c1900–present: Modern Britain
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
Understanding genetics
1. During the __*19th century*__, ==**Mendel**== showed how human characteristics could be passed between generations.
2. In the __*20th century*__ new technology (electron microscopes, X-rays) let scientists analyse human cells in greater detail. They found that every cell in the body contains DNA – codes controlling the genes of each person.
3. ==**James Watson and Francis Crick**== worked together on how the genetic codes of DNA fitted together.
4. They analysed X-ray crystallography by Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin at King’s College Hospital (London) and eventually worked out the double helix structure of DNA (1953).
5. In 1990 James Watson led the ==**Human Genome Project**== and started identifying and mapping every gene in human DNA.
3
New cards
Discovering the structure of DNA and the work of the Human Genome Project has led to:
✔️ a better understanding of some genetic conditions, such as Down’s syndrome
✔️ predicting whether individuals are at higher risk of developing some cancers
✔️ the discovery that stem cells can be grown into different cells.
better vaccines for some conditions
✔️ predicting whether individuals are at higher risk of developing some cancers
✔️ the discovery that stem cells can be grown into different cells.
better vaccines for some conditions
4
New cards
probs with discovery of structure of dna
__**However, there is not yet a:**__
❌ cure or effective treatment for most genetic conditions
❌ way of preventing most genetic diseases.
❌ cure or effective treatment for most genetic conditions
❌ way of preventing most genetic diseases.
5
New cards
lifestyle factors
==**Smoking**== Research now links smoking with many diseases, such as emphysema, high blood pressure, heart disease and many cancers.
\
**Drinking alcohol** Research now links drinking too much alcohol to many cancers, as well as liver and kidney disease.
\
%%**Diet**%% Scientific research has confirmed that eating a balance of different foods and limiting sugar and fat reduces the chances of getting certain types of cancer or heart disease
\
**Drinking alcohol** Research now links drinking too much alcohol to many cancers, as well as liver and kidney disease.
\
%%**Diet**%% Scientific research has confirmed that eating a balance of different foods and limiting sugar and fat reduces the chances of getting certain types of cancer or heart disease
6
New cards
Improvements in diagnosis
The 20th century saw huge changes in the ways that doctors diagnosed illness. Although doctors today still use their own knowledge and medical books, they combine this with medical testing, using science and technology to discover what is wrong.
\
*This includes the use of:*
• laboratories to test skin or blood
• x-rays, scans and endoscopes to ‘see’ inside the body with more clarity than ever before
• monitors to see what is going on over a period of time.
\
Improved scientific understanding and technology has made diagnosing disease far more accurate.
\
*This includes the use of:*
• laboratories to test skin or blood
• x-rays, scans and endoscopes to ‘see’ inside the body with more clarity than ever before
• monitors to see what is going on over a period of time.
\
Improved scientific understanding and technology has made diagnosing disease far more accurate.

7
New cards
Examples of technology used in 20th and 21st century medicine
1. Incubators
2. X-rays
3. Microscopes
4. MRI, CT and ultrasound scans
5. Endoscopes
6. Insulin pumps
7. Hypodermic needles
8. Prosthetic limbs
9. Dialysis machines
10. Pacemakers
11. Blood pressure and blood sugar monitors
8
New cards
Magic Bullets timeline
1. %%**Koch**%% discovered that different chemical dyes stained specific microbes & %%**Behring**%% discovered the body manufactures antitoxins that only attack the microbe causing a disease.
2. %%**Paul Ehrlich**%% and his team of researchers searched for a ***‘magic bullet’*** – a chemical compound that would attack and kill the microbe causing a specific disease.
3. The team, helped by German government funding, worked for many years. They tested many compounds of %%**Salvarsan to find one to cure syphilis.**%%
4. In 1909, %%**Dr Hata**%% joined the team and discovered they had rejected a compound that worked – the 606th!
1. Other scientists checking %%**Domagk’s**%% work found that the key ingredient in Prontosil, sulphonamide, also cured pneumonia, scarlet fever and meningitis.
\
9
New cards
Antibiotics
1. Antibiotics destroy bacteria or prevent its growth. The **first to be discovered was penicillin.**
\
2. Scientists, inspired by the discovery of penicillin, experimented with other moulds and found more antibiotics that were effective against different diseases throughout the 1940s, 50s and 60s.
\
1. Once the chemical structure of different antibiotics was discovered, scientists were able to make antibiotics, which solved the problem of having to grow them first in order to amend them to treat further diseases.
\
3. Antibiotics have saved and extended millions of lives but due to overuse, **super-bacteria,** which are resistant to antibiotics, have evolved.
10
New cards
Where possible, always use specific examples to demonstrate your knowledge. Examples of high-tech medical and surgical treatments include:
1. radiotherapy and chemotherapy
2. kidney dialysis
3. fitting pacemakers
4. organ transplants.
