atomic structure
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what are protons + neutrons held together by?
strong nuclear force
what is carbon dating?
all things absorb carbon from atmosphere
its age can determined by the amount of C14 they contain after dying when they have stopped absorbing
what is the arrangement of electrons in shells?
2,8,18,32
relative atomic/molecular mass?
1/12 mass of 1 atom/molecule of C12
electron impact ionisation?
sample vaporised
fired at with electron gun, which knocks off an e-
+ion formed
electron impact acceleration?
+ions accelerate towards negatively charged plate due to attraction
how does mass/charge affect ion acceleration?
lighter/more charged ions travel faster
electron impact ion drift?
ions pass through hole in negatively charged plate
forming a beam along the tube to the detector
electron impact detection?
flight times recorded
+ions pick up e-, creating a current
electron impact data analysis?
signal from detector passed to computer
electrospray ionisation?
sample dissolved in volatile solvent
forced through fine needle connected to a high voltage supply
forms fine mist/aerosol
droplets gain proton from solvent - form +ions
solvent evaporates from droplets into vacuum
drops get smaller until they can only contain 1 +ion
calculate average Ar from mass spec graph?
(mass/charge ratio x abundance)
total abundance
calculate average mass of isotopes?
(mass no. x isotope %) of each isotope
100
how many electrons can be held in each orbital?
s - 2
p - 6
d - 10
f - 14
how are the orbitals filled?
1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2,3p6, , 4s2
→ 4s orbital is filled before 3d
how are electrons in the same orbital w/ opposite spin drawn?
drawn 2 at a time
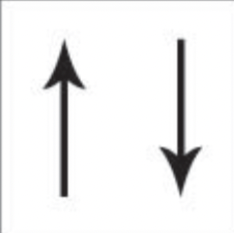
what is ionisation energy?
energy required to remove 1 e- from a mole of atoms to form a mole of +ions as a gas
why does the second IE req. more energy?
as it is from a +1 atom, not a neutral one
so the electrons are more strongly attracted to the positive charge
how does IE change within the periodic table?
increases across a period
decreases down a group
why is the first IE the easiest?
furthest from the nucleus
inner electrons shield it from the positive centre, weakening attractive forces
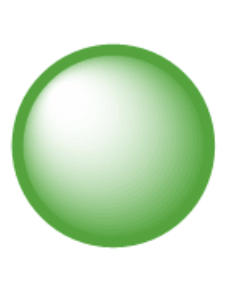
what does the s orbital look like?
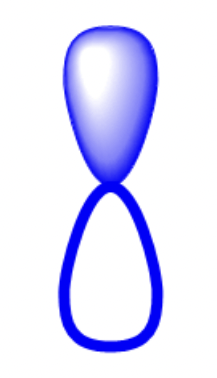
what does the p orbital look like?
why is alumium’s IE less than magnesium’s, when it should be higher?
less energy req
as e- is being removed from 3p orbital, which is further away from the nucleus