Dx of Respiratory D/O: CMIII Pulm
1/342
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
343 Terms
most common respiratory d/o and primary d/o of the airway. examples include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary dz, bronchiectasis, bronchiolitis. airway dz.
obstructive lung diseases
respiratory d/o category: examples include parenchymal lung dz, abnormalities of the chest wall and pleura, neuromuscular dz
restrictive d/o
respiratory d/o category: examples include pulmonary embolism, pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary veno occlusive dz
abnormalities of the vasculature.
infective and neoplastic processes are technically
other respiratory d/
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, asbestos, desquamative interstitial pneumonitis, and sarcoidosis
parenchymal restrictive d/o examples
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), guillain barre, myasthenia gravis
neuromuscular dz: restrictive d/o
kyphoscoliosis, ankylosing spondylitis, chronic pleural effusions
abnormalities of the chest wall and pleura: restrictive d/o
cardinal sx of respiratory dz
dyspnea and cough
causes of acute SOB (sudden physiological changes)
laryngeal edema, bronchospasm, myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, pneuothorax
causes of gradual progression of dyspnea on exertion
COPD and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF)
sx of asthmatic pt
intermittent dyspnea, cough, and chest tightness. usually w specific triggers like a URI or allergen
what is the cause of acute cough, productive of phlegm
infection. can be of the upper airway (sinusitis, tracheitis), lower airway (bronchitis or bronchiectasis), lung parenchyma (pneumonia)
blood streaked or frankly bloody describes what about the sputum?
the quantity and quality
how long does chronic cough persist for, and what is it commonly associated w?
>8 weeks. commonly associated w obstructive lung dz (asthma, COPD, and chronic bronchiectasis). can also be seen in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). can be seen in "nonrespiratory dz" like postnasal drip and GERD
when you hear wheezing, what should you think?
Asthma (airway dz)
infections of the respiratory tract, bronchogenic carcinoma, pulmonary embolism can all cause what sx
hemoptysis
Why would a pt have chest pain?
usually from either dz of the parietal pleura (pneumothorax) or pulmonary vascular dz (pulmonary HTN)
current or previous cigarette smoking is a RF especially for...
COPD, bronchogenic lung cancer, parenchymal lung dz
additional important pt hx
-inhalation exposure at work (asbestos or silica), or home (wood smoke, excrement from pet birds)
-travel (TB)
-exposure to fungi
-fever and chills
-therapy for other conditions (irradiation and meds)
parts of the physical exam include
-respiratory rate
-pulse oximetry
-inspection (distress has accessory mm use; can have conversational dyspnea)
-percussion (dull in pleural effusion; hyperresonant in pneumothorax)
-palpation, auscultation, pedal edema, jugular venous distention, clubbing (in further flashcards)
Palpation inc vs dec tactile fremitus?
-inc TF in consolidation
-dec TF in pleural effusion
auscultation: wheezes
airway obstruction in asthma primarily. also in CHF, bronchogenic carcinoma, etc
auscultation: rhonchi
obstruction of medium sized airways, most often w secretions. in COPD and bronchiectasis
Auscultation: crackles or rales
-indicate alveolar dz
-ex: pulmonary edema and pneumonia
fibrosis of interstitium (IPF) sounds like velcro
auscultation: lack or diminution of breath sounds
pneumothorax or pleural effusion
this sx, if symmetric, may suggest cor pulmonale. Asymmetrically may be due to DVT/PE
pedal edema
jugular venous distention indicates
RIGHT heart failure
Clubbing of nails indicates
cystic fibrosis, IPF, lung cancer
dx evaluation of respiratory d/o
-pulmonary function testing (not specific)
-arterial blood gas testing
-chest imaging (radiography, US, CT, PET, MRI, pulmonary angiography)
medical techniques for obtaining biologic specimens
-collect blood and sputum
-percutaneous needle aspiration (transthoracic) for cytologic/histologic or microbiologic analysis. guided by CT or US
-thoracentesis for sampling of pleural liquid or dx/therapeutic purposes
-bronchoscopy
direct visualization of the tracheobronchial tree to the level of the subsegmental bronchi. can obtain samples from airway lesions (washing, brushing, biopsy, needle aspiration). performed mostly w flexible fiberoptic instruments. (rigid bronchoscopy indicated in certain situations only)
bronchoscopy technique for biologic specimens
particularly useful for the recovery of fluid for culture when performing a bronchoscopy
bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)
tissue biopsy and histopathologic examination technique
surgical
via suprasternal approach. rigid mediastinoscope is inserted at the suprasternal notch and passed into mediastinum. tissue is obtained w biopsy forceps passed through the scope
mediastinoscopy
via parasternal approach. aortopulmonary lymph nodes are not accessible. parasternal incision and dissection directly down to a mass or node that requires biopsy
mediastinotomy
mediastinoscopy and mediastinotomy is to maintain tissue biopsy of...
suspicious mediastinal nodes
operative technique for the dx and management of pleural and parenchymal lung dz, performed in OR. passage of rigid scip through a trocar inserted into the pleura. operator manipulates instruments passed into pleural space via other small incisions. open thoracotomy is replaced by this technique
Video assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS)
severity of illness scoring systems should be used to complement clinical bedside decision making. what are the most commonly used systems?
-SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment
-APACHE: Acute physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation
-SAPS (Simplified Acute Physiology Score) is frequent in Europe
Most commonly used severity of illness scoring system in north america? predicts hospital mortality rate.
APACHE (acute physiology and chronic health evaluation)
Factors and components of the APACHE score system
-rectal temp
-mean BP
-HR
-RR
-arterial pH
-oxygenation
-serum sodium
-serum potassium
-serum creatinine
-hematocrit
-WBC
-glasgow coma scale
-age
-hx of chronic health conditions
Approach to the patient in shock (diagram)
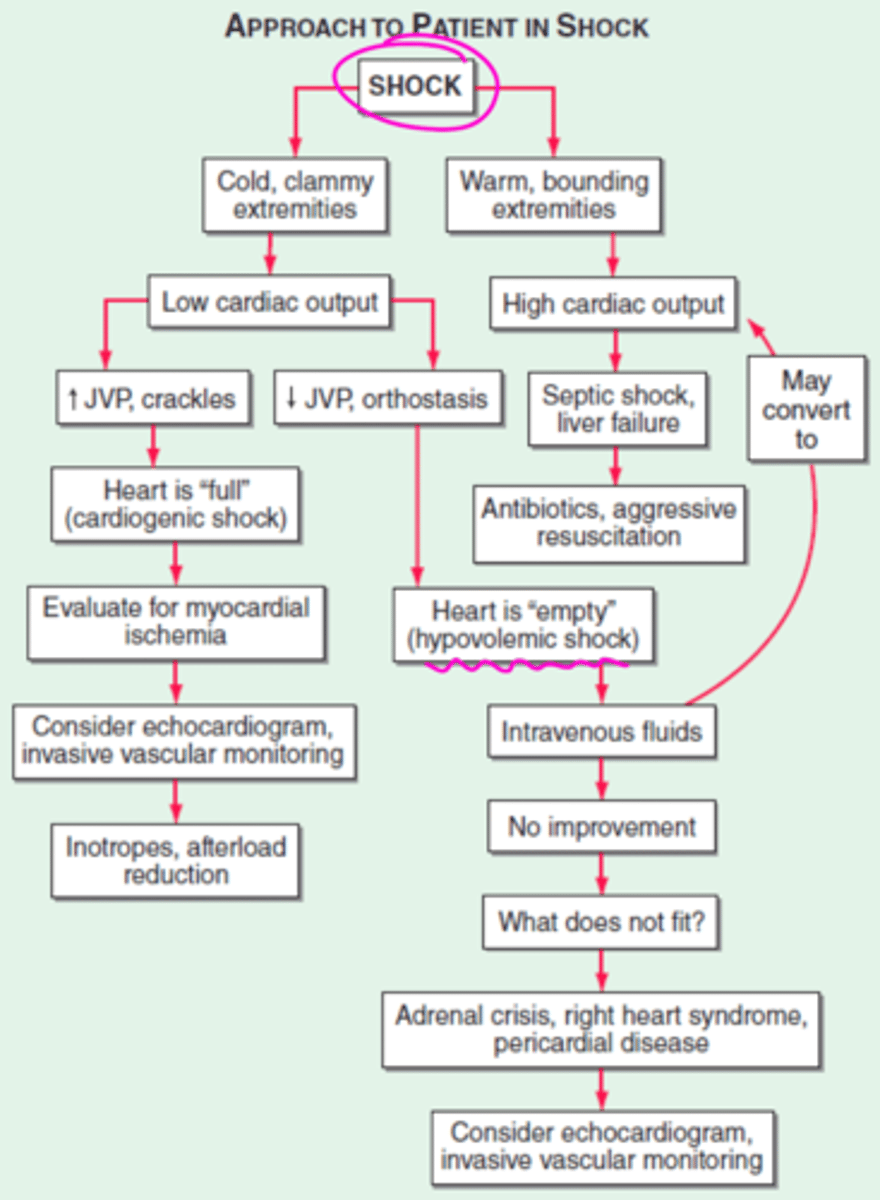
initial resuscitation of pt in shock?
