Abrasives, Abrasion and Polishing
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Mechanical Properties
Characteristics of dental materials that determine their performance under stress.
Polymerization
The process of reacting monomer molecules together to form polymer chains.
Hydrocolloid Impression Materials
Materials that form gels when mixed with water, used for dental impressions.
Elastomeric Impression Materials
Flexible materials that record tooth and gum structures when set.
Lost-Wax Casting Technique
A method for creating dental restorations where a wax pattern is melted away.
Surface Roughness
The texture of a surface, determined by small-scale deviations or irregularities.
Finishing
The refinement of a surface prior to polishing, ensuring proper fit and shape.
Polishing
The process of making a surface smooth and glossy by abrasion.
Abrasive Index (AI)
A measure of the amount of material abraded from a dental surface in a specified time.
Dental Cements
Materials used to bond or affix dental restorations to tooth structures.
Mechanical Testing
A method to evaluate the properties of a material under various mechanical loads.
Diamond Burs
Dental tools embedded with diamond particles used for cutting and polishing.
Air-Water Spray Coolants
A mixture of air and water used to reduce heat during dental procedures.
What kind of prosthesis is finishing?
Interim
What kind of prosthesis is polishing?
Definitive
State the steps of a direct restoration
Diagnostic
Tissue Management
Isolation
Decay Removal
Cavity Preparation
Sectional Matrix
Lingual Matrix
Bonding
Composite
Placing, Shaping, Blending and Curing
Finishing
Polishing
Procedure systems
Define Abrasion
Wear or material loss from a surface as a result of scratching or other mechanical means
What is a substrate in dental abrasion
Material being abraded
What is abrasive?
Material that causes wear
What is two-body abrasion?
Abrasive particles are tightly bonded to the abrasive instrument that is removing material from the substrate surface
What is three-body abrasion?
Involves the use of non-bonded abrasives, abrasive particles are free to translate and rotate between two surfaces
What is airborne particle abrasion?
Abrasive particles are propelled (sandblasted) against a substrate by air pressure to remove surface material
What are some factors that affect the rate of abrasion?
Hardness between the abrasive and the substrate
Particle size of abrasive
Particle shape of abrasive
speed & pressure
lubrication
What is the hardness between the abrasive and the substrate?
Relative hardness of minerals using a scale
What does the Mohs values indicate?
The resistance to scratching of one material by another
What is the Mohs Hardness Test?
This test compares the resistance of a mineral by scratching with ten reference minerals known as the Mohs Scale Materials
What is the Mohs Hardness Scale
It is determined by scratching the surface of the tile with different minerals and subjectively assigning a “Mohs” number
When/how is pumice created?
When super-heated, highly pressurized rock is violently ejected from a volcano
What is the hardness of pumice?
6
What is the hardness of dentin and hard gold alloy?
3-4
What is the hardness of enamel?
5-6
What is the indentation hardness test?
The size or the depth of the indentation and the amount of force used to calculate a hardness value
What is the particle size of superfine abrasive?
<10 micrometers
What is the particle size of fine abrasive?
10-20 micrometers
What is the particle size of medium abrasive?
20-100 micrometers
What is the particle size of coarse abrasive?
100-500 micrometers
For the same applied pressure, larger particles
leave larger scratches in the substrate
For the same applied pressure, smaller particles
leave smaller scratches in the substrate
A sharp particle produces
Deeper abrasion than rounder particle under the same applied force
Equivalent sized scratches can be produced by different sizes of particles by
Varying the applied pressure
What is the purpose of lubrication?
To reduce heat build up, and to wash away debris to prevent clogging of the abrasive instrument
What stops metal to metal contact and reduces wear in engines
Oil or maintenance as a lubricant
What is the rotational speed of a low speed rotary grinding instrument?
< 20,000 rpm
What is the rotational speed of a medium speed rotary grinding instrument?
20,000 to 200,000 rpm
What is the rotational speed of a high speed rotary grinding instrument?
> 200,000 rpm
What is an air turbine?
