Psych 250 Exam 1 Study Guide
1/259
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
260 Terms
Definition of development
A process of age-related changes across the lifespan, changes in growth, feelings, patterns of thinking.
Five assumptions of life-span perspective
Development is lifelong
Development is multidimensional
Development is multidirectional (a joint expression of growth and decline)
Development is highly plastic (open to change)
Development is affected by multiple interacting influences
Elaborate on “Development is multidirectional”
Multiple mechanisms (biological, psychological, social)
Multiple domains (physical, cognitive development, psychosocial)
Elaborate on “Development is affected by multiple interacting influences”
Age-graded influences, history-graded influences, nonnormative influences
Age-graded influences
Influences that are similar for individuals in a particular age group (e.g. most kids learn to walk at age 1)
History-graded influences
Forces that influence the behavior and attitudes of individuals in a certain generation at a formative time of their lives (e.g. pandemic, war)
Non-normative influences
Unusual occurrences that have a major impact but not applicable to many people (e.g. car crash, cancer, winning lottery)
Resilience
The ability to adapt effectively and achieve positive outcomes despite adversity or risk
Major protective factors that foster resilience
Personal characteristics (e.g. high intelligence, easygoing, self-regulated temperament, talents)
Warm relationship with at least one parent
Supportive relationships outside the immediate family
Community resources and opportunities
Definition and function of theory
A theory is an orderly, integrated set of statements that describes, explains, and predict behavior. Useful because they offer practical guidance in our everyday decision making.
Dimensions on which theories differ
View of the developing person —> organismic vs. mechanistic
View of the course of development —> continuous vs. discontinuous development
View of the determinants of development —> contributions of nature vs. nurture
View of the developing person
Organismic theories – change stimulated from within the organism, active
Mechanistic theories – change stimulated by the environment, passive
View of the course of development
Continuous development – gradually adding on more
Discontinuous development – new understandings emerge at particular periods/stages… qualitative changes
View of the determinants of development
Nature – genetic, inborn qualities
Nurture – learning and experiences
Premises of Freud’s Psychosexual theory
A. Basic personality and psychological functioning is determined by:
Id: (1) present at birth, (2) represents biological needs/desires, (3) requires immediate gratification; unconscious
Ego: (1) conscious, rational, problem-solving part, (2) emerges in early infancy, (3) restricts id; masters and controls urges
Superego: (1) moral and ethical component, (2) develops from ages 3 to 6, (3) includes conscious and ego-ideal
B. Personality development is determined by how parents manage child’s early sexual and aggressive drives
General premises of Erikson’s theory
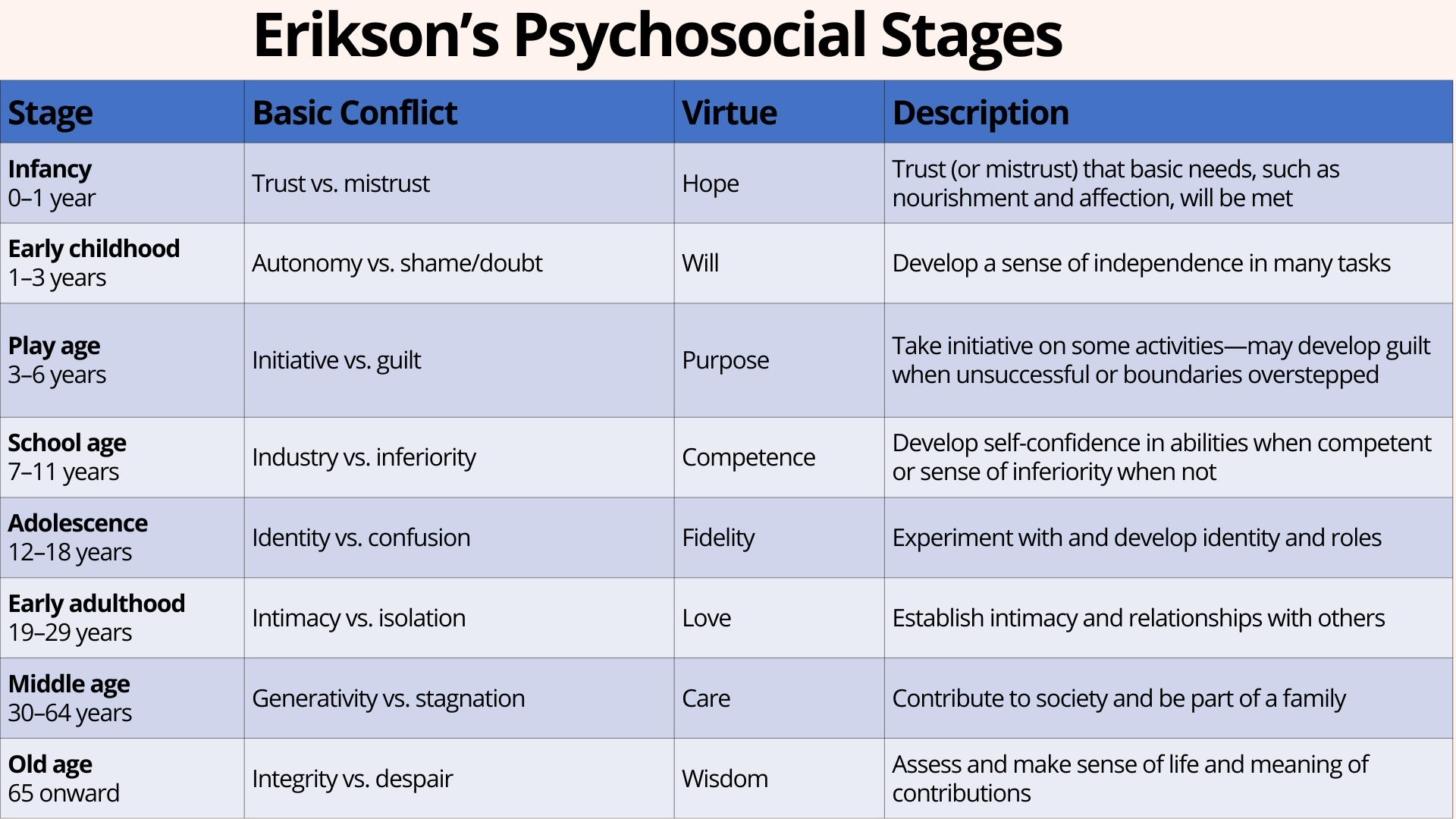
Similarities & differences between Freud’s & Erikson’s theories
Covers the lifespan
Viewed personality development as a psychosocial process (social interactions + culture)
Emphasized psychosocial crisis/conflict – successful mastery results in personality strength/virtue
More emphasis on ego than id
Ego identity
Basic sense of who we are as individuals in terms of self-concept and self-image
