Chem Final Exam take 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/221
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:02 PM on 12/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
222 Terms
1
New cards
the structure of ionic compounds
ionic compounds form symmetrical arrangements which result in crystalline structures
2
New cards
Binary compounds
compounds composed of two or more elements
3
New cards
Nomenclature
full name of the metal + stem of nonmetal + “ide”
4
New cards
When do you write the roman numeral for nomenclature?
metal cations
5
New cards
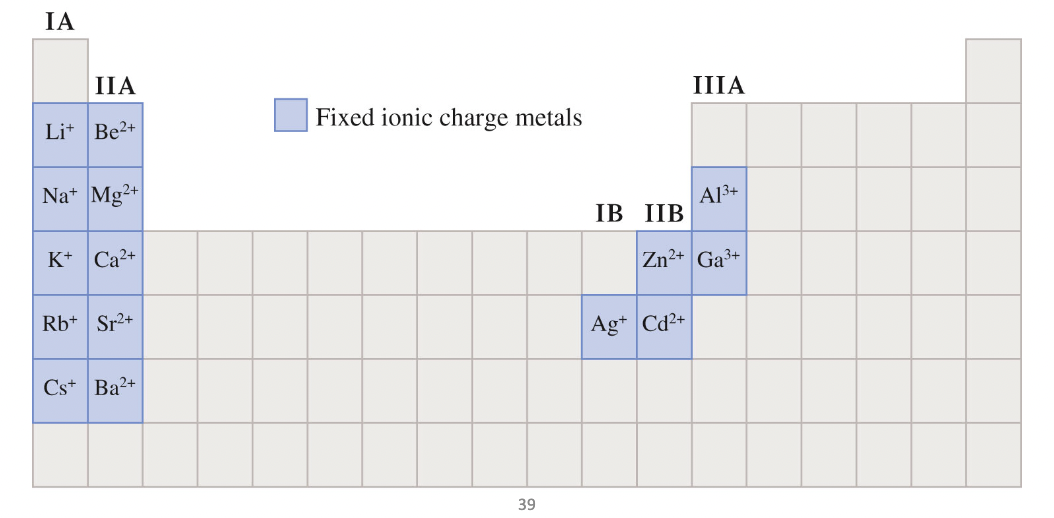
Fixed charge metals
metals that do not require roman numerals
6
New cards
Monoatomic ions
formed from a single electron
7
New cards
Polyatomic ions
formed from a group of atoms held together by covalent bonds
8
New cards
1+ polyatomic ions
NH4+ = ammonium
H3O+ = hydronium
H3O+ = hydronium
9
New cards
2- polyatomic ions
SO4 = sulfate
HPO4 = hydrogen phosphate
CO3 = carbonate
HPO4 = hydrogen phosphate
CO3 = carbonate
10
New cards
3- polyatomic ions
phosphate
11
New cards
\-1 polyatomic ions
NO3 = nitrate
NO2 = nitirite
HSO4 = bisulfate
H2PO4 = dihydrogen phosphate
HCO3 = hydrogen carbonate
CN = cyanide
OH = hydroxide
NO2 = nitirite
HSO4 = bisulfate
H2PO4 = dihydrogen phosphate
HCO3 = hydrogen carbonate
CN = cyanide
OH = hydroxide
12
New cards
Rules for chemical formulas for polyatomic ions
1\. More than one polyatomic ion: use parenthesis and subscript outside
2\. A chemical symbol can be used multiple times in one formula
2\. A chemical symbol can be used multiple times in one formula
13
New cards
Modifications when naming an ionic compound with polyatomic ions
1\. positive polyatomic ion: substitute metal
2\. negative polyatomic ion: substitute stem of nonmetal + “ide”
3\. Both positive and negative polyatomic ions: dual name substitutions
2\. negative polyatomic ion: substitute stem of nonmetal + “ide”
3\. Both positive and negative polyatomic ions: dual name substitutions
14
New cards
Formula mass
mass of an ionic compound formula obtained by adding the masses of individual atoms in the formula
15
New cards
Ionic bonds
\- bonds that form between a metal and a nonmetal
\- Involve electron transfer
\- Solid at room temp
\- soluble ionic solids from aqueous solutions that conduct electricity
\- Involve electron transfer
\- Solid at room temp
\- soluble ionic solids from aqueous solutions that conduct electricity
16
New cards
Covalent bonds
\- form between 2 nonmetals
\- involve electron sharing
\- can be solids, liquids, or gases
\- produce a nonconducting aqueous solution
\- involve electron sharing
\- can be solids, liquids, or gases
\- produce a nonconducting aqueous solution
17
New cards
Bonding electrons
Pairs of valence electrons that are shared between atoms in a covalent bond
\- represented with dashes
\- represented with dashes
18
New cards
nonbonding electrons
valence electrons not involved in bonding
AKA lone pair electrons
AKA lone pair electrons
19
New cards
Single bond (sigma)
two atoms share one pair of electrons
20
New cards
double bonds (sigma + pi bond)
two atoms share two pairs of electrons
21
New cards
triple bond (sigma + 2 pi bonds)
two atoms share three pairs of electrons
22
New cards
How many covalent bonds can be formed when there are 6 valence electrons?