Balance between speed and torque, faster and consistent cutting and grinding
Air driven handpieces have a faster bur speed, but are also
High-pitched (lounder sound)
Name some finishing and polishing instruments
Carbide burs
Diamond burs
Dental stones
Rubber wheels
Disks and strips
What are the three basic parts of carbide and diamond burs?
The shank, the neck, and the head
This portion of the bur can vary to accommodate contra-angled or straight handpieces
The shank
What are the two difference types of shanks?
Friction (high speed), and Latch-type for slow speed
What material are bur shanks made of?
stainless steel
What material are cutting blades made of?
Tungsten carbide
What are carbide burs used for
Contouring and finishing
This is how mnay fluted blades you can see on a carbide bur
8-30 either straight or twisted
What is the straight blade design?
One blade on toothW
What is the spiral blade design?
Several blades on tooth
What are the components of a carbide bur blade design?
Clearance Face
Rake Faces
Rake Angle
Radical Line
Direction of Rotation
What is the rake angle
The angle made between the rake face and the line connecting the edge to the axis of the bur
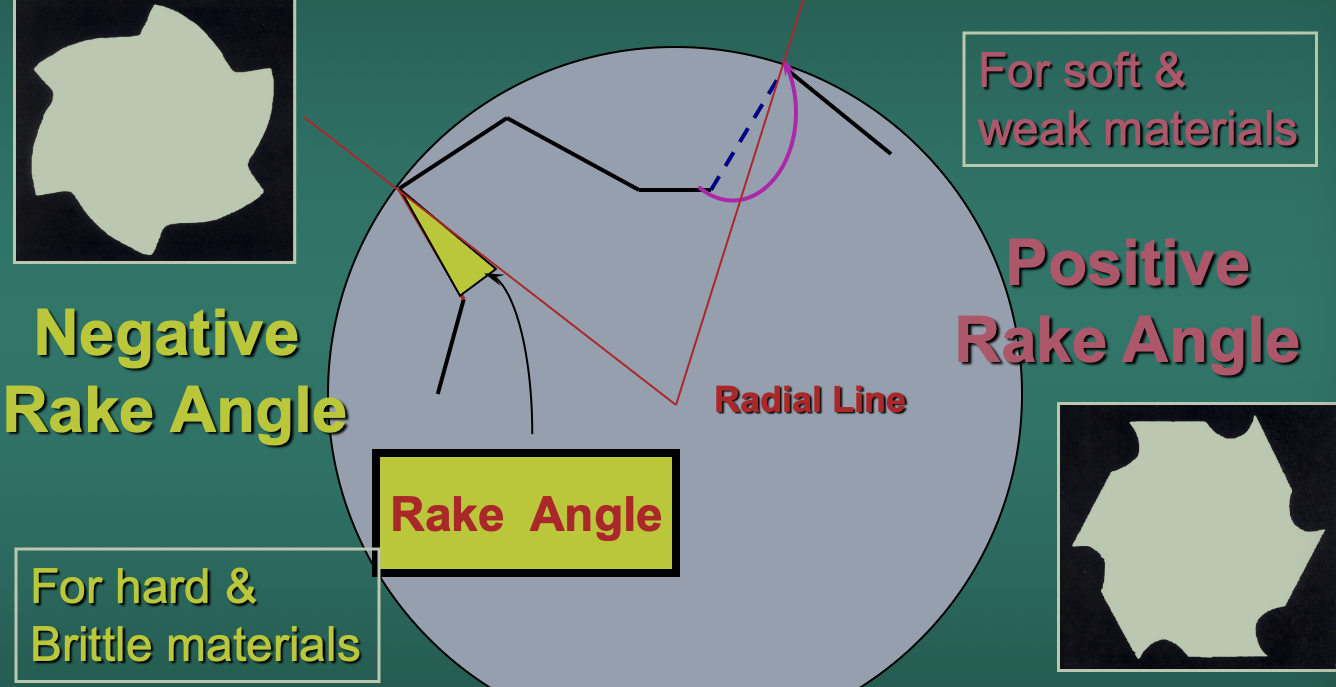
What is a negative rake angle?
