Module 3 Additional Practice
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
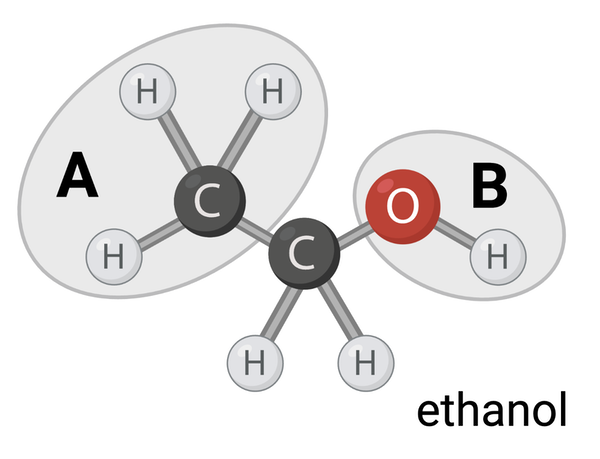
Which terms accurately describe Region A? Select all that apply.
a. nonpolar
b. polar
c. hydrophobic
d. hydrophilic
a. nonpolar
c. hydrophobic
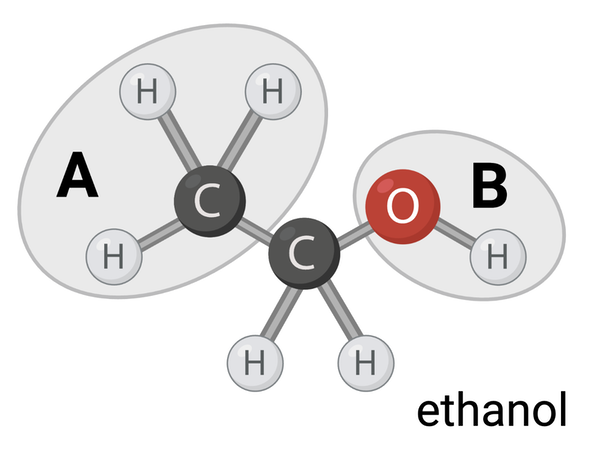
Which terms accurately describe Region B? Select all that apply.
a. nonpolar
b. polar
c. hydrophobic
d. hydrophilic
b. polar
d. hydrophilic
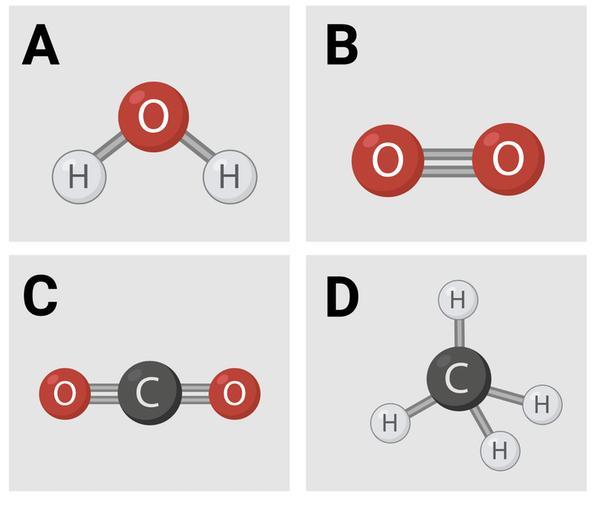
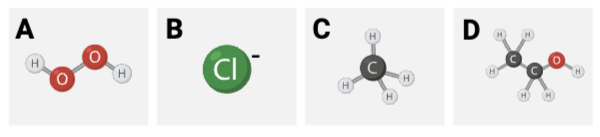
Which molecules are polar or have polar regions? Select all that apply.
a. Image A
b. Image B
c. Image C
d. Image D
a. Image A
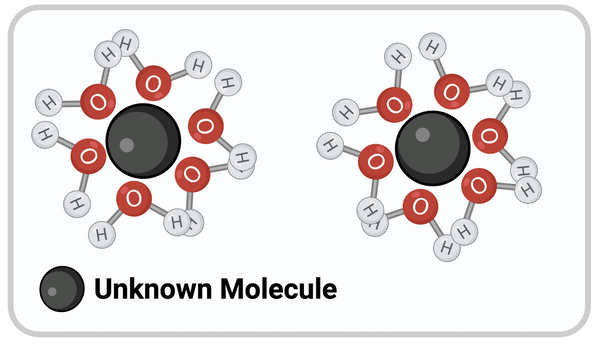
Which chemical property most likely describes the unknown molecule?
a. negatively charged
b. positively charged
c. without a charge
d. hydrophobic
e. nonpolar
b. positively charged
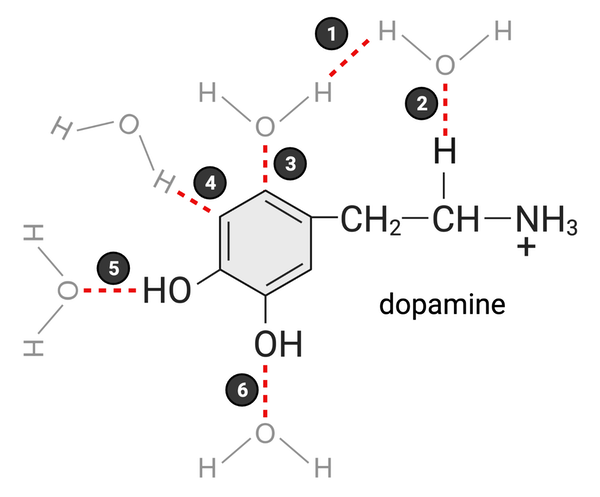
Which of these bonds accurately represents a hydrogen bond? Select all that apply.
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. 5
f. 6
b. 2
e. 5
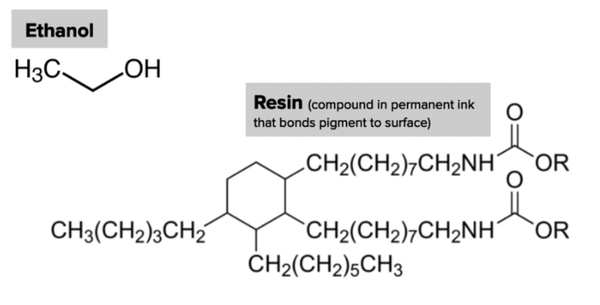
Which statement best describes why ethanol was better than water at removing the ink?
a. Ethanol has a charged region, making it a better solvent for the resin molecules than water.
b. Ethanol has a polar region, making it a better solvent for the resin molecules than water.
c. Ethanol has a nonpolar region, making it a better solvent for the resin molecules than water.
c. Ethanol has a nonpolar region, making it a better solvent for the resin molecules than water.
Which series lists the molecules in order of hydrophilicity, from most hydrophilic to least hydrophilic?
a. C > B > D > A
b. A > D > B > C
c. B > A > D > C
c. B > A > D > C
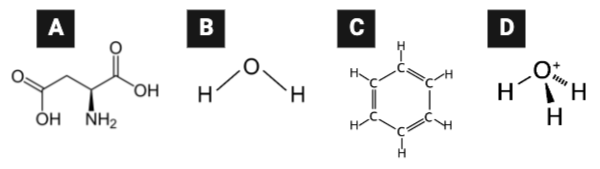
Which series lists the molecules in order of their ability to diffuse through a phospholipid bilayer, from most likely to least likely?
a. C, B, A, D
b. B, C, A, D
c. D, A, C, B
d. D, B, C, A
a. C, B, A, D
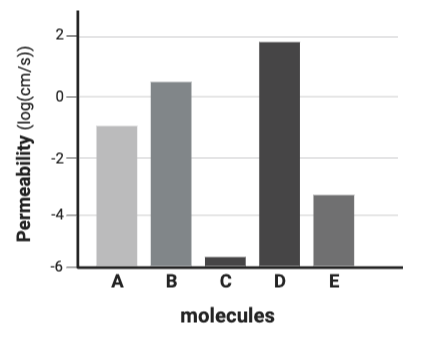
Which molecule is likely the least charged or polar?
Molecule D
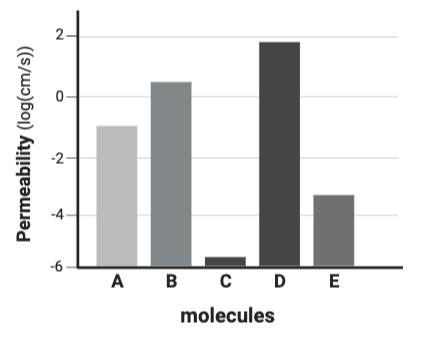
Which molecule is likely the most charged or polar?
Molecule C
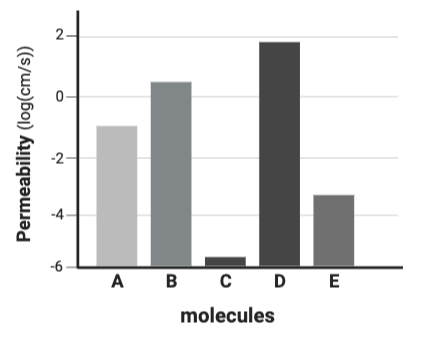
Which molecule is likely the most hydrophilic?
Molecule C
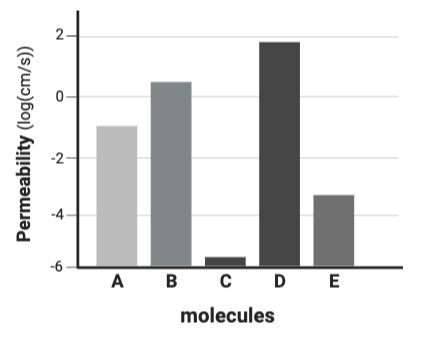
Which molecule is likely the least hydrophilic?
Molecule D
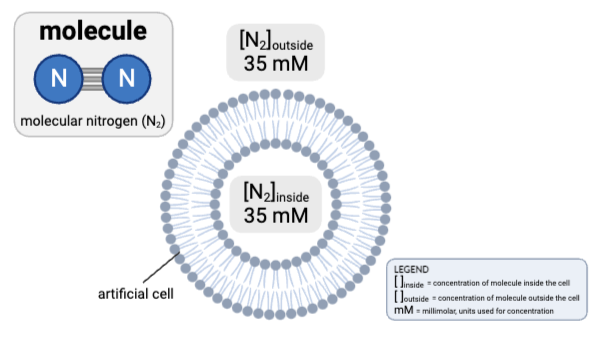
How would osmosis affect the concentration of N2 in the cell?
a. The concentration of N2 inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
b. The concentration of N2 inside the cell will decrease, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
c. The concentration of N2 inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside.
d. The concentration of N2 inside the cell will decrease, because water will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside.
e. The concentrations will remain the same.
e. The concentrations will remain the same.
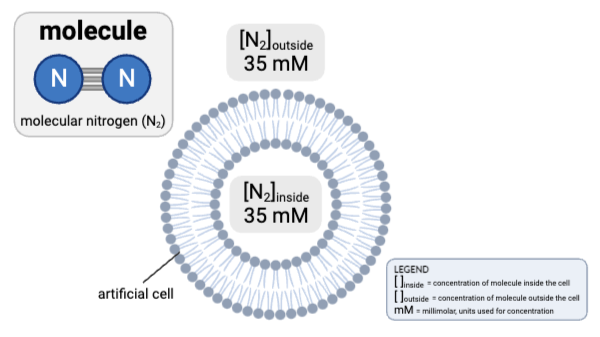
Which claims are accurate? Select all that apply.
a. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of N2 out of the cell.
b. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of N2 into the cell.
c. The concentration gradient would not favor the net diffusion of N2 in either direction.
d. Because N2 is charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
e. Because N2 is partially charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
f. Because N2 is uncharged, it can pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
c. The concentration gradient would not favor the net diffusion of N2 in either direction.
f. Because N2 is uncharged, it can pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
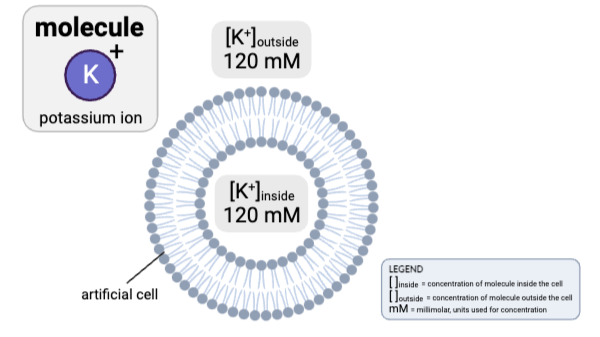
How would osmosis affect the concentration of K+ in the cell?
a. The concentration of K+ inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
b. The concentration of K+ inside the cell will decrease, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
c. The concentration of K+ inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside.
d. The concentration of K+ inside the cell will decrease, because water will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside.
e. The concentrations will remain the same.
e. The concentrations will remain the same.
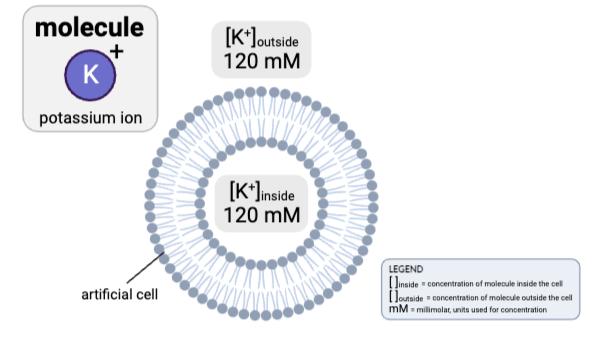
Which claims are accurate? Select all that apply.
a. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of K+ out of the cell.
b. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of K+ into the cell.
c. The concentration gradient would not favor the net diffusion of K+ in either direction.
d. Because K+ is charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
e. Because K+ is partially charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
f. Because K+ is nonpolar, it can pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
c. The concentration gradient would not favor the net diffusion of K+ in either direction.
d. Because K+ is charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
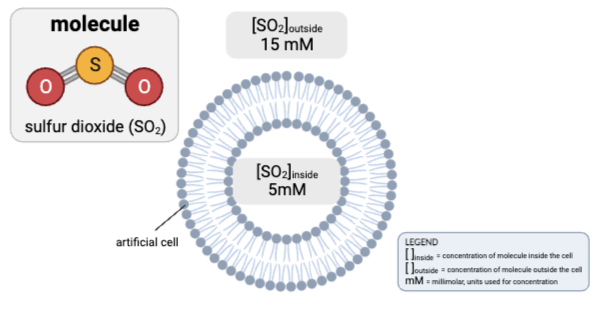
How would osmosis affect the concentration of SO2 in the cell?
a. The concentration of SO2 inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
b. The concentration of SO2 inside the cell will decrease, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
c. The concentration of SO2 inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside.
d. The concentration of SO2 inside the cell will decrease, because water will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside.
e. The concentrations will remain the same.
a. The concentration of SO2 inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
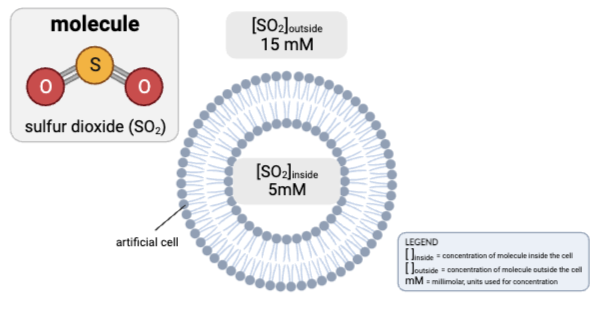
Choose the reasoning that supports your answer. Select all that apply.
a. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of SO2 out of the cell.
b. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of SO2 into the cell.
c. The concentration gradient would not favor the net diffusion of SO2 in either direction.
d. Because SO2 is charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
e. Because SO2 is partially charged but small in size, it can pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
f. Because SO2 is nonpolar, it can pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
b. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of SO2 into the cell.
e. Because SO2 is partially charged but small in size, it can pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
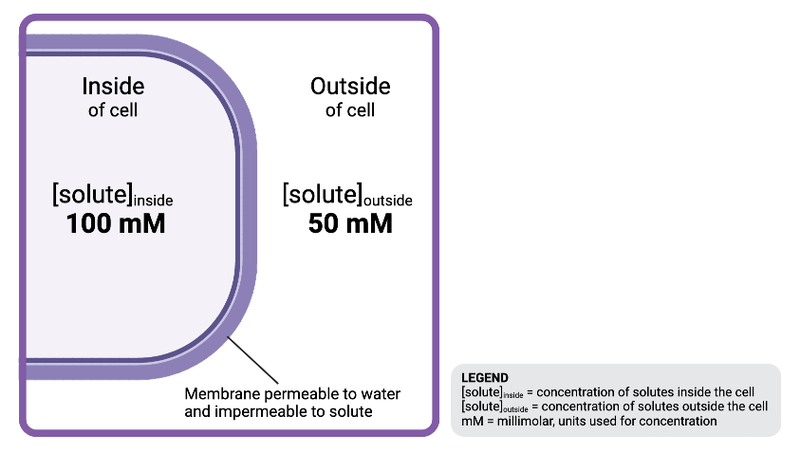
The solution inside the cell is ______________ to the solution outside the cell.
a. hyperosmotic
b. isosmotic
c. hypoosmotic
a. hyperosmotic
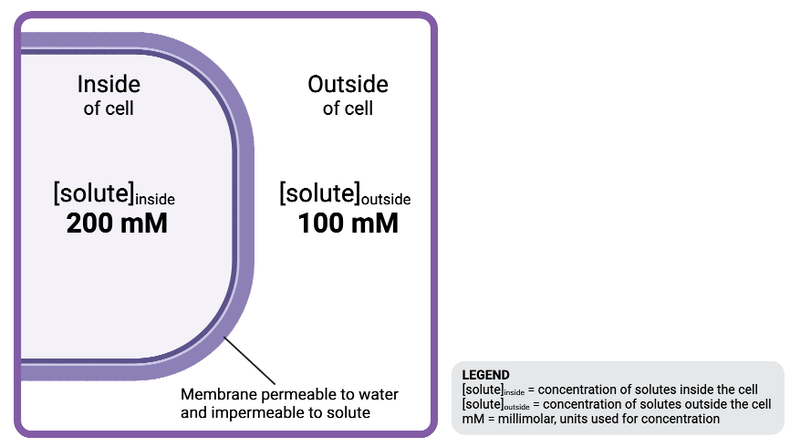
The solution inside the cell is ______________ to the solution outside the cell.
a. hyperosmotic
b. isosmotic
c. hypoosmotic
a. hyperosmotic
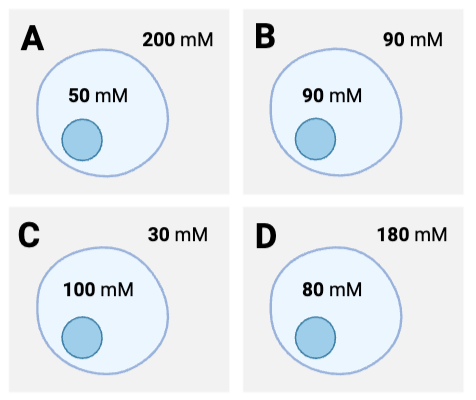
For which cells will the net diffusion of water be into the cell? Select all that apply.
a. Cell A
b. Cell B
c. Cell C
d. Cell D
c. Cell C
Which condition causes a net diffusion of water into the cell?
a. The concentration of solute inside the cell is greater than the concentration outside the cell.
b. The concentration of solute inside the cell is less than the concentration outside the cell.
c. The concentration of solute inside the cell is equal to the concentration outside the cell.
a. The concentration of solute inside the cell is greater than the concentration outside the cell.
