8: Alcohols (Ocular Toxicology)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is proof?
2x percent alcohol content
(40% AbV = 400 mL/L = 80 proof)
What are the units for blood alcohol concentration (BAC)?
g ethanol in 100 mL blood
0.08% = 0.8 mg/mL = 0.8 g/L
What are the dangerous acute effects of ethanol?
Vasodilation
Respiratory depression
Loss of protective airway reflexes
Hypothermia
Incontinence
Hypotension
Cardiovascular collapse
Death
Describe the ADME of ethanol
Passive diffusion across GI lining
90% small intestine
Highly water soluble
More body fat = less places alc to go = plasma [EtOH] increases
Hepatic metabolism
Describe ethanol mechanisms of action
Multiple mechanisms
Some CNS effects:
Nonspecific effects on cell membranes and membrane proteins
Specific effects on GABA, dopamine, and endogenous opioid signaling
Acts at NT binding site
Modifies gating mechanism inside channel
Stimulates Gs which is linked to adenylyl cyclase
Describe hepatic biotransformation of ethanol
Ethanol → alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) converts to acetaldehyde → acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) converts to acetate
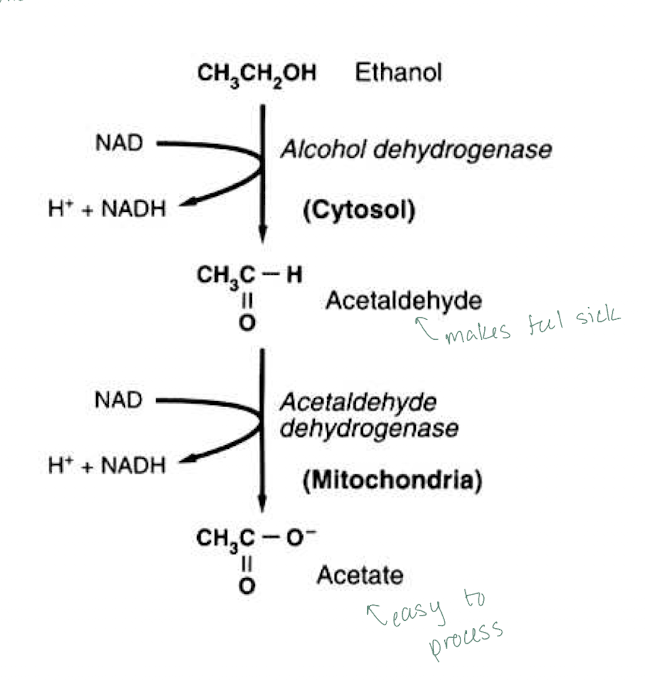
What ethanol metabolite is responsible for the dangerous effects of EtOH?
Ethanol
What ethanol metabolite makes people feel sick?
Acetaldehyde
What is a small sex difference in ethanol metabolism
Females have lower gastric ADH activity → females break down ethanol slower
Describe the genes regulating ADH
ADH1B*2 = faster
ADH1B*1 = slower
Describe the genes regulating ALDH
ALDH2*2 = slower than ALDH2*1
Explain the genetic difference for ethanol metabolism in Asian populations
Higher percentage of ADHB*2 and ALDH2*2 → produce acetaldehyde faster, produce acetate slower → experience quicker and possibly longer periods of negative effects
What are the effects of methanol in humans?
Lower doses
Drunkenness
Nausea
Headache
Moderate doses
Tachycardia
Drowsiness
Higher doses
Acidosis
Convulsions
Respiratory depression
Coma
Blindness
Infarcts of basal ganglia or striatum in brain
Describe the ADME of methanol
Absorption and distribution similar to ethanol
Humans and non-human primates have limited conversion of formate to CO2 → formate accumulates
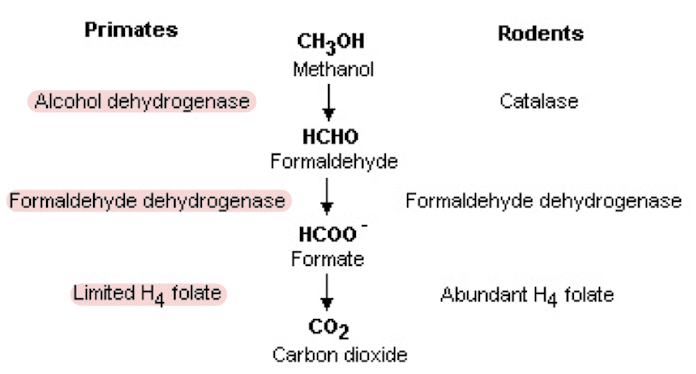
What do humans and primates lack that causes an accumulating of formate?
