BIOL 3000
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
gene
- entire nucleic acid sequence that is necessary for the synthesis of a functional polypeptide
- includes coding region and all DNA sequences required to synthesize particular RNA transcript
central dogma
DNA --> RNA --> protein
DNA
- deoxyribonucleic acid
- double helix structure composed of two intertwined strands, resembling a twisted ladder
- made of nucleotides with sugar, phosphate, and ntirogenous base
- adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine
key components of DNA function
- genetic information
- heredity
- protein synthesis
DNA vs genome
DNA is molecule that carries genetic instructions for all living organisms, while genome is the complete set of DNA within an organism
key differences: scope (genome is larger), function (DNA provides instructions, genome is complete set of instructions), and analogy (dna = lettters, genome = dictionary)
human genome project
massive, international scientific endeavor to map and sequence the entire human genome
aimed to identify all the genes within human DNA and make the resulting data publicly available for research purposes
bioinformatics
an interdisciplinary field that combines biology, computer science, and information technology to analyze and interpret biological data
non-coding DNA
the portion of an organism's DNA that does not code for proteins
open reading frames
regions of DNA that are likely to encode a protein
begin with initiation codon (ATG) and ends with termination codon (TAA, TAG, or TGA)
one way of looking for genes
each DNA sequence has six reading frames (three in one direction and three in the reverse)
effective for bacterial genomes, less for eukaryotic
intergenic
stretches of DNA sequences located between genes
codon bias
not all codons are used equally frequently in the genes of a particular organism
upstream regulatory sequences
DNA sequences located before (or upstream of) a gene's coding region that control the gene's expression
can be used to locate the regions where genes begin
CpG islands
a region of DNA with a high frequency of CpG dinucleotides
typically found near promoter regions
genbank
NIH genetic sequence database, annotated collection of all publicly available DNA sequences
mostly cDNA sequences
cDNA
complementary DNA, DNA copy of an mRNA molecules
expressed portion of a gene, lacks introns
used in genbank to represent the coding sequences of genes, particularly when studying gene expression or when cloning eukaryotic genes into prokaryotic systems
reverse transcriptase
an enzyme that synthesizes DNA from an RNA template
assembly
taking the large numbers of generated DNA sequences and finding areas of overlap between them
gradually, pieces are put together and sequenced DNA strand will get longer
mostly de novo sequencing
de novo sequencing
organism of interest is being sequenced for the first time
no existing reference genome to use as a template for the assembly of the unknown genome
assembly steps
1. fragmenting - original DNA is broken randomly into smaller pieces
2. sequencing - fragments are then sequenced, generating a large number of short DNA sequences ("reads")
3. alignment and merging - reads are aligned and merged based on overlapping sequences to create larger, contiguous sequences called contigs
4. scaffolding and ordering - further steps can involve scaffolding, where contigs are ordered and oriented using additional information, and then potentially ordering the scaffolds into chromosomes
5. annotation - assembled sequence is annotated, identifying genes and other functional elements
gibson assembly
molecular cloning method used to join multiple DNA fragments together in a single, isothermal reaction
uses 5' exonuclease, DNA polymerase, and DNA ligase
alignment
new DNA sequence generated is compared to existing DNA sequences to find any similarities or discrepancies between them and then arranged to show these features
BLAST
basic local alignment search tool
suite of programs used to generate alignments between a nucleotide or protein sequence, referred to as a "query" and nucleotide or protein sequences within a database, referred to as "subject" sequences
finds local regions of high similarity
"creates words": breaks down query sequence into short overlapping segments (words)
searches database: searches database for target sequences that contain these words or very similar ones
extending matches: once match is found, BLAST extends alignment in both directions to see how far similarity extends
alignment score (BLAST)
a numerical value reflecting the quality of the match
percent identity
how many of the nucleotides are identical between the query and target sequences
e-value
a statistical measure of how likely it is to find a match of this quality purely by chance
annotation
1. gene prediction
2. manual annotation
TATAA box
thymine and adenine rich region of a gene located in most eukaryotic promoter regions
10 bp upstream of transcription initiation start site
5' UTR
untranslated region, plays important role in initiating transcription
3'UTR
aids in transcription termination
exons
contain coding information that will be translated
introns
found between exons and are spliced or removed from the transcript before translation
poly-A tail
series of adenines added to 3' end of mRNA after transcription
start codon
AUG, signals where protein synthesis should start
stop codon
(UAA, UAG, UGA), signal protein synthesis to halt
genome browser
software tool used to visualize and explore genomic data, including DNA sequences and annotations like genes, regulatory elements, and other features
T/F: Assembly is used when there is no existing reference genome and Alignment is used to compare DNA to existing sequences.
