3. budgetary control system
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
cycle of planning and control
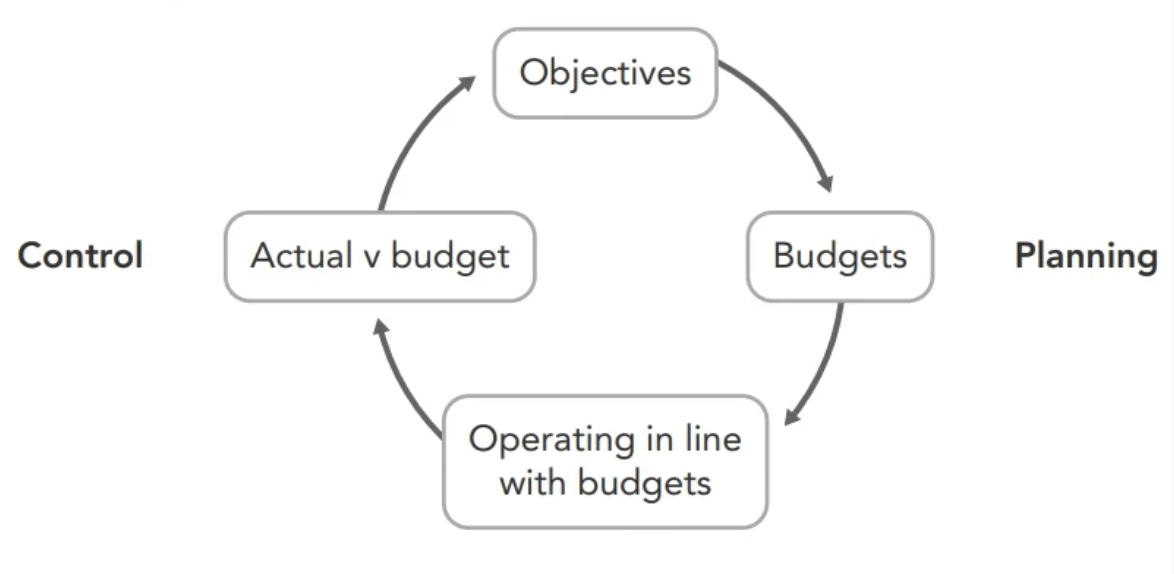
uses of budgetary control (4)
PCAC
planning
co-ordination
authorisation
cost control
What is the primary purpose of Planning in budgeting?
To plan future revenue and costs and allocate resources needed to achieve targets
Why must budgets align with strategic objectives?
To ensure short-term budgets support long-term organisational goals.
Give an example of coordination between departments.
The purchasing budget should reflect production needs, and production should reflect sales expectations.
Why can budgeting create conflict?
Over-focus on one area (e.g., cost control) may harm other objectives like growth or innovation.
internal data
data collected from inside the business such as internal documents or sourced
e.g. purchase invoices, payroll, inventory records, production information
What is external data?
Data collected from outside the business.
e.g. nternet, market research, interviews, online questionnaires, government statistics (e.g., CPI), national statistics, banks, newspapers
limitations of secondary external sources of data (4)
users unaware of any limitations
data may not be relevant
geographical area not relevant
may be out-of-date
What is a budget committee?
A committee of senior executives who oversee the preparation of budgets.
What are the responsibilities of the budget committee?
Coordinating, administering, reviewing, and authorising all individual budgets and the master budget.
Why should all business functions be represented on the budget committee?
To ensure full communication and coordination between all areas of the organisation.
What is a budget accountant?
An accountant who assists the budget committee in preparing budgets and maintaining budgetary control.
What is one key duty of a budget accountant? 3
Preparing the budget for the organisation by liaising with budget holders to produce detailed budgets.
Preparing management accounts that compare actual results to budget and explain variances.
Communicating results to senior management and providing recommendations for corrective action.
What is a budget manual?
A set of instructions explaining how the budget is to be prepared.
What might a budget manual include?
names of budget holders
manager
timescale
procedures
format
What is a budget holder?
A member of staff, usually a manager, responsible for the budget for a specific area of the business.
What role does the HR department play in budgeting?
Provides information on salaries, pension costs, and NI costs for labour budgets
What does the master budget normally include?
A budgeted statement of profit or loss
A budgeted statement of financial position
A cash budget
What is the master budget?
A consolidated budget created after the committee agrees on all resource budgets.
How do budgets motivate employees?
By setting performance targets and comparing actual vs budgeted results, creating accountability and encouraging improved performance.
What factors influence motivation in budgeting?
