Anatomy + Physiology - Chapter 6 - Muscle Cells
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
50%
percentage amount of body mass muscle is
Contract
muscles are responsible for all types of body movement due to unique ability to _________
Skeletal, Smooth, Cardiac
three basic types of muscle found in body
Skeletal + Smooth
muscle types that are elongated
Fiber
muscle cell is the same as muscle _____
Microfilaments (Myofilaments)
contraction of muscles is due to the movement of this type of filament
Muscle
what do the roots myo and mys mean?
Flesh
what does the root sarco mean?
Skeletal
muscle type that:
- most are attached by tendons to bones
- cells are multinucleate
- straited and have visible banding
- voluntary, contract rapidly, great force, tire easily
- cells are surrounded by and bundled up by connective tissue
- largest and longest muscle fibers
Endomysium
connective tissue layer around a single muscle fiber
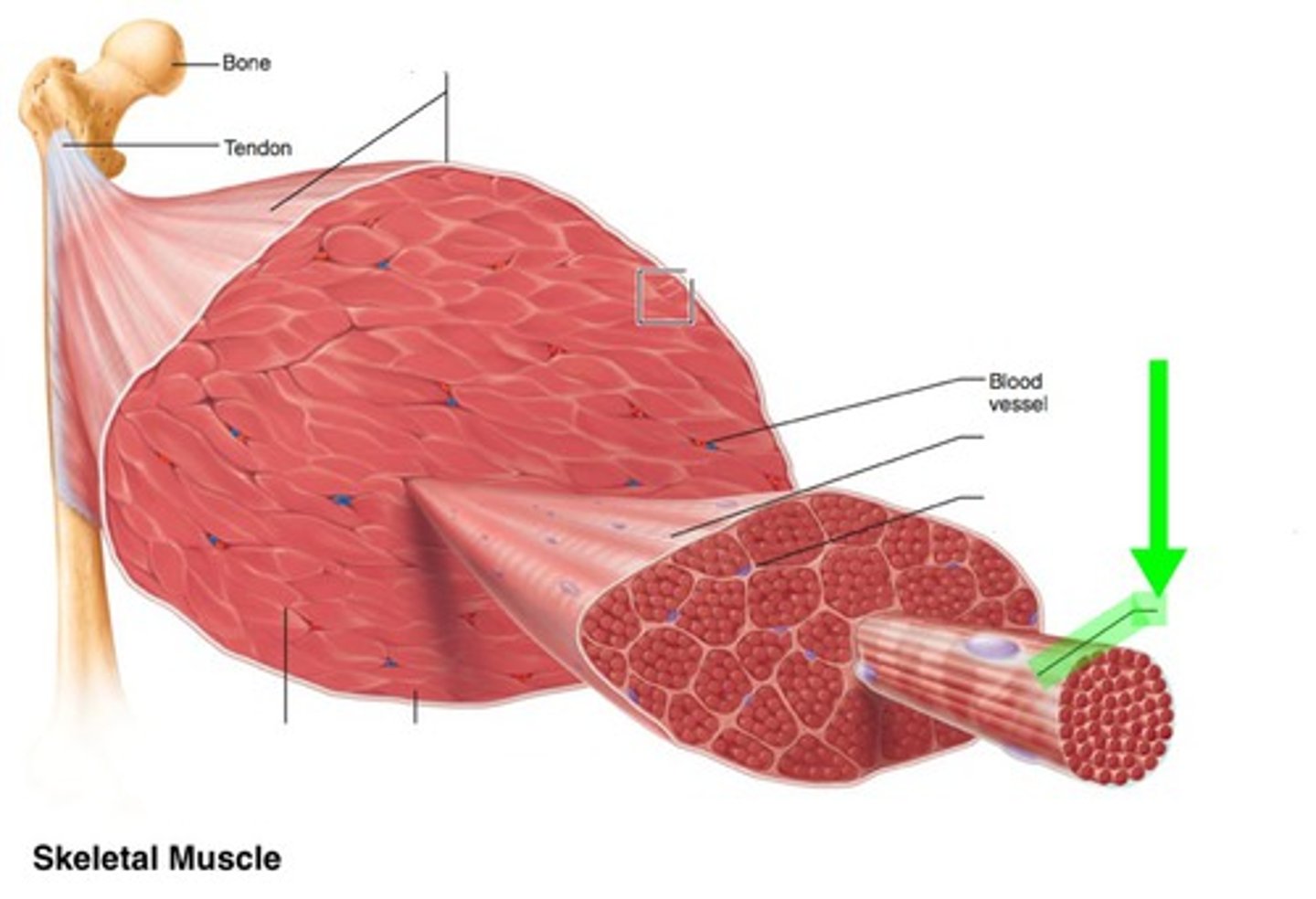
Perimysium
connective tissue layer around group of muscle fibers
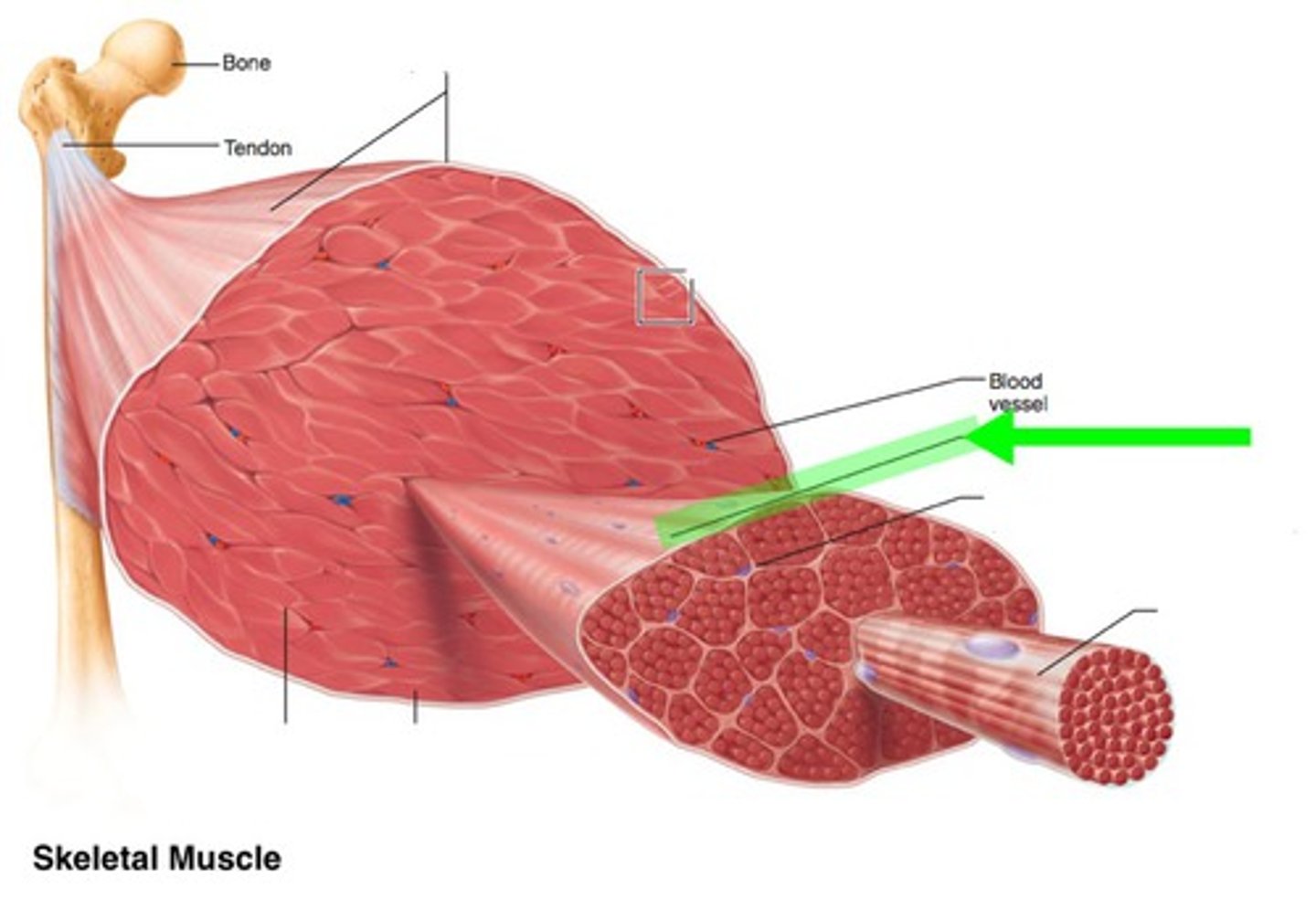
Epimysium
connective tissue layer that covers the entire skeletal muscle "overcoat"
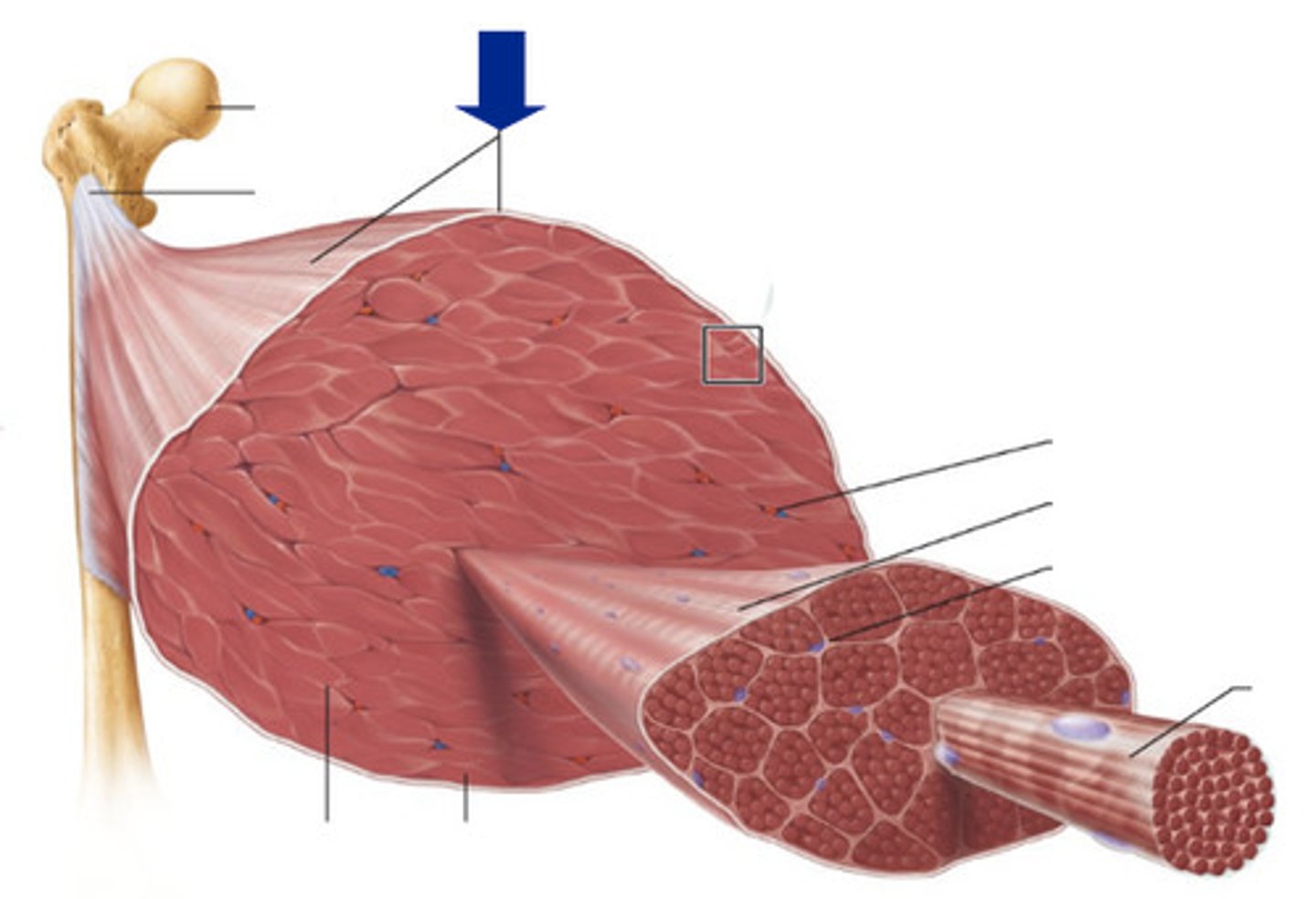
Fascia
connective tissue layer on the outside of perimysium
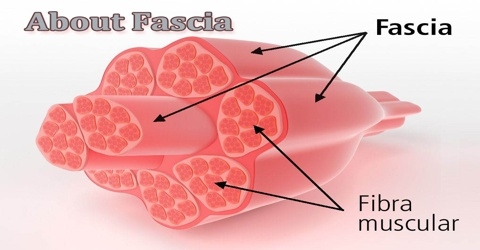
Epimysium
layer of connective tissue that blends into a connective tissue attachment
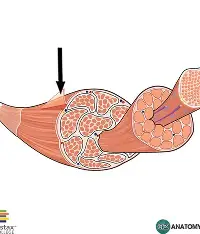
Tendon
cord-like connective tissue structure
Aponeurosis
sheet-like connective tissue structure
Bones, Cartilages, Connective Tissue Coverings
sites of muscle attachment (3)
Smooth
muscle type that:
- has no striations
- spindle-shaped cells
- uninucleate
- involuntary, slow sustained contraction
- propels substances along a pathway
- found mainly in the walls of hollow organs (stomach, bladder, resp tract)
Cardiac
muscle type that:
- has striations
- usually uninucleate
- joined to another muscle at an intercalated disc
- involuntary
- found only in heart where it serves as a pump to propel blood
All Types
which muscle types produce movements?