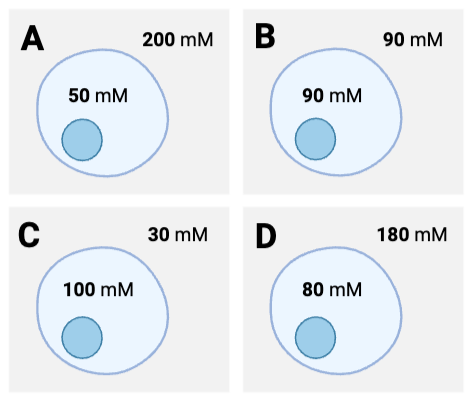
For which cells will there be no net diffusion of water? Select all that apply.
a. Cell A
b. Cell B
c. Cell C
d. Cell D
b. Cell B
Which condition causes no net diffusion of water?
a. The concentration of solute inside the cell is greater than the concentration outside the cell.
b. The concentration of solute inside the cell is less than the concentration outside the cell.
c. The concentration of solute inside the cell is equal to the concentration outside the cell.
c. The concentration of solute inside the cell is equal to the concentration outside the cell.
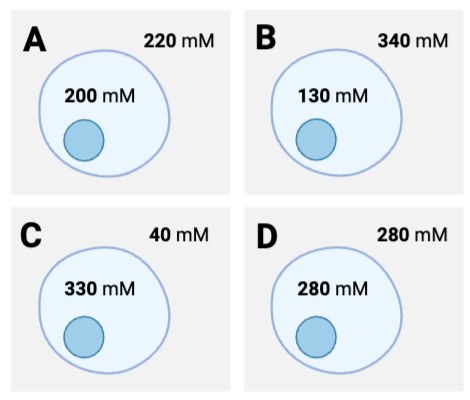
Which cells will experience the greatest net diffusion of water from outside to inside?
a. Cell A
b. Cell B
c. Cell C
d. Cell D
c. Cell C
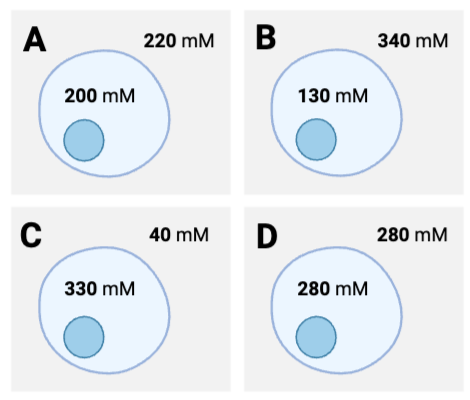
Which cells will experience the greatest net diffusion of water from inside to outside?
a. Cell A
b. Cell B
c. Cell C
d. Cell D
b. Cell B
A student placed a slice of potato in each of two solutions: salt water (500 mM of NaCl) and pure water (0 nM of NaCl). By comparison, a plant cell contains 150 mM of NaCl, which accounts for most of the cell's osmotically active solutes. After 30 minutes, the potato slices were removed and observed.
In which solution should a potato slice gain water?
pure water
A student placed a slice of potato in each of two solutions: salt water (500 mM of NaCl) and pure water (0 nM of NaCl). By comparison, a plant cell contains 150 mM of NaCl, which accounts for most of the cell's osmotically active solutes. After 30 minutes, the potato slices were removed and observed.
In which solution should a potato slice lose water?
a. pure water
b. salt water
c. Both solutions would cause a potato slice to gain water.
d. Neither solution would cause a potato slice to gain water.
b. salt water
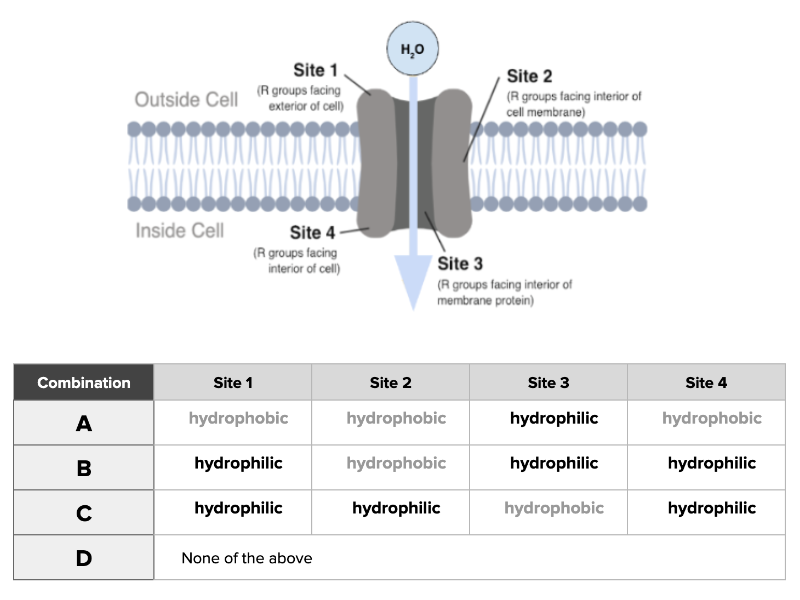
Which combination accurately describes a channel capable of transporting water molecules across a membrane?
a. Combination A
b. Combination B
c. Combination C
d. Combination D
b. Combination B
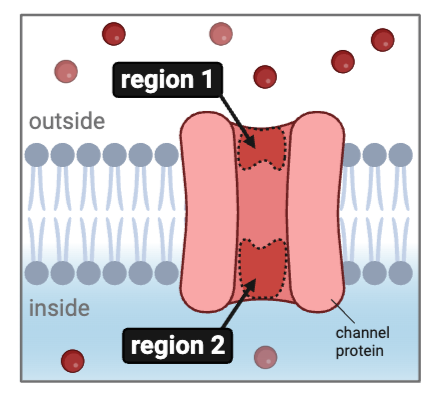
The figure shows a cell membrane with a channel protein. Regions 1 and 2 contain numerous amino acids with a partial negative charge.
What types of ions could diffuse through this channel? Select all that apply.
a. glucose
b. K+
c. Cl-
d. Na+
e. Ca2+
b. K+
d. Na+
e. Ca2+
You are studying how a molecule called SRH5 moves through the membrane of a plant cell. Through some measurements, you observe the following points:
- SRH5 is a small, nonpolar molecule.
- SRH5 can move across the membrane in either direction
- SRH5 always moves from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
- No ATP is required for SRH5 to move through a membrane.
- SRH5 moves at the same rate through a cell membrane with transport proteins and a synthetic membrane without transport proteins.
Based on these observations, SRH5 is most likely transported by ________.
a. simple diffusion
b. a channel protein
c. a carrier protein
a. simple diffusion
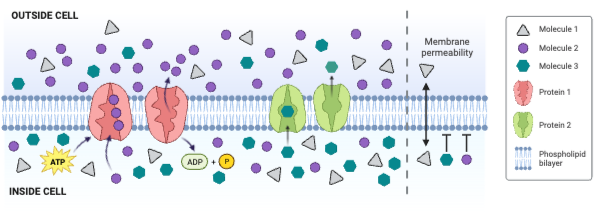
The concentration of Molecule 2 is ___________.
a. greater outside the cell than inside the cell
b. greater inside the cell than outside the cell
c. the same inside and outside of the cell
a. greater outside the cell than inside the cell
The net movement of Molecule 1 is from ___________.
a. low concentration to high concentration
b. high concentration to low concentration
c. There is no net movement of Molecule 1.
c. There is no net movement of Molecule 1.
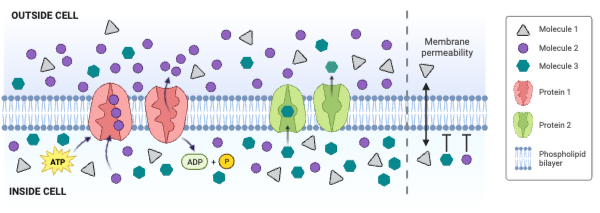
The net movement of Molecule 3 is from ___________.
a. low concentration to high concentration
b. high concentration to low concentration
c. There is no net movement of Molecule 1.
b. high concentration to low concentration
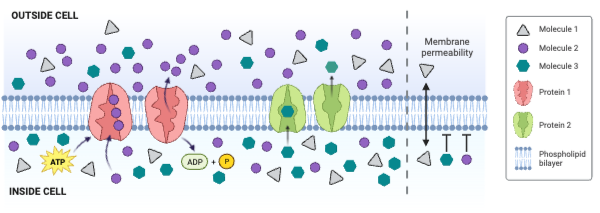
Molecule 1 could be ____________. Select all that apply.
a. charged
b. large and partially charged
c. small and partially charged
d. nonpolar
c. small and partially charged
d. nonpolar
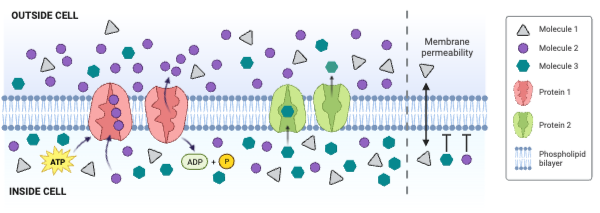
Which type of molecule moves through the membrane by simple diffusion?
a. Molecule 1
b. Molecule 2
c. Molecule 3
d. None of the molecules moves through the membrane by simple diffusion.
a. Molecule 1
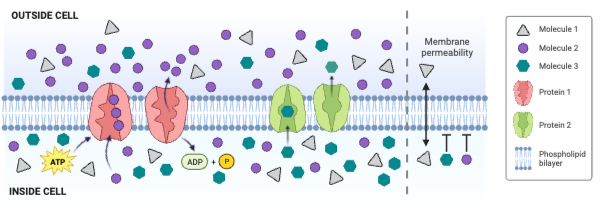
Which type of molecule moves through the membrane by facilitated diffusion involving a carrier protein?
a. Molecule 1
b. Molecule 2
c. Molecule 3
d. None of the molecules moves through a carrier protein.
c. Molecule 3
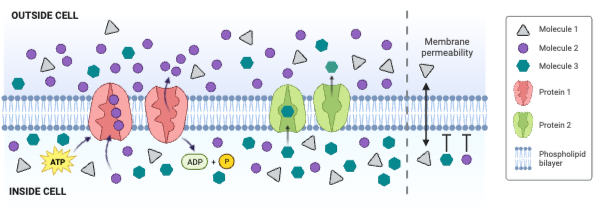
Which type of molecule moves through the membrane by primary active transport?
a. Molecule 1
b. Molecule 2
c. Molecule 3
d. None of the molecules moves through the membrane by primary active transport.
b. Molecule 2
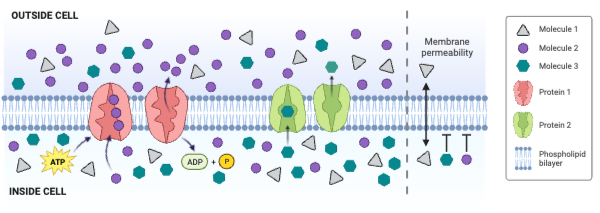
Which type of protein is a channel engaged in facilitated diffusion?
a. Protein 1
b. Protein 2
c. None of the proteins is a channel engaged in facilitated diffusion.
c. None of the proteins is a channel engaged in facilitated diffusion.
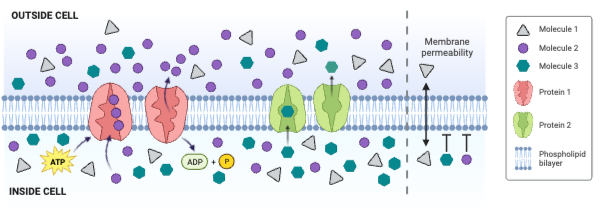
Which type of protein is an antiporter engaged in secondary active transport?
a. Protein 1
b. Protein 2
c. None of the proteins is an antiporter engaged in secondary active transport.
c. None of the proteins is an antiporter engaged in secondary active transport.
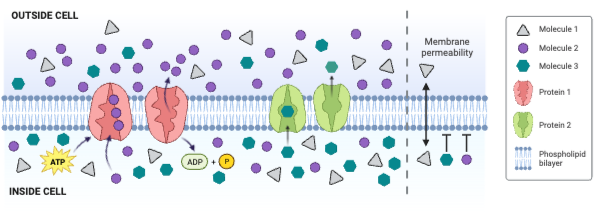
Which type of protein decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 1?
a. Protein 1
b. Protein 2
c. None of the proteins decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 1.
c. None of the proteins decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 1.
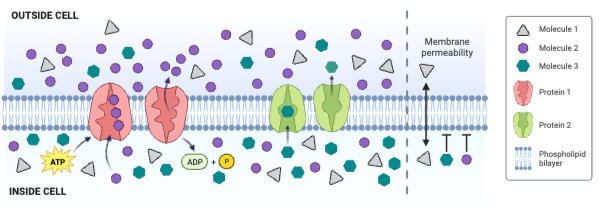
Which type of protein decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 2?
a. Protein 1
b. Protein 2
c. None of the proteins decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 2.
c. None of the proteins decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 2.
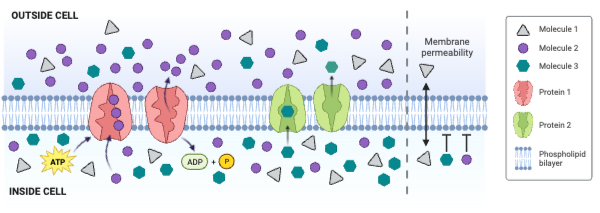
Which type of protein decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 3?
a. Protein 1
b. Protein 2
c. None of the proteins decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 3.
b. Protein 2
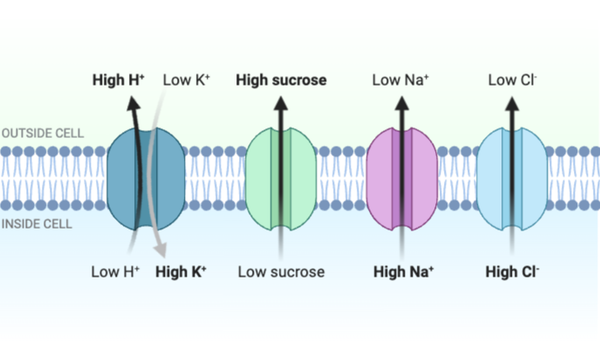
Which statement accurately describes the transport shown in the figure?
a. The transport of K+ into the cell requires energy in the form of ATP.
b. The transport of Na+ out of the cell requires energy in the form of ATP.
c. The transport of H+ into the cell requires energy in the form of ATP.
d. The transport of Cl- out of the cell occurs by active transport.
e. The transport of sucrose into the cell requires energy in the form of ATP.
a. The transport of K+ into the cell requires energy in the form of ATP.
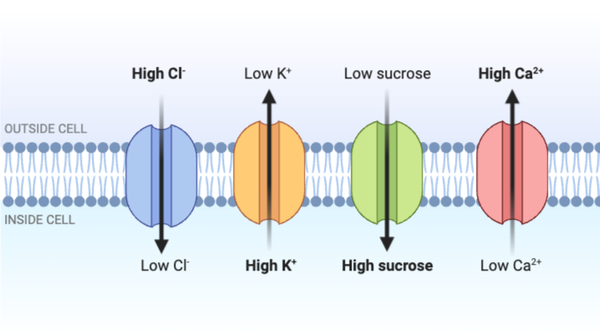
Which statement accurately describes the transport shown in the figure?
a. The transport of Cl- into the cell requires energy in the form of ATP.
b. The transport of K+ into the cell does not require energy in the form of ATP.
c. The transport of sucrose into the cell occurs by simple diffusion.
d. The transport of Ca2+ out of the cell occurs by active transport.
d. The transport of Ca2+ out of the cell occurs by active transport.
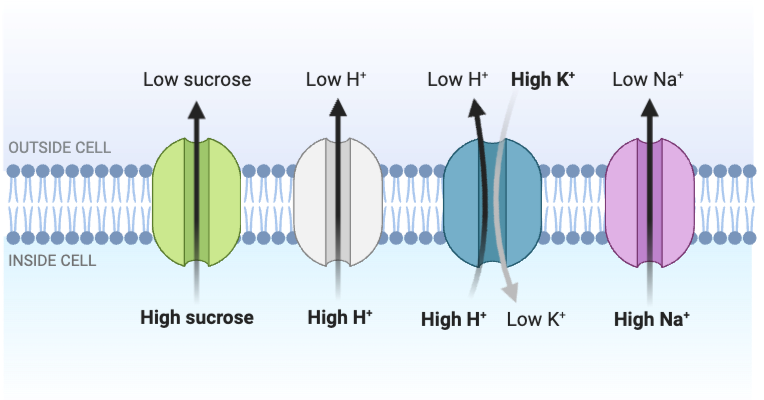
Which statements accurately describe the transport shown in the figure? Select all that apply.
a. The transport of K+ into the cell does not require energy in the form of ATP.
b. The transport of H+ out of the cell does not require energy in the form of ATP.
c. The transport of Na+ out of the cell requires energy in the form of ATP.
d. The transport of sucrose out of the cell occurs by active transport.
a. The transport of K+ into the cell does not require energy in the form of ATP.
b. The transport of H+ out of the cell does not require energy in the form of ATP.