true
Which of the following is in the correct 5' to 3' order as they would line up on a gene?
Promotor, Exon, Intron, Exon, Terminator
De Novo sequencing refers to which of the following?
sequencing an organism for the first time
T/F: Genes are a random sequence of nucleotides undefined by any distinctive features, and consist of both coding and non-coding DNA regions.
false
T/F: The term cDNA is also used, typically in a Bioinformatics context, to refer to an mRNA transcript's sequence, expressed as DNA bases (deoxy-GCAT) rather than RNA bases (GCAU).
true
The Genome Browser shows how many reading frames for any particular gene?
6
electrophoresis
technique commonly used in biology laboratories to separate biomolecules according to their size
with DNA (negatively charged), DNA will migrate towards positive electrode and be separated by size (shorter lengths move faster)
migration
movement of biomolecules through a matrix or gel
"run to red" - positive electrode is red one
smaller molecules move through matrix more quickly
genotyping
the process of determining differences in the genetic makeup of an individual by examining the individual's DNA sequence using biological assays and comparing it to another individual's sequence or a reference sequence
microsatellites
a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs are repeated, typically 5-50 times
DNA sequencing
process of determining order of nucleotides within a DNA molecule
chain termination sequencing
works by synthesizing new DNA strands complementary to a template, but the process is terminated when a dideoxynucleotide is incorporated instead of a normal deoxynucleotide; this creates fragments of varying lengths, which are then separated by gel electrophoresis and analyzed to reveal DNA sequence
microsatellite genotyping
molecular biology technique used to identify and analyze variations within microsatellites, also known as short tangem repeats (STRs) or simple sequence repeats (SSRs), in DNA
microsatellite allele - homozygote
one band
microsatellite allele - heterozygote
two bands
Performing electrophoresis in water, instead of buffer:
won't work because the buffer provides ions to allow the current to move
__________ is a series of techniques by which biomolecules can be separated based on size, length and/or shape.
electrophoresis
T/F: Due to its relative negative charge, DNA will tend to move towards the positive end of the gel.
true
It will be very easy to distinguish homozygotes from heterozygotes during this lab exercise. Homozygotes will all show _______ band(s) and heterozygotes will all show __________ band(s).
1, 2
_______________ can compare translated nucleotides to proteins.
BLAST
BLAST stands for _______________________________________.
basic local alignment search tool
When genotyping to determine relationships, we are looking for alleles that _______________?
exclude someone from the potential relationship
T/F: We use genotyping to determine relationships because it is provides indisputable scientific facts.
false
DNA profiling
the analysis of DNA from samples of body tissues or fluids, especially when conducted in order to predict susceptibility to a specific disease
DNA extraction
The cell and nuclear membranes need to be broken up to allow the DNA to be free in solution. Once the DNA is free, it can be separated from all other cellular components. After the DNA has been separated in solution, the remaining cellular debris can then be removed from the solution and discarded, leaving only DNA.
RFLP analysis
DNA is collected from cells and cut into small pieces using a restriction enzyme (a restriction digest). This generates DNA fragments of differing sizes as a consequence of variations between DNA sequences of different individuals. The fragments are then separated on the basis of size using gel electrophoresis. The separated fragments are then transferred on to a nitrocellulose or nylon filter; this procedure is called a Southern blot.
southern blot
A Southern blot is a method used in molecular biology for detection of a specific DNA sequence in DNA samples. Southern blotting combines transfer of electrophoresis-separated DNA fragments to a filter membrane and subsequent fragment detection by probe hybridization.
