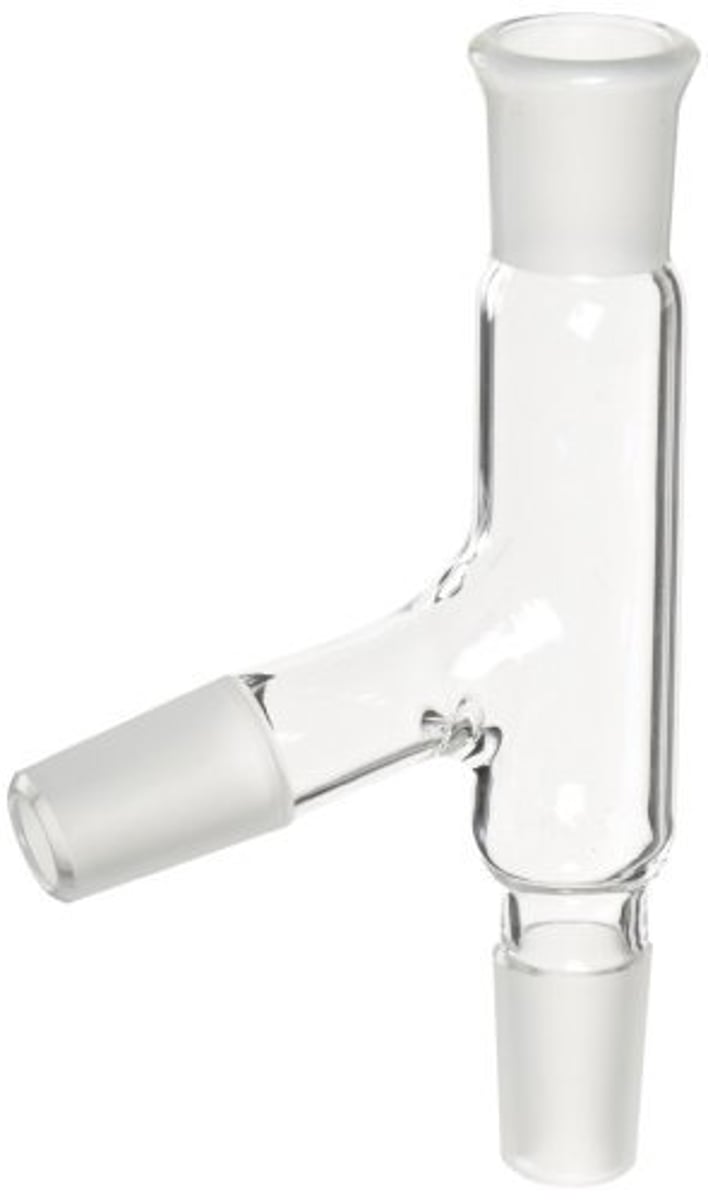
Still head (adaptor)

condenser
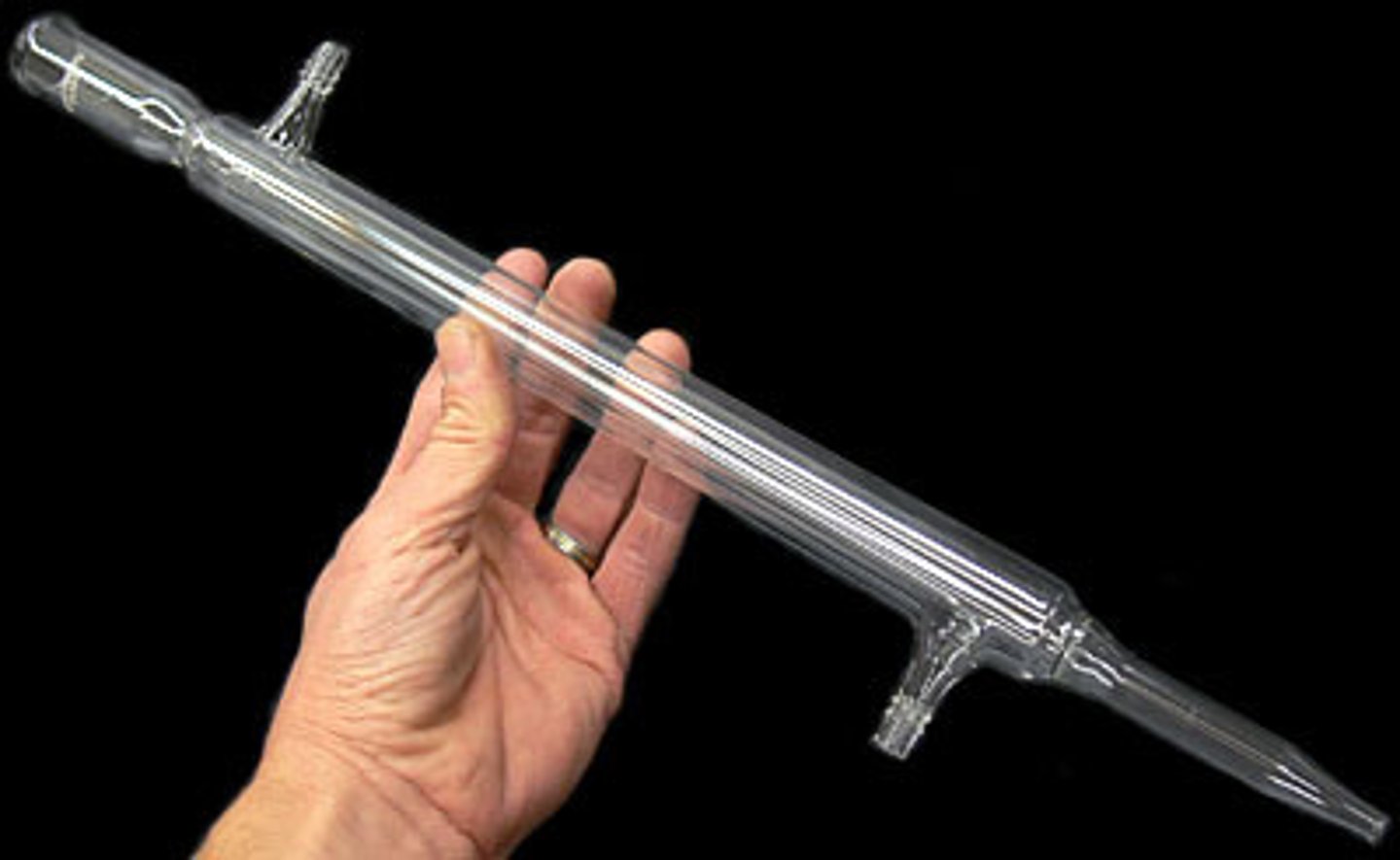

vigreux column
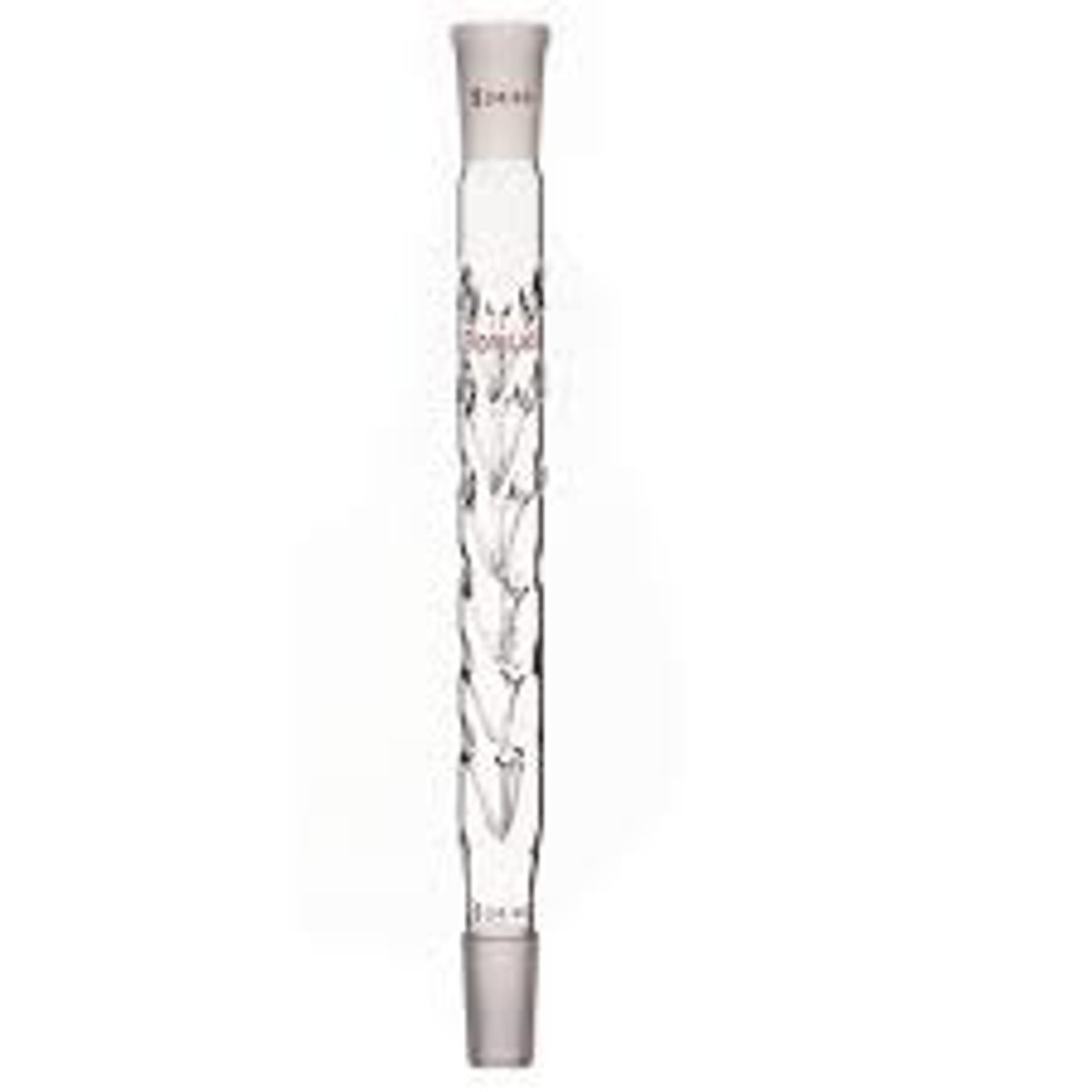

claisen adapter
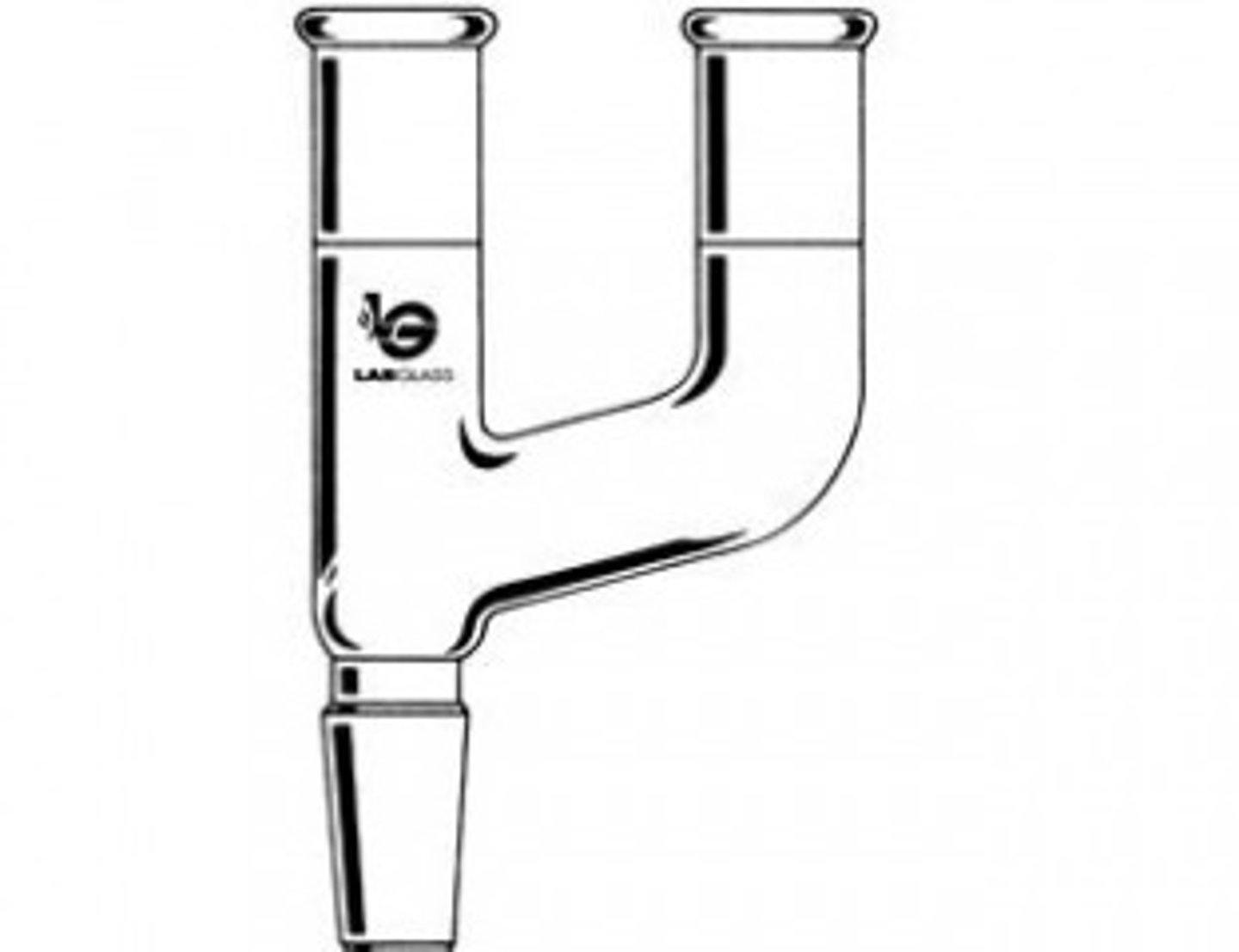
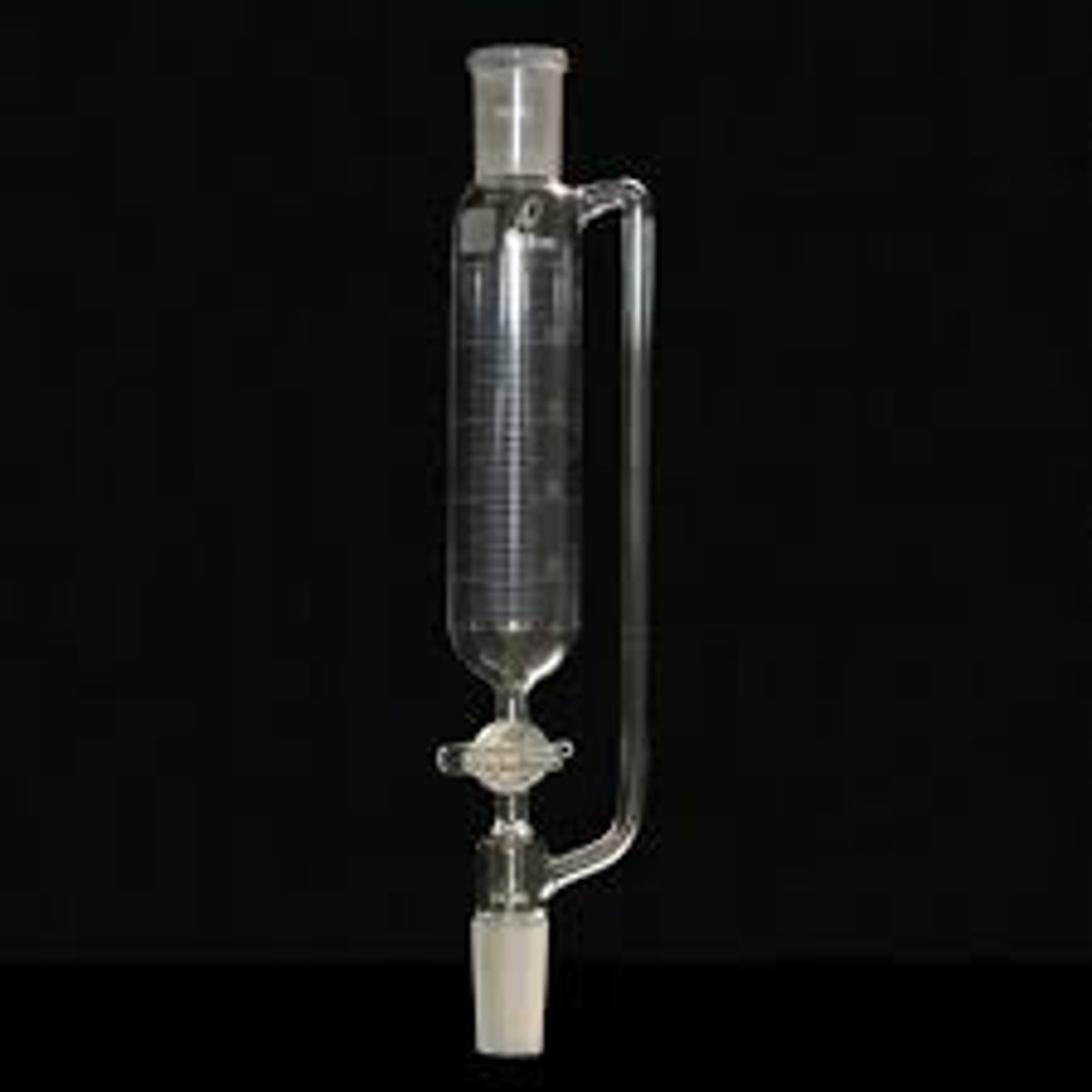
addition funnel

vaccum adapter
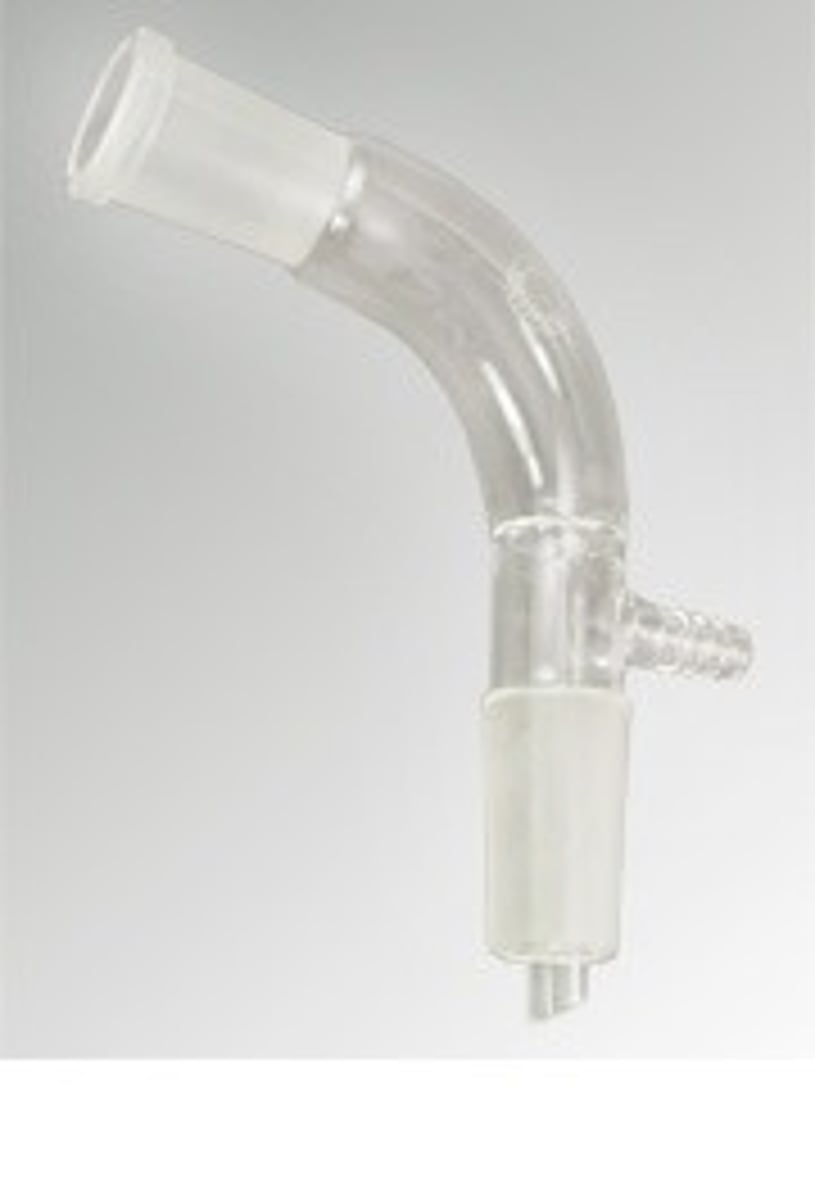
NMR sample tube
see book, skinny long tube
Pipette bulb
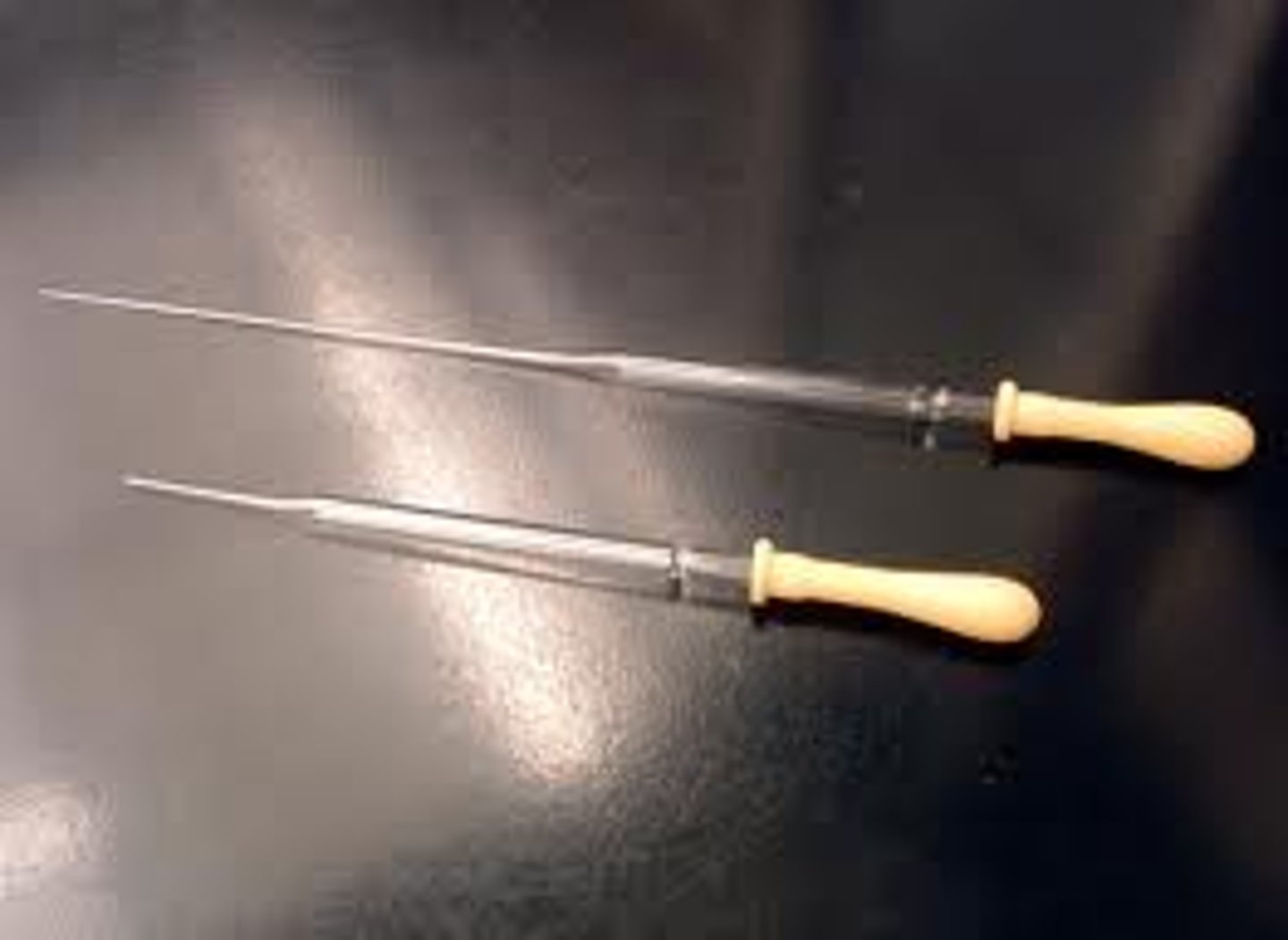
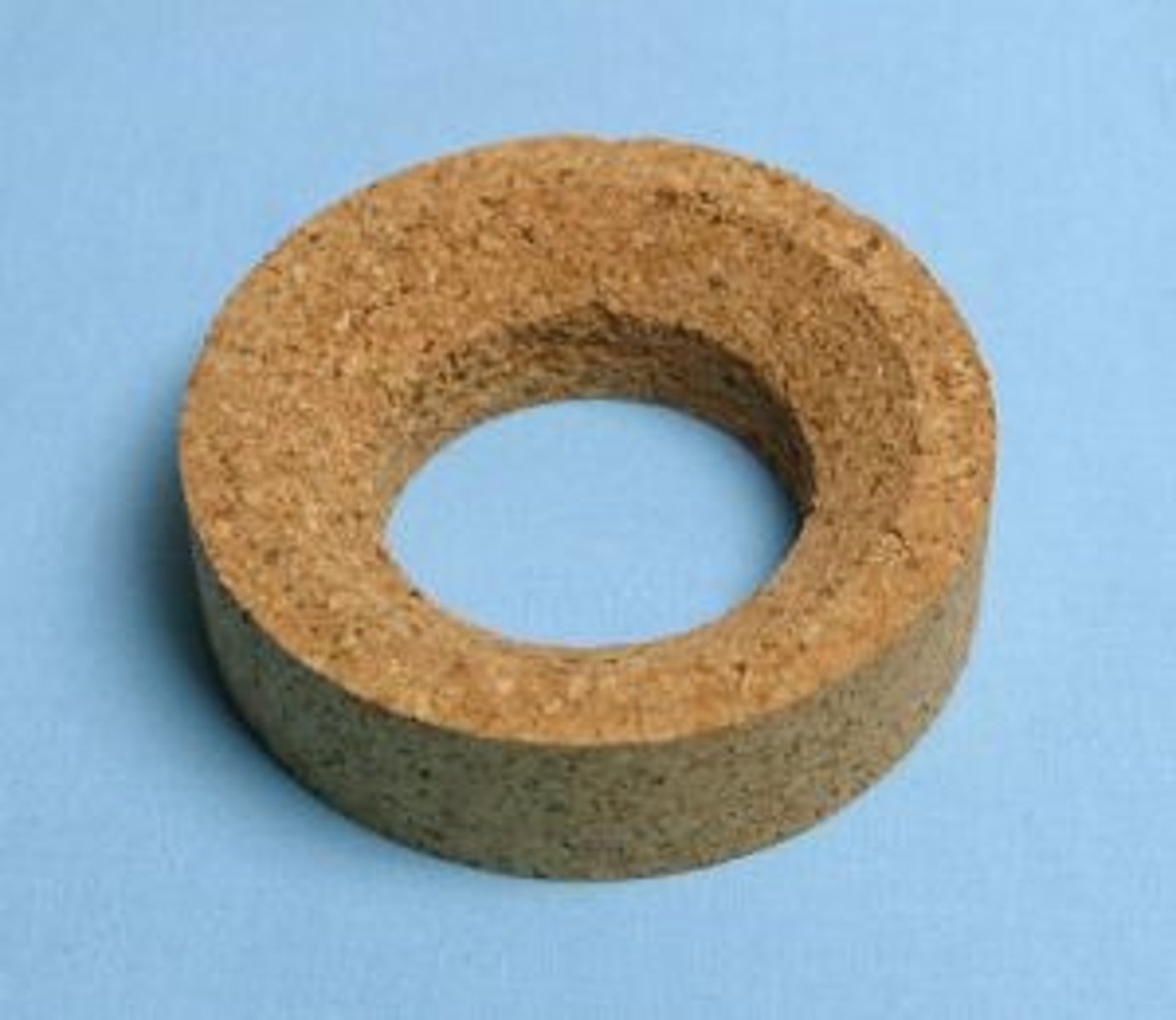
cork ring

Keck clip

glass rod/ rubber policeman

pestle and mortar

thermometer

theoretical yield
Maximum quantity of product that can be obtained from a reaction. Theoretical yield is dependent on the (amount of) limiting reagent in the reaction flask
percent yield