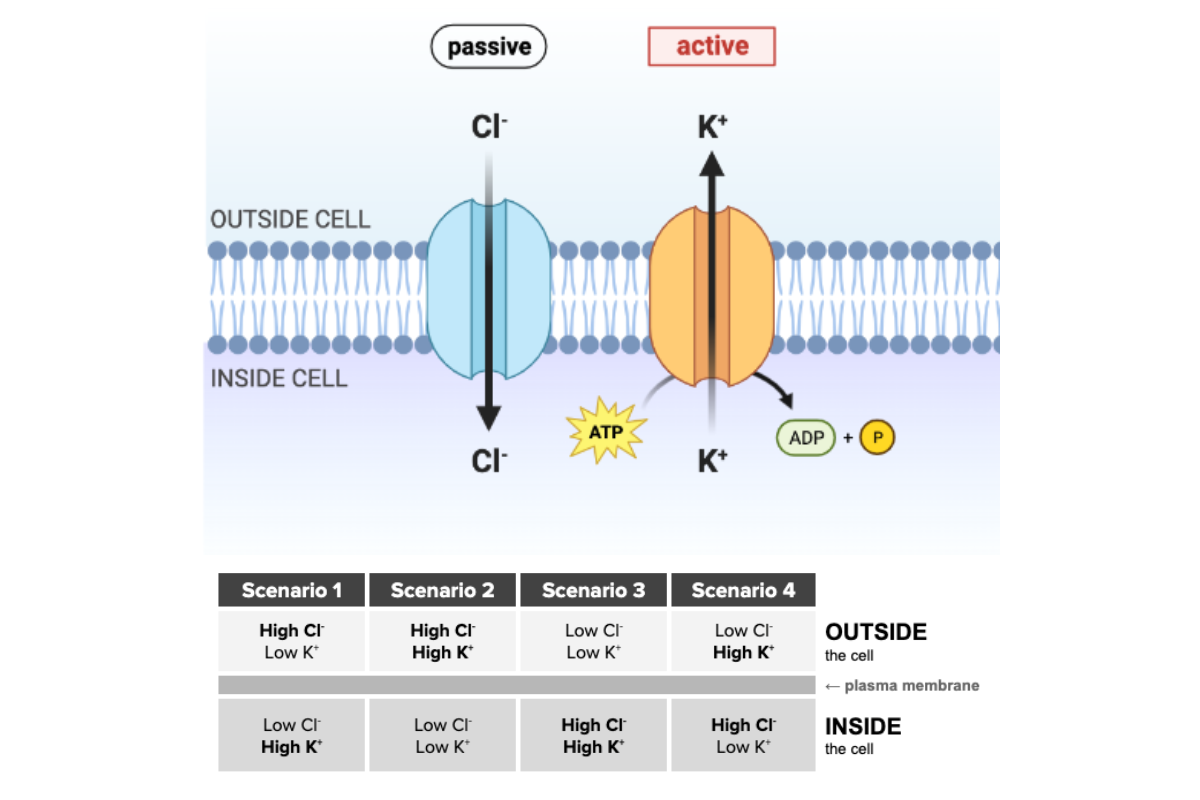
Which scenario is most likely given the function of the transport proteins shown in the figure?
a. Scenario 1
b. Scenario 2
c. Scenario 3
d. Scenario 4
b. Scenario 2
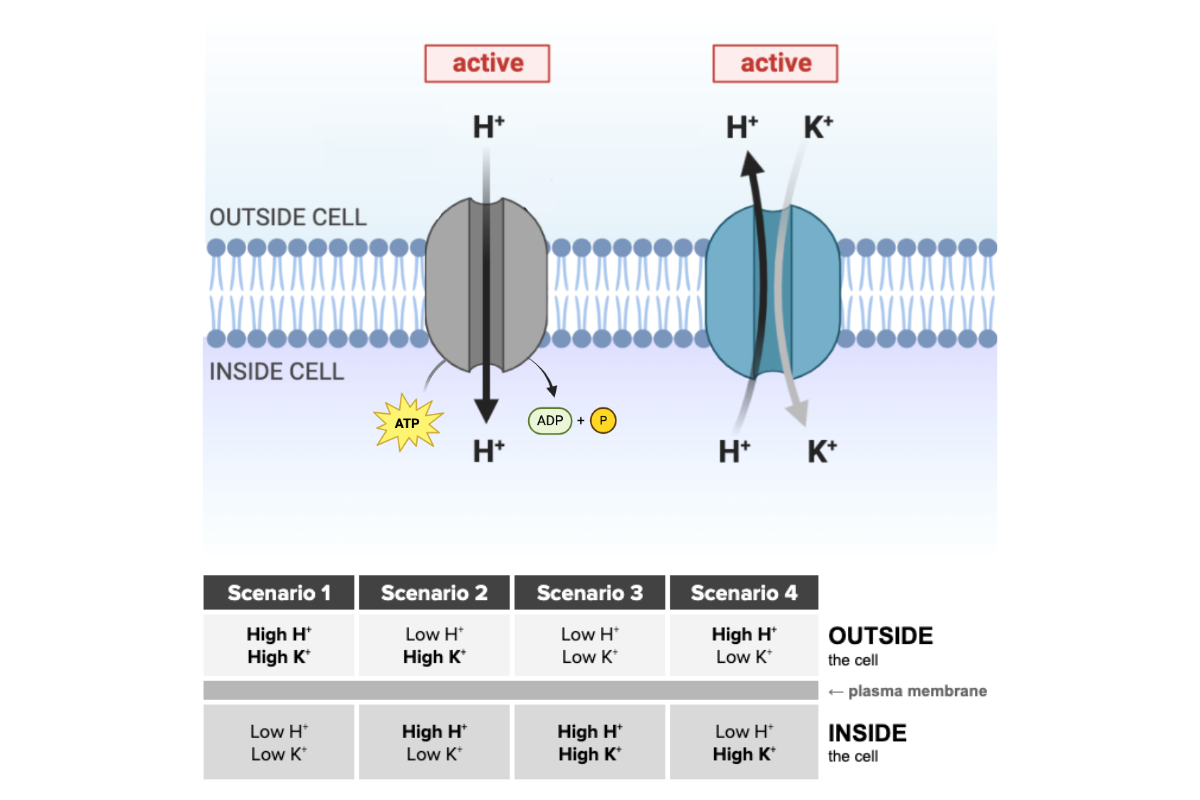
Which scenario is most likely given the function of the transport proteins shown in the figure?
a. Scenario 1
b. Scenario 2
c. Scenario 3
d. Scenario 4
c. Scenario 3
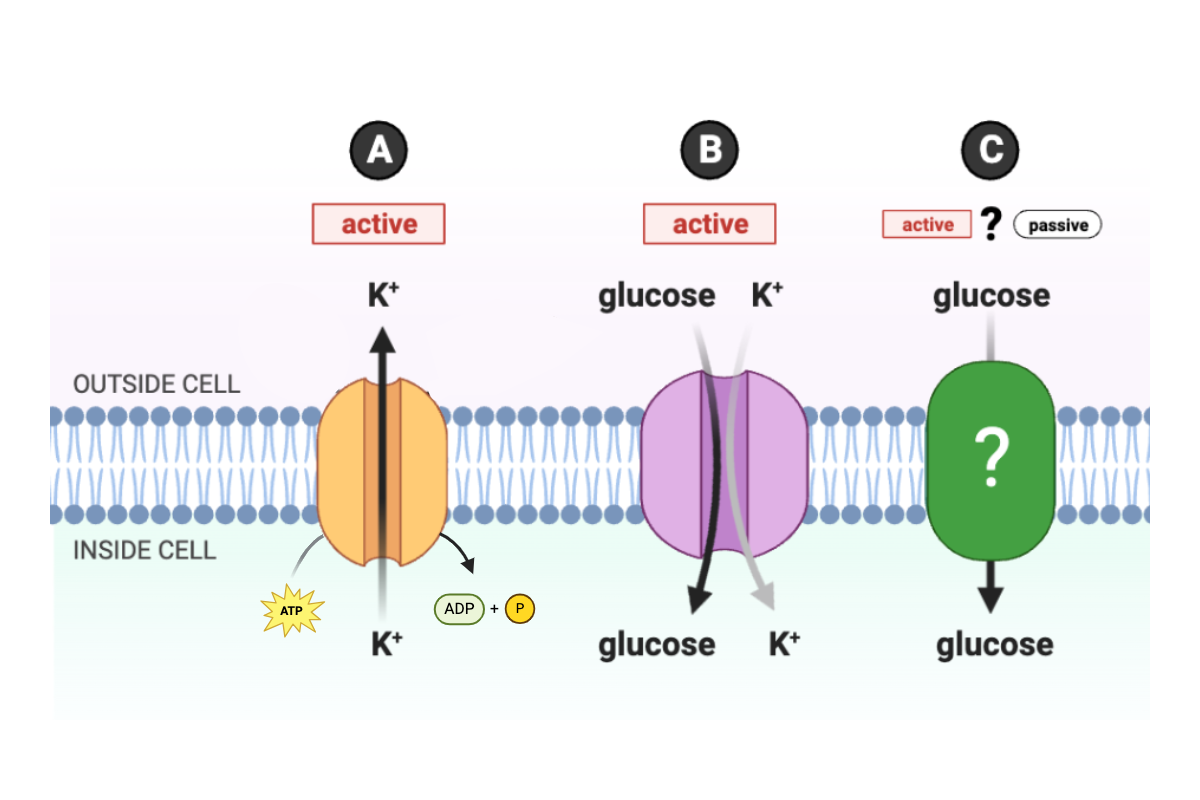
Given the function of proteins A and B, is protein C is an ATPase pump engaged in active transport or a channel engaged in facilitated diffusion?
a. Protein C is an active transport protein.
b. Protein C is a passive transport protein.
c. There is insufficient information to make a conclusion.
a. Protein C is an active transport protein.
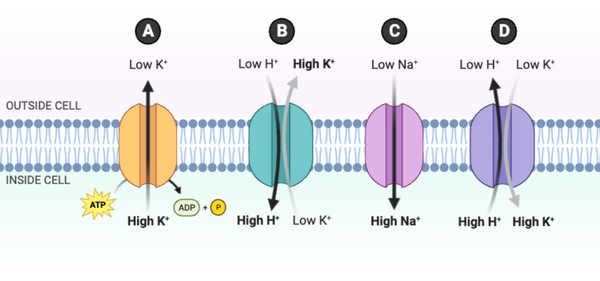
For which protein is the transport process accurately represented?
a. Protein A
b. Protein B
c. Protein C
d. Protein D
d. Protein D
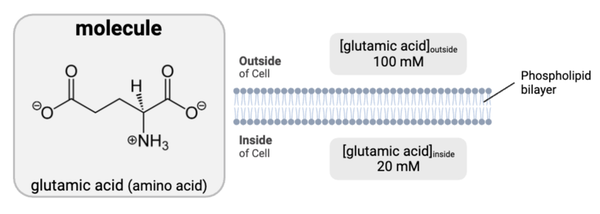
True or false? This molecule likely needs a transport protein to move through the cell membrane.
True
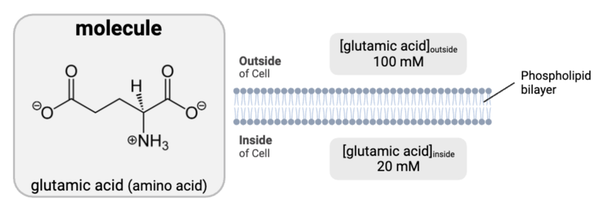
Which statement is accurate?
a. The molecule has charged or partially charged regions and cannot diffuse through a phospholipid bilayer.
b. The molecule has charged or partially charged regions and can diffuse through a phospholipid bilayer.
c. The molecule is uncharged and cannot diffuse through a phospholipid bilayer.
d. The molecule is uncharged and can diffuse through a phospholipid bilayer.
a. The molecule has charged or partially charged regions and cannot diffuse through a phospholipid bilayer.
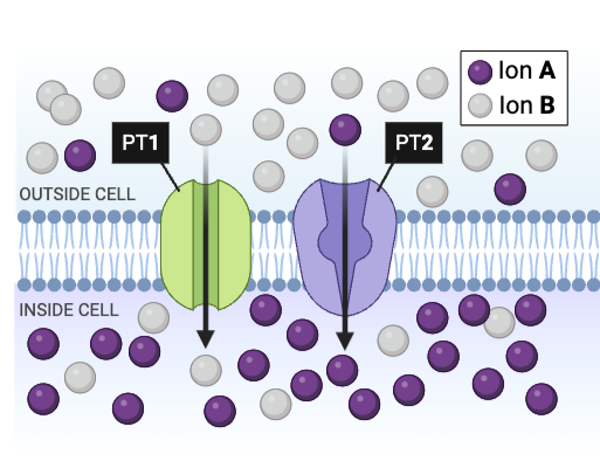
Which type of ion is moving against a concentration gradient?
a. Ion A
b. Ion B
c. Both Ion A and Ion B
d. Neither Ion A nor Ion B
a. Ion A
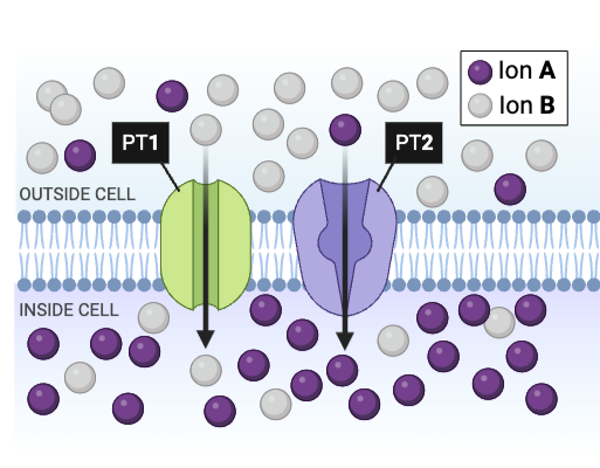
True or false? Removing ATP from the cell would immediately stop the transport of Ion B by PT1.
False
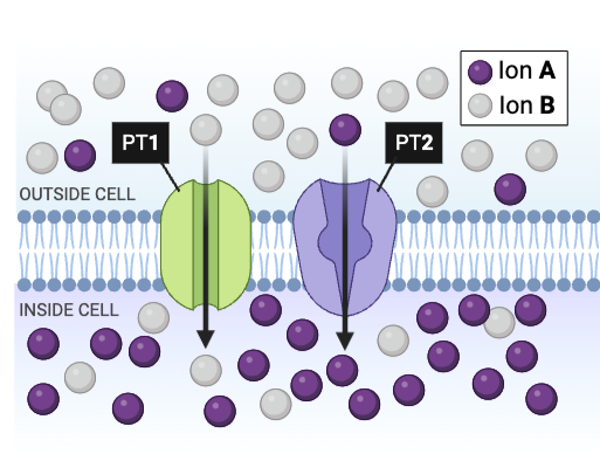
True or false? PT2 is most likely an ATPase pump.
True
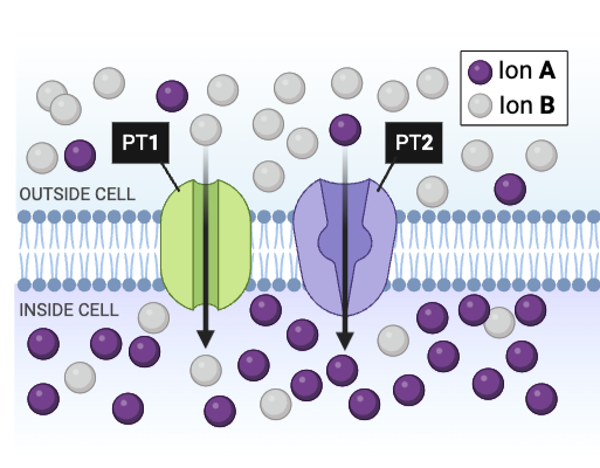
rue or false? PT1 is most likely a channel protein engaged in facilitated diffusion.
a. true
b. false
True
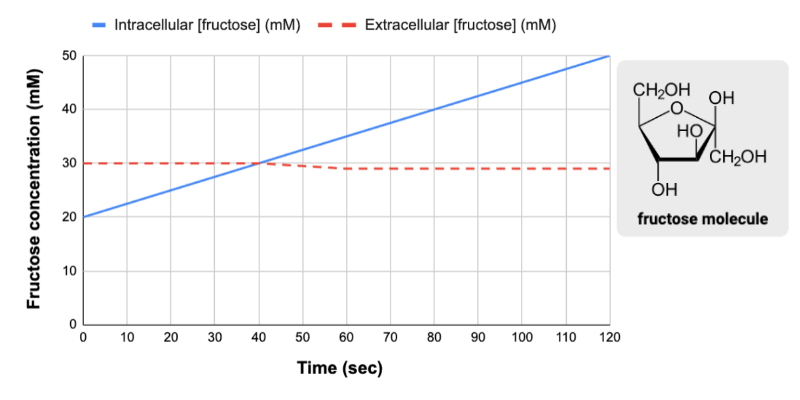
True or false? Between 0 and 120 seconds, the net movement of fructose was from outside the cell to inside the cell.
True
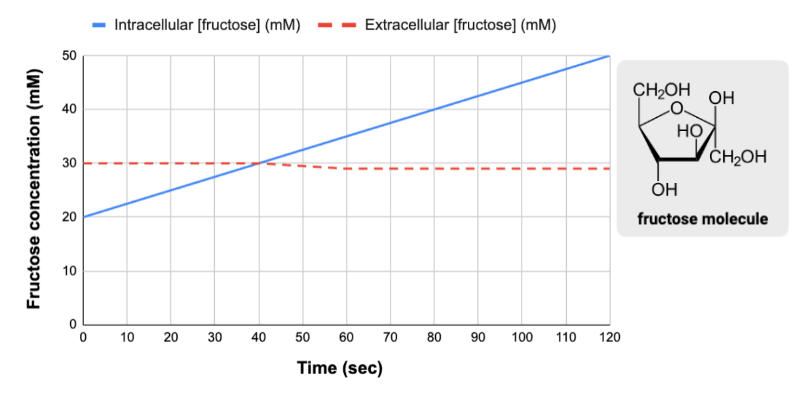
True or false? The change in the intracellular concentration of fructose was most likely caused by active transport.
True
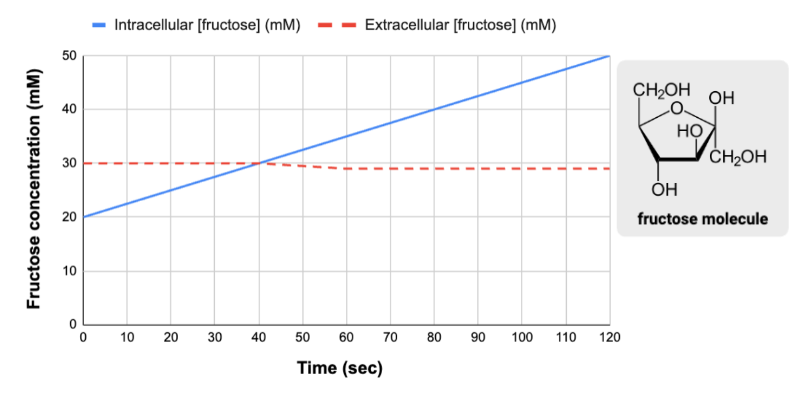
True or false? The change in the intracellular concentration of fructose could have occurred without a transport protein.
False
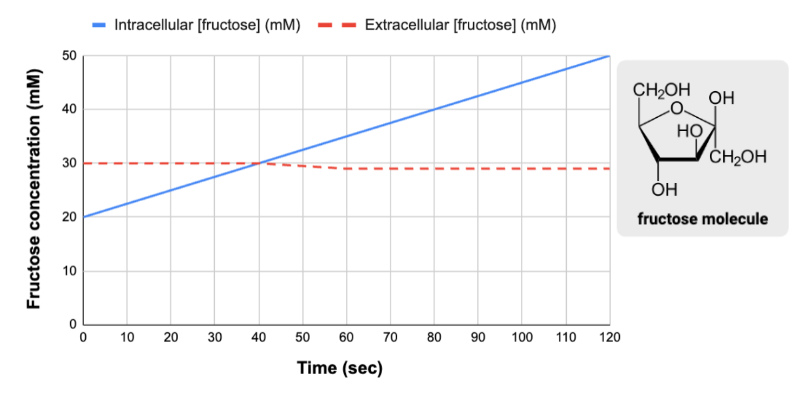
True or false? The change in the intracellular concentration of fructose required energy in the form of either ATP or an electrochemical gradient.
