Exam 2 Ligaments, Tendons, and structures
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Tibiofibular Joint Proximal
Synovial, gliding
Ligamentous support: Anterior proximal tibiofibular ligament and Posterior proximal tibiofibular ligament
Tibiofibular Joint Distal
Gliding joint, synovial
Ligamentous support: Anterior distal tibiofibular ligament, Posterior distal tibiofibular ligament, and Interosseous (tibiofibular) ligament
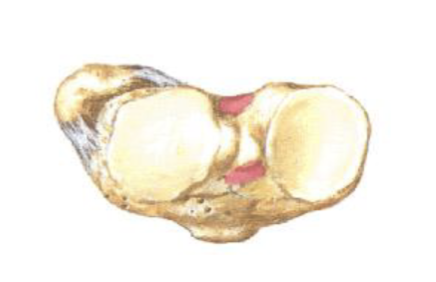
Middle Tibiofibular Joint
Fibrous Joint
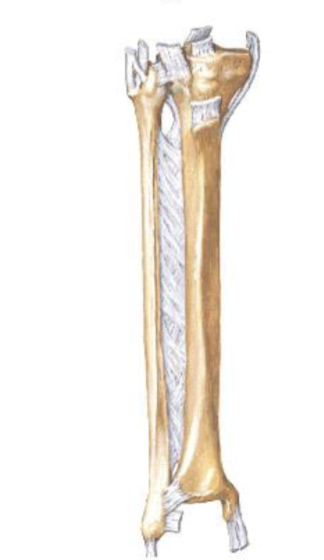
Crural Interosseous Membrane
Attachments: Connects the interossous borders of the tibia and fibula
Functions: Separates the anterior compartment from the posterior compartment, serves as sites for muscular attachments
Ankle Joint
Talocrural
Bones: Tibia, Fibula, Talus (trochlear surface)
Synovial - Hinge
Ankle Joint Movement
Sagittal Plane: dorsiflexion and plantarflexion
