Global warming
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What roles do greenhouse gases play in relation to solar radiation
They absorb, reflect, and scatter incoming solar radiation
What does water vapour do with heat radiated from Earth’s surface
It absorbs the heat and radiates it in all directions
How does carbon dioxide interact with Earth's radiated heat
It absorbs the heat radiated from the Earth’s surface
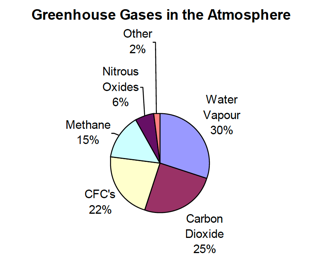
What percentage of incoming solar radiation is reflected back to space by clouds and atmospheric particles
26%
What percentage of solar energy is absorbed by clouds, gases, and particles in the atmosphere
19%
How much of the incoming solar energy passes through the atmosphere
55%
What percentage of solar energy is reflected from Earth’s surface back to space
4%
How much solar energy is absorbed by Earth’s land, oceans, and vegetation
51%
What does the absorbed solar energy on Earth power
It heats Earth’s surface, melts ice and snow, evaporates water, creates wind and currents, and fuels photosynthesis
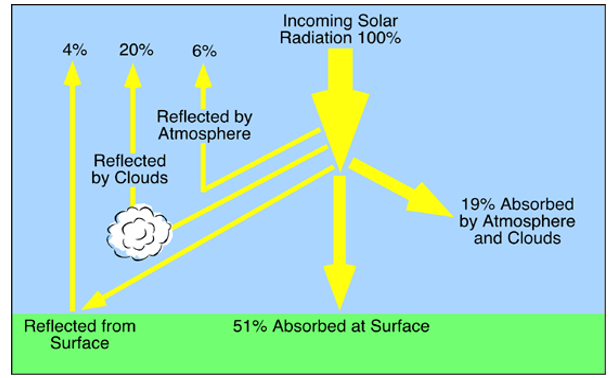
What type of radiation is mainly absorbed at Earth's surface
Visible light from solar radiation
What happens after Earth’s surface absorbs solar radiation
The surface warms and re-radiates heat as longwave infrared radiation
What absorbs most of the infrared radiation emitted from Earth’s surface
Greenhouse gases in the troposphere
What percentage of Earth’s infrared radiation is absorbed and re-emitted by greenhouse gases
About 90%
What is the result of greenhouse gases re-emitting infrared radiation back to Earth
The greenhouse effect, which warms the Earth’s surface
What is the source of all radiation and energy reaching Earth
The Sun
What happens to sunlight when it reaches different landscapes on Earth
Part is absorbed and part is reflected back (depending on surface type
Which surfaces have high reflectivity (albedo)
Bright surfaces like ice and snow
Does reflection occur only at Earth’s surface
No, it also occurs at the top of clouds