True
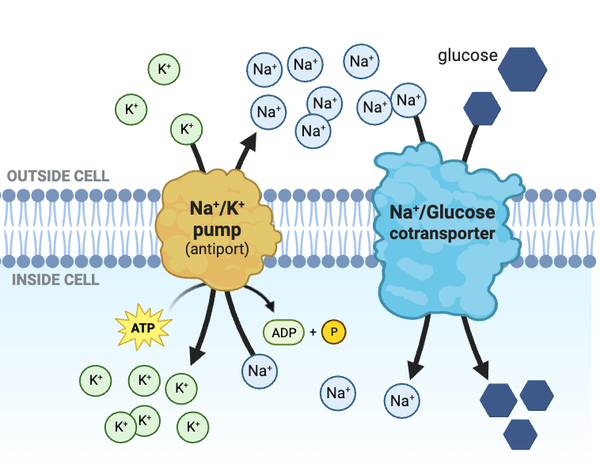
Which condition would increase the rate at which glucose enters the cell?
a. decreasing the concentration of glucose outside the cell
b. decreasing the concentration of ATP inside the cell
c. increasing the concentration of Na+ inside the cell, such that the concentration inside the cell greatly exceeds the concentration outside the cell
d. increasing the concentration of Na+ outside the cell, such that the concentration outside the cell greatly exceeds the concentration inside the cell
d. increasing the concentration of Na+ outside the cell, such that the concentration outside the cell greatly exceeds the concentration inside the cell
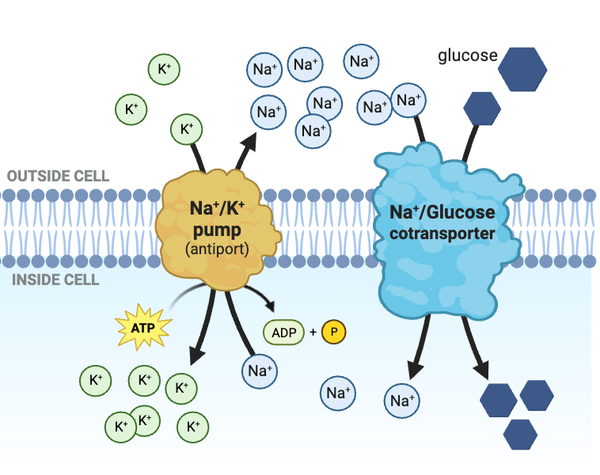
Which statement accurately describes how the transport of glucose would change if Na+ channels were added to the membrane?
a. The Na+ channels would decrease the concentration gradient of Na+, slowing the transport of glucose into the cell.
b. The Na+ channels would increase the concentration gradient of Na+, speeding the transport of glucose into the cell.
c. The Na+ channels would not affect the rate at which glucose is transported into the cell.
a. The Na+ channels would decrease the concentration gradient of Na+, slowing the transport of glucose into the cell.
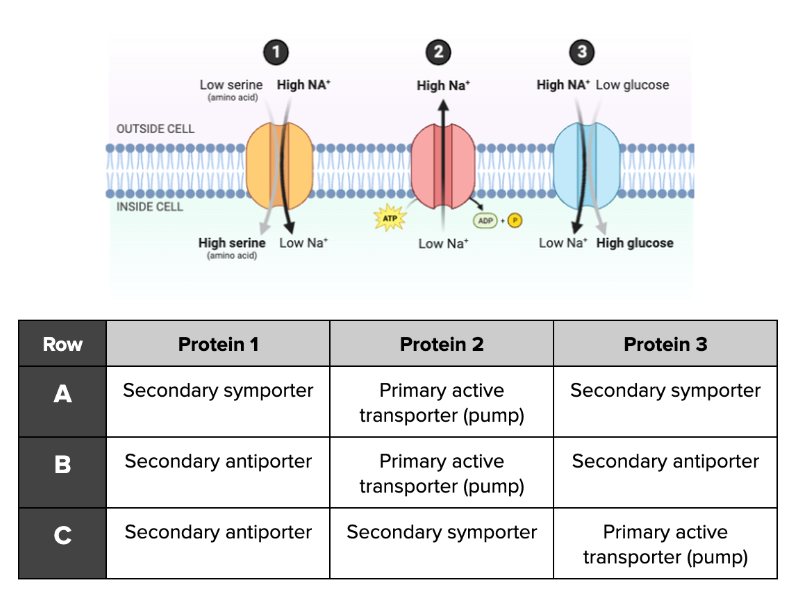
Which row in the table provided accurately describes the functions of Proteins 1, 2, and 3 shown in the figure?
Row A
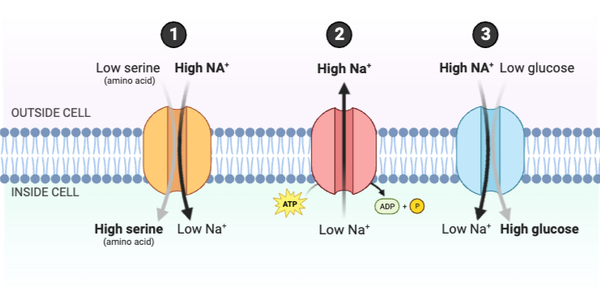
Which statements accurately describe how the rates of transport would change if the concentration of Na+ outside the cell increased? Select all that apply.
a. Serine would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
b. Serine would be transported out of the cell at a slower rate.
c. Glucose would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
d. Glucose would be transported out of the cell at a slower rate.
a. Serine would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
c. Glucose would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
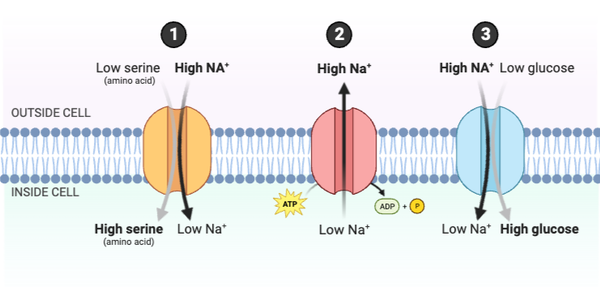
Which statements accurately describe how the system would change if the concentration of ATP in the cell decreased? Select all that apply.
a. The concentration gradient of Na+ would increase.
b. The concentration gradient of Na+ would decrease.
c. Serine would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
d. Serine would be transported into the cell at a slower rate.
e. Glucose would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
f. Glucose would be transported into the cell at a slower rate.
a. The concentration gradient of Na+ would increase.
d. Serine would be transported into the cell at a slower rate.
f. Glucose would be transported into the cell at a slower rate.
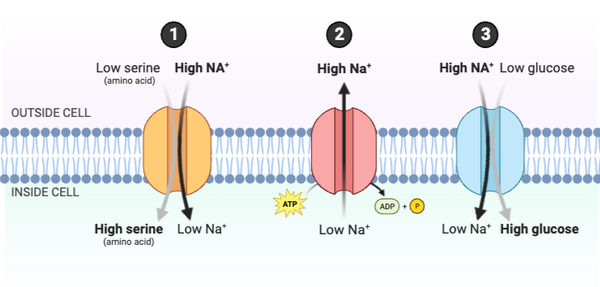
Which statements accurately describe how the system would change if the concentration of Protein #2 in the membrane increased? Select all that apply.
a. The concentration gradient of Na+ would increase.
b. The concentration gradient of Na+ would decrease.
c. Serine would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
d. Serine would be transported into the cell at a slower rate.
e. Glucose would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
f. Glucose would be transported into the cell at a slower rate.
b. The concentration gradient of Na+ would decrease.
c. Serine would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
e. Glucose would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
Which statements about concentration gradients are accurate? Select all that apply.
a. The concentration of K+ outside the cell exceeds the concentration inside the cell.
b. The concentration of K+ inside the cell exceeds the concentration outside the cell.
c. The concentration of Na+ outside the cell exceeds the concentration inside the cell.
d. The concentration of Na+ inside the cell exceeds the concentration outside the cell.
e. The concentration of H+ outside the cell exceeds the concentration inside the cell.
f. The concentration of H+ inside the cell exceeds the concentration outside the cell.
g. The concentration of phosphate outside the cell exceeds the concentration inside the cell.
h. The concentration of phosphate outside the cell exceeds the concentration outside the cell.
i. The concentration of Ca2+ outside the cell exceeds the concentration inside the cell.
j. The concentration of Ca2+ outside the cell exceeds the concentration outside the cell.
b. The concentration of K+ inside the cell exceeds the concentration outside the cell.
c. The concentration of Na+ outside the cell exceeds the concentration inside the cell.
f. The concentration of H+ inside the cell exceeds the concentration outside the cell.
g. The concentration of phosphate outside the cell exceeds the concentration inside the cell.
i. The concentration of Ca2+ outside the cell exceeds the concentration inside the cell.
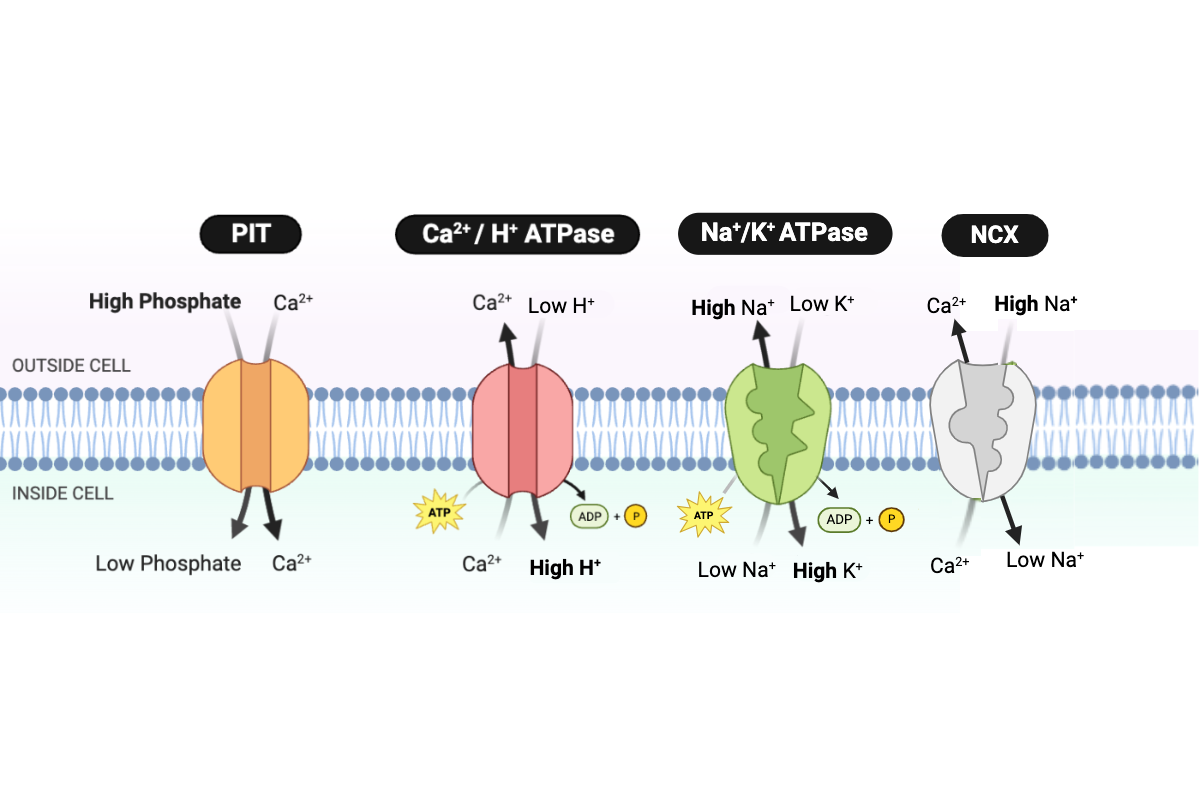
Which type of transport is performed by the PIT protein?
a. simple diffusion
b. facilitated diffusion
c. primary active transport
d. secondary active transport
b. facilitated diffusion
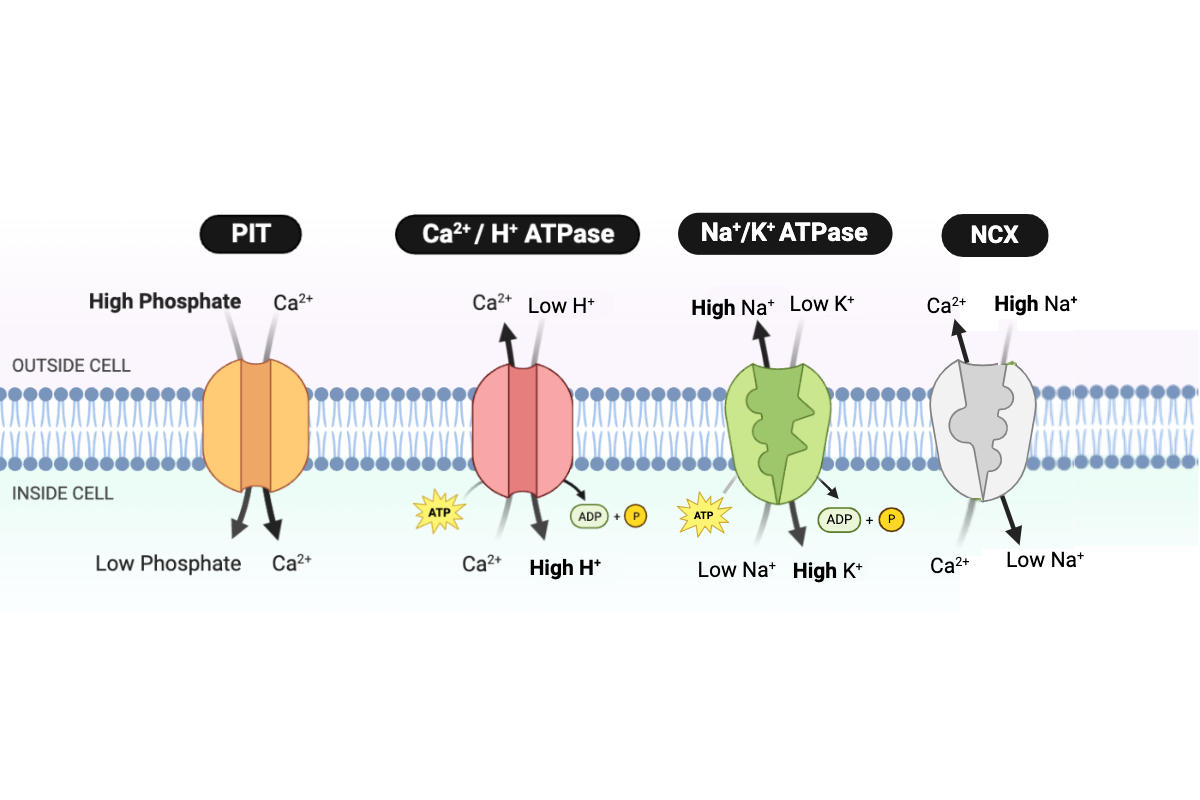
Which type of transport is performed by the NCX protein?
a. simple diffusion
b. facilitated diffusion
c. primary active transport
d. secondary active transport
d. secondary active transport
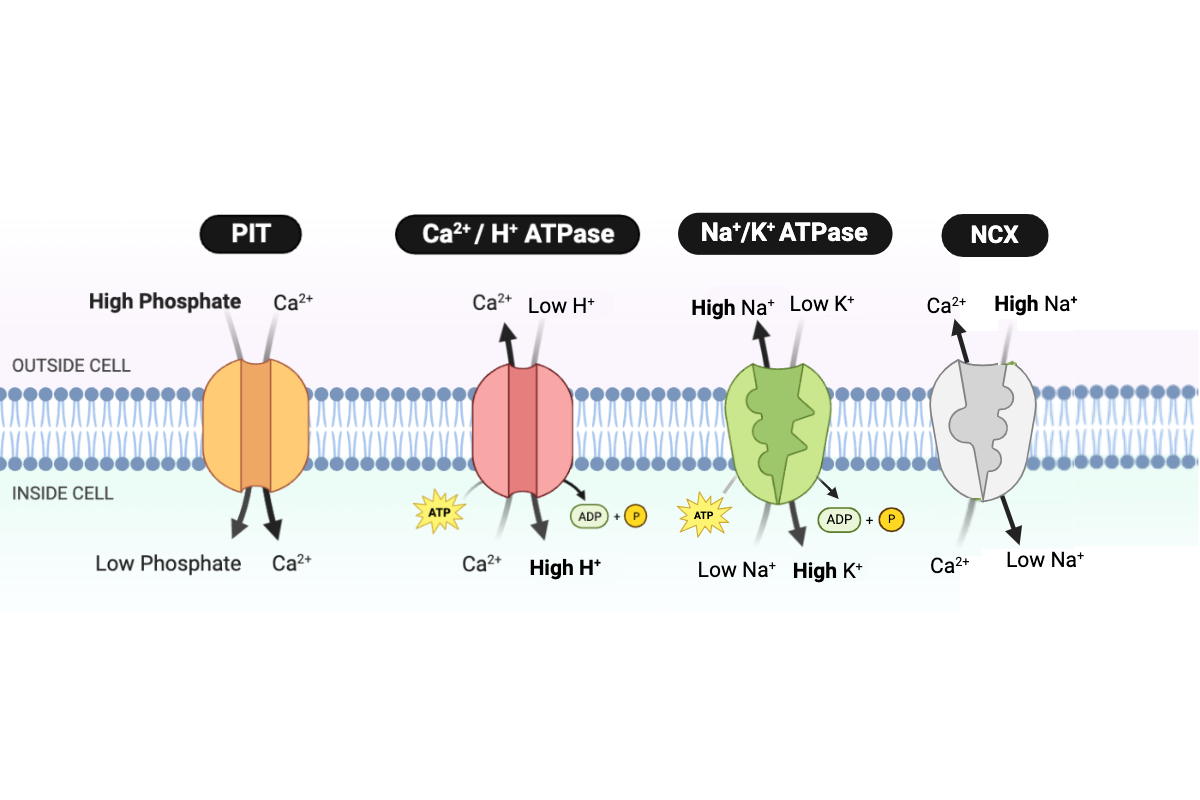
Which type of transport is performed by the Ca2+/H+ ATPase?