11
New cards
Advances: keyhole and microsurgery
With the development of tiny cameras and surgical instruments, surgeons can use small incisions instead of large cuts to access the body, which reduces patients’ recovery time. The small instruments also make it possible to reattach nerves and blood vessels.
12
New cards
Advances: robotic surgery
Some surgery can now be carried out remotely, with surgeons controlling robots through computers. This has also made surgery more precise.
13
New cards
The NHS
Since 1948, taxes have funded a wide range of healthcare provided by the National Health Service, such as:
\
1. seeing a GP
1. hospital care and operations
2. health visitors for pregnant women and young children
3. ambulances and emergency treatment
4. health care for the elderly.
\
1. seeing a GP
1. hospital care and operations
2. health visitors for pregnant women and young children
3. ambulances and emergency treatment
4. health care for the elderly.
14
New cards
Improved access to care
The establishment of the NHS improved access to healthcare because all treatment was entirely free, so everyone could access the same care.
However, healthcare provision was unequal across different parts of the country, both in terms of the number of doctors and hospitals and their standards, and this took time to improve.
Some types of healthcare are still difficult to access. For example, few people receive NHS dental treatment due to a lack of NHS dentists.
\
In general though, far more people access healthcare today than in 1900.
However, healthcare provision was unequal across different parts of the country, both in terms of the number of doctors and hospitals and their standards, and this took time to improve.
Some types of healthcare are still difficult to access. For example, few people receive NHS dental treatment due to a lack of NHS dentists.
\
In general though, far more people access healthcare today than in 1900.
15
New cards
Compulsory vaccinations
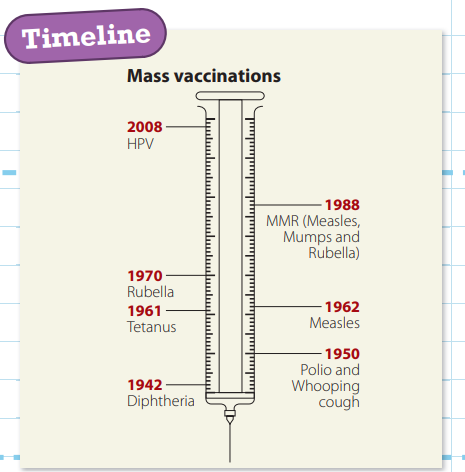
Although many vaccines that successfully prevented some diseases had been developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, people had to pay to receive them and many could not afford to do so. In 1938, 3000 people died in a diphtheria epidemic, which led to a government-funded immunisation programme. This has been followed by many others. Vaccination is still controversial, however, and some people choose not to have their children vaccinated.
16
New cards
Prevention measures
Since 1948, the government has taken more action to prevent people getting ill.
• Funding more testing and vaccinations.
• Better disposal of rubbish and sewage.
• Laws reducing air and water pollution.
• Laws banning the advertising of cigarettes and smoking in public places.
• Laws improving health and safety at work.
• Environmental health officers inspecting food outlets.
• Funding more testing and vaccinations.
• Better disposal of rubbish and sewage.
• Laws reducing air and water pollution.
• Laws banning the advertising of cigarettes and smoking in public places.
• Laws improving health and safety at work.
• Environmental health officers inspecting food outlets.
17
New cards
Lifestyle campaigns
Since 1948, the government has funded publicity to raise awareness of illnesses and dangers to health, such as smoking and binge-drinking, with some success: the 1980s ‘AIDS: don’t die of ignorance’ campaign reduced cases of HIV infection. More recently, events and initiatives such as the Change4Life campaign, have encouraged healthy behaviour to prevent disease.
18
New cards
Alexander Fleming
Fleming worked on the battlefields of the First World War. Part of his job was to study soldiers’ infected wounds and try to find treatments. Many died from their infections. After the War, he worked at St Mary’s Hospital in London, where he continued his work to try to find a way of healing bacterial infections.

19
New cards
Howard Florey and Ernst Chain
Florey was an Australian pathologist who was researching ways to kill bacteria at Oxford Medical School. He assembled a group of scientists to help him. One of his first recruits was the German biochemist, Ernst Chain. They, together with Fleming, won the Nobel prize in Physiology or Medicine, in 1945.

20
New cards
Discovery of penicillin
1. In 1928, Alexander Fleming noticed that bacteria in a Petri dish was being killed by a penicillium mould. He tested it on other bacteria and discovered that the mould produced an excellent antibiotic (penicillin).
2. In 1929, Fleming published his findings but did not believe that penicillin would work on living people and did not ask for funding to continue his research.
3. Several years later, Howard Florey, Ernst Chain and their team continued Fleming’s research on penicillin.
4. It proved effective on mice, so they tested it on humans. Penicillin killed bacteria and therefore the infection – it was a miracle drug!
21
New cards
Timeline of the journey of penicilin
%%**1928**%% Fleming recognises that mould kills bacteria.