Skeletal
which muscle types maintain posture?
Skeletal
which muscle types stabilize joints?
Skeletal
which muscle types generate heat?
Multinucleate
muscle cells generally have many nuclei, or are _____________
Sarcolemma
specialized plasma membrane surrounding a muscle fiber
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SR)
- sends final "go" signal for muscle contraction
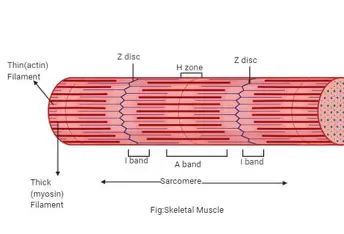
Myofibrils
bundles of myofilaments
- align to give distinct bands
- I band = light
- A band = dark
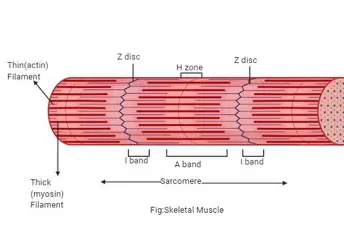
Z Disc
midline interruption (darker area) in i band
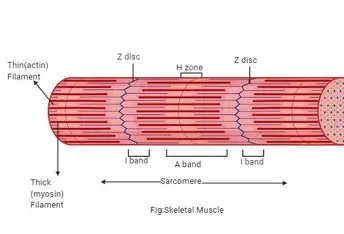
H Zone
lighter central area of A band
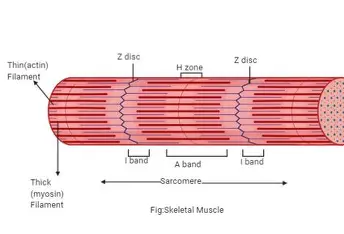
M Line
in middle of the h-zone; tiny protein rods that hold together adjacent filaments
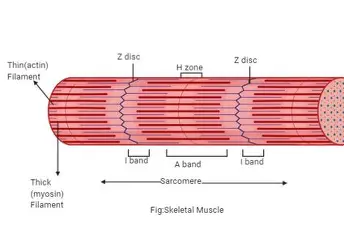
Sarcomere
contractile unit of a muscle fiber; z to z
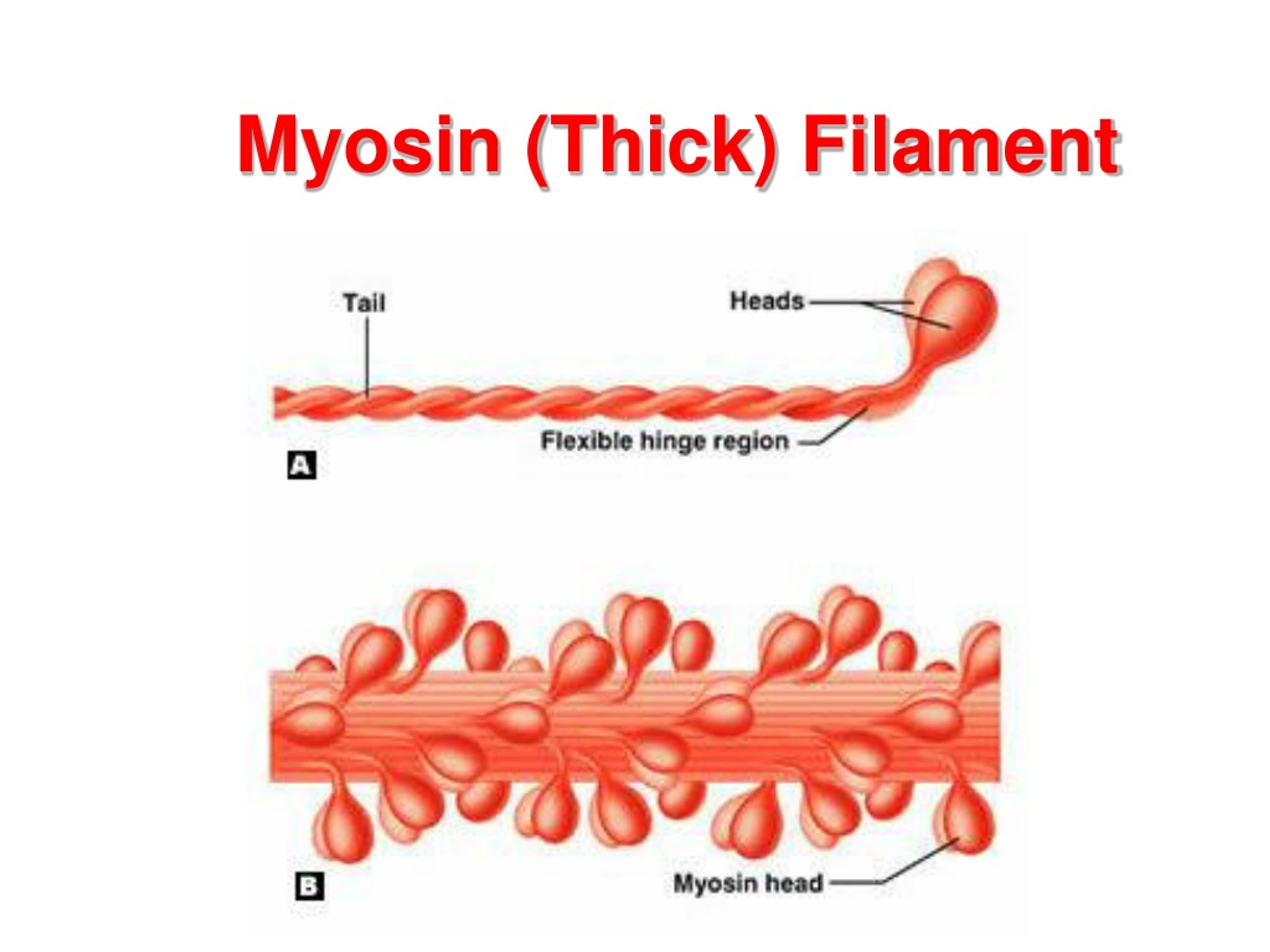
Myosin (Thick) Filament
filaments that have ATPase enzymes; splits ATP to release energy
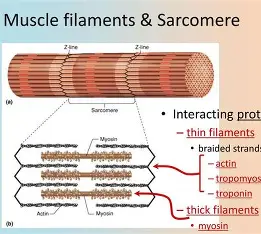