a. simple diffusion
b. facilitated diffusion
c. primary active transport
d. secondary active transport
c. primary active transport
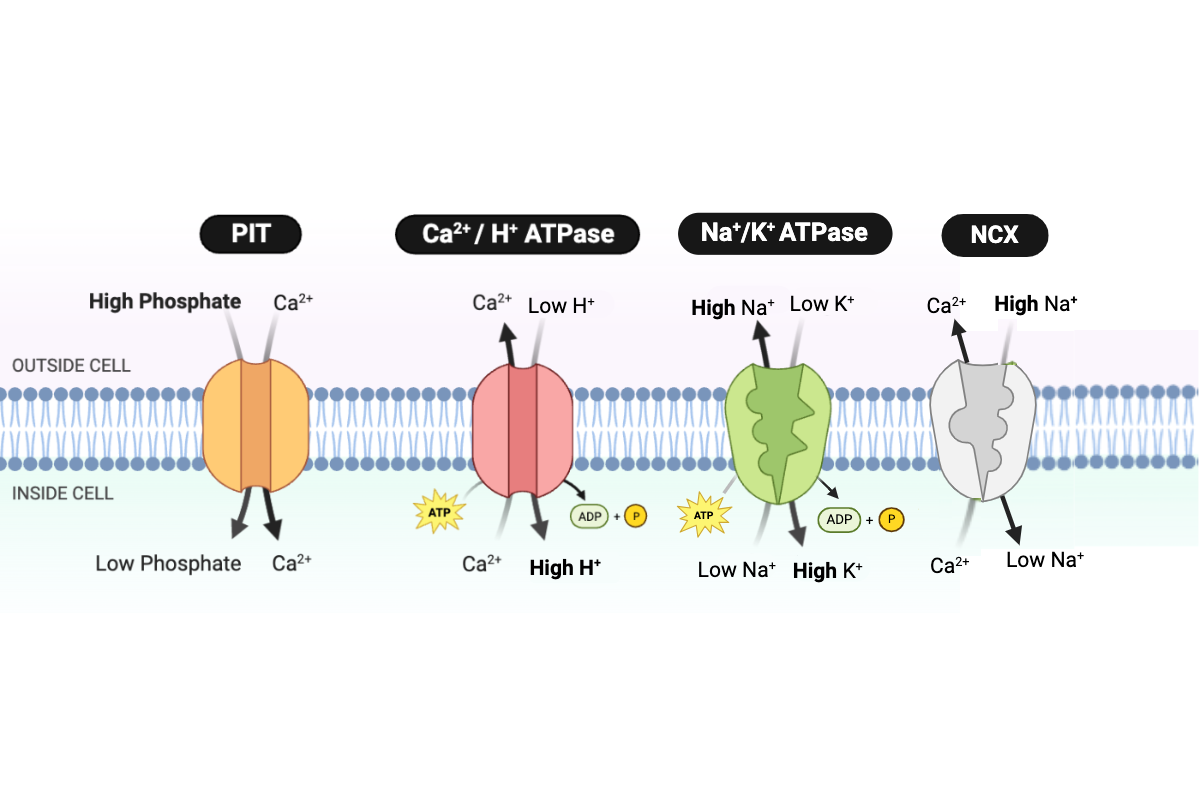
Which type of transport is performed by the Na+/K+ ATPase?
a. simple diffusion
b. facilitated diffusion
c. primary active transport
d. secondary active transport
c. primary active transport
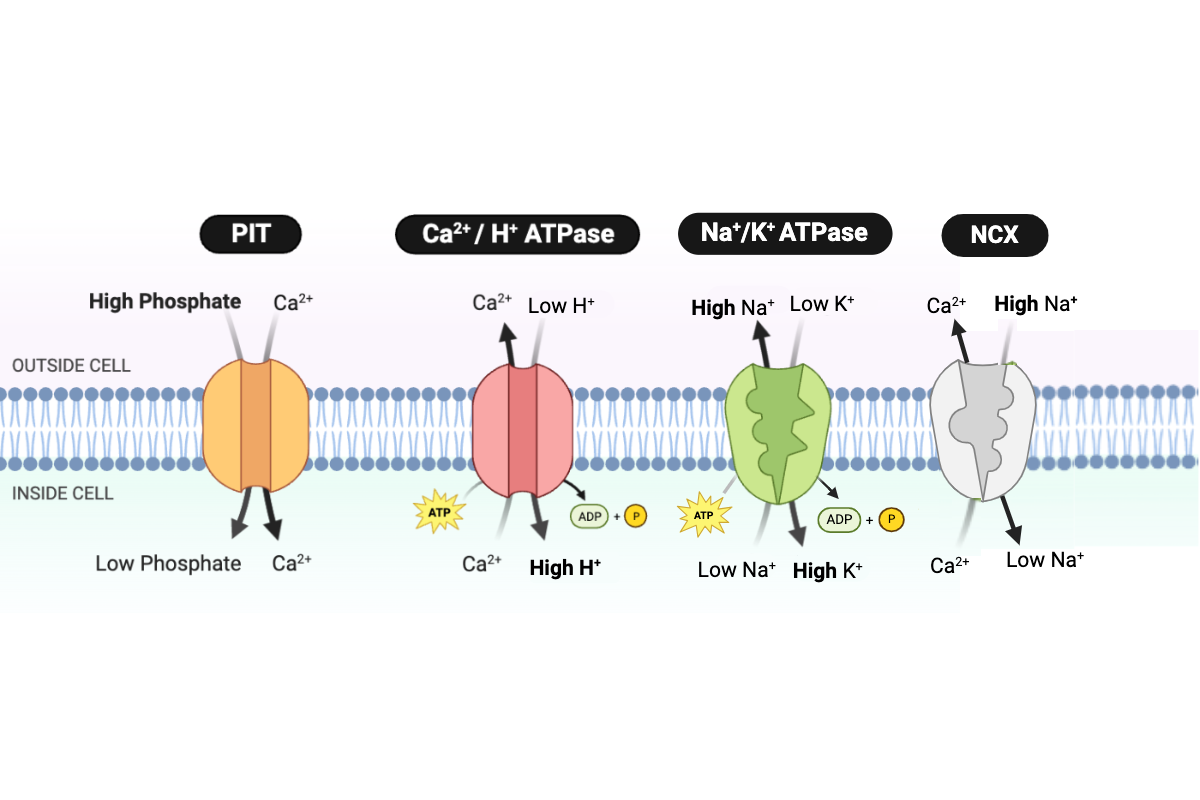
Which protein transports Ca2+ into the cell?
a. PIT
b. NCX
c. Ca2+/H+ ATPase
d. Na+/K+ ATPase
a. PIT
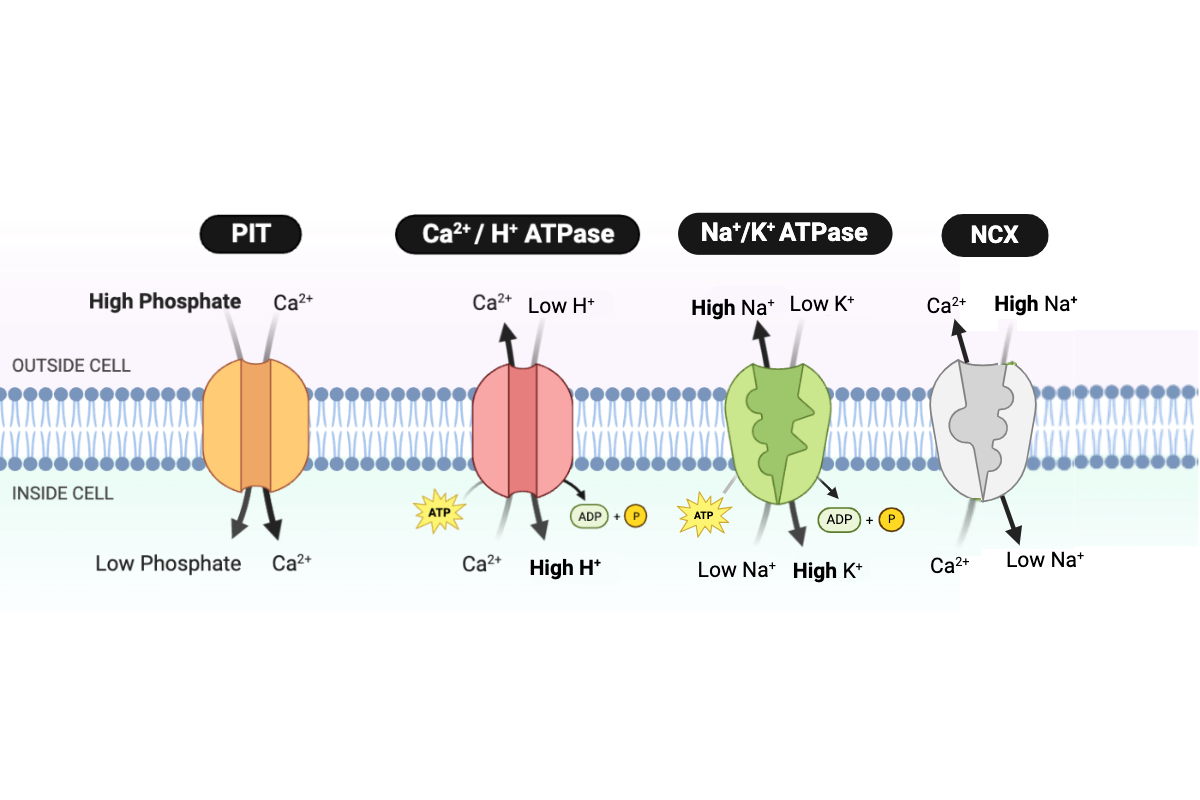
Which proteins transport Ca2+ out of the cell? Select all that apply.
a. PIT
b. NCX
c. Ca2+/H+ ATPase
d. Na+/K+ ATPase
b. NCX
c. Ca2+/H+ ATPase
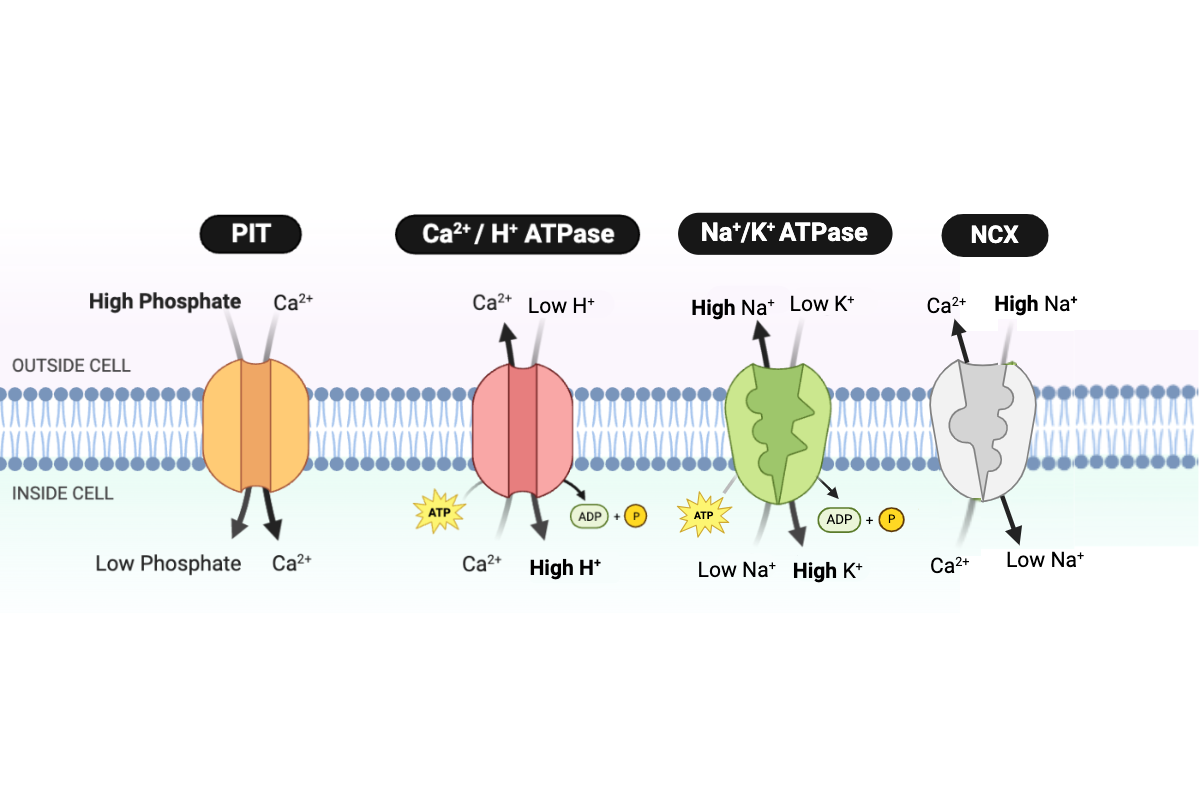
Which protein transports H+ into the cell?
a. PIT
b. NCX
c. Ca2+/H+ ATPase
d. Na+/K+ ATPase
c. Ca2+/H+ ATPase
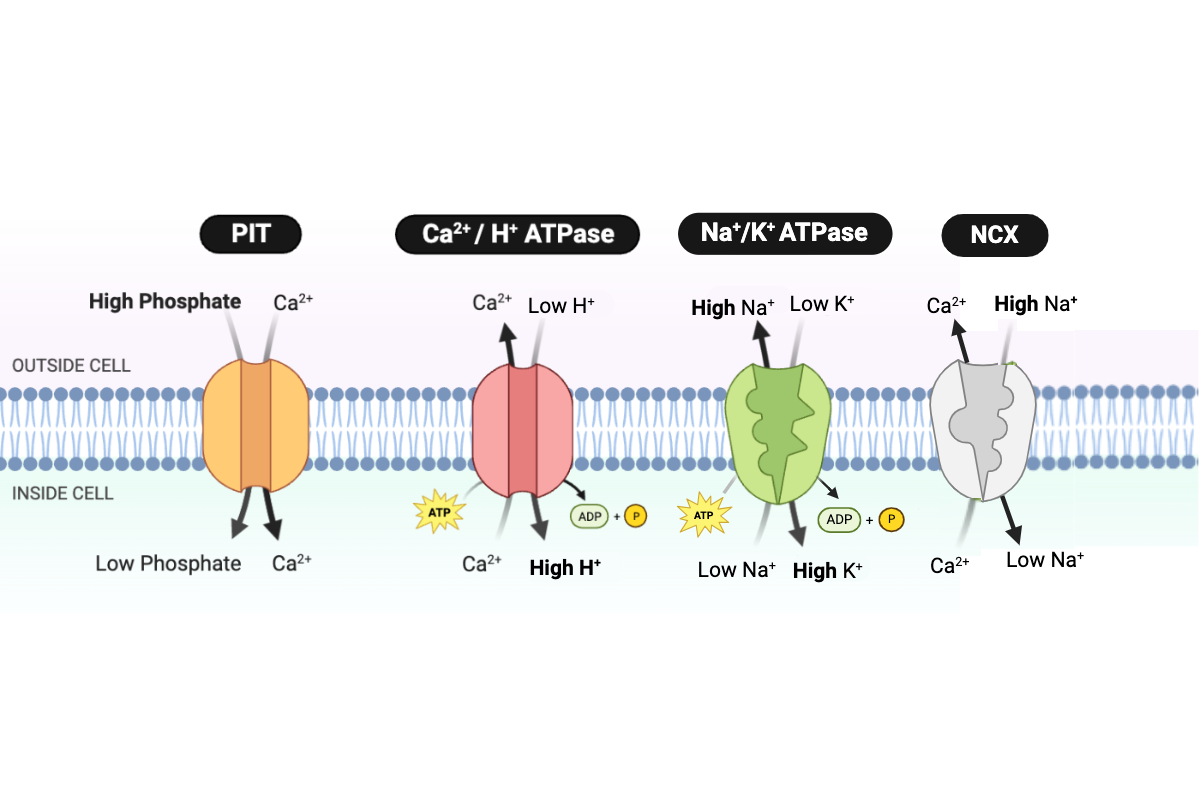
Which protein transports Na+ into the cell?
a. PIT
b. NCX
c. Ca2+/H+ ATPase
d. Na+/K+ ATPase
b. NCX
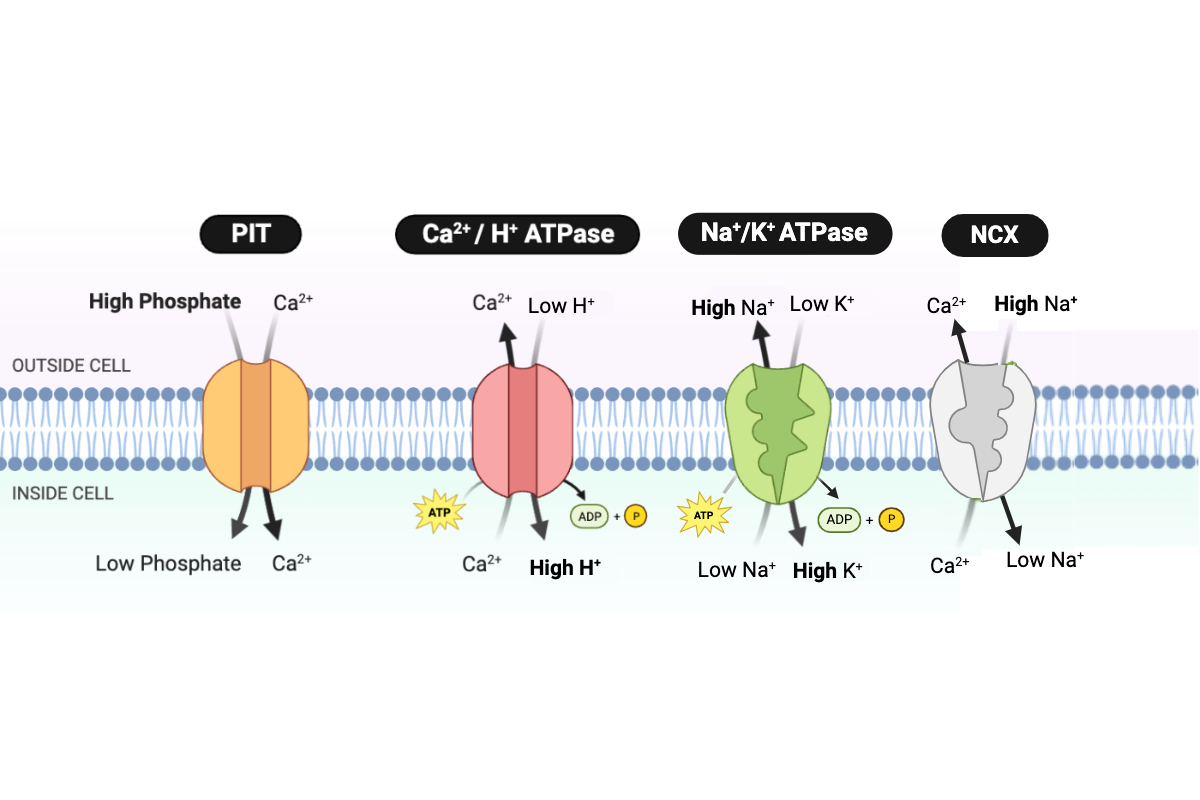
Which protein transports Na+ out of the cell?