The radial line lies behind the rake face and entirely within the blade
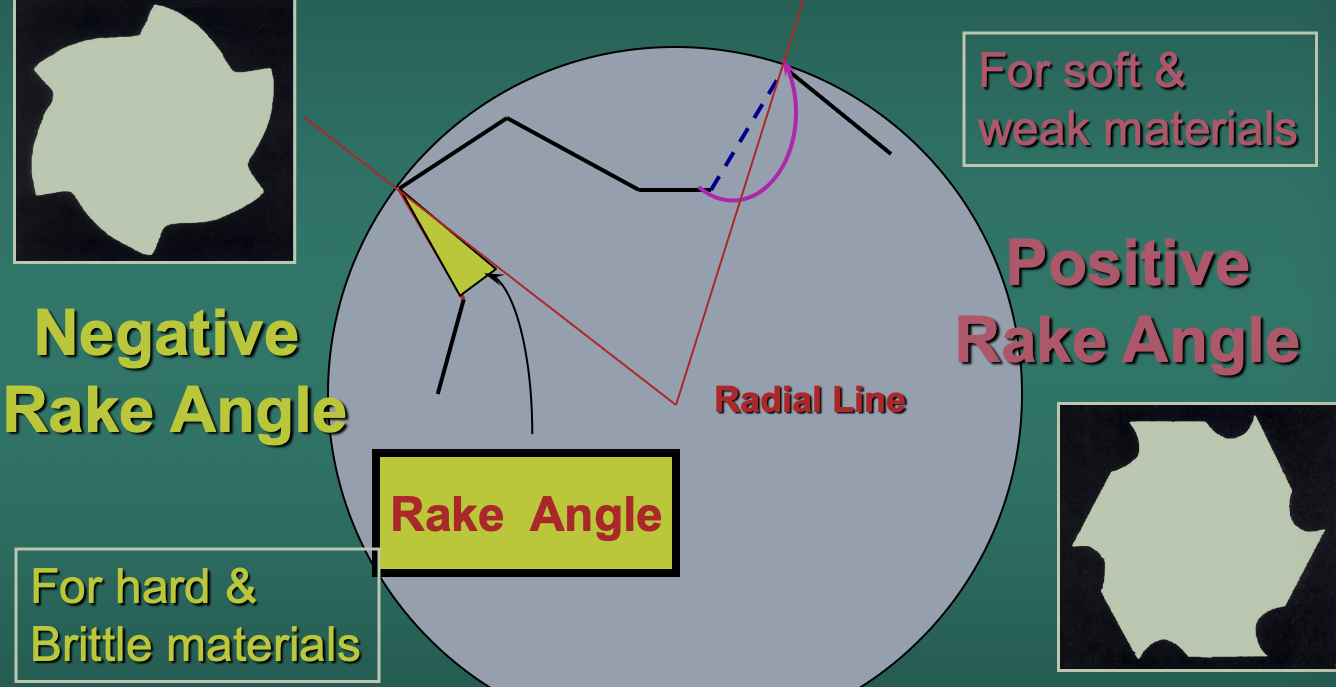
What is a positive rake angle?
