Chapter 1 exam review bio 101
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Biology
The study of life
Evolution
the change in genetic material of a population of organisms from one generation to the next. A gradual change overtime.
Information transfer
The process by which genetic instructions, stored in DNA, are passed on to different parts of a cell/ to offspring through processes like transcription (DNA to RNA) and translation (RNA to protein)
Energy transfer
the movement of energy from one organism to another within an ecosystem
Primary
The structure of biological molecules, the growth of plants, or the production of organic molecules
secondary
the local, regular folding patterns within a polypeptide chain, primarily formed by hydrogen bonds between the atoms of the polypeptide backbone
Consumers
An organism that cannot produce its own food and must obtain energy by eating other organisms, like plants or animals
Decomposers
An organism that breaks down dead plants and animals, essentially recycling them by releasing nutrients back into the environment as they eat decaying matter.
The basic characteristics of all living organisms
Composed of the same four classes of organic molecules
Engage in metabolism
respond to internal and external stimuli
specific biological structures have specific functions
maintain homeostasis
reproduce offspring
experience growth and development
subject to evolutionary forces
Receptor
A protein that binds to a specific molecule
control center
Receives and processes information from the receptor
effector
a molecule that binds to a specific protein and regulates its biological activity.
Inheritance
the way that genetic information is passed from a parent to a child
Atoms
the basic building blocks of matter and the smallest unit of a chemical element that retains its properties.
Molecules
a group of two or more atoms that form the smallest identifiable unit of a pure substance.
organelles
are compartments within the cell that perform specific functions.
cells
basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed.
tissues
is an aggregation of cells that function together and have a similar function.
organs
a self-contained group of tissues that performs a specific function in the body.
organ systems
a group of organs that work together to perform a certain function in an organism’s body.
organism
is a living system that functions as an individual entity.
population
the number of organisms of the same species that live in a particular geographic area at the same time, with the capability of interbreeding.
community
an interacting group of various species in a common location.
ecosystem
single environment and every living (biotic) organism and non-living (abiotic) factor that is contained within it or characterizes it.
biosphere
is where living organisms are found on, above, and below the Earth’s surface.
DNA
(deoxyribonucleic acid) is the hereditary material in cells, carrying instructions for making proteins.
Genes
are segments of DNA that produce proteins.
Mutations
Are changes in DNA, RNA or chromosomes that can lead to genetic variation and contribute to evolution.
Domain
highest taxonomic rank used to categorize and group organisms based on shared characteristics and evolutionary history.
Bacteria
Archaea
Eukarya
Kingdom
second highest taxonomic rank. Are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum).
Phylum
taxonomic ranking that comes third in the hierarchy of classification. Organisms in this share a set a characteristics that distinguishes them from organisms in another one of these.
Class
is a taxonomic rank above the order and below the phylum. It is a group of related taxonomic orders. Members of a class share more characteristics with each other than they do with other organisms in the same phylum.
Order
A taxonomic rank above family and below class.
It groups related families based on shared characteristics.
Each order is split into families, and a group of closely related families forms an order.
Family
is a taxonomic rank that falls between genus and order. It is a group of one or more genera that share common attributes. The name of a family typically ends with "idae" for animals and "aceae" for plants.
Genus
A group of species that are closely related through common descent.
A taxonomic rank above species and below family.
Comprised of species grouped based on shared attributes or being phylogenetically related.
One of the eight major taxonomic ranks in the biological classification of living things.
Species
is a group of organisms that share a genetic heritage, are able to interbreed, and produce fertile offspring. It is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism
Binomial nomenclature
a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts.