Dorsiflexion
Anterior angle decreasing or less than 90 degrees (toes pointed up)
Plantarflexion
Anterior angle increasing or greater than 90 degrees (toes pointed down)
Intertarsal Joints
Synovial - gliding
Composed of 7 Tarsal Bones: talus (trochlea), calcneus, navicular, cuboid, medial (#1) cuneiform, intermediate (#2) cuneiform, lateral (#3) cuneiform
Intertarsal Movement
Frontal Plane (mostly)
Inversion = supination, adduction, varus
Eversion = pronation, abduction, valgus
Intertarsal Joints - Rearfoot motion
Most movement occurs at the subtalar joint (talocalcaneo ligament) and talonavicular joint
Lateral Ankle and Intertarsal ligaments
Anterior talofibular, Calcaneofibular, and Posterior talofibular
Prevents: Excessive Inversion (or lateral ankle sprain)
Medial Ankle Ligaments
Deltoid Ligaments, Anterior talotibial, Tibionavicular, Calcaneotibial, Posterior talotibia
Prevents excessive eversion
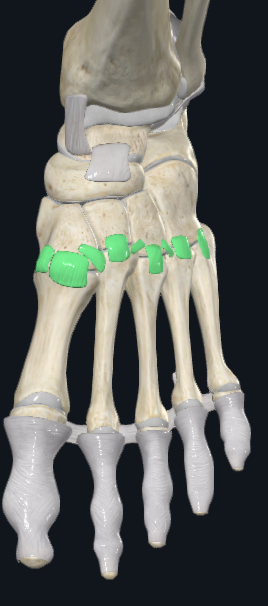
Tarsometatrsal Joints
Cuneiforms, cuboid and bases of metatarsals
Synovial - gliding
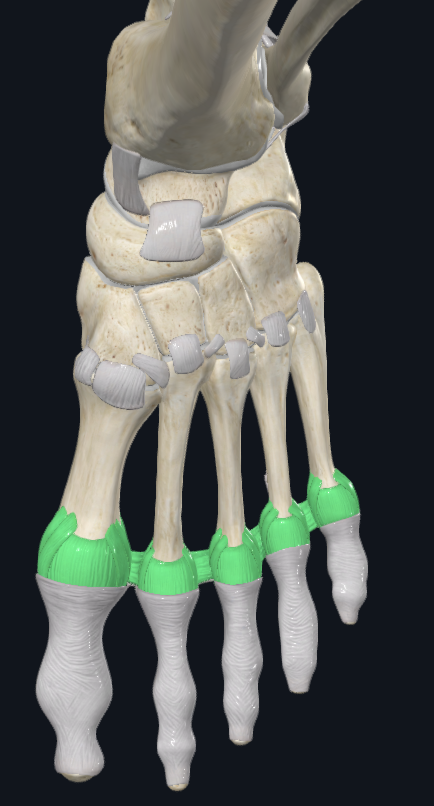
Metatarsophalangea Joints (MP)
Heads of metatarsals and base of proximal phalanages
Synovial condyloid
Movements: sagittal and transverse (3rd toe is midline)
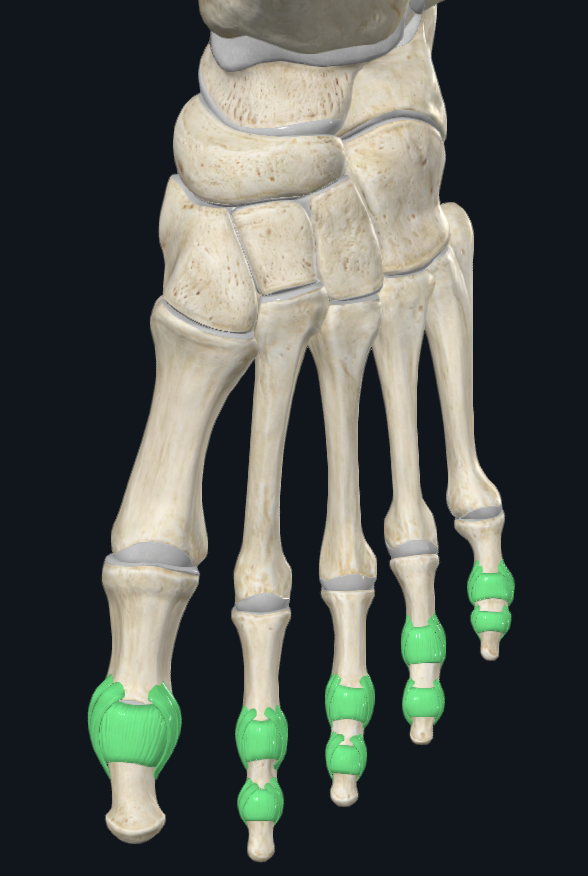
Interphalangeal Joints (IP) (9)
Synovial - condyloid, but function as hinge joint due to tight lateral ligaments
PIP = Proximal IP joints
DIP = Distal IP joints
Movements: Sagittal
Sagittal Movement
Flexion, extension, hyperextension
Transverse Movement
Abduction and Adduction
Medial Longitudinal Arch
Bones: calcaneus, talus, navicular, cuneiforms, 1st three metatarsals
Flexible
Important in shock absorption upon contact with ground
Transverse arch in mid-foot
Bones: Cuboid, cuneiforms, metatarsals (base)
Transverse arch in forefoot