The radius lies outside the blade, the rake angle is positive
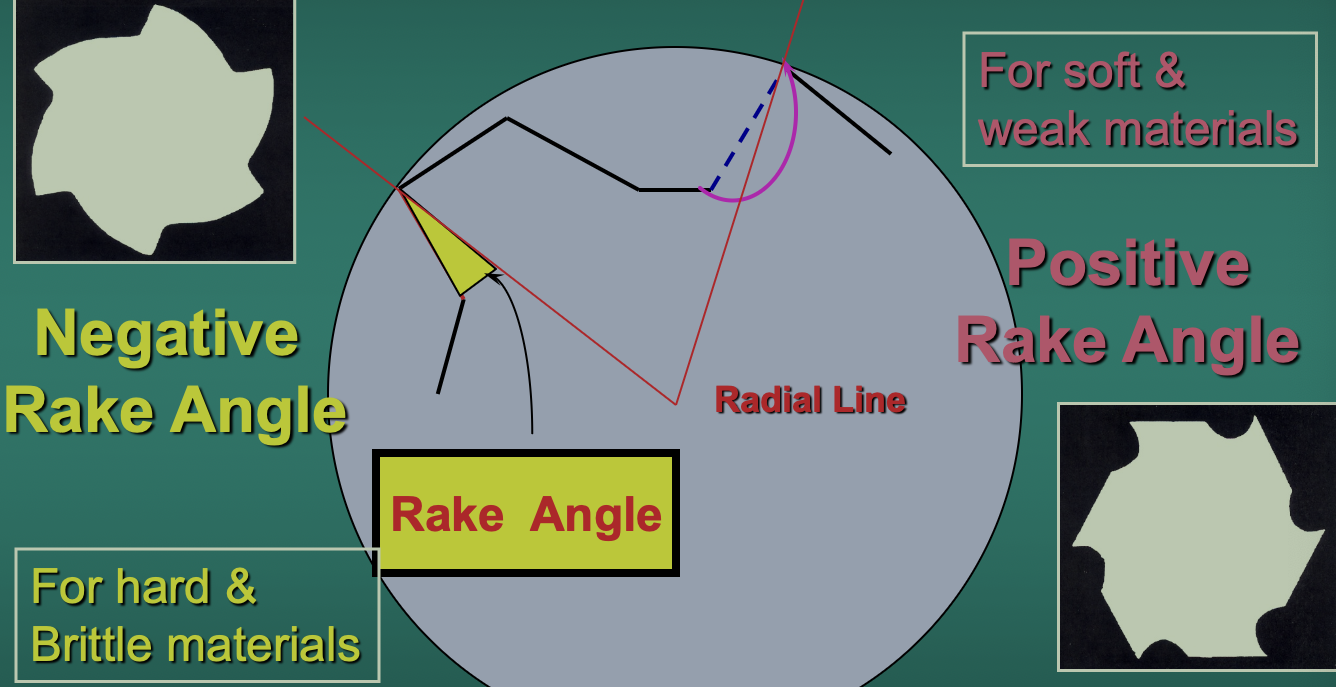
What does a large rake angle mean?
Lower strength of cutting edge
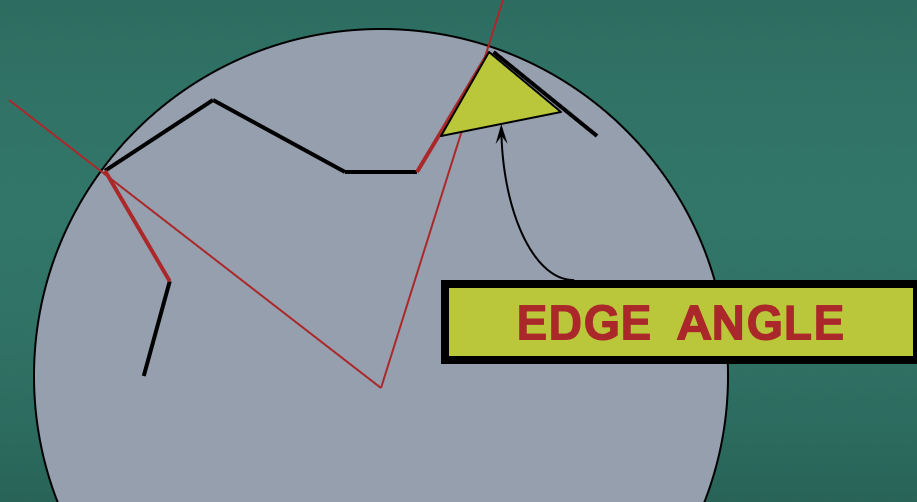
What is the edge angle?