a. PIT
b. NCX
c. Ca2+/H+ ATPase
d. Na+/K+ ATPase
d. Na+/K+ ATPase
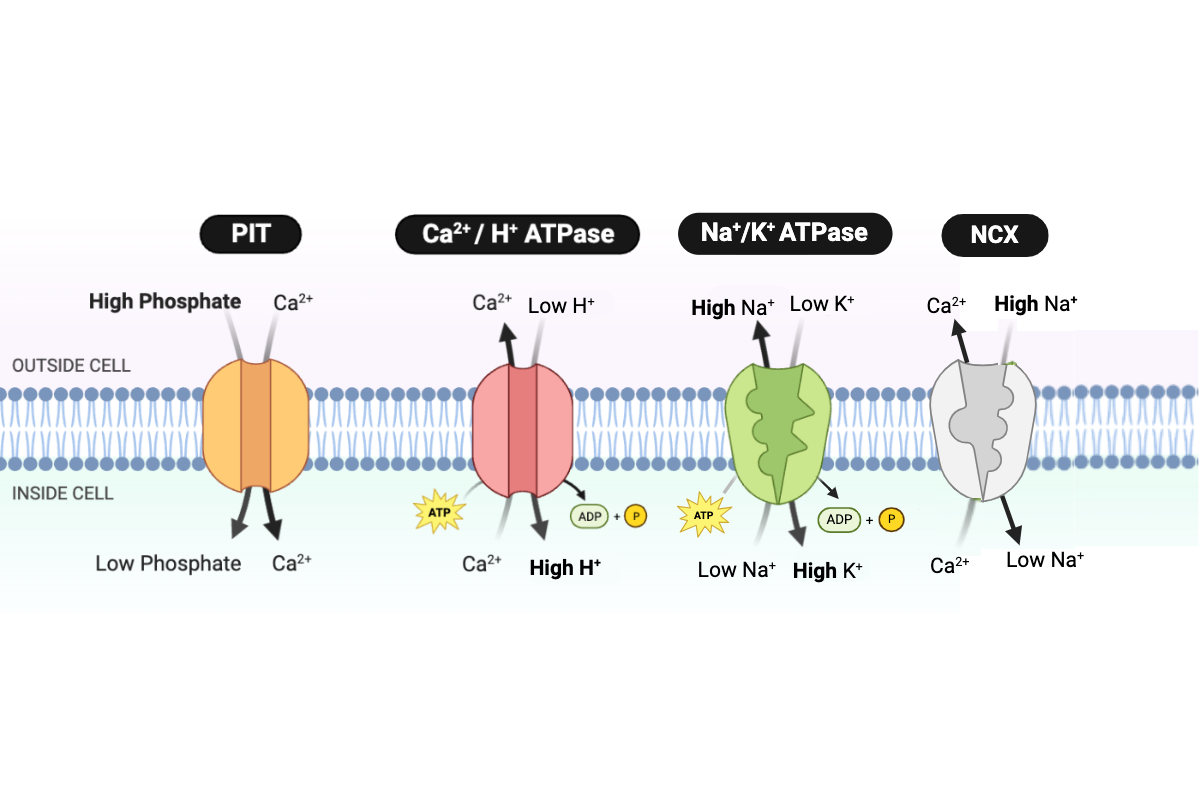
Which protein transports K+ into the cell?
a. PIT
b. NCX
c. Ca2+/H+ ATPase
d. Na+/K+ ATPase
d. Na+/K+ ATPase
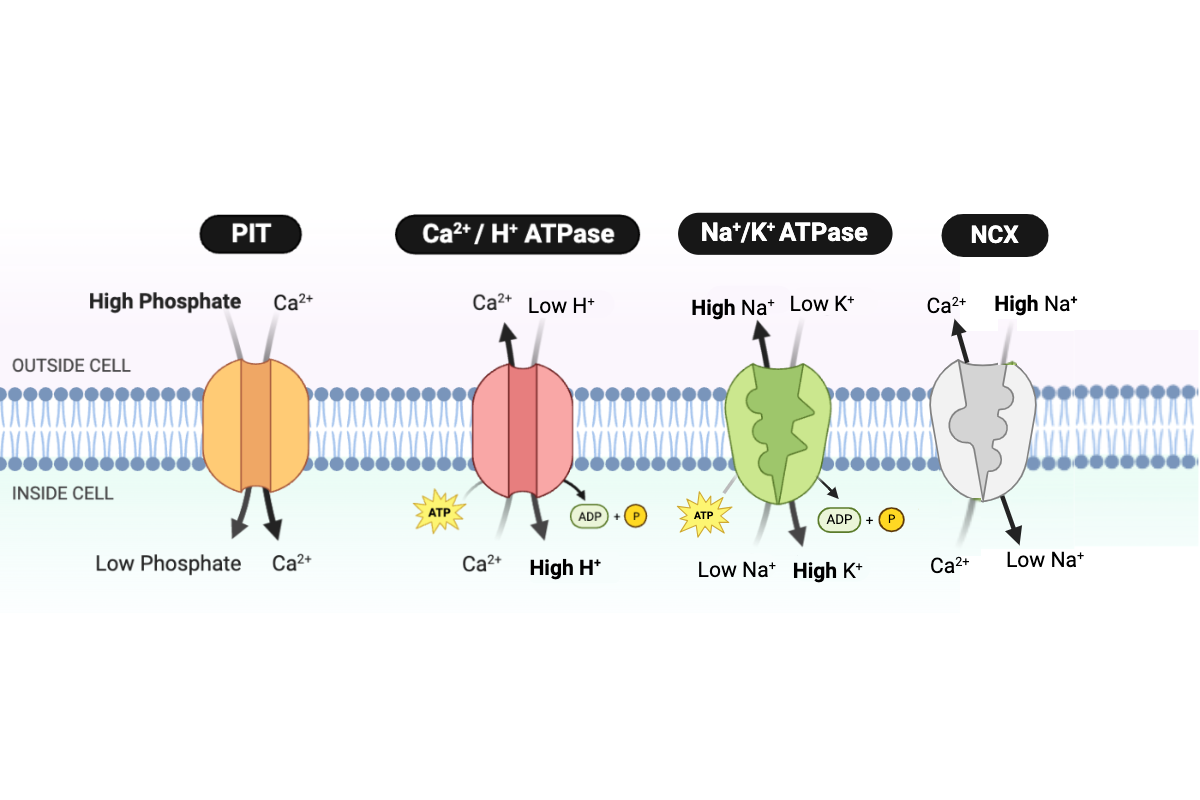
Which protein transports phosphate into the cell?
a. PIT
b. NCX
c. Ca2+/H+ ATPase
d. Na+/K+ ATPase
a. PIT
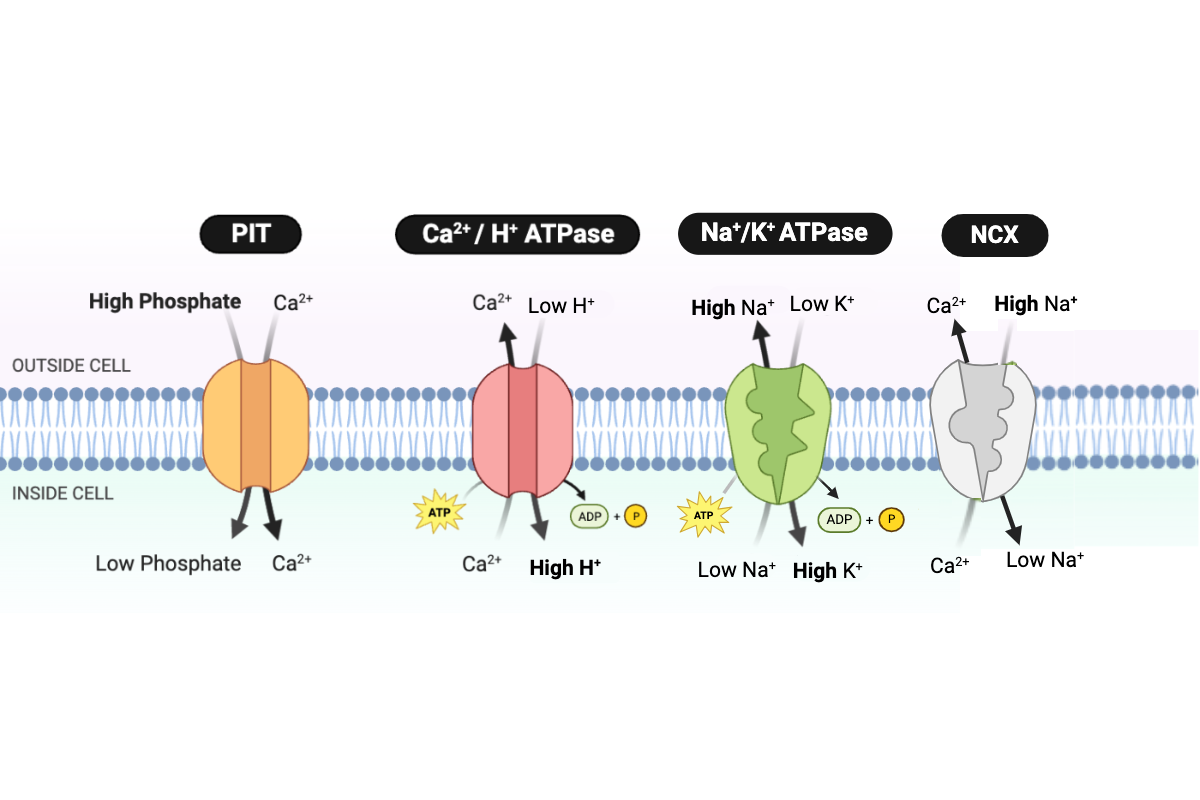
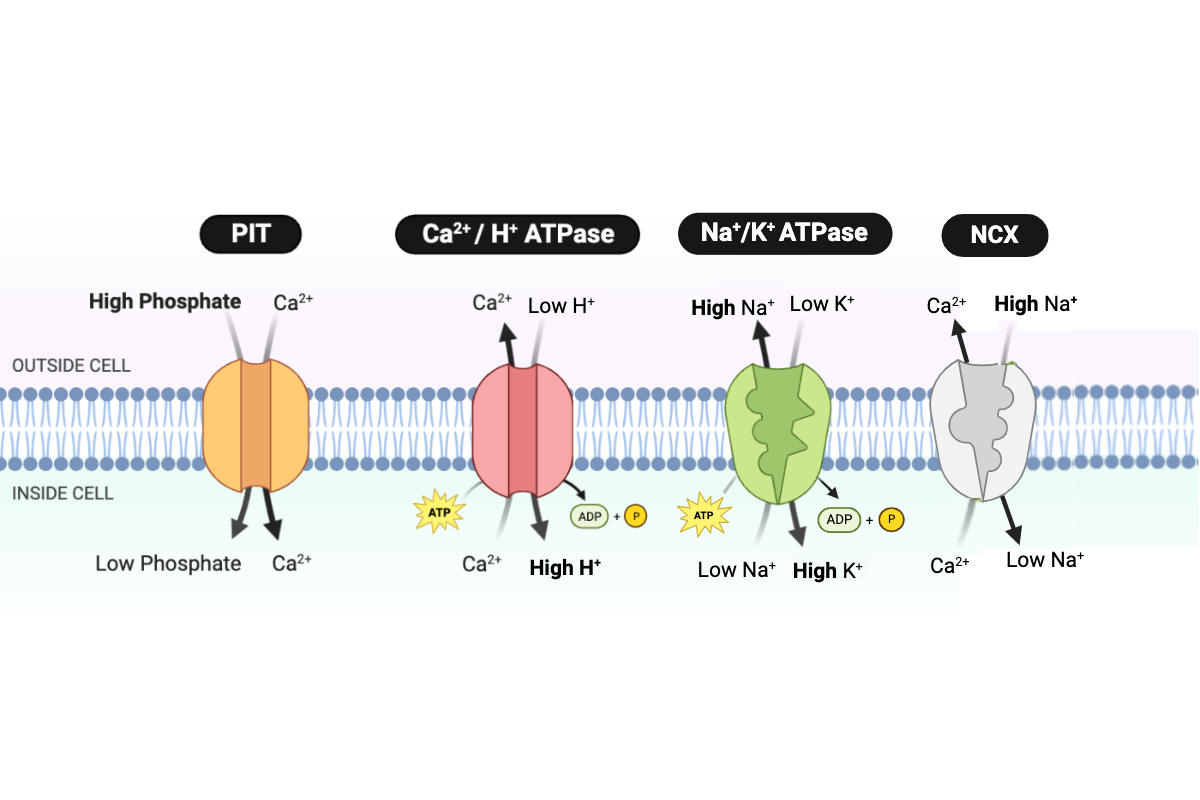
Which ions require energy in the form of ATP to be transported through the cell membrane? Select all that apply.
a. sodium ions (Na+)
b. calcium ions (Ca2+)
c. hydrogen ions (H+)
d. potassium ions (K+)
e. phosphate
a. sodium ions (Na+)
b. calcium ions (Ca2+)
c. hydrogen ions (H+)
d. potassium ions (K+)
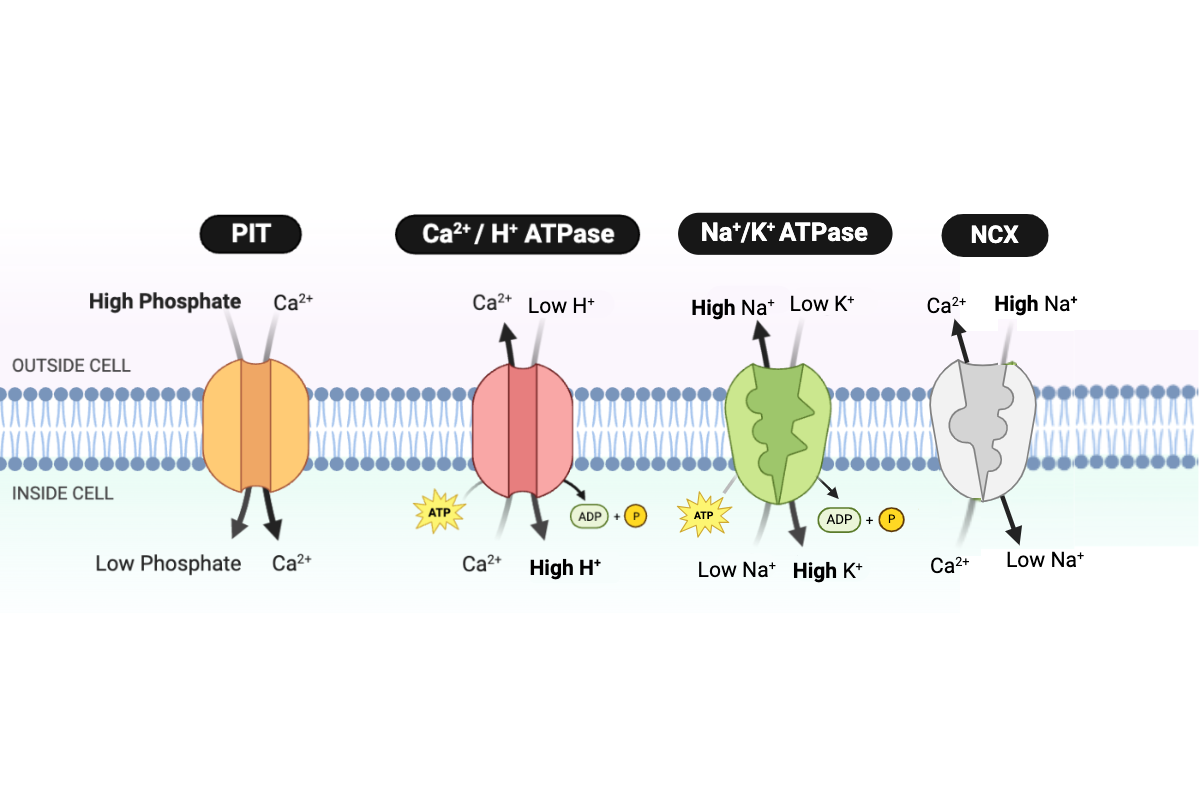
The transport of Ca2+ out of the cell requires ___________. Select all that apply.
a. only the kinetic energy of Ca2+
b. energy in the form of ATP
c. energy in the form of a concentration gradient of Na+
d. energy in the form of a concentration gradient of phosphate
b. energy in the form of ATP
c. energy in the form of a concentration gradient of Na+
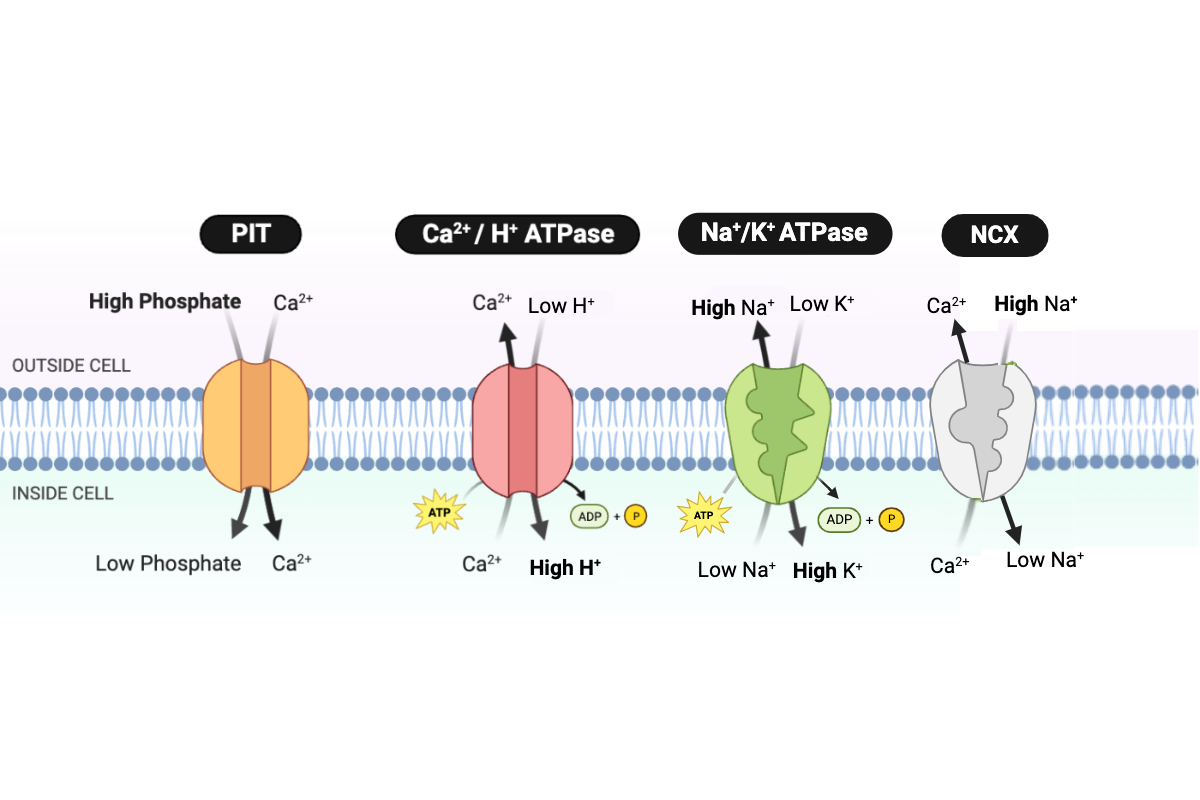
Which pattern would occur if the concentration of ATP in the cell decreases? Select all that apply.
a. The activity of the Ca2+/H+ ATPase would decrease.
b. The activity of the Ca2+/H+ ATPase would increase.
c. The activity of the Ca2+/H+ ATPase would not change.
d. The concentration of Ca2+ in the cell would decrease.
e. The concentration of Ca2+ in the cell would increase.
f. The concentration of Ca2+ in the cell would not change.
a. The activity of the Ca2+/H+ ATPase would decrease.
e. The concentration of Ca2+ in the cell would increase.
