psych unit XI and VIII
5.0(1)Studied by 5 people
0%Unit Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:23 PM on 2/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
1
New cards
intelligence
the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
2
New cards
factor analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (called factors) on a test; used to identify different dimensions of performance that underlie a person's total score.
3
New cards
Charles Spearman
believed we have one general intelligence (g) that is at the heart of all out intelligent behavior
4
New cards
general intelligence (g)
according to Spearman and others, underlies all mental abilities and is therefore measured by every task on an intelligence test
5
New cards
L.L. Thurstone
identified seven clusters of primary abilities (word fluency, verbal comprehension, spatial ability, perceptual speed, numerical ability, inductive reasoning, and memory)
6
New cards
Howard Gardiner
identified eight relatively independent intelligences (Linguistic, Logical/Mathematical, Spatial, Bodily-Kinesthetic, Musical, Interpersonal, Intrapersonal, and Naturalist)
7
New cards
savant syndrome
a condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill, such as in computation or drawing
8
New cards
Robert Sternberg
agrees with Gardner, came up with Triarchic Theory (3 intelligences)
\-analytical (problem-solving)
\-creative intelligence
\-practical intelligence
\-analytical (problem-solving)
\-creative intelligence
\-practical intelligence
9
New cards
emotional intelligence
the ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions
10
New cards
creativity
the ability to produce novel and valuable ideas
11
New cards
intelligence test
a method for assessing an individual's mental aptitudes and comparing them with those of others, using numerical scores
12
New cards
Alfred Binet
commissioned by the French government to design fair and unbiased intelligence tests to administer to the French schoolchildren
13
New cards
mental age
a measure of intelligence test designed by Binet; the level of performance typically associated with children of a certain chronological age
14
New cards
Lewis Terman
standford professor, modified Binet's tests for use as a numerical measure of inherited intelligence, adapting some of Binet's original items, adding others, and establishing new age norms, Terman extended the upper end of tests range from teenagers to "superior adults"
15
New cards
Flynn effect
people from 100 years ago would fail IQ tests today, whereas people today would get the highest scores on IQ tests from 100 years ago
16
New cards
Stanford-Binet
the widely used American revision (by Terman at Stanford University) of Binet's original intelligence test.
17
New cards
intelligence quotient (IQ)
IQ = mental age/chronological age x 100
\-doesn't work for adults past puberty
\-doesn't work for adults past puberty
18
New cards
aptitude test
a test designed to predict a person's future performance; aptitude is the capacity to learn
\-ACT/SAT
\-ACT/SAT
19
New cards
achievement test
a test designed to assess what a person has learned
\-EOC
\-EOC
20
New cards
Wechler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
the WAIS and its companion versions for children are the most widely used intelligence tests; they contain verbal and performance (nonverbal) subtests