%%**1929**%% Fleming publishes his findings.
%%**1939**%% Florey and Chain continue Fleming’s research.
%%**1940**%% Penicillin proves effective on mice.
%%**1941**%% US drug companies agree to help fund the production of penicillin. Penicillin proved effective on humans. In December the USA enters the Second World War.
%%**1942**%% Mass production of penicillin by US drug companies financed by US government.
%%**1943**%% Mass production of penicillin by UK drug companies.
%%**1945**%% Crowfoot Hodgkin identified penicillin’s chemical structure.
%%**1951**%% First chemical copy of penicillin created.
%%**1929**%% Fleming publishes his findings.
%%**1939**%% Florey and Chain continue Fleming’s research.
%%**1940**%% Penicillin proves effective on mice.
%%**1941**%% US drug companies agree to help fund the production of penicillin. Penicillin proved effective on humans. In December the USA enters the Second World War.
%%**1942**%% Mass production of penicillin by US drug companies financed by US government.
%%**1943**%% Mass production of penicillin by UK drug companies.
%%**1945**%% Crowfoot Hodgkin identified penicillin’s chemical structure.
%%**1951**%% First chemical copy of penicillin created.
22
New cards
Mass production of penicillin
Penicillin still wasn’t used for medical
treatment because huge amounts were
needed to treat one person, and growing
the mould took time and lots of space and
was therefore expensive.
1. Florey asked UK drug companies and factories to help, but these were being used for the war effort.
2. In 1941, Florey asked US drug companies. Some agreed to help but on a very small scale.
3. The effectiveness of penicillin was demonstrated.
4. After the USA joined World War Two, the government saw the need for more penicillin to treat casualties and funded 21 companies to mass-produce it.
5. US drug companies began mass production of penicillin in 1942 and British drug companies did so in 1943.
treatment because huge amounts were
needed to treat one person, and growing
the mould took time and lots of space and
was therefore expensive.
1. Florey asked UK drug companies and factories to help, but these were being used for the war effort.
2. In 1941, Florey asked US drug companies. Some agreed to help but on a very small scale.
3. The effectiveness of penicillin was demonstrated.
4. After the USA joined World War Two, the government saw the need for more penicillin to treat casualties and funded 21 companies to mass-produce it.
5. US drug companies began mass production of penicillin in 1942 and British drug companies did so in 1943.
23
New cards
Diagnosis of lung cancer
Symptoms of lung cancer include a persistent cough, coughing up blood, breathlessness, tiredness, unexplained weight loss and repeated chest infections, but these can be symptoms of many other conditions, too, and the cancer is often very developed when symptoms show up. If lung cancer is suspected, most patients are given a **CT** scan and if this shows a mass, a sample of the cells are collected and tested.
24
New cards
Treatment of lung cancer
The following are treatments that can cure the cancer or prolong the life of the patient.
1. Surgery to remove the tumour or carry out a lung transplant.
2. Radiotherapy to try to shrink the tumour or prevent its growth.
3. Chemotherapy to try to shrink the tumour, or prevent the cancer returning.
1. Surgery to remove the tumour or carry out a lung transplant.
2. Radiotherapy to try to shrink the tumour or prevent its growth.
3. Chemotherapy to try to shrink the tumour, or prevent the cancer returning.
25
New cards
Prevention of lung cancer
The UK government has tried various methods to reduce the number of people smoking, to prevent them developing lung cancer.
1. TV advertising for cigarettes was banned in 1965, and for cigars and tobacco in 1991. All forms of advertising have since been banned.
2. Tax on tobacco products is regularly increased to make smoking more expensive and to encourage people to stop.
3. In England in 2007, smoking was banned in public places where people worked and this ban was extended in 2015 to cars carrying under-18s.
4. In 2007, the legal age for buying tobacco products was raised from 16 to 18.
5. Various campaigns have been funded to educate people about the risks of smoking, to encourage them to stop or not to start.
6. Today, shops are not allowed to publically display tobacco products.
7. Cigarette packaging became standardised in May 2016, all cigarettes are sold in green packets and with graphic warnings of the dangers, whatever the brand.
1. TV advertising for cigarettes was banned in 1965, and for cigars and tobacco in 1991. All forms of advertising have since been banned.
2. Tax on tobacco products is regularly increased to make smoking more expensive and to encourage people to stop.
3. In England in 2007, smoking was banned in public places where people worked and this ban was extended in 2015 to cars carrying under-18s.
4. In 2007, the legal age for buying tobacco products was raised from 16 to 18.
5. Various campaigns have been funded to educate people about the risks of smoking, to encourage them to stop or not to start.
6. Today, shops are not allowed to publically display tobacco products.
7. Cigarette packaging became standardised in May 2016, all cigarettes are sold in green packets and with graphic warnings of the dangers, whatever the brand.