PCR
The process mimics the biological process of DNA replication, but confines it to specific DNA sequences of interest. With the invention of the PCR technique, DNA profiling took huge strides forward in both discriminating power and the ability to recover information from very small (or degraded) starting samples
STR analysis
Simple sequences or short tandem repeats (STR), uses highly polymorphic regions that have short repeated sequences of DNA (the most common is 4 bases repeated, but there are other lengths in use, including 3 and 5 bases). Because unrelated people almost certainly have different numbers of repeat units, STRs can be used to discriminate between unrelated individuals. These STR loci (locations on a chromosome) are targeted with sequence-specific primers and amplified using PCR. The DNA fragments that result are then separated and detected using electrophoresis. There are two common methods of separation and detection, capillary electrophoresis (CE) and gel electrophoresis.
DNA databases
There are now several DNA databases in existence around the world. Some are private, but most of the largest databases are government-controlled. The United States maintains the largest DNA database, with the Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) holding over 13 million records as of May 2018.
what was the first heritable variation detected in human DNA called?
restriction fragment-length polymorphism
What was the first public use of genetic fingerprinting?
proving a boy was the biological child of his mother
DNA from skeletal remains was able to prove that the remains belongs to Josef Mengele because of what development(s)?
PCR, STR
In forensic cases, what is sometimes typed because samples contain many more copies of this than what is normally typed?
mitochondrial DNA
creating a DNA profile using STRs
1. obtain sample
2. isolate DNA
3. run PCR to amplify DNA
4. determine size of STRs
5. determine if a match exists
pedigree assumptions
1. complete penetrance
2. rare-in-population
3. not y-linked
pedigree
