neck, vertebrae, rib
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
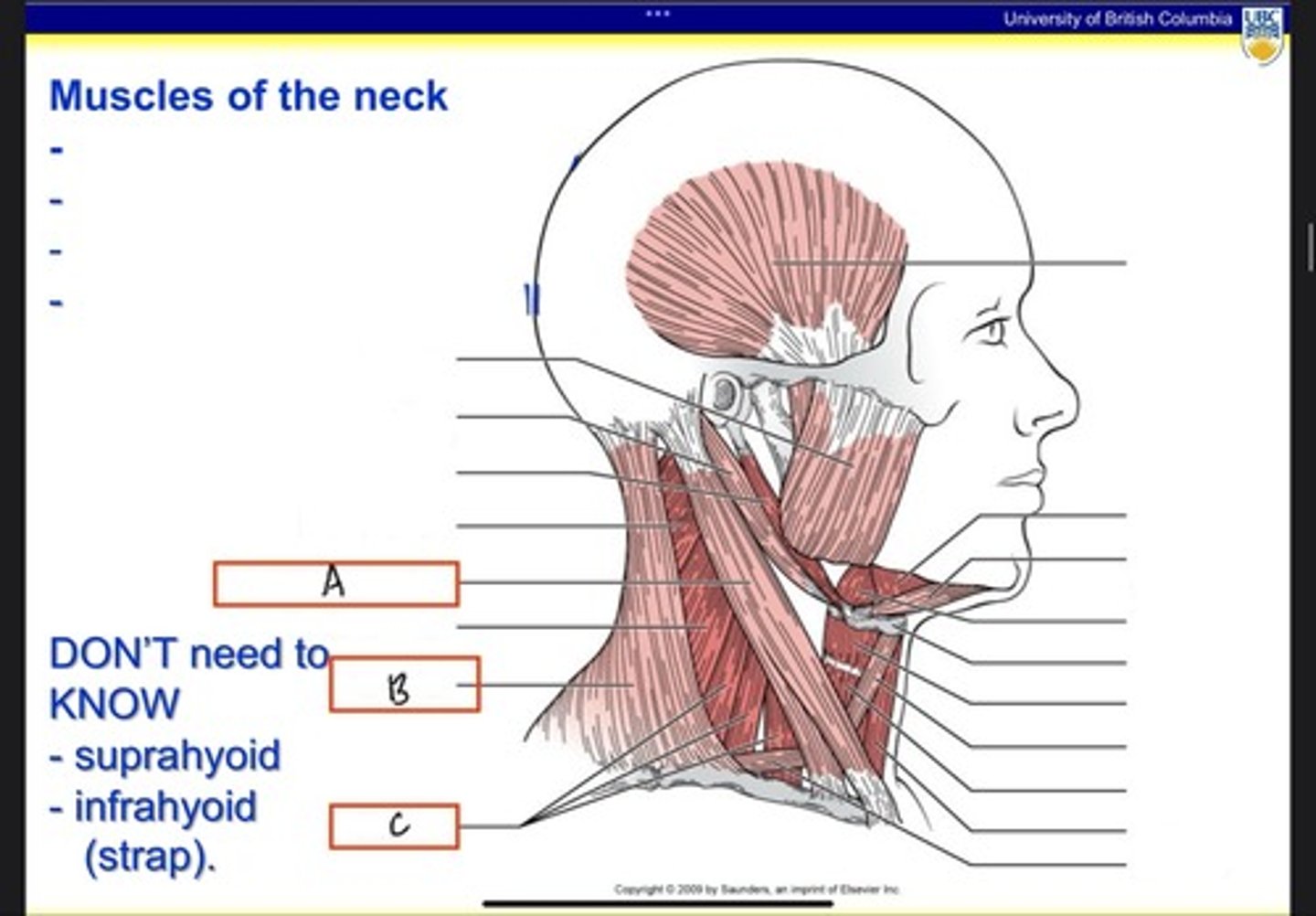
Sternocleidomastoid (SCM)
What is A?