H4 folate
What are methanol-related effects?
Similar to ethanol tox:
Ataxia
CNS depression
Hypotension
Acidosis
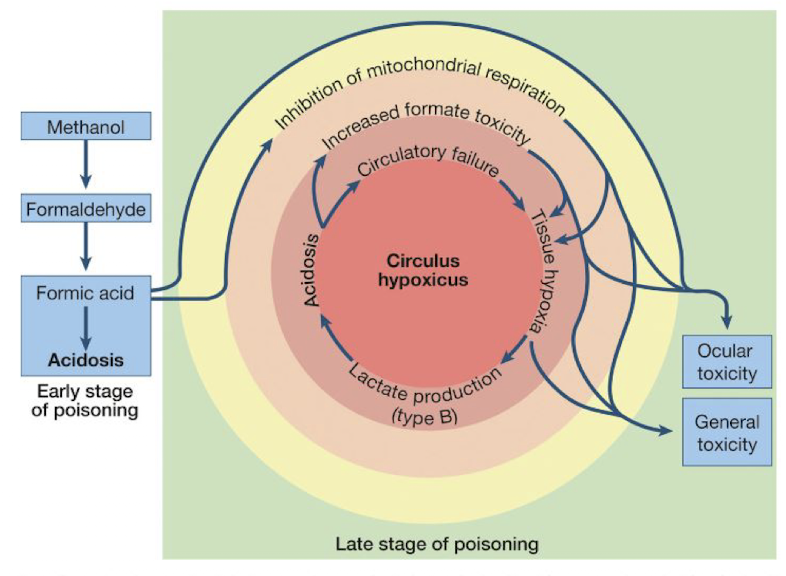
What are formate effects?
Self-perpetuating cycle of acidosis & lack of O2 in tissues → blindness and brain infarcts
Severe lactic acidosis → decrease cardiac contractility → decrease responsiveness of vasculature to vasopressors (EPI, NE)
Describe the ocular effects of methanol in humans
Initial optic neuritis
Swollen optic discs visible from inflammation of optic nerves
Optic nerve atrophy
Demyelination of optic nerve fibers contributes
What are the treatments of methanol toxicosis
All: treat signs as ethanol toxicosis
Primates
Inhibit ADH with fomepizole or ethanol
Provide folinic acid
Hemodialysis recommended
Describe the metabolism of methanol
methanol → formaldehyde → formate → CO2
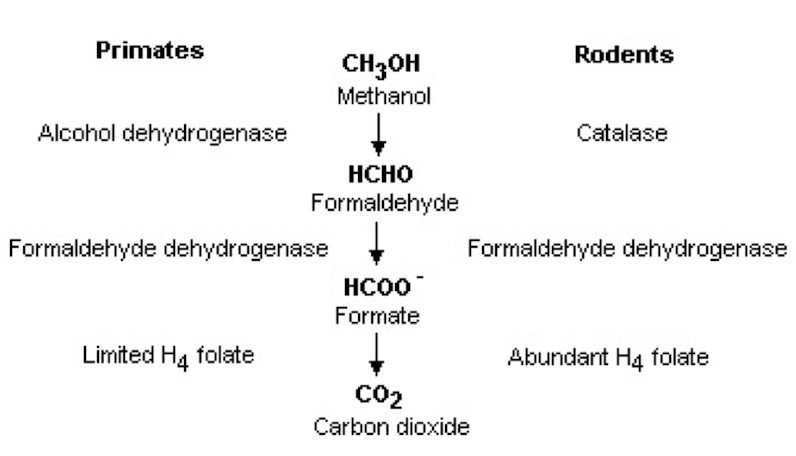
Why is fomepizole or ethanol used to treat methanol toxicosis?
Inhibiting ADH inhibits the transformation of methanol into dangerous metabolites → prevents formation of formate
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) is important for what 3 related toxicoses?
Methanol → formaldehyde (eventually folic acid)
Ethanol → acetaldehyde (eventually CO2 and H2O)
Ethylene glycol → glycol aldehyde (eventually organic acids)