experimental/theoretical yield and multiplying everything by 100%(can be done with mols OR grams)
mole fractions
the number of moles of a component/the sum of the number of moles of all components in the mixture
mass percentage
the mass of a component/the total mass of the mixture and multiplying everything by 100%
percent recovery
actual amount of compound obtained after a process/expected amount of that same compound and multiplying everything by 100%
relationship between acidity of hydrocarbon and hybridization of the carbon attached to the H
as hybridization gets lower, acidity increases
What relationship exists between the pKas of compounds and the charge distribution of their corresponding conjugate bases?
As pKa decreases and charge of conjugate bases becomes better spread the compound is more acidic.
recrystallization process
impure solid->dissolve in hot solvent(insoluble impurities)(water in this ex)->cool solution for crystalization->isolate soluble impurities(vaccum filtration)
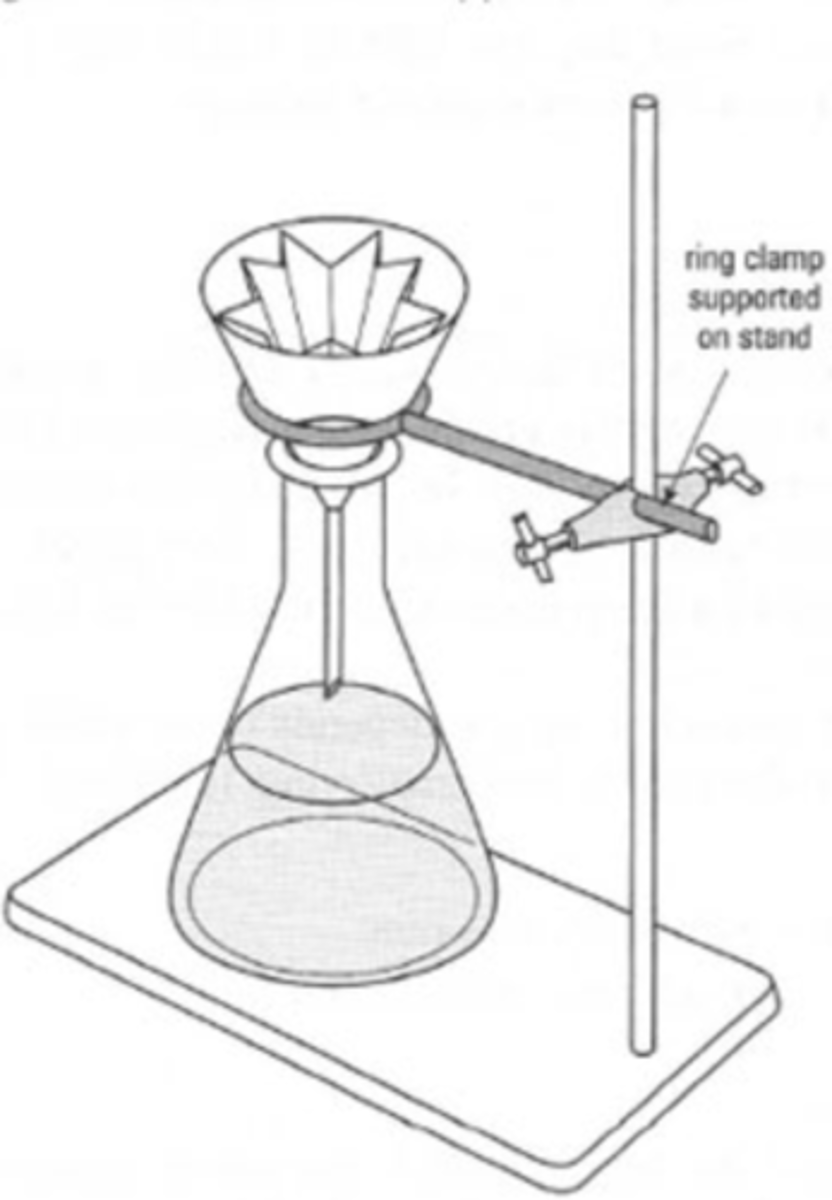
hot gravity filtration
used to remove insoluble materials from the solution while the desired solid remains dissolved in the hot solution
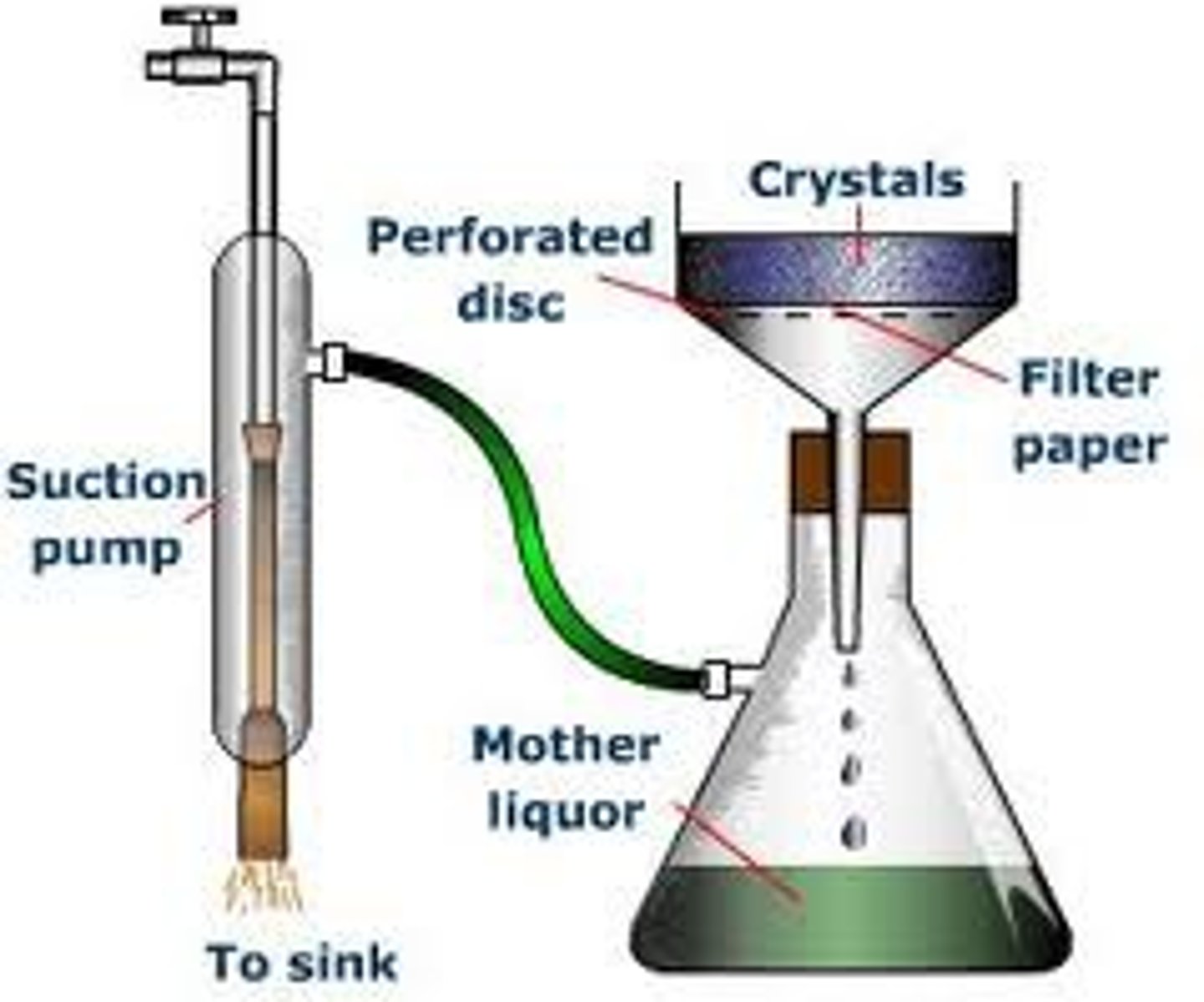
vacuum filtration
-used when the product of interest is the solid
-vacuum is connected to the flask to pull the solvent through more quickly
how are color impurities removed
decolarizing charcoal
attributes of a good recrystallization solvent
based on temp and solubility
solvent should have diff solubility from solute