General contributions & limitations of psychoanalytic perspective
Contributions:
Emphasis on the individuals’ unique life history
Inspired research on many aspects of emotional and social development
Limitations:
So strongly committed to in-depth study of individuals failed to consider other methods
Many psychoanalytical ideas are too vague to be tested empirically
Traditional behaviorism - Watson
Observable stimulus – response associations
Classical conditioning
Skinner’s Operant Conditioning
Consequences of a behavior determine whether or not it will be repeated in the future
Reinforcement – increases likelihood (positive = something added, negative = something removed)
Punishment – decreases likelihood
Bandura’s Social Cognitive Theory
Model/observational learning – results from observing other people
Humans as cognitive beings – active processing of info from the environment plays a major role in learning
Complex process – many factors govern decision-making – e.g. who to model?
Piaget’s Cognitive Development Theory
Nature of child: active, naïve, scientist – constructivist
Nature of change: learning in stages; thinking becomes qualitatively different across these stages
Processes of change
Assimilation – children incorporate new info into existing knowledge systems
Accommodation – children change existing knowledge systems to accommodate new info
Contributions and limitations of Piaget’s theory
Contributions
Convinced the field that children are active learners whose minds consist of rich knowledge
Increased research on children’s conceptions of themselves, other people, and human relationships
Encouraged the development of educational philosophies and programs that emphasize discovery learning and direct contact with the environment
Limitations
Underestimated the competencies of infants and preschoolers
Children’s performances on Piagetian problems can be improved with training
Information Processing Theory
Human mind as symbol manipulating system through which information flows - use computer analogies to model - focus on steps involved in mental activities
Not stagelike - perceive change as increases in children’s knowledge
Developmental neuroscience
Studies the relationship between changes in the brain and the developing person’s cognitive processing and behavior patterns
Ethology
Concerned with the adaptive, or survival, value of behavior and it’s evolutionary history
Sensitive period
A time that is biologically optimal for certain capacities to emerge because the individual is especially responsive to environmental influences
Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory of Cognitive Development
Focuses on how culture is transmitted
Higher mental functions grow out of social interactions and dialogues - cooperative dialogues
Cognitive development is a socially mediated process
Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory
Person develops within a multi-layered system of relationships
5 systems
Microsystem - person’s immediate environment
Mesosystem - connections between microsystems
Exosystem - outside contexts that affect microsystem
Macrosystem - cultural laws, values, customs
Chronosystem - temporal component - change over lifecourse and history
Systematic observation
Organized observation of behavior without self report (naturalistic observation, structured observation)
Naturalistic observation
Observing behavior in a natural real-world setting
Example: Watching children on a playground
Strength - high realism
Limitation - no control, no cause and effect
Structured observation
Observing behavior in a controlled setting using predefined categories.