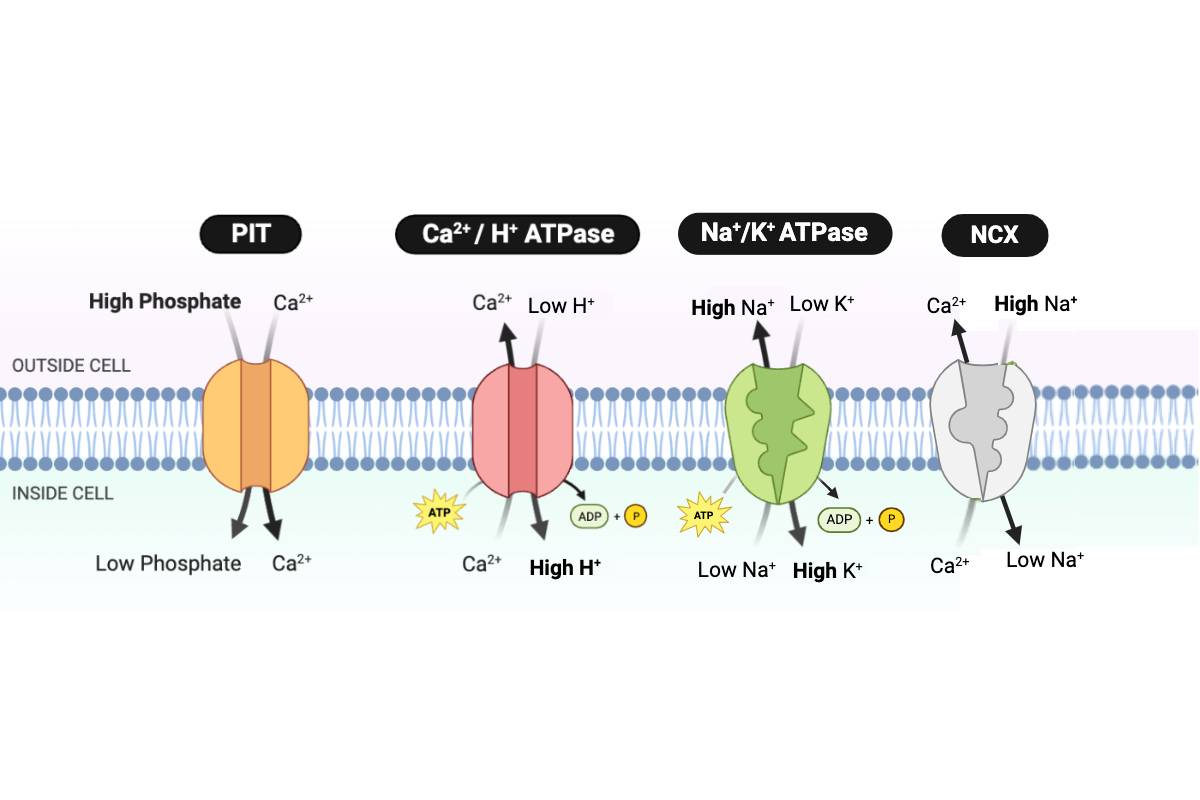
Which pattern would occur if the concentration of H+ outside the cell decreases? Select all that apply.
a. The activity of the Ca2+/H+ ATPase would decrease.
b. The activity of the Ca2+/H+ ATPase would increase.
c. The activity of the Ca2+/H+ ATPase would not change.
d. The concentration of calcium in the cell would decrease.
e. The concentration of calcium in the cell would increase.
f. The concentration of calcium in the cell would not change.
a. The activity of the Ca2+/H+ ATPase would decrease.
e. The concentration of calcium in the cell would increase.
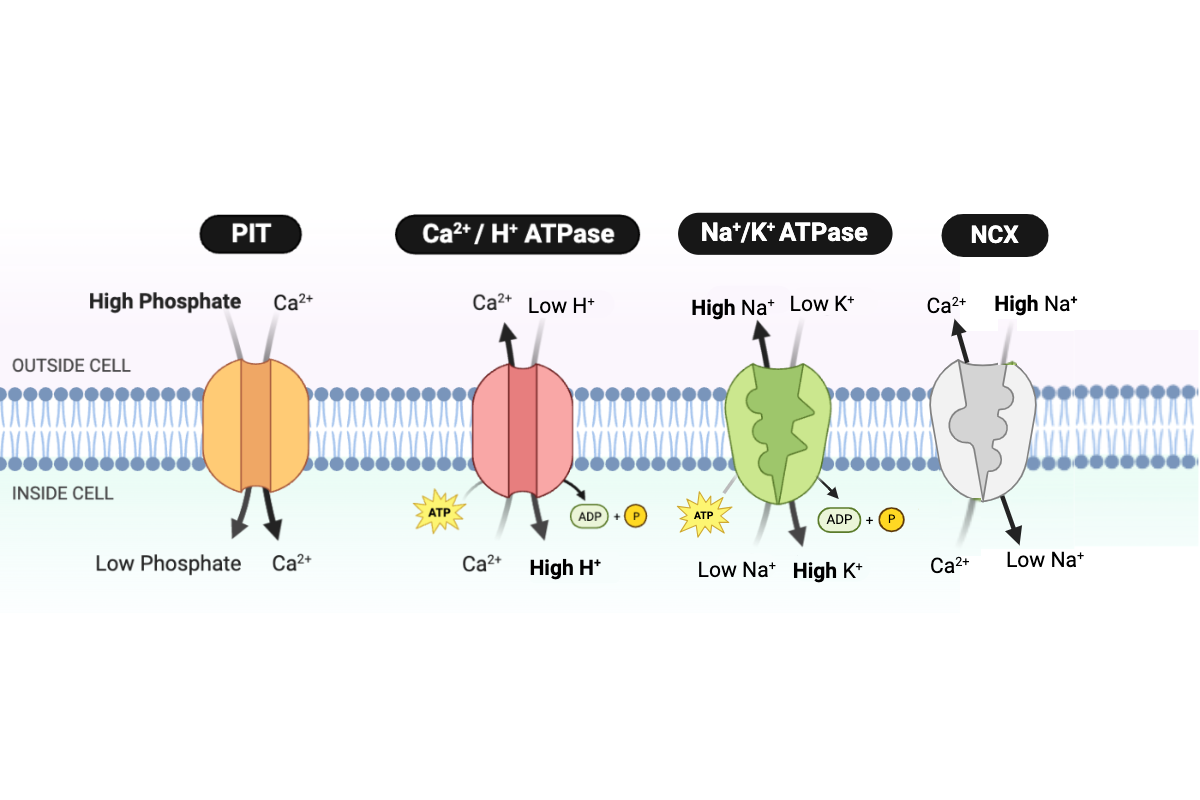
Which pattern would occur if the concentration of phosphate outside the cell decreases? Select all that apply.
a. The transport rate of the PIT protein would decrease.
b. The transport rate of the PIT protein would increase.
c. The transport rate of the PIT protein would not change.
d. Ca2+ would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
e. Ca2+ would be transported into the cell at a slower rate.
f. The rate of Ca2+ transport would not change.
a. The transport rate of the PIT protein would decrease.
e. Ca2+ would be transported into the cell at a slower rate.
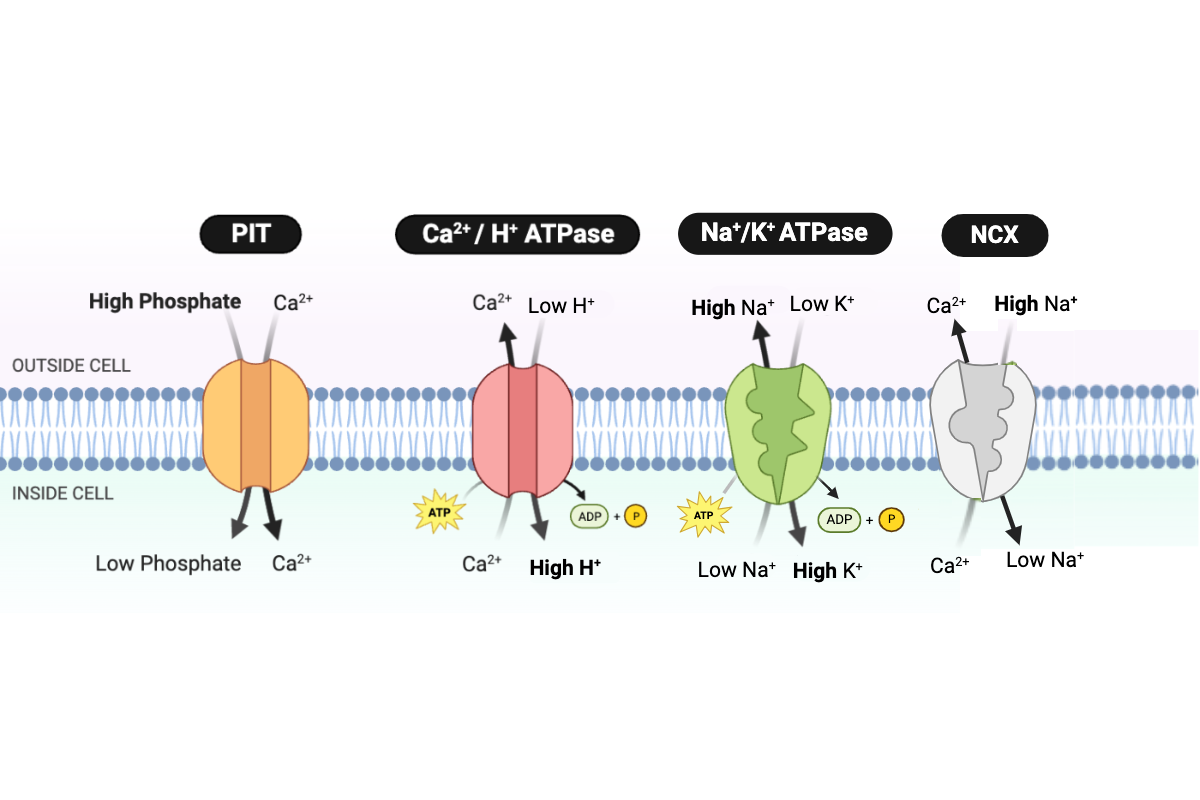
Which pattern would occur if the concentration of Na+ outside the cell decreases? Select all that apply.
a. The transport rate of the NCX protein would decrease.
b. The transport rate of the NCX protein would increase.
c. The transport rate of the NCX protein would not change.
d. The concentration of Ca2+ in the cell would decrease.
e. The concentration of Ca2+ in the cell would increase.
f. The concentration of Ca2+ in the cell would not change.
a. The transport rate of the NCX protein would decrease.
e. The concentration of Ca2+ in the cell would increase.
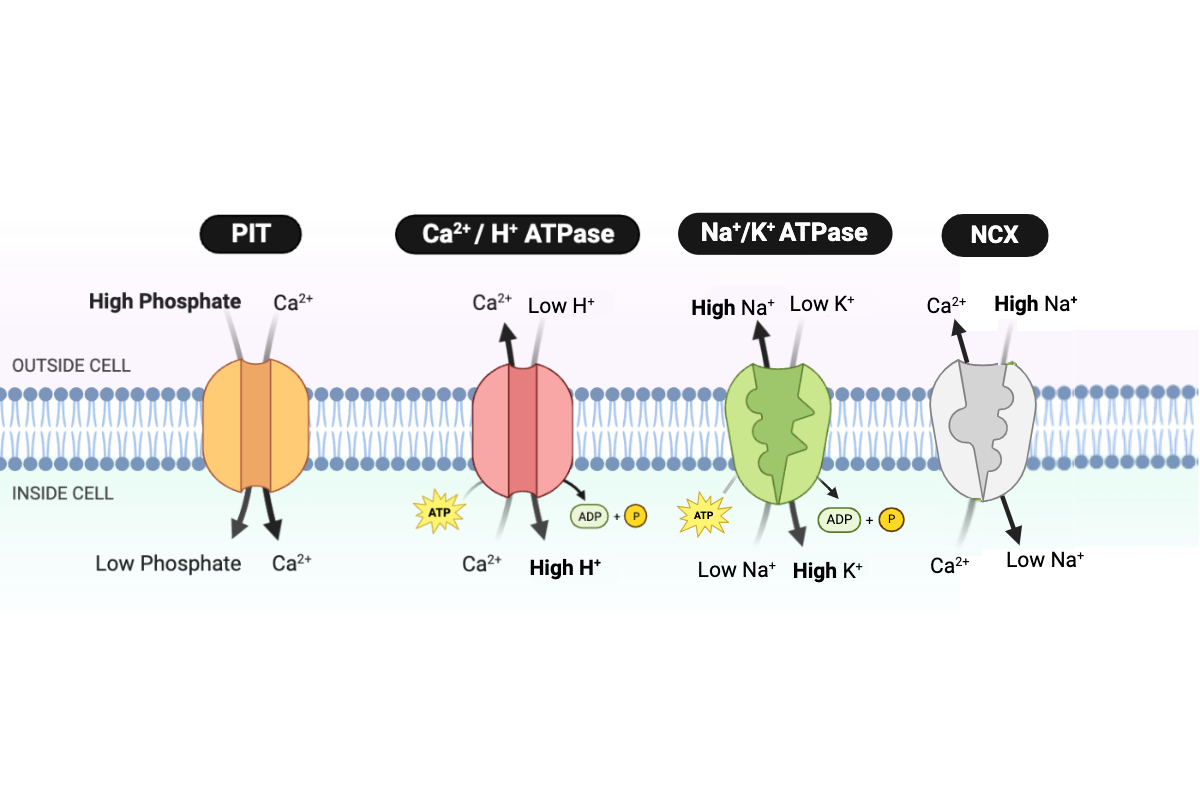
Which pattern would occur if the number of NCX proteins in the cell membrane increases?
a. Ca2+ would be transported into the cell at a slower rate.
b. Ca2+ would be transported out of the cell at a slower rate.
c. Ca2+ would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
d. Ca2+ would be transported out of the cell at a faster rate.
e. The rate of Ca2+ transport would not change.
d. Ca2+ would be transported out of the cell at a faster rate.
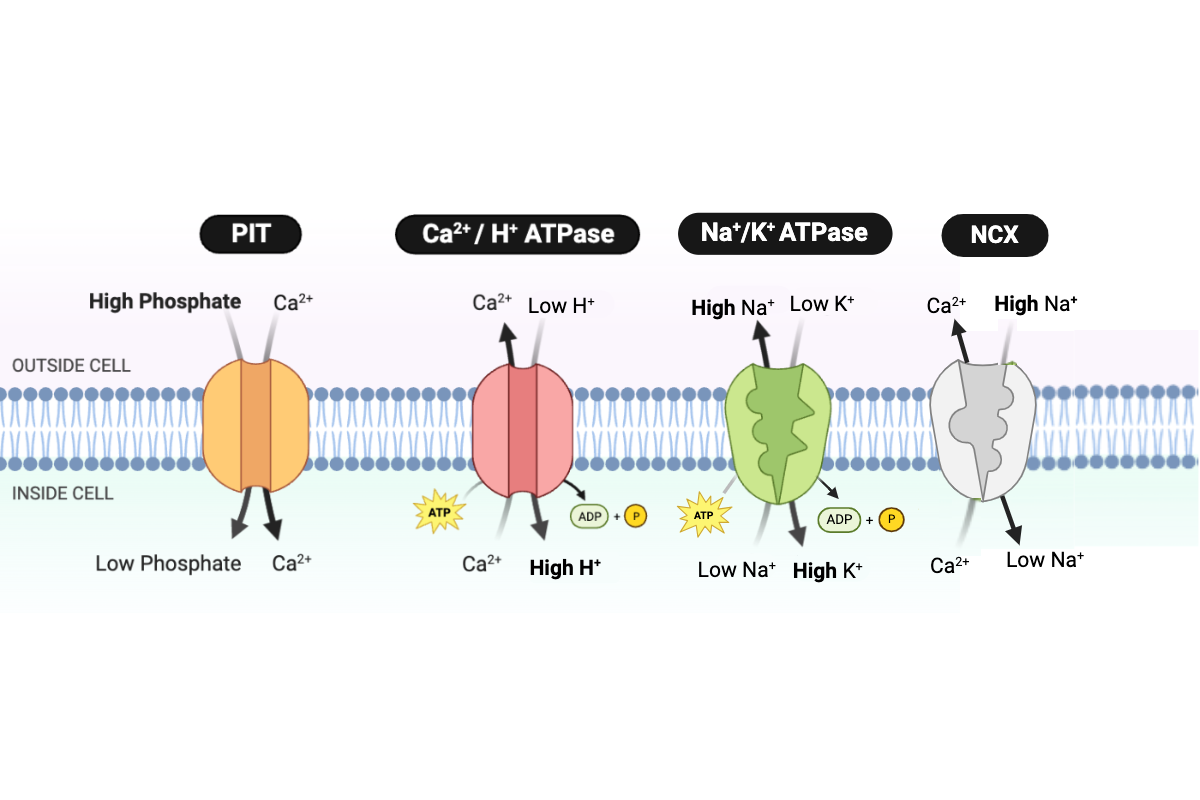
Which pattern would occur if the number of PIT proteins in the cell membrane increases?
a. Ca2+ would be transported into the cell at a slower rate.
b. Ca2+ would be transported out of the cell at a slower rate.
c. Ca2+ would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
d. Ca2+ would be transported out of the cell at a faster rate.
e. The rate of Ca2+ transport would not change.
c. Ca2+ would be transported into the cell at a faster rate.
