Unit 7.5 - Economic change
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Economic factors that will influence businesses
Inflation - sustained rise in the price level
Unemployment - how many people are willing and able to work but don't have a job
Interest rates - cost of borrowing and reward for saving
Exchange rate - value of one currency expressed in terms of another
Gross domestic product - value of a country's total output
Government policy - i.e tax, spending etc
GDP (gross domestic product)
value of a country's output of goods and services over a period of time (usually one year)
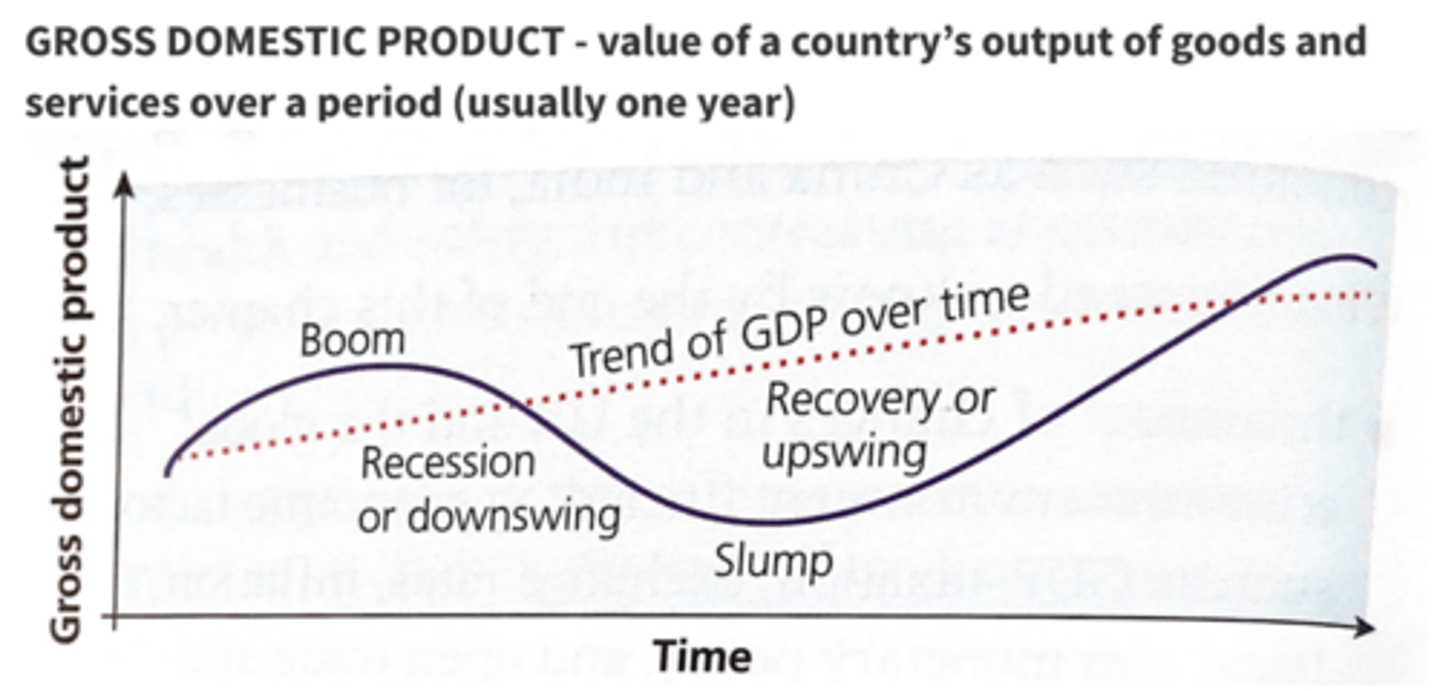
Economic cycle
The fluctuation in the rate of growth (level of GDP) in the economy over a period of time. Key parts:
- Recovery
- Boom
- Recession
- Slump
Recovery (economic cycle)
- Economy is coming out of a slump
- Production and employment both begin to increase. - Consumers will generally spend more as they are more confident in job security.
- Businesses may respond cautiously and meet rising demand by utilising idle capacity instead of increasing capacity.
Boom (economic cycle)
- high levels of production and expenditure by firms, consumers and the government.
- Firms will start taking strategic decisions to invest in non current assets.
- However, sectors with high skilled workers may experience pressure as workers become scarce and firms need to offer higher wages to compete.
- As the economy approaches maximum production, it may be difficult to meet demand as there are insufficient raw materials and prices get dragged up.