-minimal to no solubility at low temps
-complete solubility at boiling
-completely dissolves impurities at all temps OR doesnt dissolve impurities at ANY temp
what happens if you use less solvent then needed
diminished purity, high recovery
opposite for more solvent than needed
how do impurities affect MP
they lower the MP
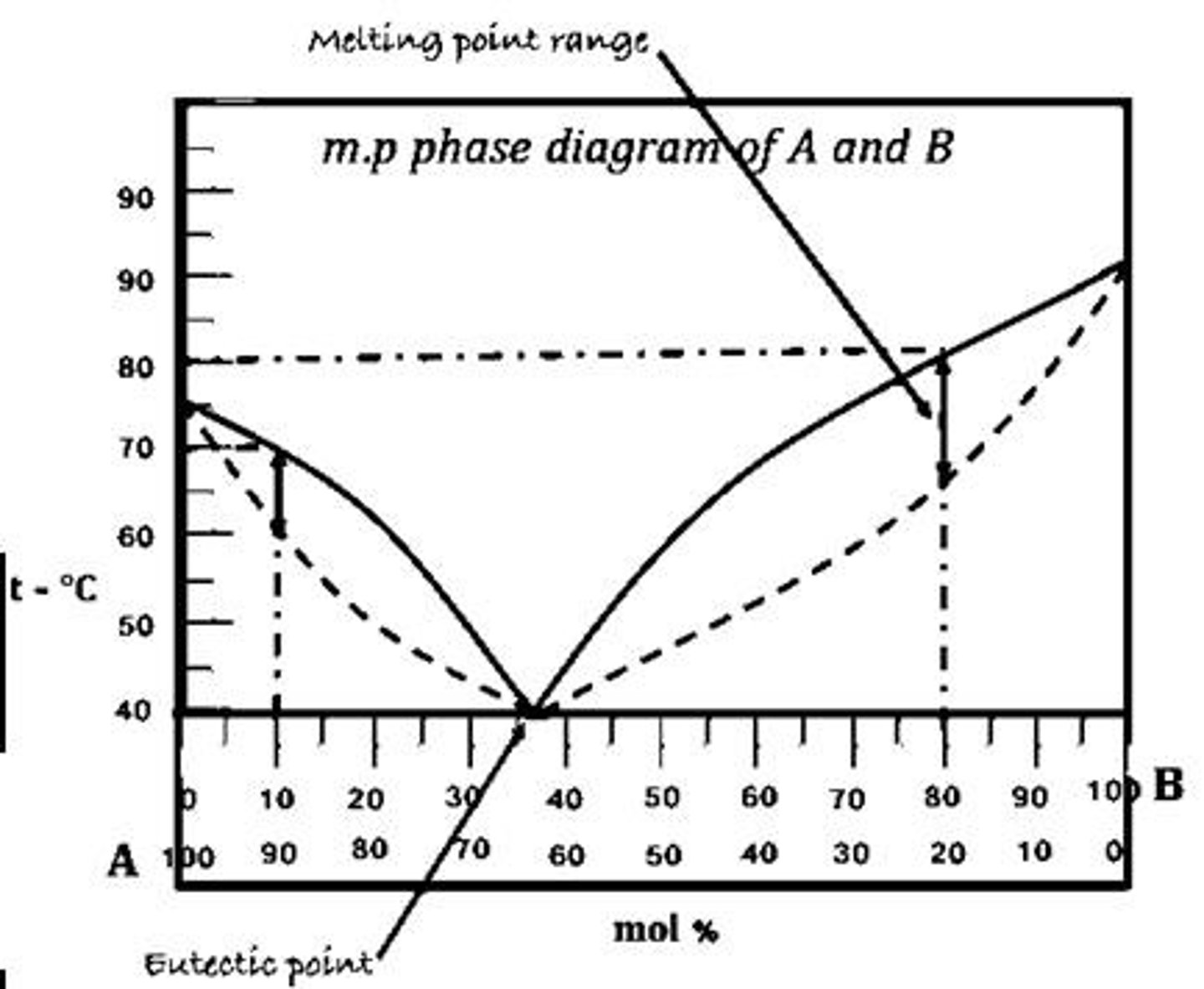
Eutectic Point
Lowest melting point of a mixture
What does direct proportionality mean?
When the ratio of two variables equals a constant.
What does indirect (inverse) proportionality mean?
When the product of two variables equals a constant.
How do you calculate the volume of a substance given its moles and density?
Volume (mL) = (moles x molar mass (g/mol)) / density (g/mL).
What is the significance of the limiting reagent in a reaction?