Actin (Thin) Filaments
filaments that are composed of actin and regulatory proteins that allow/prevent myosin heads from binding to actin
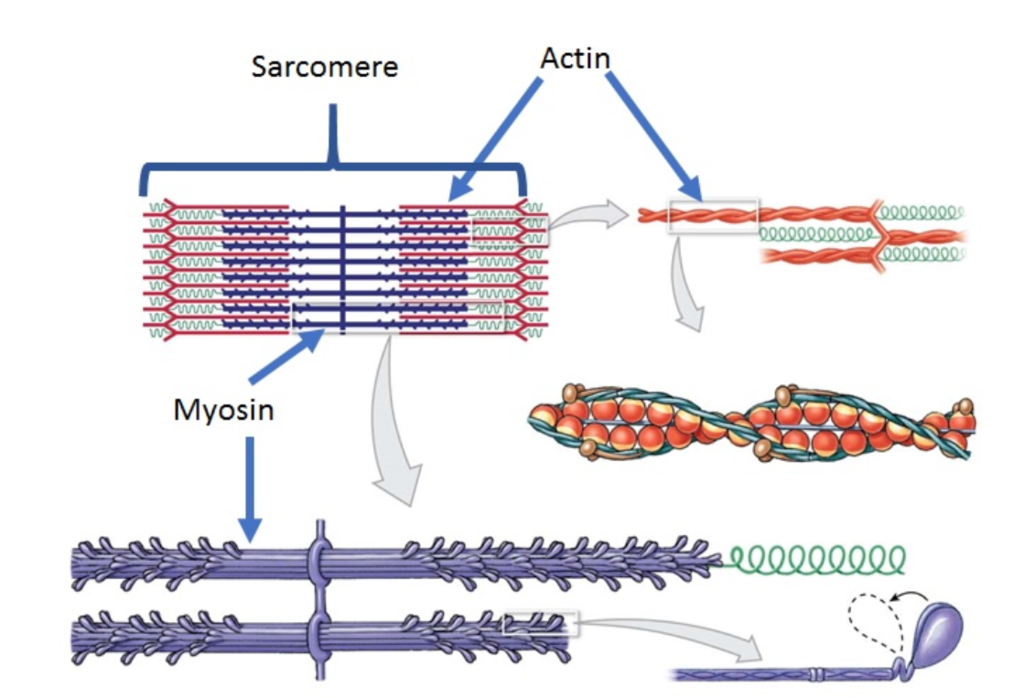
Myosin Filaments
filaments that have heads (extensions, or cross bridges)
Overlap
myosin and actin filaments _______ somewhat
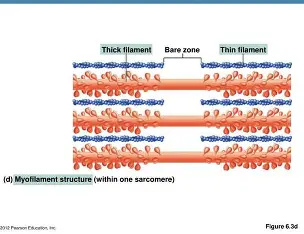
Bare
when at rest, there is a ____ zone that lacks actin filaments
Irritability
activity to receive/respond to a stimulus
Contractility
ability to shorten (unique to muscle tissue)
Nerve
skeletal muscles must be stimulated by a _____ to contract
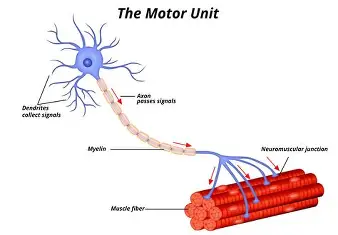
Motor Unit
one neuron + the muscle cells signaled by that neuron
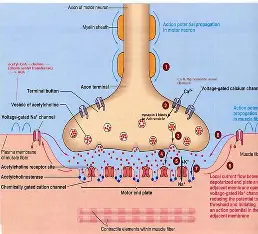
Neuromuscular Junction
association site of nerve and muscle
Synaptic Cleft
gap between nerve and muscle
- area is filled with interstitial fluid
Neurotransmitter
chemical released by nerve upon arrival of nerve impulse (acetylcholine for skeletal muscles)
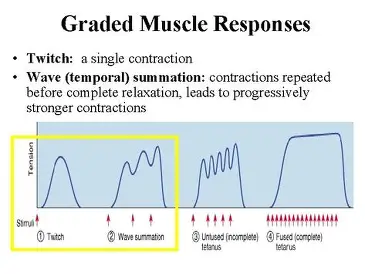
Graded Responses
different degrees of skeletal muscle shortening
Twitch