ACLS. early intubation and mechanical vent is often required (relieves the work of breathing and allows redistribution of limited cardiac output to other vital organs)
what does the physical exam of a pt in shock look like?
-inability to speak full sentences
-accessory mm use
-paradoxical abdominal mm activity
-extreme tachypnea (>40 breaths/min)
-low RR despite an increasing drive to breathe due to exhaustion
respiratory failure is a common reason for...
ICU admission
Name that respiratory failure!
Acute hypoxemic respiratory failure-- "hypoxemia" (low O2)
type I
Name that respiratory failure!
Respiratory failure-- "hypercapnic" (high CO2)
Type II
Name that respiratory failure!
respiratory failure-- "Perioperative"
Type III
Name that respiratory failure!
Respiratory failure-- "shock"
Type IV
Hypoxemic pt. acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. due to alveolar flooding of water, blood, or pus. Examples include pulmonary edema, lung injury, pneumonia, alveolar hemorrhage. (also can be from sepsis, gastric aspiration, near-drowning, multiple blood transfusions, and pancreatitis)
Type I respiratory failure
Hypercapnic pt. Inability to eliminate CO2 effectively--alveolar hypoventilation. Three types of mechanisms: impaired CNS drive to breathe, impaired strength w failure of neuromuscular function in respiratory system, and increased load on the respiratory system.
Type II respiratory failure
Impaired CNS drive to breathe can cause type II resp failure (Hypercapnic). this can be from...
drug OD, brainstem injury, sleep disordered breathing
Impaired strength w failure of neuromuscular function in the respiratory system will have impaired neuromuscular transmission (like in myasthenia gravis, guillain barre, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis). can also have respiratory muscle weakness (like in myopathy, electrolyte derangements, fatigue). causes hypercapnia.
another cause of Type II respiratory failure
Increased loads on the respiratory system (cannot exchange air) can cause pt to go into hypercapnic Type II respiratory failure. examples of this include...
COPD, bronchospasm, atelectasis, pneumothorax
Perioperative (type III) respiratory failure is a result of
lung atelectasis (post op lungs don't open as they should)
"Shock" (type IV) respiratory failure results from...
hypoperfusion of respiratory mm in pt in shock (NO BLOOD)
What is the proper care of the mechanically ventilated pt?
-nonbenzo sedatives
-analgesia: opiates
-all pts should undergo daily screening of respiratory function (spontaneous breathing trials)
What is the spontaneous breathing trial?
-breathing through the ET tube w/out ventilator support for 30-120 min
-RR and tidal volume in liters (fVt) calculation
Failure declared in spontaneous breathing trial if....
1. respiratory rate >35/min for >5 min
2. O2 saturation
3. HR >140/min or a 20% inc or dec from baseline
4. systolic BP
5. inc anxiety or diaphoresis
sepsis in the critical care unit is a leading cause of
DEATH
how to prevent nosocomial infections in the ICU
-invasive therapeutic interventions (endotracheal intubation, indwelling vascular catheters, transurethral bladder cath, etc). REMOVE AS SOON AS NO LONGER NEEDED
-prevent w infection control
Prevention of DVT in critical illness
-SubQ low dose heparin injections + SCD's (compression device)
Prevention of stress ulcers in stomach in critically ill pt? can be administered to high risk pt (coagulopathy or respiratory failure)
Histamine receptor 2 antagonists to prevent stomach ulcers
Nutrition and glycemic control to prevent complications of critical illness
enteral feeding preferred over parenteral nutrition
how to prevent ICU acquired weakness in critically ill pt? weakness occurs frequently-SIRS and/or sepsis. Neuropathies, myopathies
very early PT/OT in mechanically ventilated pt. significant improvement in functional independence at hospital discharge
Anemia, which is mostly related to chronic inflammation, can be prevented in critically ill pt by
conservative transfusion strategy
hypoperfusion and/or nephrotoxic agents cause tubular necrosis. this happens commonly. what can be done to prevent this acute kidney failure?
No preventive pharmacologic agents exist
4 signs of delirium in critically ill pt
1. acute onset of changes or fluctuations in mental status
2. inattention
3. disorganized thinking
4. altered level of consciousness
screening checklist for delirium
Confusion assessment method (CAM)-ICU or the Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist
DDX is very broad for delirium in critically ill pt. how can delirium be prevented?
very early PT/OT
Anoxic cerebral injury is common after CARDIAC ARREST. this causes severe and permanent brain injury (not perfusing) in survivors. What should we do for this pt?
active cooling of pt after cardiac rest
common cause of neurologic critical illness is stroke. how can this be prevented
-manage HTN carefully
-tPA
Subarachnoid hemorrhage may occur secondary to aneurysm rupture. How can this complicate?
complicated by cerebral vasospasm, rebleed, hydrocephalus
recurrent relentless seizure activity is a MEDICAL EMERGENCY. cessation of seizure activity is required. what can you give to this pt?