a chart that shows the presence or absence of a trait within a family across generations
complete penetrance
the gene or genes for a trait are expressed in all the population who have the genes
incomplete penetrance
the gene or genes for a trait that is expressed in only part of the population who have the genes
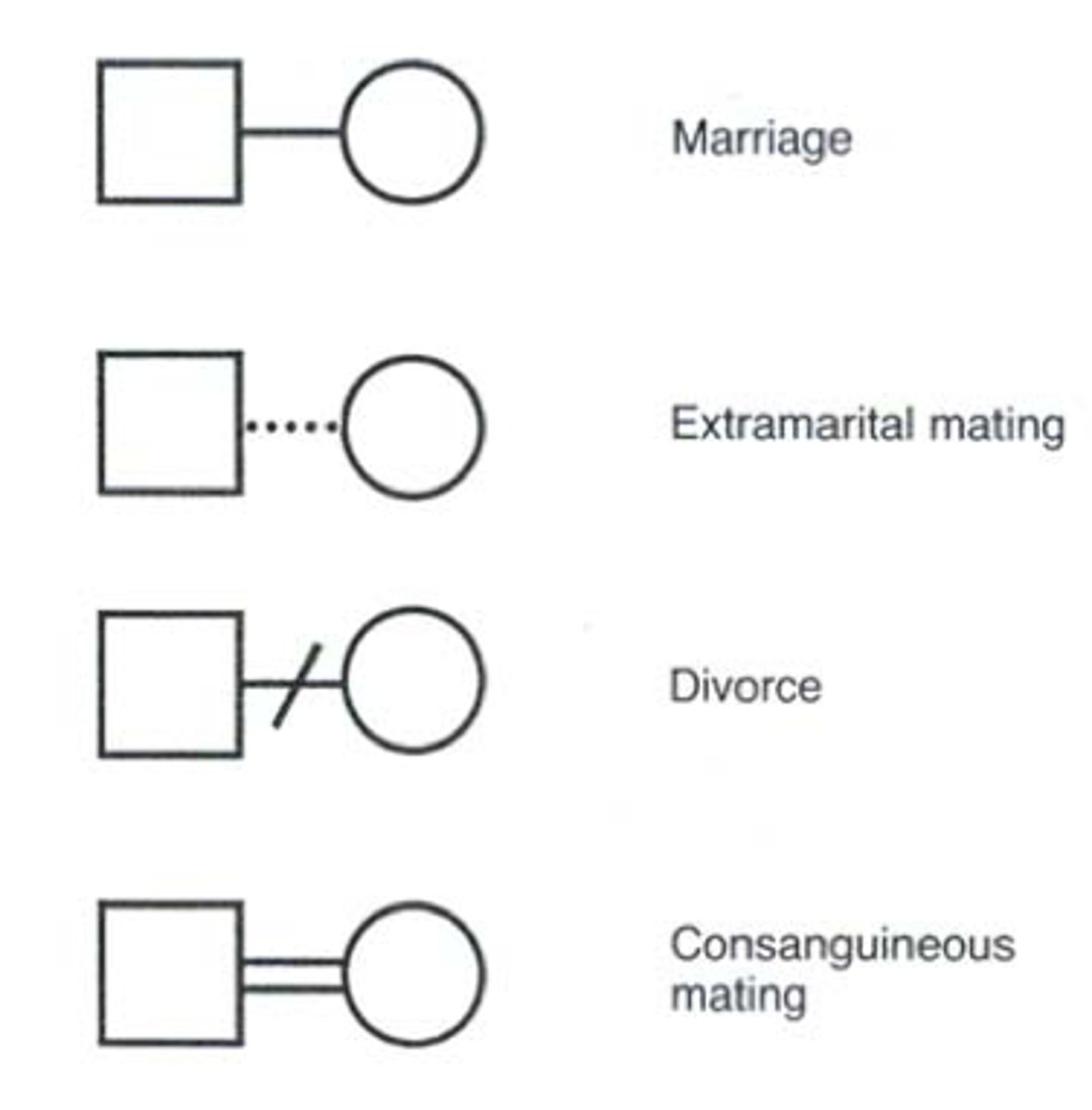
female
male

affected individuals

carriers

dead
gender not specified

spontaneous abortion (miscarriage)
still born
terminated pregnancy
dizygotic twins (fraternal)
monozygotic twins (identical)
mating
consanguineous mating
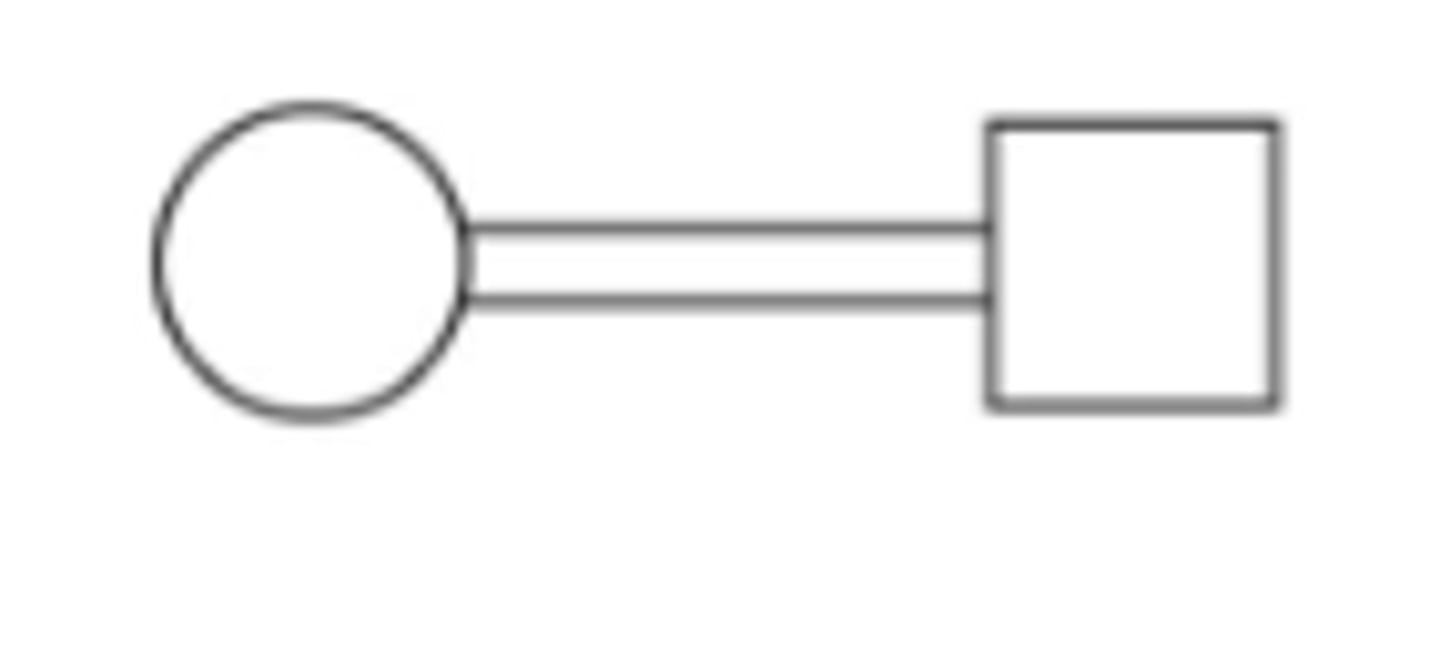
extramarital relationship
pedigree clues
1. unaffected individual cannot have any alleles of a dominant trait
2. individuals marrying into the family are assumed to have no disease alleles
3. unaffected individual can be a carrier of a recessive trait
4. when a trait is x-linked, a single recessive allele is sufficient for a male to be affected
5. a father transmits his allele of x-linked genes to his daughters, but not his sons. a mother transmits an allele of x-linked genes to both her daughters and her sons
autosomal recessive
- if any affected founding daughter has 2 unaffected parents the disease must be autosomal recessive
- an affected individual must inherit a recessive allele from both parents, so both parents must have an allele
- if the father had an x-linked recessive allele, he would have to be affected
recessive
- if an affected founding son has 2 unaffected parents, we cannot determine if the recessive disease is autosomal or x-linked
- if the trait is autosomal, both parents can be unaffected carriers of the disease
- if the trait is x-linked, the son must have inherited his allele from his mother only, and his father can be unaffected
x-linked recessive
- when an affected non-founding son has 2 unaffected parents the disease must be x-linked recessive
- the father, who is marrying in, does not have any disease alleles; so affected son inherits an allele only from his unaffected mother
- a male cannot be affected by a single autosomal recessive allele, but can be affected by a single x-linked recessive allele
