HB TOPIC 2 HOMEOSTASIS
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Homeostasis- define
how is it achieved (what and loops)?
maintaining a constant internal environment in the body eg. blood pressure, ph etc.
nervous and endocrine system moniter changes to internal and external environment+ respond via feedback loops
Difference between negative and positive feedback loops
Negative- body senses change and activates reactions to reduce/reverse in opposite direction
Positive- body senses change and activates mechanisms to increase change in same direction
Steps to feedback system
Stimulus
Receptor
Modulator
Effector
Response
Feedback
Define Dynamic Equilibirum
Fluctuation of homeostasis around a set point
define tolerance limits
upper and lower limits that body can function normally
Define thermoregulation and why do we need it?
process which maintain the balance between heat production and loss
needed as cell activity is heat sensitive
Central thermoreceptors
found where
role
found in hypothalamus
moniters INTERNAL body temp and controls activities to increase or decrease temo
Peripheral thermoreceptors
found where
role
skin and mucus membranes
moniters EXTERNAL environment via heat and cold receptors
Responses to high body temp
list them all
Vasodilation
Decreasing Metabolic rate
Sweat
Behavioural responces
Responses to high body temp- Vasodilation
Define
Effect- how is heat lost
high BT= increased blood flow to skin via relaxation and dilation of peripheral blood vessels
heat loss via radiation and evaporation= cooling of blood flowing through skin
Responses to high body temp- Decreasing metabolic rate
define
effect
hypothalamus decreases release of TSH from anterior pituitary
decreased TSH = decreased thyroxine from thyroid into blood = decreased metabolic rate = decreased body temp
Responses to high body temp- sweat
define
controlled by
response
secreted via sweat glands to skin- controlled by sympathetic nervous system
evaporation = decreased body temp
Responses to high body temp- behavioural responces
decreased movement
less clothing
shade
aircon
Response to low body temp- list
vasoconstriction
decrease metabolic rate
shivering
behavioral responses
Response to low body temp- vasoconstriction
define
effect (heat prod or decreasing heat loss)
decreased body temp= restriction of blood vessels to decrease blood flow
decreased blood flow to decrease heat loss
Response to low body temp- increasing metabolic rate
hormones released
explain each
effect of each (heat prod or decrease heat loss)
adrenaline and noradrenaline- hypothalamus stimulated adrenal medulla to secrete A+N to blood= increase metabolic rate= increase heat prod
Thyroxine- anterior pituitary released TSH to thyroid to release thyroxine = increased metabolic rate and increase heat prod.
Response to low body temp- shivering
define
effect (heat prod or decrease heat loss)
rhythmic muscle tremors caused by hypothalamus to muscle tone
muscle tone= movement = heat production
Response to low body temp- behavioral responses
huddling
curlling into ball
increased clothes
heat devices
Osmoregulation- define dehydration
low water concentration in blood plasma
water intake should =
water output
3. role of kidney in osmoregulation
role
how is it controlled?
filters water out from blood and back into blood via collecting duct to urine to bladder.
controlled by ADH
ADH- antiduretic hormone
define
role
released from
affects permeability of collecting duct in kidney
controls reabsorption of water back into body
released from posterior pituitary
how does increased adh affect reabsorption? and what will the concentration of urine be
increased permeability of collecting duct = increased reabsorption= concentrated urine
how is osmoregulation detected?
receptors
define osmotic pressure and eg.
osmoreceptors in hypothalamus detect osmotic pressure
the tendency of water to move into a solution eg. high osmotic pressure= concentrated and low amount of water- water wants to move in
Aldosterone
secreted by
effect
adrenal cortex into blood
water follows via osmosis to decrease osmotic pressure
= increased sodium reabsorption into blood and increase potassium excreted into urine
thirst reflex
define
give flow chart
consious responce to drinking water when high osmotic pressure is detected
Stimulus- low water concentration and high osmotic pressure
Receptor - thermoreceptors in hypothalamus stimulated
Modulator- hypothalamus
Effector- cerebral cortex generates thirst feeling
Responce- drink water and absorbed into blood via alamentary cana
feedback- negative- water leaves blood and fluid returns to normal
Feeback loop of ADH release
Stimulus - low water concentration and high osmotic pressure
Receptor - osmoreceptors in hypothalamus stimulated
Modulator - hypothalamus
Effector - causes posterior pituitary to release ADH
Response - increased permiability in collecting duct = increased water reabsorbed into blood
Feedback - blood water levels return to normal and osmotic pressure decreases
Cellular respiration equation
oxygen + glucose = carbon dioxide + water + energy
Liver uses glucose in blood by
list all 4
removed for energy
stored as glycogen
left in blood
stored as fat
Steps to decrease high blood glucose
chemoreceptors in beta cells of islet of langerhans detect high BSL
Insulin secreted
glucose absorbed by cells where either 1. GLYCOGENESIS or 2. LIPOGENESIS occurs IN PANCREAS
protein synthesis and increased cell respiration
decreased BSL
Define Glycogenesis
glucose to glycogen in liver and muscles
Define Lipogenesis
glucose to fat
3 ways to increase low blood sugar levels
Conversion via Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis
adrenal cortex
adrenal medulla
Steps to increase low BSL via glycogenolysis and gluceogenesis
chemoreceptors in ALPHA CELLS IN ISLET OF LANGERHANS detect low BSL
GLUCAGON is secreated
IN PANCREAS either 1. glycogenolysis or 2. gluceogenesis or 3. lactic acid to glucose
Blood glucose levels increase
Adrenal cortex to increase low BSL
releases what hormone and from where
3 effects of hormone
glucocorticosteroids stimulated by adreonocorticotropic hormone from anterior pituitary
regulated carb and fat metabolism
energise cells
stimulate glycogenolysis and gluceogenesis
Adrenal medulla to increase low BSL
effect
counteracts effect of insulin by causing glycogen → lactic acid → glucose
Breathing
how does it occur
controlled by
contractions and relaxation of diaphragm and intercostal muscles
respiratory centre in medulla oblongata
How are changes to gas concentrations detected?