Bones: Metatarsals (head)
Ligaments that support arches
Plantar aponeurosis, Long plantar, Spring
Classification of Hip Joint
Synovial, Ball and socket, multiaxial, complex, stable
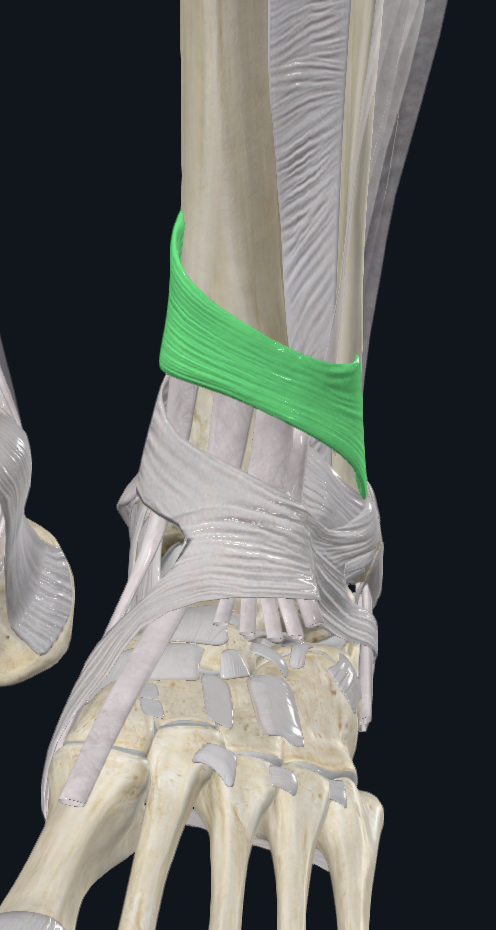
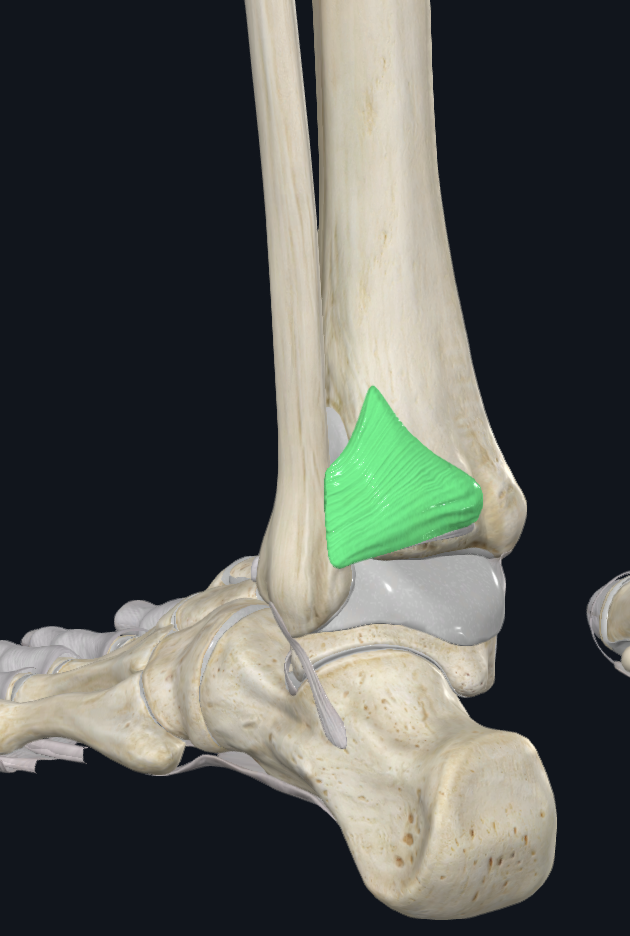
Extensor Retinaculum Superior
Characteristics: Proximal to the talocrural joint
Attachments: Laterally to the distal anterior border of the fibula, Medially to the distal anterior border of the tibia
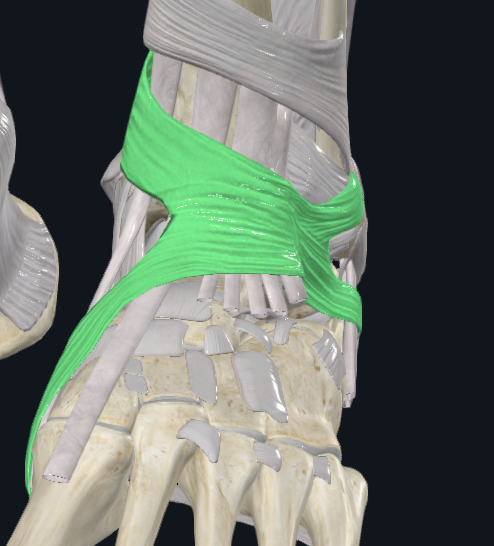
Extensor Retinaculum Inferior
Characteristics: Anterior to the talocrural joint, Y shaped
Attachments: Stem (lateral part): attaches to the upper surface of the calcaneus, Proximal Band: reaches the medial malleolus, Distal Band: extends infermedially to the plantar aponeurosis
Holds: TA, EHL, EDL, PT
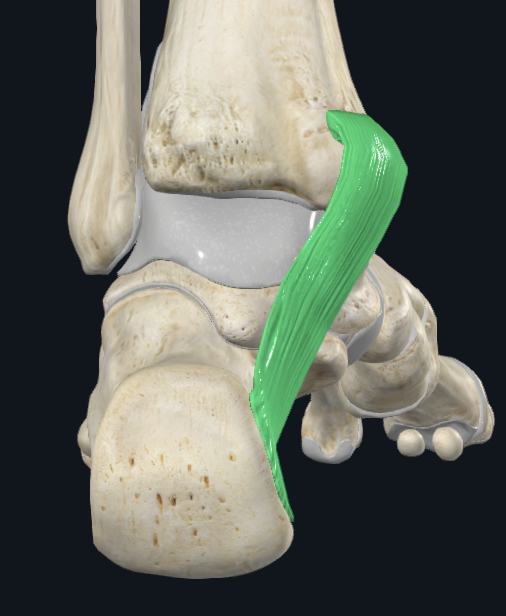
Flexor Retinaculum
Characteristics: Medial to the talocrural joint