21
New cards
standardization
to make score meaningful, they are compared to a pretested sample population
22
New cards
normal curve
scores form a bell-shaped pattern call the "bell curve", most scores fall near the average, fewer and fewer near extremes
23
New cards
reliability
the test gives consistent scores no matter who takes it or when they take the test
24
New cards
validity
the test measures or predicts what it is supposed to
25
New cards
content validity
the extent to which a test samples the behavior that is of interest (it has what was promised on the test)
26
New cards
criterion
what it supposed to be on the test
27
New cards
predictive validity
The success with which a test predicts the behavior it is designed to predict; it is assessed by computing the correlation between test scores and the criterion behavior
28
New cards
cohort
a group of people from a given time period sharing the same characteristics
29
New cards
crystalized intelligence
our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age
30
New cards
fluid intelligence
our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease during late adulthood
31
New cards
intellectual disability
a condition of limited mental ability, indicated by an intelligence score of 70 or below and difficulty in adapting to the demands of life; varies from mild to profound
32
New cards
down syndrome
a condition of mild to severe intellectual disability and associated physical disorders caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21)
33
New cards
heredity
the proportion of variation among individuals in a group that we can attribute to genes
\-genetic influence explains about 50% of the observed variation among people
\-genetic influence explains about 50% of the observed variation among people
34
New cards
steryotype threat
a self-confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype
35
New cards
motivation
(david mecclelland) a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior
36
New cards
instinct
a complex behavior that is rigidly patterned throughout a species and is unlearned
37
New cards
drive-reduction theory
we have a physiological need like hunger or thirst and actions satisfy the behavior are aroused
38
New cards
homeostasis
a tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state; the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry, such as blood glucose, around a particular level
39
New cards
incentive
positive or negative environmental stimuli that lure or repel us
40
New cards
hierarchy of needs
Maslow's pyramid of human needs, beginning at the base with physiological needs that must first be satisfied before higher-level safety needs and then psychological needs become active
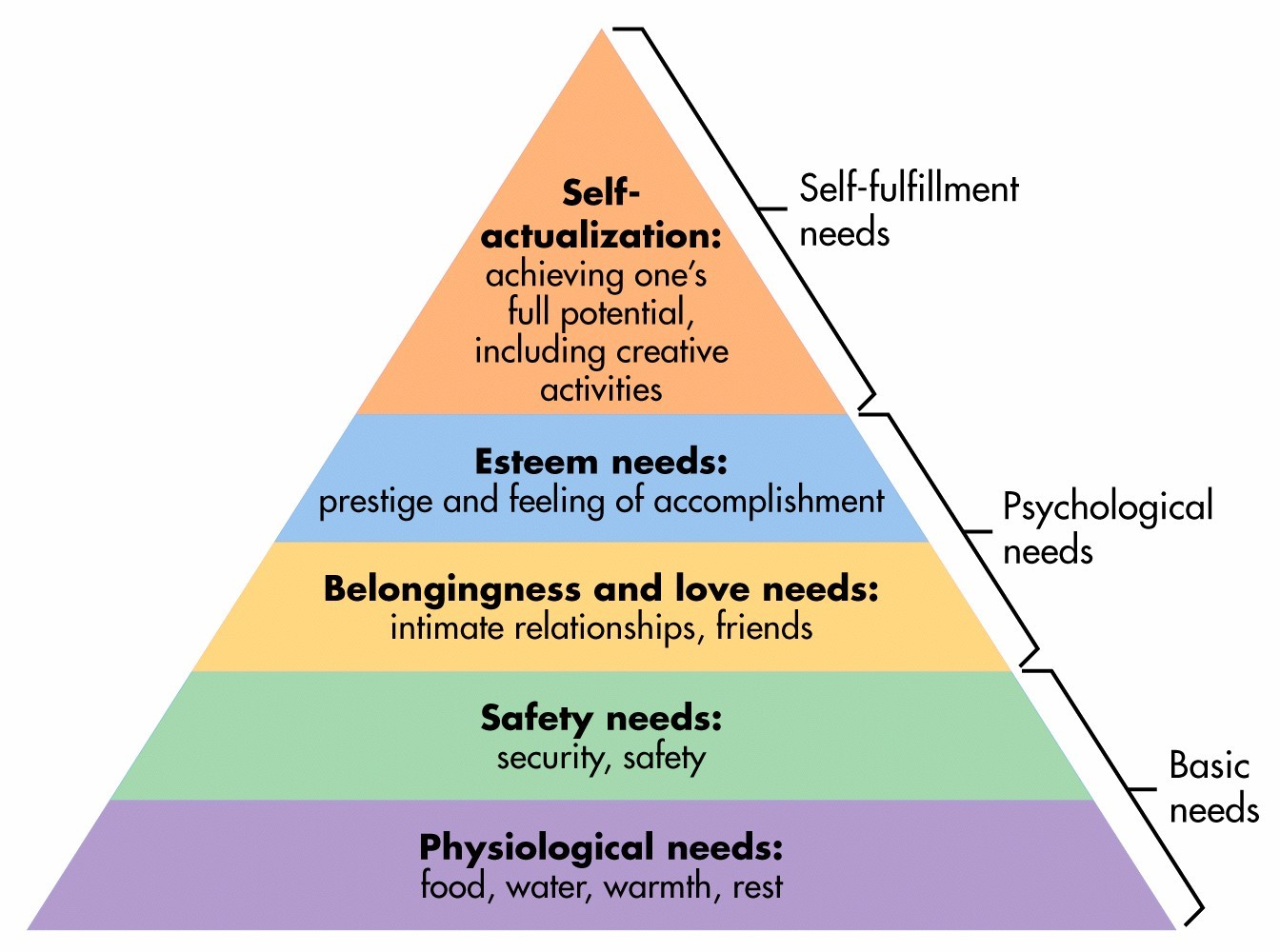
41
New cards
Abraham Maslow
theorized that human needs are hierarchical, some have priority over others
42
New cards
Yerks-Dodson Law
we seek a certain level of arousal, if performing an easy task, you need stress added to do your best. Difficult tasks need to be done with no stress
\-moderate arousal leads to optimal performance
\-moderate arousal leads to optimal performance
43
New cards
glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues. When its level is low, we feel hunger.