• Who sets the budgets
• How achievable budgets are
• Goal congruence
• Performance-related pay
What is the difference between motivation and control in budgeting?
Control assesses performance; motivation influences behaviour. Managers should be assessed only on controllable items to avoid demotivation.
What is top-down budgeting?
Senior management sets the budget and imposes it on junior managers.
Advantages of top-down budgeting?
• Aligns with strategic plans
• Harmonised resource budgets
• Faster to produce
• Senior management has full overview
Disadvantages of top-down budgeting?
• Demotivating for managers
• Ignores managers’ detailed knowledge
• Stifles initiative
• May cause inter-departmental resentment
What is bottom-up budgeting?
Operational managers prepare budgets based on detailed knowledge; budgets are then negotiated with senior management.
Advantages of bottom-up budgeting?
• Based on detailed operational knowledge
• Higher manager motivation and ownership
• Stronger commitment to strategic goals
Disadvantages of bottom-up budgeting?
• Time-consuming
• May cause conflict during negotiations
• Risk of budgetary slack
• Coordination issues between resource budgets
What is an ideal vs attainable budget?
• Ideal: Impossible to achieve; demotivating
• Attainable: Challenging but realistic; motivating
What is sub-optimal performance in budgeting?
When managers fail to attempt a budget because it is perceived as unrealistic.
key requirements for Performance Related Pay to work effectively?
• Managers understand strategic goals
• Budgets are achievable
• Managers have control over measured costs
• Rewards are significant and timely
Limitation of Performance Related Pay ?
May encourage short-term focus and neglect long-term strategy.
What is budgetary slack?
Deliberate overestimation of costs or underestimation of sales to make targets easier to achieve.
Why is budgetary slack unethical?
It leads to inefficient resource use, inaccurate planning, and lack of transparency.
Why might managers deliberately overspend at year-end?
To avoid future budget cuts (“use it or lose it” behaviour).
What is goal congruence?
When employees’ and managers’ actions align with the organisation’s strategic goals.
What is incremental budgeting?
Budgeting based on last year’s budget plus adjustments for price changes or activity changes.
appropriate. for businesses whose costs are not expected to change signficantly
Advantages of incremental budgeting?
• Simple
• Stable
• Easy coordination
Disadvantages of incremental budgeting?
• Repeats past inefficiencies
• No incentive for innovation
• Encourages slack
• May become outdated
What is Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB)?
the budget is looked at from scratch for each period, Each cost must be justified
Advantages of ZBB?
• Challenges existing practices
• Removes budgetary slack
• Encourages cost efficiency
Disadvantages of ZBB?
• Time-consuming
• Complex
• Focuses on short-term benefits
costly
What is Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB)?
Budgeting based on activities and their cost drivers.
Advantages of Activity-Based Budgeting
• More meaningful cost information
• Reflects complexity of operations
• Identifies overhead drivers
Disadvantages of Activity-Based Budgeting
• Time-consuming
• Not all costs can be linked to drivers
• Single cost driver may not fully explain behaviour
What is Priority-Based Budgeting?
Resources allocated to decision packages based on priority (often used in public sector).
What are rolling budgets?
Budgets updated continuously by adding the next period when one expires.
Advantages of rolling budgets?
• More up-to-date
• Better responsiveness
• Reduces uncertainty
Disadvantages of rolling budgets?
• Time-consuming
• Frequent re-forecasting required
What are contingency budgets?
Budgets set aside to cover unexpected events.
What is PEST analysis?
Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors affecting costs and sales.
Examples of political factors affecting forecasts?
Legislation, minimum wage laws, trade policies, safety requirements.
What are the four stages of the economic cycle?
Recession, Depression, Recovery, Boom.
Social factors affecting cost forecasts?
Demographics, lifestyle trends, family size, health concerns, cultural changes.
Technological factors affecting forecasts?
innovation pace, automation, product obsolescence, changing cost structures.
What two elements are essential for control within the budgeting process?
The budget manual and the budget committee.
Why is the budget manual important?
It outlines procedures, responsibilities, timescales, and formats for preparing budgets, ensuring consistency and control.
Why is the budget committee important?
It reviews, coordinates, authorises, and integrates all departmental budgets into a cohesive master plan.
choose: authorisation / co ordination / cost control / planning
in order to meet a profit target the managing director reduces the fugure in next years budget for the party by 25%
cost control
choose: authorisation / co ordination / cost control / planning
sales director divides costs for 2 sales teams, and gives manager permission to spend within that limit
authorisation
choose: authorisation / co ordination / cost control / planning
retail planning to expand so includes rental costs in its budget
planning