Attachments: Anteriorly to the tip of the medial malleolus, Continues posteriorly to the medial calcaneal process and plantar aponeurosis
Holds: TP, FDL, & FHL
Notes: Tendinous synovial sheaths and bursae
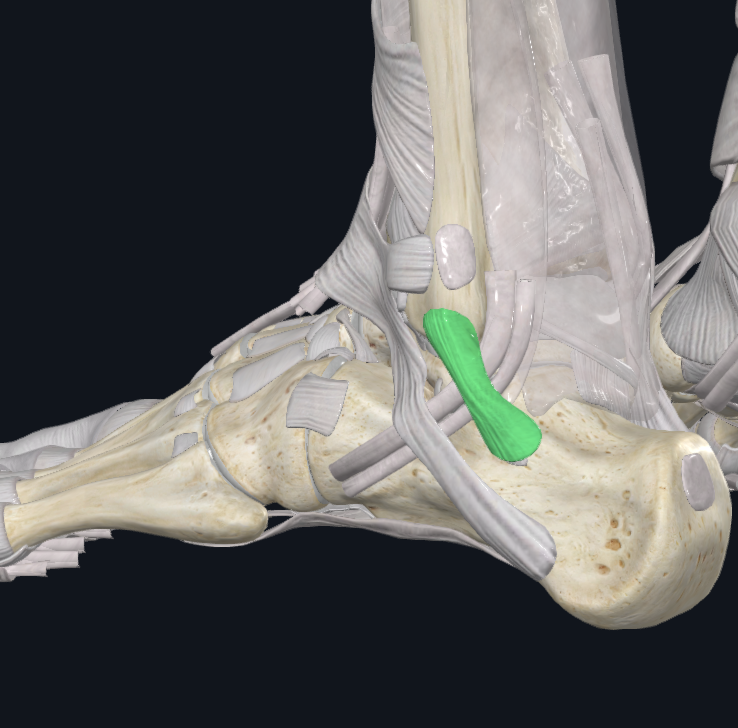
Peroneal Retinaculum Superior
Characteristics: Lateral to the talocrural joint
Attachments: Back of the lateral malleolus, To the lateral calcaneal surface
Holds PL, PB
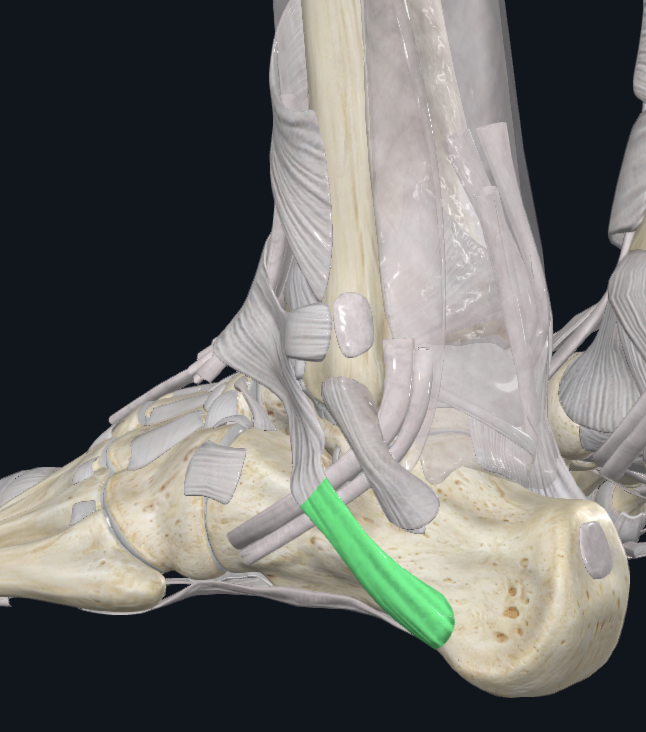
Peroneal Retinaculum Inferior
Characteristics: Lateral to the talocural joint
Attachments: Continues anteriorly with the inferior extensor retinaculum, To lateral calcaneal surface
Hip Joint Movement
Sagittal: flexion, exension, hyperextension
Frontal pane: abduction, adduction
Transverse: external rotation, internal rotation, horizontal abduction, horizontal adduction
Circumduction: all three planes
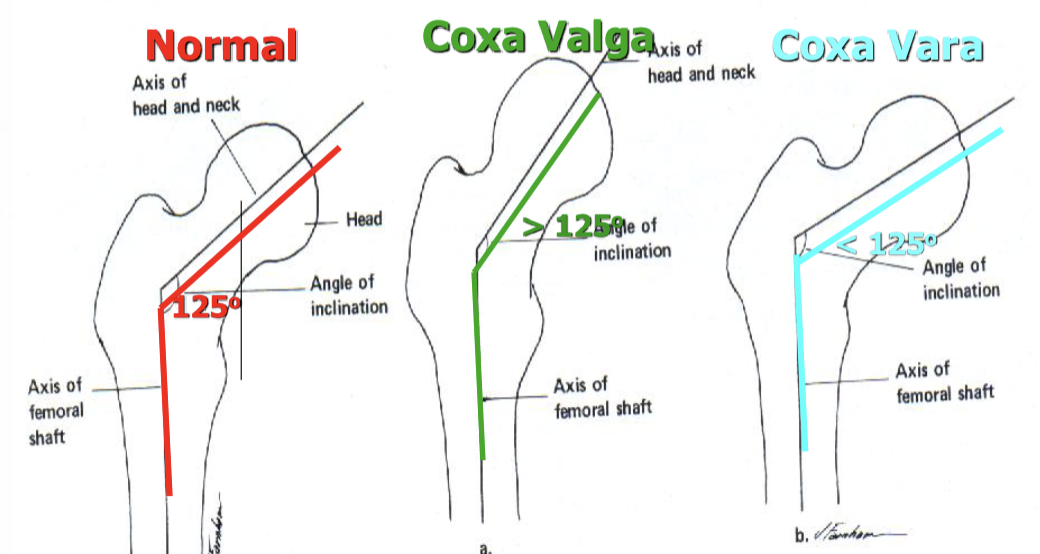