The internal angle at the edge formed by the two faces of the bur blade, it is related to the resistance of the blade to fracture
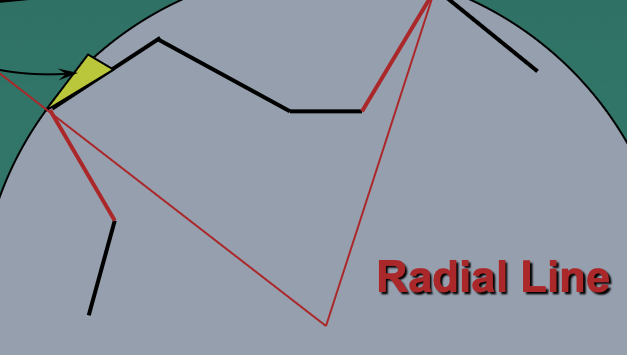
What is a clearance angle?
The angle between the clearance face immediately behind the edge and a tangent to the path of rotation
What are the purposes of the clearance angle?
To eliminate rubbing friction of the clearance face of the blade against the new tooth surface
To provide a stop to prevent the bur edge from digging into the tooth structure excessively
To provide adequate clearance space for the chips formed ahead of the following blade
What is a rake angle?
Cutting edge strength
What is an edge angle?
Blade strength
What is a clearance angle
Provide a stop and space
What are diamond instruments used for?
Finishing diamonds are used to contour, adjust, and smooth composites or porcelain
What is a diamond bur?
A stainless steel shank
Powered diamond abrasive
DiA metallic bonding material that holds the diamond powder onto the shank
Diamond burs should always be utilized with
water spray
Other polishing instruments, such as rubber polishing instruments or pastes, will usually
follow the use of diamonds
What are carbide burs better for?
End-cutting, produce lower heat, and have more blade edges for cutting
What are diamond burs better for?
More effective for tooth preparation, beveling enamel margins and enameloplasty
Name some cutting recommendations
Using a (contra-angle) handpiece
air-water coolant system
high-operating speed
light pressure
a carbide bur or diamond bur
What are dental stones?
Abrasive particles that have been sintered together or bound with an organic resin to form a cohesive mass
What are dental stones used for?
Contouring and finishing restorations, where maximum abrasion is needed
What are the types of dental stones
Silicon Carbide
Aluminum Oxide
Diamond Stone
What are rubber wheels used for
Fine grinding to remove coarse scratches from rough grinding
How are rubber wheels made?
By molding the fine abrasives (aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, and chromium oxide) in a rubber matrix
What are rubber polishers used for?
Adjusting and polishing acrylic material
What are point shape instruments used for
Occlusal fine finishing and polishing
What can happen if you apply heavy pressure when using rubber polishing instruments?
They can produce excessive friction heat
How is heat dangerous in rubber polishing?
It can be deleterious to the restoration, rubber instrument and to the tooth itself
What are disks made of?
A stiff plastic or paper backing coated with abrasive particles
What are disks used for?
Gross reduction, contouring, finishing, and polishing restorations
What are enhance finishing and PoGo Polishing systems designed for
To finish and polish all types of composite restoration surfaces
What are enhance aluminum oxide finishers (disks, cups, and points) used for?
For preparing composite for their final polish
What are PoGo diamond polishers used for?
Single-use resin polishing devices designed for the final polishing of all accessible composite resin restorations
What are polishing strips useful for
In finishing and polishing interproximal areas
Polishing of a surface relies on
Using sequentially smaller and smaller abrasives
Larger abrasive particles do what?
Remove large amounts of material from the substrate
Smaller particles do what?
Smooth out the roughness produced by larger particles
What does proper polishing do?
Reduces peak-to-valley height and active surface area of the restoration
What is required to control frictional heat at the cutting site
Coolants
Name some types of coolants
Air, water, and air-water spray
When visibility is a problem, what should be used?
Air coolant
Air coolants are used:
at high cutting speeds, less heat is produced, air coolant combined with lower speed and light intermittent application
Water is used as a coolant when?
In controlling temperature increase
Visibility is not an issue in which type of coolant?
Air-water spray