type of graded response:
- single, brief contraction
- not a normal muscle function
Tetanus
type of graded response:
- summary of contractions
- one contraction is immediately followed by another
- the muscle does not completely return to a resting state
Unfused Tetanus
type of graded response:
- some relaxation occurs between contractions
- the results are summed
Fused Tetanus
type of graded response:
- no evidence of relaxation before next contractions
- the result is a sustained muscle contraction
Seconds
Only 4-6 _______ worth of ATP is stored by muscles
Direct Phosphorylation
pathway for energy for muscle contraction that uses creatine phosphate, exhausted in about 15-20 seconds
Oxygen Debt
common reason for muscle fatigue (unable to contract)
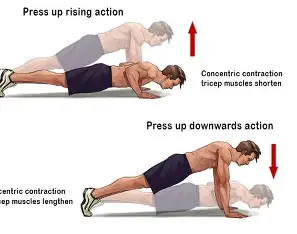
Isotonic
contraction type where myofilaments are able to slide past each other during movement /contractions and the muscle shortens (flex elbow)
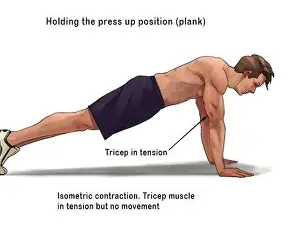
Isometric
contraction type where tension in the muscles increases and the muscle is unable to shorten (hold a plank)