Angle of inclination
Normal = 125 degrees, Coxa valga = >125 degrees, Coxa varum = <125 degrees
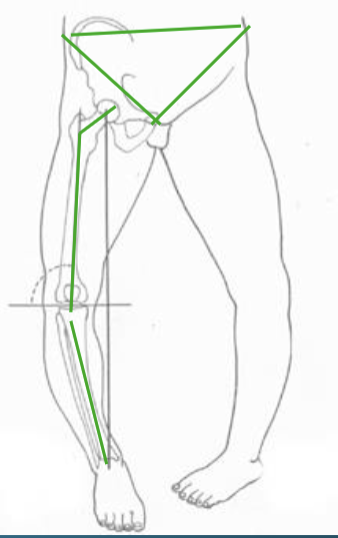
Coxa Valga
Coxa valga, genu varum, structurally long leg
Coxa Vara
Coxa vara, genu valga, pes planus (eversion), structurally short leg
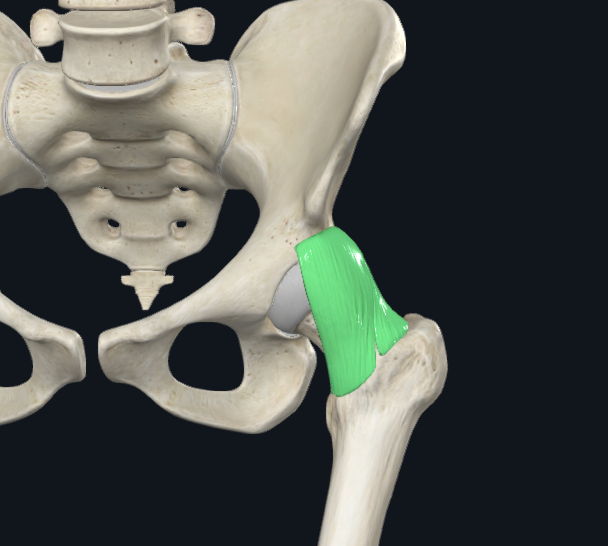
Iliofemoral Ligament
Proximal Attachment: Below AIIS, Ilial rim of acetabulum
Distal Attachment: Intertrochanteric Line
Extrinsic
Function: Checks Hip hyperEXT, Check hip ABD
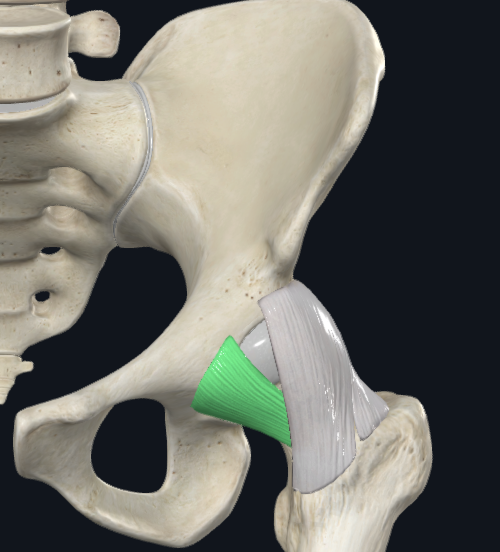
Pubofemoral Ligament
PA: Pubic rim of acetabulum
DA: Blends with iliofemoral Ligament at intertrochanteric line
Capsular
Function: Checks Hip hyperEXT and ABD
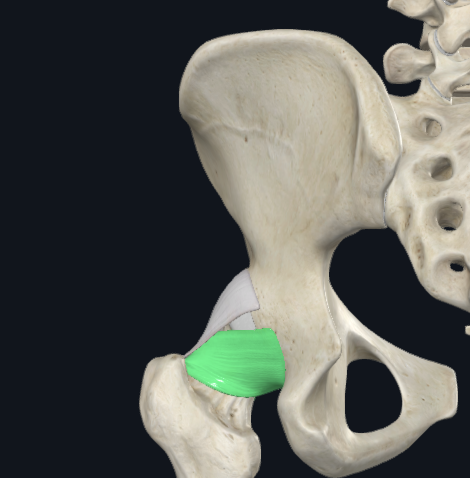
Ischiofemoral Ligament
PA: Ischial rim of acetabulum
DA: Intertrochanteric crest and medial surface of GT
Capsular
Posteriorly located
Function: Oblique Fibers check hip hyperEXT and Int. Rot.