Where does absorption of sunlight occur
At Earth's surface and by gases and particles in the atmosphere
What type of radiation does Earth emit after warming up
Longwave infrared radiation
What process uses some of the Sun's energy on Earth's surface
Evaporation of water
What do clouds do with infrared radiation
Absorb and re-emit it back to Earth, acting like a blanket
Why are deserts often cold at night
Lack of clouds to trap infrared radiation
What do greenhouse gases do with Earth's infrared radiation
Absorb and retain the heat near the surface
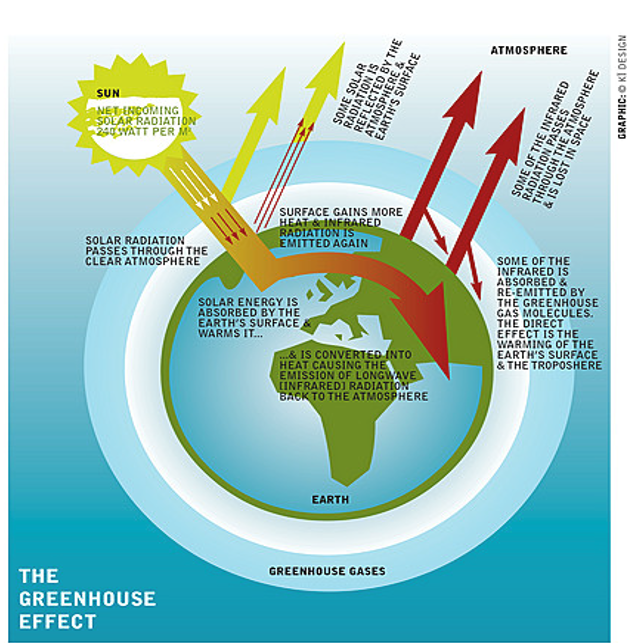
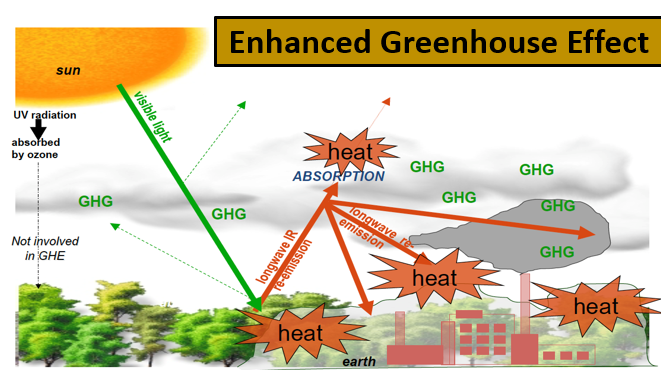
Describe and draw the diagram
1.The sun is the source of all radiation and energy coming to the Earth from space.
2.A part of the sunlight reaches the Earth surface and all its different landscapes: forests, oceans, deserts, savannah, cities, ice and snow
3.The Earth's surface does not take up all the sunlight, but sends a certain part of it directly back (reflection). In particular very bright surfaces like ice and snow are excellent reflectors (albedo).
4.Reflection does not only occur at the Earth surface. Some light is already sent back from the top side of clouds.
5.The uptake of the light (absorption) does not only take place at the Earth surface, but gas molecules and particles in the air absorb some sunlight. The portion of the sunlight reaching the Earth warms up the surface. The Earth sends this warmth back as infrared radiation.
6.The Earth's surface warmed up by the sun is a source of heat radiation (long wave infrared radiation).
7. A bit of the energy is needed to evaporate water.
8.Some infrared radiation goes directly back to the space.
9.Clouds do not only reflect sunlight, they also absorb and reemit infrared radiation back to the Earth. A cloudy sky keeps the Earth warmer, like a blanket (part of the reason why deserts are cold at night are because of no clouds).
10.Finally there are greenhouse gases that absorb the infrared radiation given off. They keep the energy of this heat radiation near the ground.