Lorazepam- longer acting antiepileptics should be given concomitantly
irreversible cessation of all functions of the entire brain, there is absence of cerebral function and brainstem function. Must have established cause and be permanent w/out possibility of recovery
brain death
no response to any external stimulus
cerebral brain death
unreactive pupils, lack of ocular mvmt in response to head turning or water irrigation of ear canals, positive apnea test (no drive to breathe)
brainstem death
Severe dyspnea of rapid onset + hypoxemia + diffuse pulmonary infiltrates
respiratory failure
Onset of acute respiratory distress syndrome
w/in 1 week of clinical insult or new/worsening respiratory sx
chest radiographs of ARDS
b/l opacities consistent w pulmonary edema, not fully explained by effusions, lobar/lung collapse, or nodules
direct lung injury
-Pneumonia
-Aspiration of gastric contents
-Pulmonary contusion
-Near-drowning
-Toxic inhalation injury
indirect lung injury
-sepsis
-severe trauma
-multiple bone fractures
-flail chest
-head trauma
-burns
-multiple transfusions
-drug overdose
-pancreatitis
-post cardiopulmonary bypass
etiology of ARDS
-pneumonia and sepsis (MC!)
-aspiration of gastric contents, trauma, multiple transfusion, drug OD
-trauma: pulmonary contusion, multiple bone fx, chest wall trauma/flail chest
Inc risk of ARDS??
-multiple comorbidities
-older age
-chronic alcohol abuse
-metabolic acidosis
-pancreatitis
-severity of critical illness
what are the three phases of ARDS?
Exudative
Proliferative
Fibrotic
First 7 days of illness in ARDS after exposure and onset of respiratory sx. dyspnea, tachypnea, inc workload of breathing. all causes respiratory fatigue, and eventually respiratory failure. Severe hypoxemia +/- hypercapnia (low O2, high CO2 in blood).
Exudative phase
what does CXR look like in Exudative phase ARDS?
opacities consistent w pulmonary edema involving >75% of the lung fields
DDX of exudative phase of ARDS
cardiogenic pulmonary edema, b/l pneumonia, alveolar hemorrhage
Days 7-21 of ARDS. most pt are extubated at this phase
proliferative phase
Phase of ARDS. Some pt require long term MV support and/or supplemental O2. there is extensive alveolar duct and interstitial fibrosis.
Fibrotic phase. here, there is intimal fibroproliferation in the pulmonary microcirculation, leading to progressive vascular occlusion and pulmonary HTN
General principles of ARDS tx
1. recognize tx of underlying med/surg d/o (ex. pneumonia, sepsis, aspiration, trauma)
2. minimize unnecessary procedures and complications
3. standardized "bundled care" approaches for ICU pt (ex. prophylaxis against VTE, GI bleed, aspiration, excessive sedation, prolonged MV, and central venous cath infxn)
4. prompt recognition of nosocomial infxn
5. provision of adequate nutrition via the enteral route when feasible
mechanical ventilation can aggravate lung injury in ARDS, so you must
manage vent settings carefully
vent induced lung injury:
from repeated alveolar overdistention from excess tidal volume
Volutrauma
vent induces lung injury: from recurrent alveolar collapse
Atelectrauma
How should you position your ARDS pt to improve arterial oxygenation and reduces mortality?
Prone positioning
Risk of prone positioning in ARDS pt
accidental endotracheal extubation, loss of central venous catheter, orthopedic injury
How should you manage fluids in ARDS pt?
aggressive attempts to reduce left atrial filling pressures w fluid restriction and diuretics. limited hypotension and hypoperfusion of critical organs (kidneys)
mortality of acute respiratory distress syndrome
34.9%-46.1%. most pt regain normal lung function. exercise limitation and dec physical QOL common years later despite normal PFTs. (significant rates of depression and PTSD)
formerly known as hyaline membrane dz
respiratory distress syndrome in the newborn
caused primarily by deficiency of pulmonary surfactant in an immature lung. surfactant deficiency leads to alveolar collapse. then there is low lung compliance and volume, leading to mismatch of ventilation and perfusion. ultimately leads to hypoxemia. (others include inflammation and pulmonary edema). there is inc incidence w decreasing gestational age.
respiratory distress syndrome in newborn
dx of RDS in newborn
clinical findings of preterm infant w progressive respiratory failure shortly after birth + characteristic chest imaging