Example: Behavior recorded in a lab with a checklist
Strength - more control and consistency
Limitation - less natural behavior
Self-report methods
Participants report their own thoughts, feelings, or behaviors.
Clinical interview
Flexible, open-ended interview.
Example: Therapist asks follow-up questions
Strength - detailed information
Limitation - interviewer bias
Structured interview
Interview with standardized questions.
Example: Everyone asked the same questions
Strength - reliable and consistent
Limitation - less depth
Questionnaire
Written or online survey
Example: Rate statements from 1 to 5
Strength - fast, inexpensive, efficient
Limitation - self-report bias
Clinical/Case Study
In-depth study of one person or small group
Example: Rare disorder studied closely
Strength - detailed insight
Limitation - cannot generalize
Ethnography
In-depth study of a culture through immersion
Example: Researcher lives in the community
Strength - rich cultural understanding
Limitation - time-consuming, researcher bias
Correlational design
Research method that examines the relationship between two variables without manipulation.
Correlational coefficient
A numerical value (–1 to +1) showing the strength and direction of a relationship.
Independent variable
The variable manipulated or measured by the researcher.
Dependent variable
The variable measured as the outcome.
Random assignment
Placing participants into groups by chance.
Field experiment
An experiment conducted in a real-world setting with manipulation of variables.
Natural (Quasi) experiment
Study where the independent variable occurs naturally and is not manipulated.
Cross-sectional design
Compares different age groups at one time.
Example: Researchers compare memory ability in 6, 12, and 18 year-olds at the same time
Strength - fast
Limitation - cohort effects
Longitudinal design
Studies the same participants over time.
Example: Researchers follow the same group of children from age 5 to age 15, testing memory every 2 years.
Strength - tracks individual development
Limitation - time-consuming; participant dropout
Sequential design
Combines cross-sectional and longitudinal designs.
Example: Researchers study two age groups (5-year-olds and 10-year-olds) and follow both groups over 10 years.
Strength - reduces cohort effects
Limitation - complex
Cohort effects
Differences in behavior or abilities caused by shared experiences of a specific age group, not by age itself.
Genotype
Genetic make-up, set of genes inherited
Phenotype
The way an individuals genotype is expressed in observable characteristics - depends on genes and environment
Gene
Segment of DNA along the length of the chromosomes - contains hereditary instructions
DNA
Active biochemical substance that programs the cells to manufacture vital protein substances
Chromosomes
Rodlike structure inside cell nucleus that store and transmit genetic info (autosome & sex chromosomes)
Autosome
Regular pairs (22/23)
Sex chromosomes
23rd pair - determine sex of child
Chromosomes are made of
DNA
Genes come in different forms known as
Alleles (homozygous & heterozygous)
Homozygous
Alleles in the pair are the same
Heterozygous
Alleles in the pair differ
Sex cells are called
Gametes (sperm, ova) - hold 23 chromosomes instead of 46
Dominant-recessive
Dominant gene in pair overrides recessive gene
Incomplete dominance
Both the dominant and recessive allele are expressed
X-linked inheritance
Recessive gene carried on X chromosome in 23rd pair
Woman are protected; men are not protected
Genomic imprinting
Genes chemically marked or imprinted & will behave differently depending on whether they came from a mother or father
Polygenic inheritance
Multiple genes interact to produce a characteristic
Mutation
A random change in a gene or DNA sequence.