two single bonds OR one double bond
23
New cards
How many covalent bonds can be formed when there are 5 valence electrons?
3 single bonds OR 1 single and 1 double OR 1 triple
24
New cards
How many covalent bonds can be formed when there are 4 valence electrons?
4 single bonds OR 2 single and 1 double OR 2 double OR 1 single and 1 triple
25
New cards
Coordinate covalent bond (dative bond)
covalent bond that forms when both electrons come from the same atom
26
New cards
electronegativity
An atom’s ability to attract and form bonds with electrons
27
New cards
electronegativity trend on the periodic table
increases going up a group and across a period
28
New cards
Electronegativity 0-0.4
nonpolar
29
New cards
Electronegativity 0.4-1.5
polar
30
New cards
Electronegativity 1.5-2.0
ionic or polar
31
New cards
Electronegativity 2.0 and on
ionic
32
New cards
Dipole moment
quantitative measure of separation of charges in a bond
Arrow points to greater electronegativity
Arrow points to greater electronegativity
33
New cards
What is a partial charge indicated by?
delta (δ+ or δ- )
34
New cards
How to draw lewis structures
1\. determine total # of valence electrons in molecule
2\. Draw skeletal structure
\- hydrogens are always terminal
\- central atom appears once in formula
3\. add nonbonding electrons
2\. Draw skeletal structure
\- hydrogens are always terminal
\- central atom appears once in formula
3\. add nonbonding electrons
35
New cards
resonance structures
one of two or more lewis structures of a molecule that have the same skeletal structure but different electron arrangement
36
New cards
electron delocalization
movement of electrons within bonds
37
New cards
Formal charge formula
FC = # of valence electrons - # of nonbonding electrons + 1/2 of bonding electrons
38
New cards
Molecular geometry
three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in molecules
39
New cards
Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VESPR) theory
A procedure of predicting geometry of molecules from their Lewis structures
40
New cards
2 electron groups 180° apart
linear
41
New cards
3 electron groups 120° apart
trigonal planar or angular
42
New cards
4 electron groups 109.5° apart
tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal/angular
43
New cards
Tetrahedral
4 bonding
44
New cards
trigonal pyramidal
3 bonding + 1 nonbonding
45
New cards
angular
2 bonding + 2 nonbonding OR 2 bonding + 1 nonbonding
46
New cards
trigonal planar
3 bonding
47
New cards
linear
2 bonding
48
New cards
Molecular polarity nonpolar molecule
symmetrical electron distribution
49
New cards
Molecular polarity polar molecule
asymmetrical electron distribution
50
New cards
Avogadro’s number
6\.02 x 10^23
51
New cards
Molar mass
mass in grams of a substance that is numerically equal to the substance’s formula mass \[measured in g/mol\]
52
New cards
Microscopic subscript
number of atoms of each element in one molecule of a substance
53
New cards
Macroscopic subscript
number of moles of each element in one mole of a substance
54
New cards
chemical reaction
a process that leads to the chemical transformation (chemical conversion) of one or more chemical substances to another
55
New cards
Chemical equation
chemical symbols and chemical formulas a re used instead of words to describe changes in a chemical reaction
56
New cards
stoichiometry
balanced reaction shows the numerical (quantitative) relationships between reactants and products
57
New cards
theoretical yield
the maximum amount of product that can be formed with the amounts given for starting materials (not usually attainable)
58
New cards
Actual yield
amount of product obtained from a chemical reaction
59
New cards
Percent yield
ratio of actual yield to theoretical yield given as a percent
60
New cards
Percent yield equation
Percent yield = (actual yield/ theoretical yield) (100)
61
New cards
compressibility
changes in volume resulting from pressure change