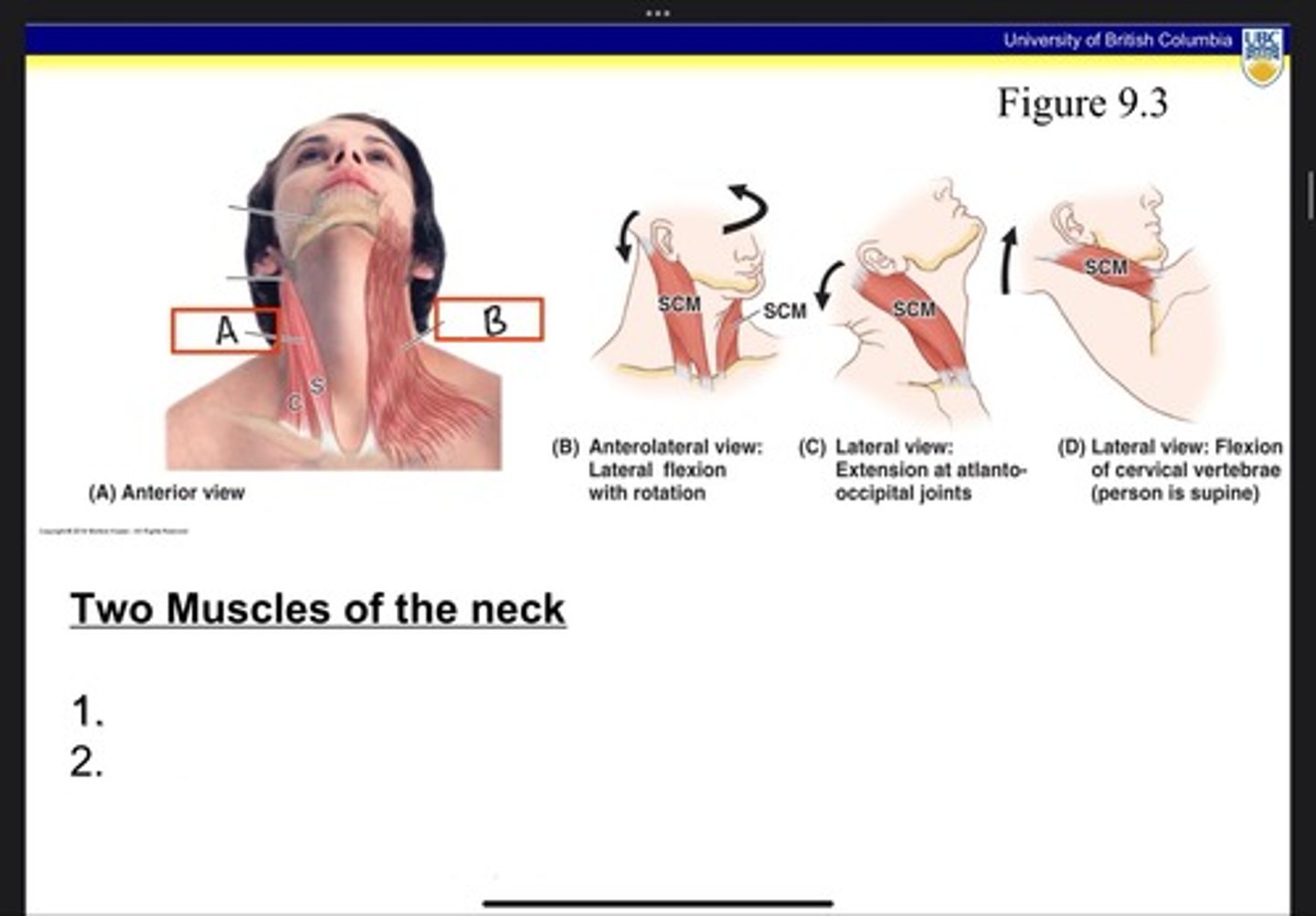
Platysma
What is B?