- The increasing prices and wages will create inflation. This usually leads to the end of the boom.
Recession (economic cycle)
- income and output starts to fall for 6 consecutive months. A recession is defined as 2 quarters of negative growth.
- Increased prices from the boom mean that businesses have higher costs of production and as a result profits fall.
- Demand will start to fall and the amount of spare capacity will rise as firms reduce production
- Decline in business confidence and investment
Slump (economic cycle)
- follows a recession. An economy may enter the recovery phase without actually moving through the slump period.
- Governments will take action to avoid a prolonged slump phase.
- For example, spending more, taxing less and reducing interest rates.
- High levels of unemployment, low consumer spending and business confidence
Economic cycle (diagram)
Exchange rate
Value of one currency expressed in terms of another
SPICED (acronym)
Strong Pound Imports Cheaper Exports Dearer
WPIDEC (acronym)
Weak Pound Imports Dearer Exports Cheaper
Exchange rates and uncertainty
Uncertainty over revenue - if firms agree deals priced in foreign currencies, they may receive more or less revenue than expected from some transactions.
Uncertainty regarding quantity demanded - domestic currency value rises, leads to an increase in prices for foreign consumers. Depending on elasticity of demand, they may reduce quantity demanded. This makes it hard to forecast sales, order from suppliers etc.
Uncertainty regarding competitors response - competitors may take decisions to protect their firms against exchange rate changes. Foreign businesses may reduce prices to offset the effects of an exchange rate change, which puts rivals under pressure.
Causes of changes in exchange rates
- Foreign demand for a country's exports
- Domestic demand for imports
- Relative interest rate changes
- Relative rates of inflation
- Investment from Abroad
- Changes in Income
-Speculation
-Use of foreign currency reserves
Overall a currencies value is decided by the supply and demand for it
Impact of exchange rates on businesses
Depends on if they export their products, only operate in the UK and compete against foreign imports, or import raw materials from overseas for their production.