44
New cards
set point
the point (weight) at which your "weight thermostat" may be set (fixed)
45
New cards
basal metabolic rate
the body's resting rate of energy expenditure for maintaining basic body functions
46
New cards
anorexia nervosa
an eating disorder in which an irrational fear of weight gain leads people to starve themselves
47
New cards
bulimia nervosa
an eating disorder characterized by episodes of overeating, usually of high-calorie foods, followed by vomiting, laxative use, fasting, or excessive exercise
48
New cards
Alfred Kinsey
studied american sexology, known for proposing rational emotivitie behavior therapy to get people with dissatisfaction with sex to realize their life was not a failure
49
New cards
sexual response cycle
excitement, plateau, orgasm, resolution
50
New cards
refractory period
a resting period after orgasm, during which a man cannot achieve another orgasm
\-men: lasts minutes to days
\-women: a lot shorter
\-men: lasts minutes to days
\-women: a lot shorter
51
New cards
sexual disorder
a lack of desire for sex
52
New cards
estrogen
sex hormone that contributes to female sex characteristics and is secreted in greater amounts by females than by males
53
New cards
testosterone
both males and females have it, but the additional testosterone in males stimulates the growth of the male sex organs in the fetus and the development of the male sex characteristics during puberty
54
New cards
sexual orientation
what sex a person is attracted to
55
New cards
lateral hypothalamus
stimulates hunger, when removed, can't stimulate hunger
56
New cards
ventronedial hypothalamus
inhibits hunger, when removed, can't send full signals
57
New cards
affiliation need
the need to build relationships and to feel part of a group, the need to belong
58
New cards
ostricism
deliberate social exclusion from a society or group
59
New cards
social networking
the creation and maintenance of personal and business relationships especially online
60
New cards
narcissism
a personality trait in which people feel self-important, self-focused, and self-promoting
61
New cards
flow
a state of energized focus
62
New cards
achievement motivation
a desire for significant accomplishment: for mastery of things, people, or ideas; for attaining a high standard
63
New cards
GRIT
passion and perseverance in the pursuit of long-term goals
64
New cards
task leadership
when the leader focuses on tasks that need to be performed in order to meet certain goals or performance
65
New cards
social leadership
produce high performance teams that work well together
66
New cards
emotion
a response of the whole organism, involving (1) physiological arousal, (2) expressive behaviors, and (3) conscious experience
67
New cards
James-Lange Theory
the theory that our experience of emotion is our awareness of our physiological responses to emotion-arousing stimuli
\-we feel sorry because we cry
\-we feel sorry because we cry
68
New cards
Cannon-Bard Theory
the theory that an emotion-arousing stimulus simultaneously triggers (1) physiological responses and (2) the subjective experience of emotion
69
New cards
Two-Factor Theory (Schachter-Singer)
the theory that to experience emotion one must (1) be physically aroused and (2) cognitively label the arousal
70
New cards
polygraph
measures emotion-linked automatic arousal, as reflected in changed breathing, heart rate, and perspiration
71
New cards
facial feedback effect
the tendency of facial muscle states to trigger corresponding feelings such as fear, anger, or happiness
72
New cards
behavior feedback effect
the tendency of behavior to influence our own and others' thoughts, feelings, and actions
73
New cards
catharsis
a release of emotional tension
\-punching the wall out of anger
\-punching the wall out of anger
74
New cards
feel-good, do-good phenomenon
people's tendency to be helpful when already in a good mood
75
New cards
subjective well being
individuals' personal perceptions of their life satisfaction
76
New cards
adaption-level phenomenon
the tendency people have to quickly adapt to a new situation, until that situation becomes the norm
77
New cards
relative deprivation
The idea that people are deprived (materially or in other ways) compared with others in society
78
New cards
behavioral medicine
an interdisciplinary field that integrates behavioral and medical knowledge and applies that knowledge to health and disease
79
New cards
health psychology
a subfield of psychology that provides psychology's contribution to behavioral medicine
80
New cards
stress
the process by which we perceive and respond to certain events, called stressors, that we appraise as threatening or challenging
81
New cards
General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)
the process your body goes through when you are exposed to any kind of stress, positive or negative
alarm, resistance, exhaustion
alarm, resistance, exhaustion
82
New cards
coronary heart disease
the clogging of the vessels that nourish the heart muscle; the leading cause of death in many developed countries
83
New cards
Type A
competitive, reactive, hard-driving, impatient, time-conscious, super-motivated, verbally aggressive, and anger-prone people
84
New cards
Type B
more relaxed and easygoing people
85
New cards
psychophysiological illness
Physical illness caused by psychological overlays (tension and migraine headaches, from stress)
86
New cards
lymphocytes
The two types of white blood cells that are part of the body's immune system:
87
New cards
B lymphocytes
fight bacterial infections
88
New cards
T lymphocytes
attack cancer cells, viruses, and foreign substances.
89
New cards
coping
dealing with problems and troubles in an effective way
90
New cards
problem-focused coping
all active efforts to manage stressful situations and alter a troubled person-environment relationship to modify or eliminate the sources of stress via individual behavior
91
New cards
emotion-focused coping
regulating your feelings and emotional responses to the problem instead of addressing the problem
92
New cards
aerobic exercise
sustained exercise that increases heart and lung function fitness; also helps alleviate stress, depression, and anxiety
93
New cards
biofeedback
a process that enables an individual to learn how to change physiological activity for the purpose of improving health and performance
94
New cards
complementary and alternative medicine
medicines and health practices that are not usually used (massage, acupuncture, tai chi, drinking green tea)