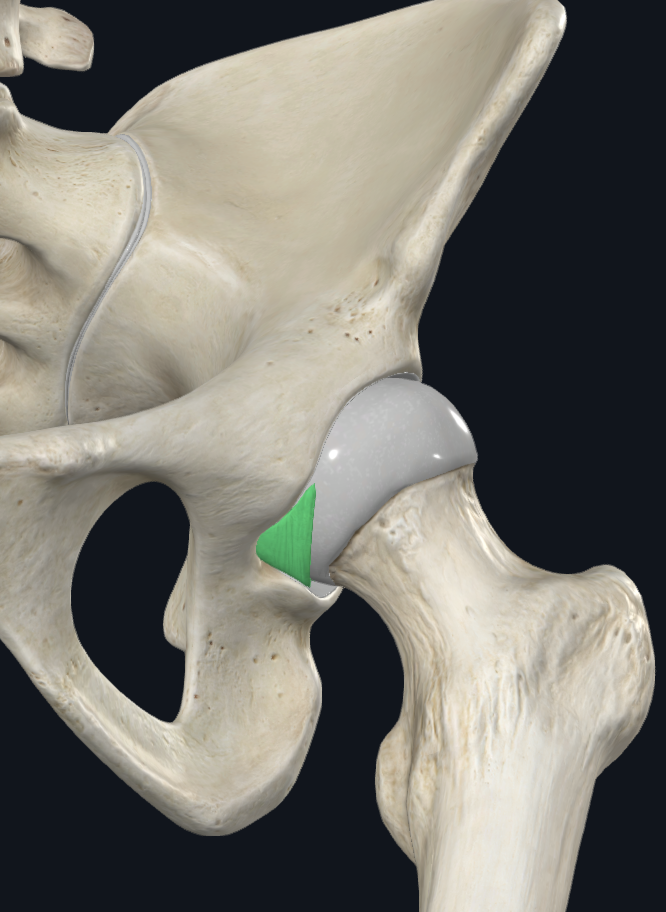
Transverse Acetabular Ligament
Extrinsic
Attaches adjacent inferior end of the acetabular notch
Function: Completes round articular surface, Protects neurovascular supply of the head of the femur
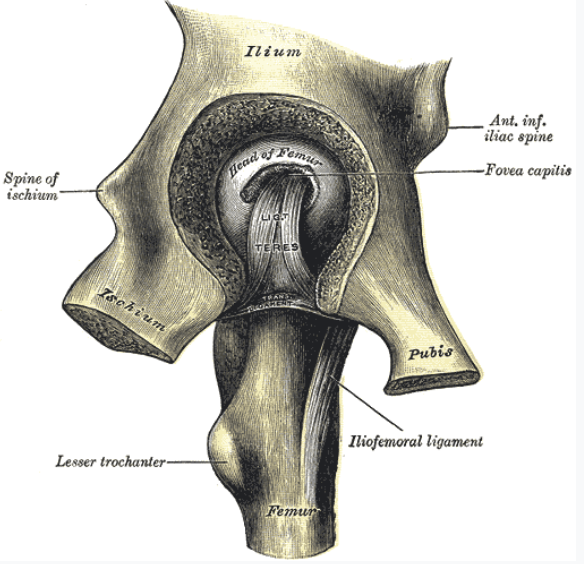
Ligamentum Teres
Intrinsic
PA: Around the margins of acetabular notch
DA: Fovea capitis of femur
Pelvic Girdle Joints
Sarcoiliac: Synovial gliding, Tight ligaments
Pubic Symphysis: Cartilaginous, Fibrocartilage
Pelvic Girdle Movement
Sagittal Plane: Anterior tilt: forward, Posterior tilt: backward (like doing a crunch) (ASIS movement)
Frontal Plane: Lateral tilt right, Lateral tilt left (lowest side)
Transverse Plane: Rotation right, Rotation left
Closed kinetic chain(CKC) vs. open kinetic chain (OKC)
Closed: proximal end moves
Open: distal end moved
Same movement but did the pelvis or femur move? Hip flexion and anterior tilt look the same, Hip flexors anteriorly tilt the pelvis
Lateral tilt muscles (hip abductors) when standing on LEFT leg with lateral tilt LEFT
Gluteus medius
Gluteus minimis
Tensor Fascia Latae
Lateral tilt muscles (hip adductors) when standing on LEFT leg with lateral tilt RIGHT
Adductor longus
Adductor brevis
Adductor magnus
Pectineus
Gracilis
Hip lateral rotators when standing on LEFT leg with rotation RIGHT
Gluetus Maximus
Six lateral rotators: Piriformis, Gemelli (2), Obtorators (2), Quadratus femoris
Adductor muscle
Hip medial rotators when standing on LEFT leg with Rotation LEFT
Gluetus medius
Gluteus minimis
TFL