Why aren’t nitrogen and oxygen considered greenhouse gases
Because they do not have two or more bonds and cannot absorb and re-emit infrared radiation
What property must a molecule have to absorb and re-emit infrared radiation
It must have two or more bonds joining the atoms
What are the three most important greenhouse gases
Water vapour
Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
Methane (CH₄
Which greenhouse gas contributes the most to the greenhouse effect
Water vapour
What is the structure of a carbon dioxide (CO₂) molecule
One carbon atom with an oxygen atom bonded on each side
What happens when carbon dioxide absorbs infrared radiation
The molecule vibrates and then emits the radiation again
What happens to the emitted radiation from a vibrating greenhouse gas molecule
It is likely absorbed by another greenhouse gas molecule
How does the absorption-emission-absorption cycle affect Earth’s temperature
It keeps heat near the surface, insulating Earth from the cold of space
What causes the enhanced greenhouse effect
Human activities that increase greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere
What are some human activities that increase greenhouse gas emissions
Burning of biomass and fossil fuels
Agricultural activities
Industrial processes
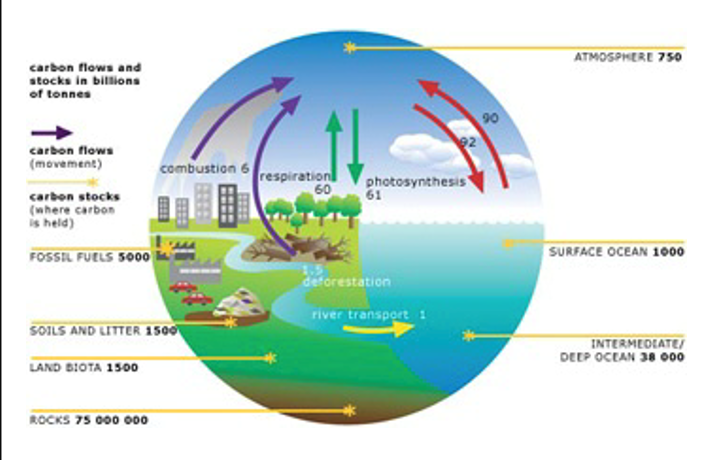
How does deforestation contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect
It reduces carbon sinks, meaning less carbon dioxide is absorbed from the atmosphere
What are carbon sinks
Natural systems like forests that absorb more carbon than they release
Enhanced greenhouse effect diagram
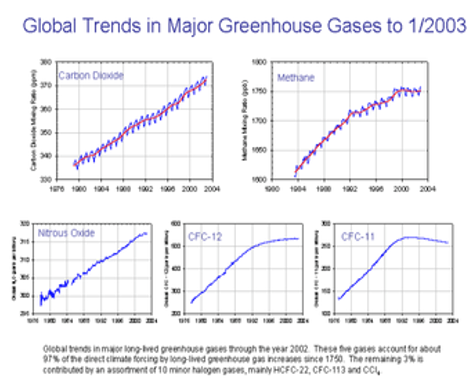
Which greenhouse gases have increased due to human activity
Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
Methane (CH₄)
Nitrous oxide (N₂O)
Ozone (O₃)
Synthetic gases like CFCs and halons
Which greenhouse gas has contributed the most to the enhanced greenhouse effect
Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
By how much has the greenhouse effect increased since pre-industrial times
By approximately one-third
How much has atmospheric CO₂ increased in the past 20 years
By 30 parts per million (ppm)
What are CFCs and halons
Synthetic greenhouse gases introduced by humans that contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect
What are examples of land use changes
Back burning and land clearing for pastoral purposes
What does land use change directly affect
Albedo
Transpiration rates
Carbon dioxide sources and sinks
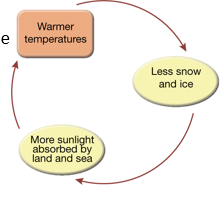
How do changes in polar regions affect global warming
They cause feedback effects that lead to further warming of the planet
What happens when ice and snow melt due to rising temperatures
Less sunlight is reflected (lower albedo), and more is absorbed by land and sea, increasing warming
What is the albedo effect
The fraction of solar energy reflected by a surface
Bright surfaces like ice have high albedo; darker surfaces absorb more heat
What is the main cause of global warming
More infrared radiation being absorbed and re-emitted in the troposphere
How does global warming affect global climates
It changes temperatures and ocean/atmospheric circulation patterns
How does global warming affect precipitation patterns
Some regions experience more precipitation, others experience less
How are soil moisture levels affected by global warming
They change due to altered precipitation and evaporation rates
What causes rising sea levels
Melting land ice and thermal expansion of seawater
What extreme weather events are becoming more frequent due to global warming
tropical storms
droughts
floods
forest fires
What does Earth's temperature depend on
The greenhouse-like action of the atmosphere
What strongly influences the amount of heating and cooling on Earth
The type of surface solar radiation encounters
What is albedo
The percentage of solar energy reflected back by a surface
How does a white icy surface affect solar radiation
It reflects most sunlight, causing minimal heating
How does dark, bare soil affect solar radiation
It absorbs most sunlight, contributing to significant surface heating
How does water vapour affect solar radiation
It reduces the amount of radiation reaching the surface but also acts as a greenhouse gas