Exporter: Want weaker pound as demand for exports will increase
UK business only: Strong pound as this will reduce competition from imported goods because they will be relatively more expensive to buy
UK business importing raw materials: Strong pound as it will make imported cheaper and therefore allow them to reduce costs
Inflation
persistent rise in the general price level and an associated fall in the value of money.
Deflation
rate of decrease of the general price level and the corresponding rise in the value of money.
Causes of inflation
Cost push - Increase in cost of production i.e wage increases, raw materials prices
Demand pull - High demand in the economy without increased supply forces prices up
Expectations - Businesses expect suppliers to increase the prices of raw materials - they increase their prices
Trade unions will build inflation expectations into their wage demands - drives up wages
Impact of inflation on businesses and decision making
- Encourage borrowing as a real value of borrowing reduces and inflation may be below interest rates
- Property prices rise improving look of balance sheet
- Firms find it easier to increase own prices
- Higher price could lead to lower sales depending on price elasticity of demand
- More awareness from consumers of prices generally
- Wage demand increase
- If inflation is higher in UK then other countries international competitiveness reduces
- Suppliers increase prices
- May tighten cash flow
- The future is uncertain
- Interest rates are likely to be high
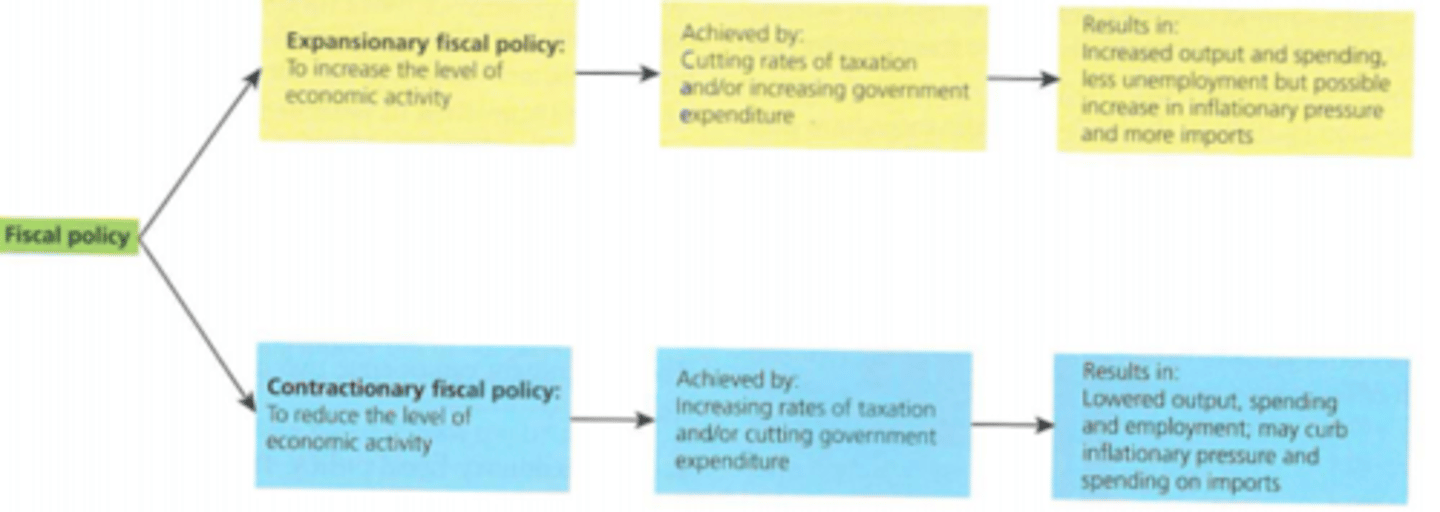
Fiscal policy
Use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy
- Budget deficit - the government is spending more than it receives in taxation
- Budget surplus - the government is spending less than it receives in taxation
- The government usually operates a budget deficit
- The extent of the deficit is realised when the chancellor of the exchequer announces the budget (around March)
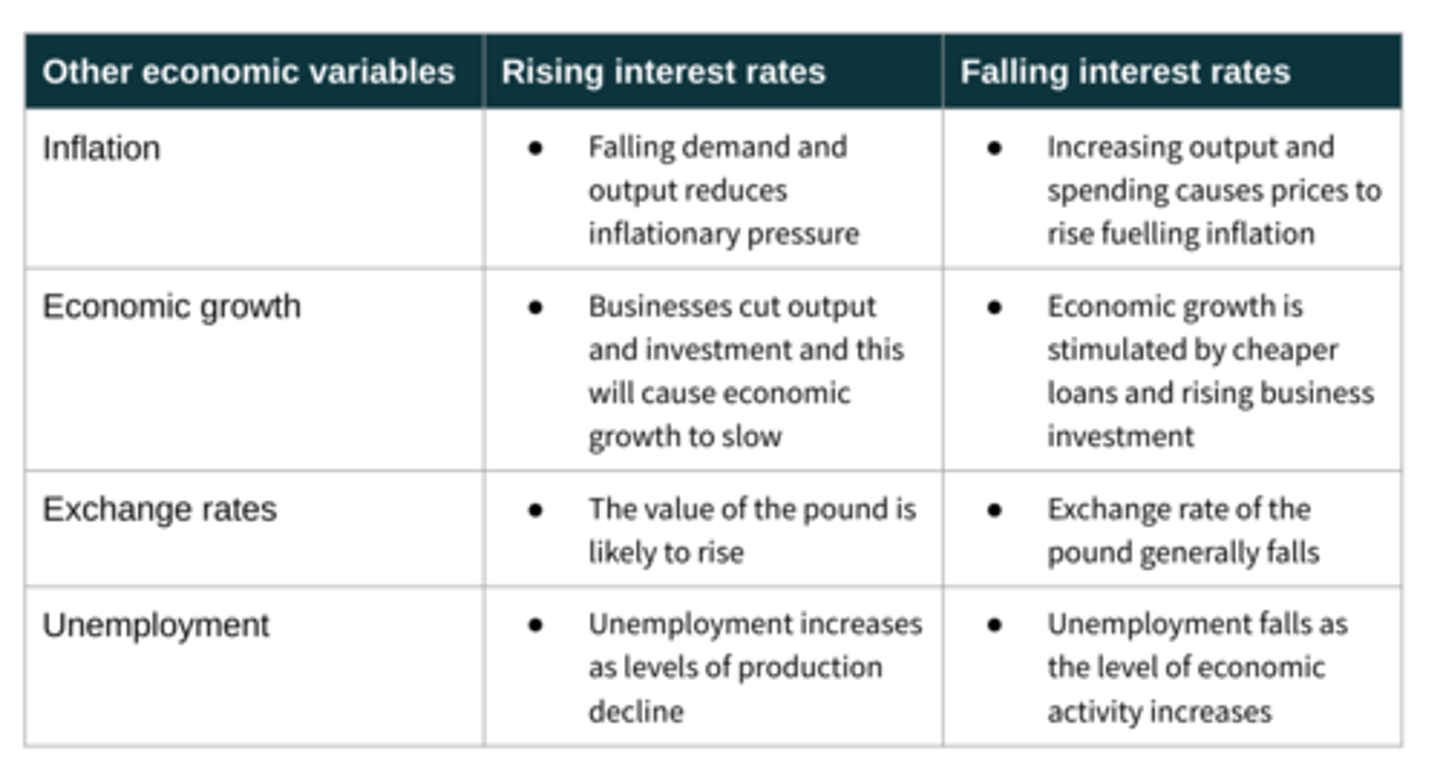
Monetary policy
The use of interest rates and the money supply to influence the economy
- Interest rates: cost of borrowing and reward for saving
- Money supply: quantitative easing. Central bank prints money and buys government and corporate bonds, and those organisations then have 'new' money in their bank.