Phylogenetic Tree of Life
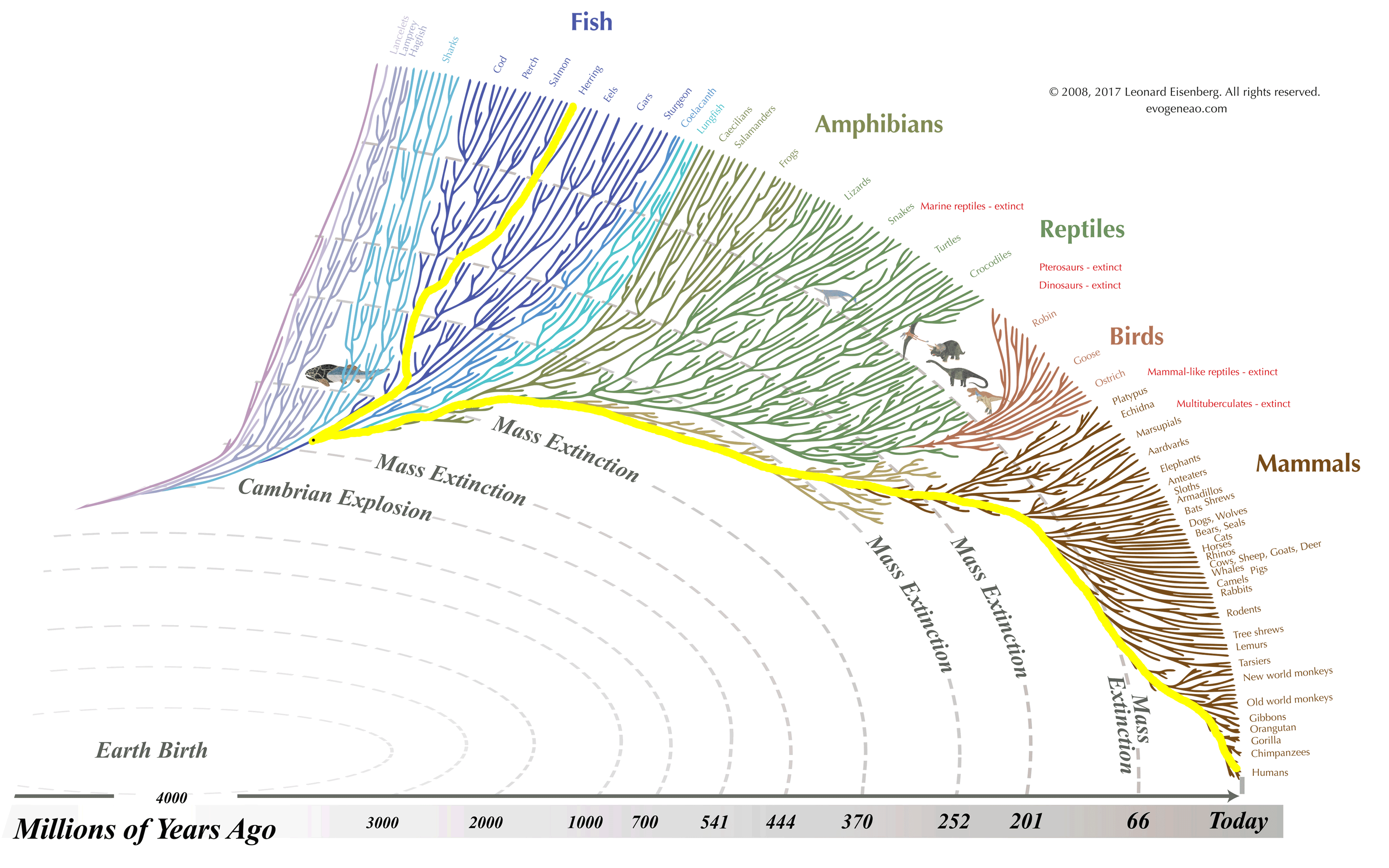
Natural evolution
the process by which species change over time through mechanisms such as natural selection, mutation, migration, and genetic drift.
Artificial evolution
evolutionary process in which humans consciously select for or against particular features in organisms
Observation
The beginning of the scientific method, leading to inferences and testable hypotheses.
Hypothesis
a testable statement proposing a potential explanation for natural phenomena. A testable statement.
in,
Experiments
The independent variable is intentionally manipulated or altered by the researcher.
The dependent variable is what is measured and depends on the modifications made to the independent variable.
Controlled variables
any factor that is controlled or held constant during an experiment.
Control and experimental groups
An experimental group is a test sample or the group that receives an experimental procedure.
A control group is a group separated from the rest of the experiment such that the independent variable being tested cannot influence the results.
Conclusion
a short paragraph that discusses the overall results of an experimental procedure and explains whether the proposed hypothesis at the beginning of the experiment was correct or not.
Theory or law
Law: A descriptive generalization about how some aspect of the natural world behaves under stated circumstances.
Theory: In science, a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world that can incorporate facts, laws, inferences, and tested hypotheses.