dominant trait
- must be dominant if every affected child of non-founding parents has an affected parent
- the unaffected mother, who is marrying in, does not carry an allele for the disease; so the affected child inherits an allele only from the affected father
- no child could be affected by a single autosomal recessive allele, or x-linked recessive allele, so the trait is dominant
autosomal dominant
when an affected son of non-founding parents has an affected father the disease must be autosomal dominant
a father does not transmit x-linked alleles to a son, so the disease cannot be x-linked dominant
when an affected daughter of non-founding parents has an affected father, we cannot determine whether the dominant disease is autosomal or x-linked
autosomal recessive trait
- trait skips generation is clue
- males/females equally affected
- unaffected mating having an affected offspring (heterozygous parents)
autosomal dominant trait
- usually found in every generation
- males/females equally affected
- affected individual must have at least one affected parent
- affected individual usually has affected offspring
x-linked recessive trait
- more males than females affected (males only need one copy)
- if no or few females are affected, likely x-linked
- affected sons receive the allele on the X from their mothers
- an affected female must have an affected father
x-linked dominant trait
- more females than males affected, females have 2 chances to receive allele
- an affected individual must have at least one affected parent
- trait observed every generation (cannot skip a generation)
If a population of people had the exact same genes for a trait but only some people exhibit the trait we would say the trait has:
incomplete penetrance
One way to distinguish dominant and recessive traits in a pedigree is that the former will not skip generations but the latter will. But will recessive traits always skip generations?
no, if both parents are homozygous for the recessive trait it will not skip generations