How fast is each responce?
Oxygen, CO2 and Hyrogen Ion concentration- chemoreceptors on aortic and carotid bodies→ immediate responce
CO2- +medulla too→ several minutes
Oxygen concentration change
how large is the impact on breathing
what happens if change is detected
small impact on breathing rates unless O2 is very low
Nerve impulses→ intercostal and phrenic nerves → intercostal muscles and diaphragm= increased BR
CO2 concentration change
size of impact on breathing rate
formula of carbon dioxide and water
small increase of CO2= large impact
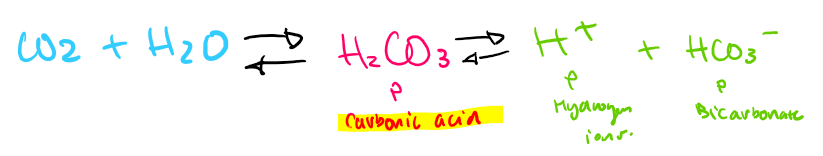
Changes to H+ iron concentration
high hyrdogen ion concentration = decrease blood plasma ph= acidic
detected and then increase breathing rate
Voluntary breathing
controlled by… and why?
role
how is breathing stimulated again
cerebral cortext- bypasses respitory in medulla oblongata
protect the body from dangerous gas or water into lungs by holding breath
build up of CO2
hyperventilation
caused by…
what happens to O2 and CO2
why is it dangerous before holding breath?
stress or anxiety
deep breathing = more O2 and less CO2 than required
lack of CO2 reduces urge to breath and too low oxygen = black out
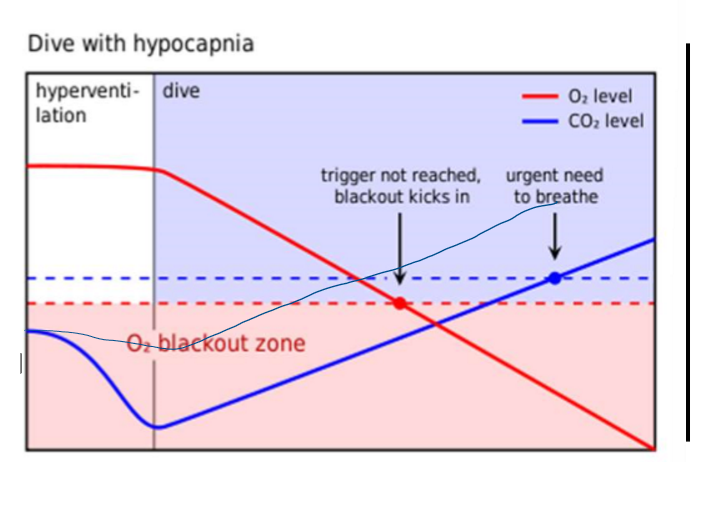
Explain this graph
Oxygen increases by little but CO2 decreases dramatically
Dive = decreased O2 and increased CO2
O2 levels reach O2 blackout zone before response to breath is met
Disruptions to homeostasis
list all 4
type 1 diabetes
type 2 diabeted
hyperthyroidism
hypothyroidism
Type 1 diabetes
define
causes/ risks
when autoimmune system destroys beta cells in ISLET OF LANGERHANS= no production of insulin= always high BGL
autoimmune, genetic and environmental factors
Symptoms of type 1 and 2 diabetes
thirst
high urine production
blurry vision
weight loss
acidic blood
treatment of type 1 diabetes
insulin injection
gene therapy- transfer/ growth of new beta cells or gene cells to replace cytotoxic T cells = fixed insulin production
Type 2 diabetes
define
insulin produced but cells do not use properly
overtime, pancreas decreases/ loses ability to produce insulin
Type 2 diabetes causes
older age, obesity, genetics etc
DIET= high sugar diet= increased insulin exposure over time and cells become resistant.
type 2 diabetes treatment
careful diet
regular excersise
moniter glucose levels
medication
Hyperthyroidism
define
caused when
thyroid gland produces too much thyroxine and T3 (iodine)
caused when bodies own antibodies imitate TSH = too much thyroxine production
influenced by graves disease or genetics
Hyperthyroidism symptoms
rapid heart beat
weight loss (high metabolism)
increased appetite
sweating
anxiety
protruding eyeballs
Treatment of hyperthyroidism
drugs- blocks use of iodine
surgery to remove part/all of thyroid
drink radioactive iodine- kills thyroid cells
Hypothyroidism
define
thyroid gland produces too little thyroxine
causes for hypothyroidism
diseased thyroid
pituitary doesnt prod enough TSH
lack of iodine in diet
autoimmune disease
symptoms of hypothyroidism
slow heart rate
weight gain
fatigue
intolerance to cold
swelling of face
goiters
Cretinism- retardnation, decreased growth, motor and sensory function in babies
treatments for hypothyroidism
increased iodine diet
thyroid hormone tablets