It determines the maximum amount of product that can be formed in a chemical reaction.
What is the typical melting point range for pure substances?
0.5-2℃.
What are the characteristics of carboxylate salts?
They have high melting points and decompose upon heating.
What is the purpose of acid-base reactions in the analysis of carboxylate salts?
To convert the salt into a carboxylic acid.
What is the first step in determining the identity of an unknown carboxylate salt?
Conduct acid-base reactions to convert it into a carboxylic acid.
What is the significance of measuring the melting point of the carboxylic acid product?
It helps determine the identity of the product.
What is the formula to calculate the percent yield of a reaction?
Percent yield = (Experimental mol / Theoretical mol) x 100%.
What is the goal of the recrystallization process?
To achieve a high level of sample purity and recover as much of the sample as possible.
What is the role of activated charcoal in recrystallization?
To remove color impurities from the solution.
What is the ideal solubility characteristic for a good recrystallization solvent?
Minimal to no solubility at lower temperatures and complete solubility at boiling point.
What happens if more than the right amount of recrystallization solvent is used?
It can lead to diminished recovery
What is the importance of isolating pure crystals during recrystallization?
To ensure the final product is free from impurities.
What determines the purity and overall recovery of a sample in recrystallization?
The amount of solvent used.
What is the minimum amount of recrystallization solvent needed?
It is determined by the solubility of the compound in the solvent at the solvent's boiling temperature.
How do you calculate the minimum amount of solvent needed for recrystallization?
Use the solubility of the compound at 100 °C to find the amount of solvent that can completely dissolve the sample.
What is the maximum expected recovery of a sample after recrystallization?
It is the ideal recovery assuming no material loss.
What is the melting point of a pure substance expressed as?
A range of temperatures over which the compound transitions from solid to liquid.
How do impurities affect the melting point of a compound?
Impurities lower the melting point and broaden the melting point range.
What is the eutectic point in a melting point phase diagram?
The lowest melting point observed across all mixing ratios of components.
How can the identity of a purified sample be confirmed?
By mixing it with a known pure sample and comparing melting points.
What is the significance of calculating the grams of acetanilide that would dissolve in the minimum amount of solvent?
To determine if the impurity is soluble or insoluble in the recrystallization solvent.
parts of vacuum filtration
a Buchner funnel, adapter, a filter flask, filter paper, a vacuum source, a trap, vacuum tubing, and a stand and clamp
parts of hot gravity filtration
stemless funnel, filter paper, Erlenmeyer flask, hot plate, iron ring stand