- Money supply is used when interest rates cannot be lowered any further.
Supply side policies
range of measures intended to to improve the operation of free markets and the amount that is produced by the economy:
(Infrastructure, improving competition, encouraging enterprise, producing training and education etc)
Expansionary fiscal policy
Government trying to expand the economy and encourage growth, used during recessions and slumps
- Increase in government spending
- Decrease in taxation
Contractionary fiscal policy
Government trying to contract the economy and slow growth, used during booms and perhaps when recovery is reaching boom
- Decrease government spending
- Increase taxation
Taxation
a payment that is made to the government or other authority by households and firms.
Some different types of taxes
- Income tax
- Corporation tax
- VAT (value added tax)
- National insurance payments - employees pay % of salary on earnings up to £ per week, employers pay %
- Customs and excise duties - custom paid on imports while excise is paid on the production of certain products such as alcohol - demand is price inelastic
What taxes are used for
Redistribution of income
Increase price of certain goods to discourage consumption
Control the economic cycle
How taxes may impact businesses
- Increase costs
- Number of people they decide to employ
- More income tax = less disposable income
- Higher prices
- Choice of location
- Lower corporation tax = higher returns on capital investment
Fiscal policy (image)
Impact of changing interest rates (table)
Globalisation
Increased interconnectedness and interdependence of economies
Why has globalisation happened
- Support of many governments and major businesses
- The falling cost of international and transport communications
- The growth of global trading blocs and the reduction of barriers to trade
- Growth of multinational companies
- Increasing global incomes and growing demand for goods and services
Benefits of globalisation (more open trade/international trade)
Increased sales, revenue and profit
Cheaper resources
Economies of scale
Developing different products for different markets
Downward pressure on prices
Drawbacks of globalisation
More competition
Increased need for investment
Increased threat of takeover
Protectionism
government policy which favours the use of measures intended to prevent the free entry of imports into a country.
Looking to protect domestic industries and firms from foreign competition
Examples of protectionist policies
- Tariffs - tax on imports
- Quotas - quantity limits on imports
- Subsidies - A payment made to a domestic producer to keep artificially low prices
- Soft loans - helping businesses by providing a loan with better terms
- Technical barriers to trade - red tape, laws, regulations to make things more difficult for foreign firms
- State procurement policies - favoring domestic suppliers for government contracts
Impacts of protectionism on businesses
- Businesses may be forced to use more expensive domestic suppliers. For example, Chinese manufacturers are using domestic coal suppliers rather than importing from Australia to avoid tariffs.
- Businesses may decide to establish production facilities within the countries that impose restrictions on imports, in order to avoid them.
- Others may lobby governments and international bodies to persuade countries to remove barriers to trade.
Global strategy
worldwide patterns of demand are similar and a single product or range of products possible with slight variants is likely to meet the needs of the global consumer e.g. Coca Cola.
Multidomestic strategy
businesses look to establish production capacity through the world and to sell differentiated products to meet the needs of consumers in local markets e.g. Toyota sells different cars in American and Asian markets.
Emerging economies
Describes a country with low incomes per head but one which is enjoying high rates of economic growth - increase in the size of an economy over time BRIC (Brazil, Russia, India and China) are examples used.
- Labour resources
- Large markets
- Rapid growth rates
- Natural resources
Emerging economies - risks
Economic risks - these countries commonly have high rates of inflation e.g Russia 15% in 2015. High rates of growth are not always guaranteed. These countries are often reliant on 1 or 2 products for their exports and can have very strict protectionist policies.
Political risk - can be accompanied by unstable governments.
Risks to brand image - operating overseas can be great for reducing costs, but is often damaging to a business reputation due to exploitation of local employees or damaging the environment.