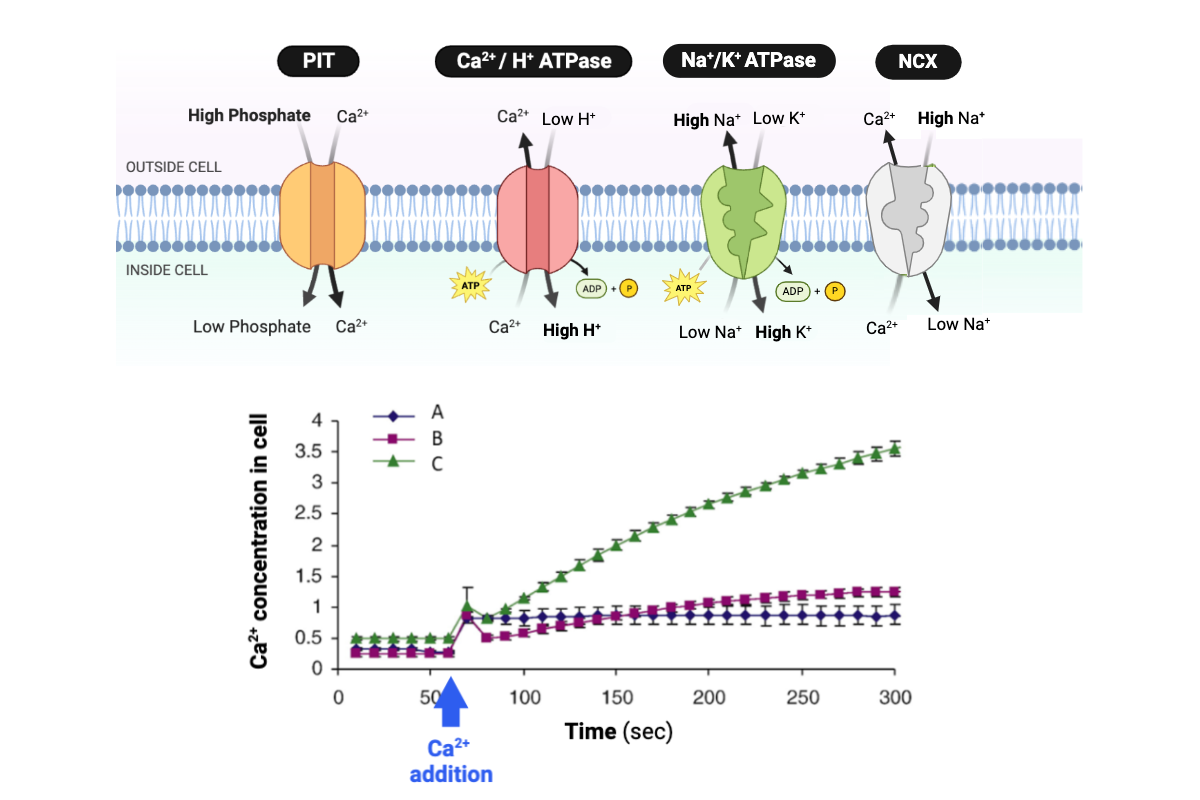
Which solution is most likely to have the lowest concentration of H+?
a. Solution A
b. Solution B
c. Solution C
c. Solution C
Which solution is most likely to have the lowest concentration of Na+?
a. Solution A
b. Solution B
c. Solution C
a. Solution A
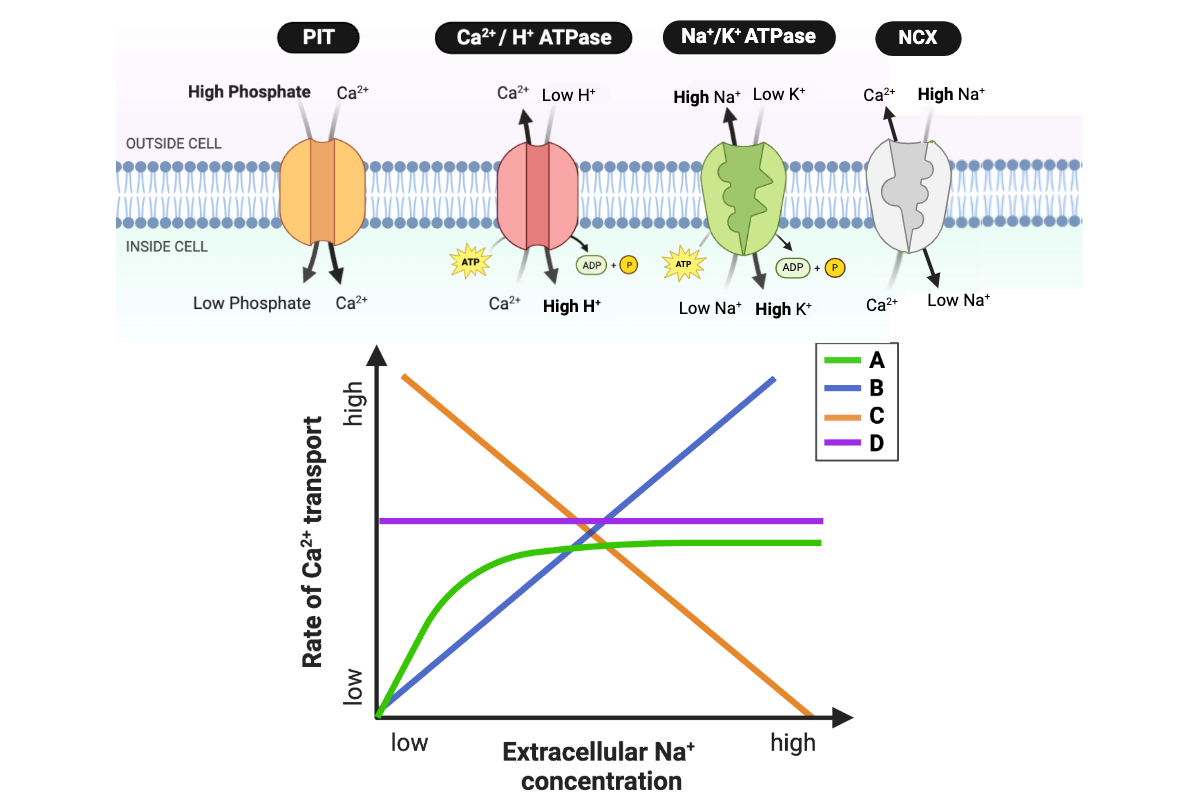
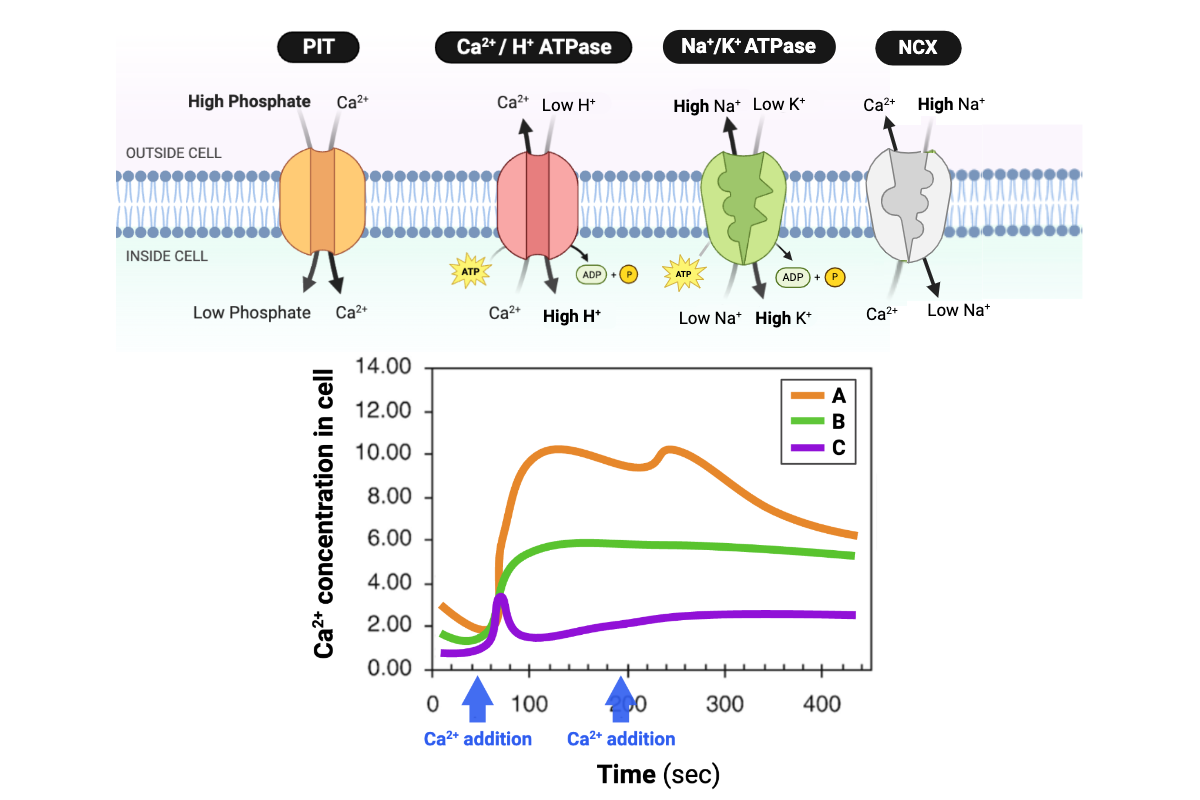
Which line accurately describes the relationship for the transport system of an E. coli cell?
a. Line A
b. Line B
c. Line C
d. Line D
a. Line A
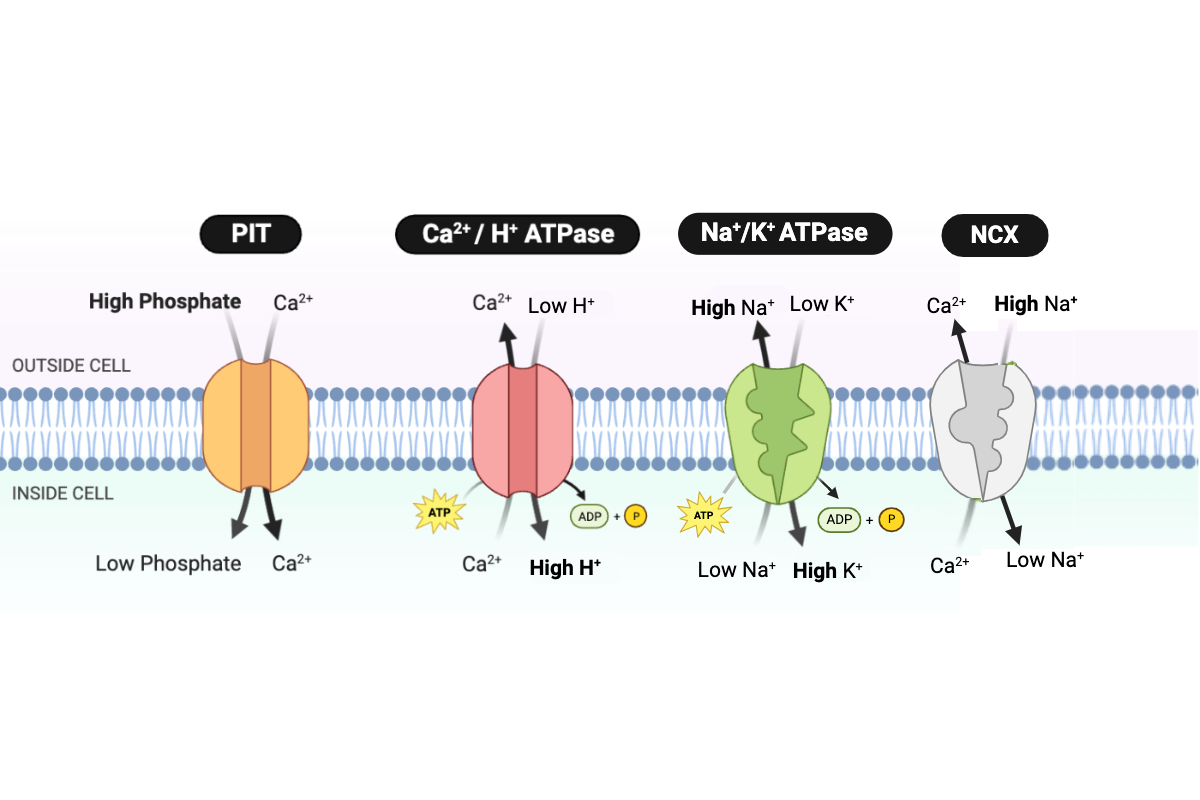
How would the rate of Ca2+ transport by E. coli cells be affected by a decrease in the concentration of H+ in a lake?
a. Ca2+ would be transported at a slower rate.
b. Ca2+ would be transported at a faster rate.
c. The rate of Ca2+ transport would not change.
a. Ca2+ would be transported at a slower rate.
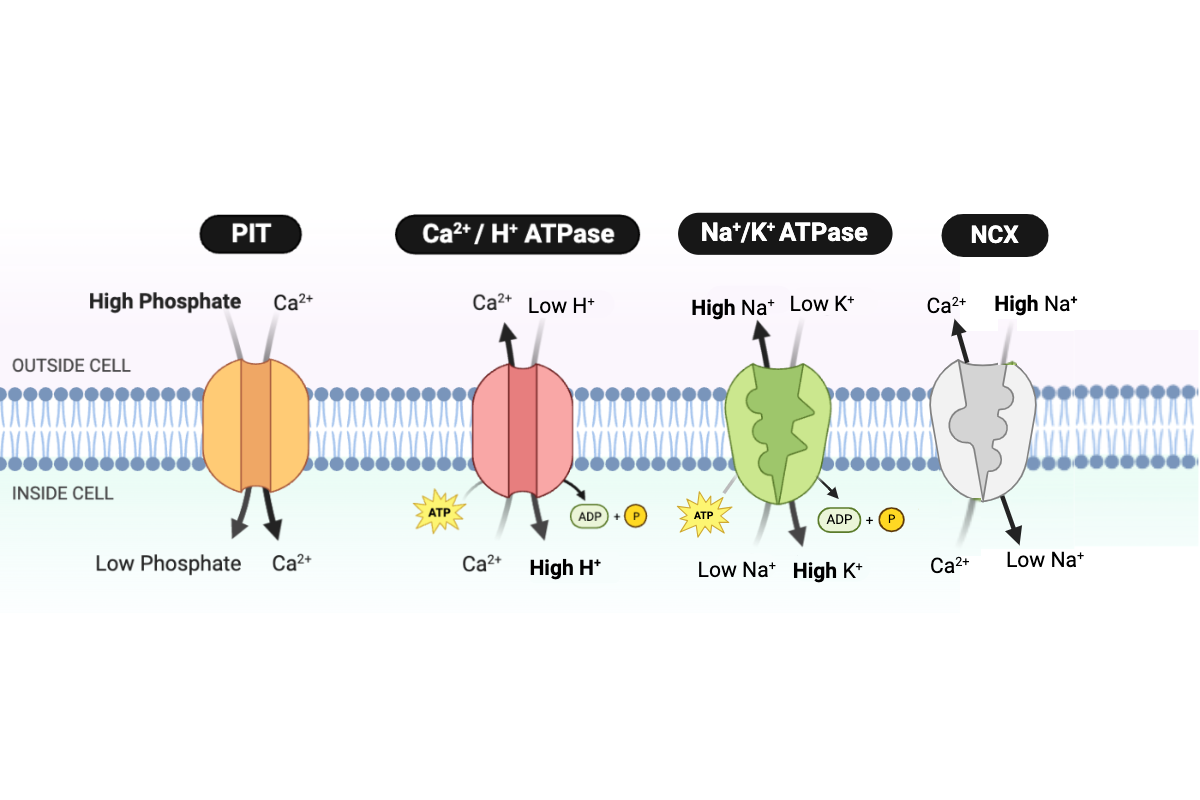
How would the rate of Ca2+ transport by an E. coli cell change as the cell leaves the high concentration of H+ in the stomach and enters the low concentration of H+ in the intestine?
a. Ca2+ would be transported at a slower rate in the intestine.
b. Ca2+ would be transported at a faster rate in the intestine.
c. The rate of Ca2+ transport would not change between the stomach and the intestine.
a. Ca2+ would be transported at a slower rate in the intestine.
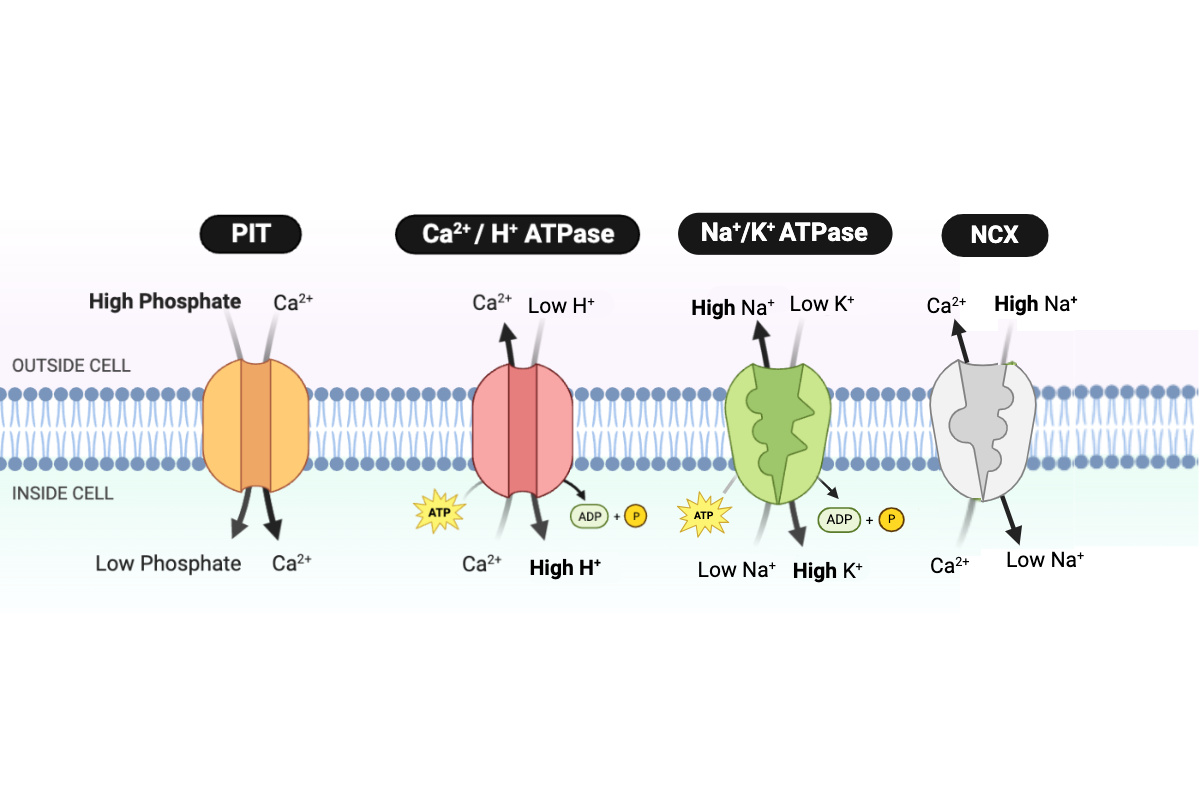
How would the rate of Ca2+ transport into an E. coli cell be affected by living in an environment with high phosphate?
a. Ca2+ would be transported at a slower rate than usual.
b. Ca2+ would be transported at a faster rate than usual.
c. The rate of Ca2+ transport would not be affected by the concentration of phosphate.
b. Ca2+ would be transported at a faster rate than usual.