62
New cards
thermal expansion
changes in volume resulting from temperature change
63
New cards
Kinetic molecular theory
used to explain the physical behavior of the 3 states of matter
64
New cards
Kinetic energy
energy from particles in motion
can be transferred through collisions
disruptive forces
can be transferred through collisions
disruptive forces
65
New cards
Potential energy
stored energy from matter’s position, condition, or composition
cohesive forces
cohesive forces
66
New cards
Solid (KMT)
cohesive forces > disruptive forces
67
New cards
Liquid (KMT)
cohesive forces = disruptive forces
68
New cards
Gas (KMT)
cohesive forces < disruptive forces
69
New cards
Gas Law
Amount = moles
Volume = L
Temperature = Kelvin
Pressure = atm
Volume = L
Temperature = Kelvin
Pressure = atm
70
New cards
Pressure conversions
1 mmHg = 1 torr
1 atm = 760 mmHg = 760 torr
1 atm = 14.7 psi
1 atm = 760 mmHg = 760 torr
1 atm = 14.7 psi
71
New cards
Boyles Law
P1 V1 = P2 V2
72
New cards
Charle’s Law
V1/ T1 = V2/T2
73
New cards
Combined Gas Law
P1 V1 / T1 = P2 V2/ T2
74
New cards
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT
R = 0.0821
R = 0.0821
75
New cards
Dalton’s Law of Partial pressures
P total = P1 + P2 + P3 …
76
New cards
Endothermic
heat absorbed
77
New cards
Exothermic
heat released
78
New cards
Sublimation
solid to gas
79
New cards
Deposition
gas to solid
80
New cards
Evaporation
a phase transition where liquid molecules escape the liquid phase to the gas phase
81
New cards
Effects of evaporation
1\. Liquid decreases
2\. Liquid losses energy (lowers in temp)
2\. Liquid losses energy (lowers in temp)
82
New cards
Vapor
evaporating gas
83
New cards
Dynamic of physical equilibrium
the concentration of molecules in the vapor phase increase until the rate at which they reenter the liquid phase = the rate at which they escape from the liquid phase
84
New cards
Vapor pressure of liquids with strong attractive forces
low
85
New cards
Vapor pressure of liquids with weak attractive forces
high
86
New cards
Volatile substance
readily evaporates at room temp. because of high vapor pressure
87
New cards
Boiling point
temperature at which vapor pressure = external pressure
88
New cards
Normal boiling point
boiling temperature at 760 mm Hg
89
New cards
Conditions that affect boiling point
1\. high altitudes \[boiling point decreases\]
2\. low altitudes \[boiling point increases\]
2\. low altitudes \[boiling point increases\]
90
New cards
dipole dipole interactions
positive end of one molecule interacts with the negative end and vice versa
91
New cards
Hydrogen Bonds
Special type of dipole dipole interaction when Hydrogen bonds to F, O or N
92
New cards
London Forces
weak temporary forces between atoms/ molecules resulting from momentary uneven electron distribution
93
New cards
How to know if a molecule is nonpolar based on lewis structure
1\. central atom has no lone pair
2\. all atoms around central atom are the same
\
ALSO:
\- C bonded with H only = nonpolar
\- Single element = nonpolar
2\. all atoms around central atom are the same
\
ALSO:
\- C bonded with H only = nonpolar
\- Single element = nonpolar
94
New cards
solution
homogenous mixture of 2 or more substances
95
New cards
Solvent
what you put solute in \[typically water\]
96
New cards
Solute
the active ingredients in the solution
97
New cards
Solubility
maximum amount of solute that dissolves in a given amount of solvent at specific conditions
98
New cards
How does temperature affect solubility?
Solubility of gases decreases with increasing temp
99
New cards
Henry’s Law
gas solubility is directly proportional to partial pressure of the gas above solvent
higher pressure = higher solubility of gas
higher pressure = higher solubility of gas
100
New cards
saturated solution
contains max solute that can dissolve
\- add solute until it cannot dissolve anymore
\- add solute until it cannot dissolve anymore