What is the relationship between water vapour and air temperature
The amount of water vapour in the atmosphere depends heavily on air temperature
Why is the extent of the enhanced greenhouse effect complex
Because it’s influenced by surface types, albedo, water vapour, and cloud cover
How does climate change affect global temperatures
Increases average temperatures, causing more frequent and intense heatwaves
What causes sea level rise due to climate change
Melting glaciers and ice sheets, and thermal expansion of ocean water
What are the effects of rising sea levels
Erosion of beaches, inundation of coastal lands, and increased cost to protect coastal communities
How does climate change affect precipitation patterns
Increases variability—some areas get more intense rainfall while others experience droughts
What are some health impacts of climate change
Increased weather-related mortality
More infectious diseases
Poorer air quality causing respiratory illnesses
How does climate change impact agriculture
Alters crop yields
Increases irrigation demands
Shifts growing seasons and crop suitability
How are forests affected by climate change
Changes in forest composition
Shifting geographic ranges
Declines in forest health and productivity
What are climate-related impacts on water
Reduced water supply
Lower water quality
Increased competition for water
How are coastal areas impacted by climate change
Erosion of beaches
Coastal flooding
Increased infrastructure costs
How does climate change affect ecosystems
Habitat loss
Species extinction or migration
Reduced biodiversity
What is happening to Earth’s cryosphere due to climate change
Diminishing glaciers, melting permafrost, and loss of polar ice
How do scientists know that climate has changed over millions of years
Fossil records show that Earth’s climate has varied naturally over time, even before humans existed
What does recent climate data show
A steady, small increase in global average temperatures over the past few decades based on worldwide weather data
What do most scientists believe is causing recent global warming
Anthropogenic (human-caused) activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation
Why is this recent warming concerning
Although within the range of past natural variability, the rapid pace and human influence make it a major environmental concern
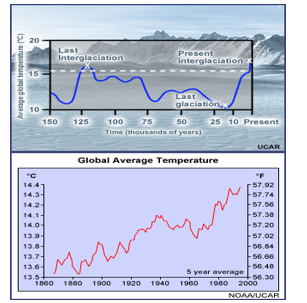
How will climate change affect the natural environment
It will cause:
Migration, population decline, and extinction of plant and animal species.
Shifts in habitats and ecosystems due to temperature and water changes.
How will climate change impact humans
It may lead to:
Reduced water availability
Loss of coastal areas due to rising sea levels
Spread of diseases
Negative effects on industries like agriculture, fishing, and tourism that rely on stable climate and natural resources
Summary of greenhouse effect
(1-6)
1. Solar Radiation Reaches Earth
The Sun emits shortwave radiation (mainly visible light and UV).
This radiation passes through the atmosphere and is absorbed by Earth’s surface, warming it.
2. Earth Re-emits Energy as Infrared Radiation
The warmed Earth re-emits energy back toward space as longwave infrared (IR) radiation (heat).
3. Greenhouse Gases Absorb Infrared Radiation
Greenhouse gases (like carbon dioxide, methane, water vapour, and nitrous oxide) in the atmosphere absorb some of this infrared radiation.
These gases are transparent to incoming shortwave radiation but trap outgoing longwave IR radiation.
4. Re-radiation in All Directions
After absorbing the infrared radiation, greenhouse gases re-radiate the energy in all directions, including back toward Earth’s surface.
5. Surface Warming
The downward re-radiated infrared energy increases the temperature of the lower atmosphere and Earth’s surface.
This is what creates the natural greenhouse effect, which keeps Earth’s average temperature around 15°C.
6. Enhanced Greenhouse Effect (Human Impact)
Human activities (burning fossil fuels, deforestation, agriculture) increase concentrations of greenhouse gases.
This leads to more infrared radiation being trapped, enhancing the natural greenhouse effect and causing global warming.