In Vitro Fertilization
Fertilization of an egg outside the body, then implanted in the uterus.
Surrogate Motherhood
A woman carries a pregnancy for another person or couple.
Reproductive Frontiers
New and advancing technologies that expand reproductive possibilities.
Heritability estimates
Measure the extent to which individual differences in complex traits in a specific population are due to genetic factors
Cannot be applied to a single individual
Not a precise statistic
Personality traits - rates typically range from .4 to .5
Schizophrenia - .8
Kinship studies
Examine patterns of behaviors and traits in family members
Concordance rates
Percentage of instances in which both twins show a trait when it is present in one twin
Dizygotic (fraternal) twins
Two fertilized ova - share 50% of genes
Monozygotic (identical) twins
One zygote that divides into 2 individuals - share 100% of genes
Gene-environment interaction
Individuals, because of their different genetic makeups, will differ in their reactions to qualities of the environment
Passive genotype/environment interactions
Parents provide environment influenced by own heredity
Because they are genetically related, child may be predisposed to be responsive to this environment
Evocative genotype/environment interactions
Different genetically-based attributes evoke certain responses
Niche-picking/Active influences
Individuals seek out environments most compatible with their genetic predispositions
Niche-picking is more central as children age
Epigensis
Development results from ongoing bidirectional exchanges between heredity and all levels of environment
Epigenetic transmission of maternal stress
Stress experienced by a mother can alter gene expression in her child without changing the DNA sequence.
Socioeconomic status
Assessed by parents education, occupation prestige, income
Families confronted with issues due to poverty
Inadequate housing and dangerous and unhealthy neighborhoods
More household disruption, daily hassles, frequent crises
Fewer neighborhood resources (parks, supermarkets)
Fewer cognitive enrichment opportunities, both at home and in their neighborhoods
Consequences of poverty for the child
Discipline and parenting
Physical health status
Socio-emotional functioning
Cognitive functioning
Evans & English (2002)
Examined the impact of poverty, testing exposure to multiple risks and their impact on stress and socio-emotional adjustment
168 U.S. households that fell at or below poverty lines and 119 middle-income families
Focused on children in grades 3-5 (97% white)
Measures
3 psychosocial stressors: exposure to violence, family turmoil, family separation
3 physical stressors (crowding, noise level, housing quality)
Socio-emotional adjustment
Chronic stress
Findings
Poor children exposed more often to each stressor domain than middle-income children
Poverty —> greater psychological distress & more chronic stress
Collectivism
Prioritizing group goals and harmony over individual desires.
Individualism
Prioritizing personal goals and independence over group needs.
Development niche
The interaction of components that affect what goes on within the microsystem and determines the unique world of the child.
Developmental niche components
Culture shapes multiple dimension of our everyday physical and social settings
Size and type of living space
Sleeping and eating schedules & locations
Social conditions (resources, people, material goods)
Daily activities of children
Culture shapes childcare & childrearing customs
Culture shapes overall psychology of the caregivers
Goals
Expectations
Morals
What is a Bad Kid? (Crystal & Stevenson, 1995)
Expected that perceptions of deviance, like perceptions of normalcy, would be influenced by sociocultural values
Surveyed 200+ 11th graders & their mothers: Minneapolis, Taipei, Sendai
Think of what a “bad kid” would be
Cultural differences in responses
General dynamics of conception
Ovulation - approx. every 28 hours
Ovum survives 24 hours
Sperm cells survive up to 5 or 6 days
Brief window
Fertilization = union of sperm & ovum; genetic material fuses
3 prenatal periods
Germinal, embryonic, fetal
Period of the Zygote (Germinal Period)
First stage of prenatal development
From fertilization —> implantation
Lasts about 2 weeks (ends with implantation…7-9 days after fertilization)
Zygote
Fertilized egg (germinal period)
Blastocyst
Hollow-fluid filled ball of cells (germinal period)
Embryonic disk
Cells on inside - become new organism (germinal period)
Trophoblast
Outer ring of cells - will develop into these 3 lie-support systems (germinal period)
Trophoblast #1 - Amnion
Protective covering - encloses organism in amniotic fluid, a cushion & temperature regulator (germinal period)
Placenta
A disc-shaped mass of tissue-partial filter - permits food and oxygen to reach organism and waste products to be carried away (germinal period)