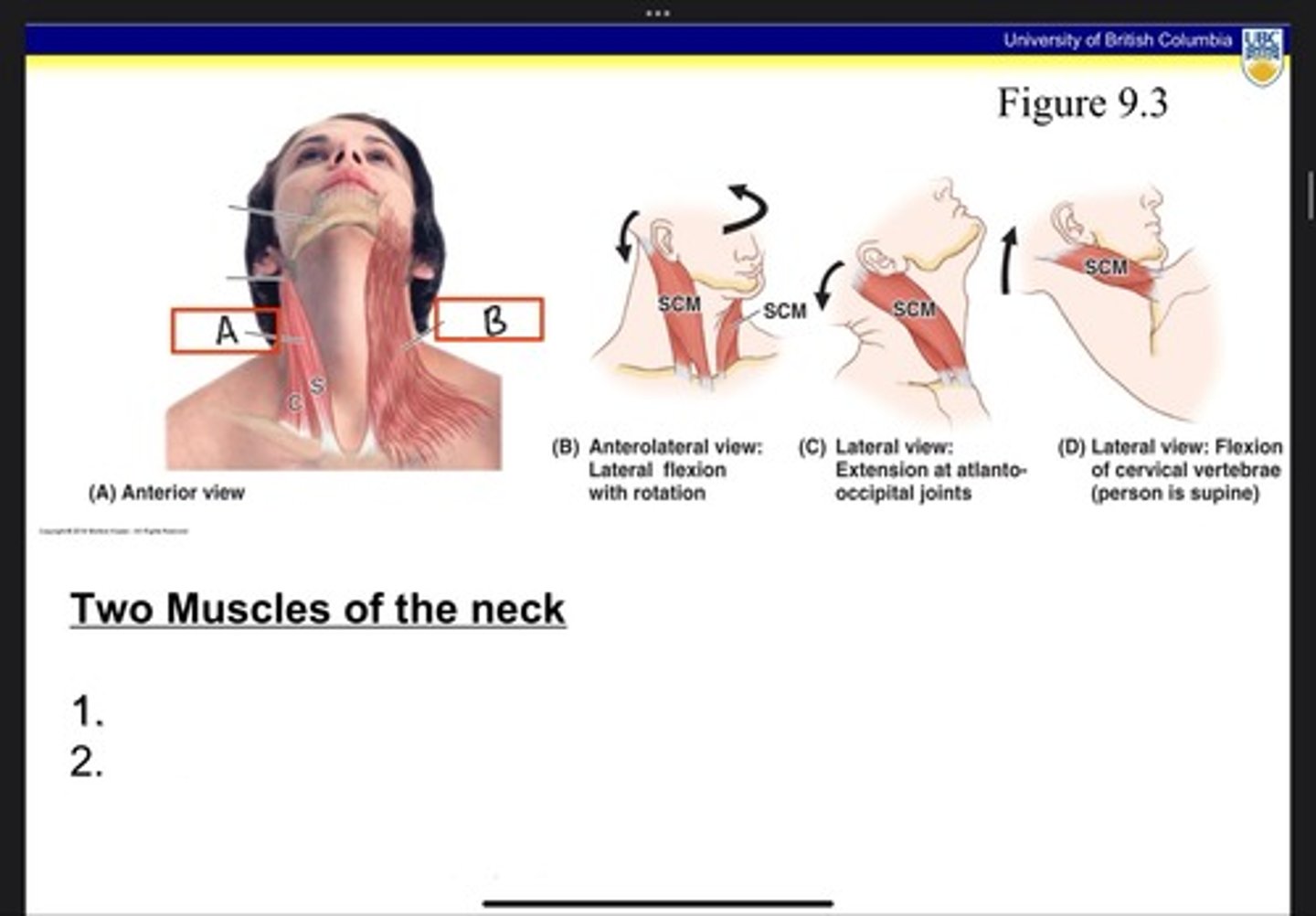
Sternocleidomastoid (SCM)
What is A?
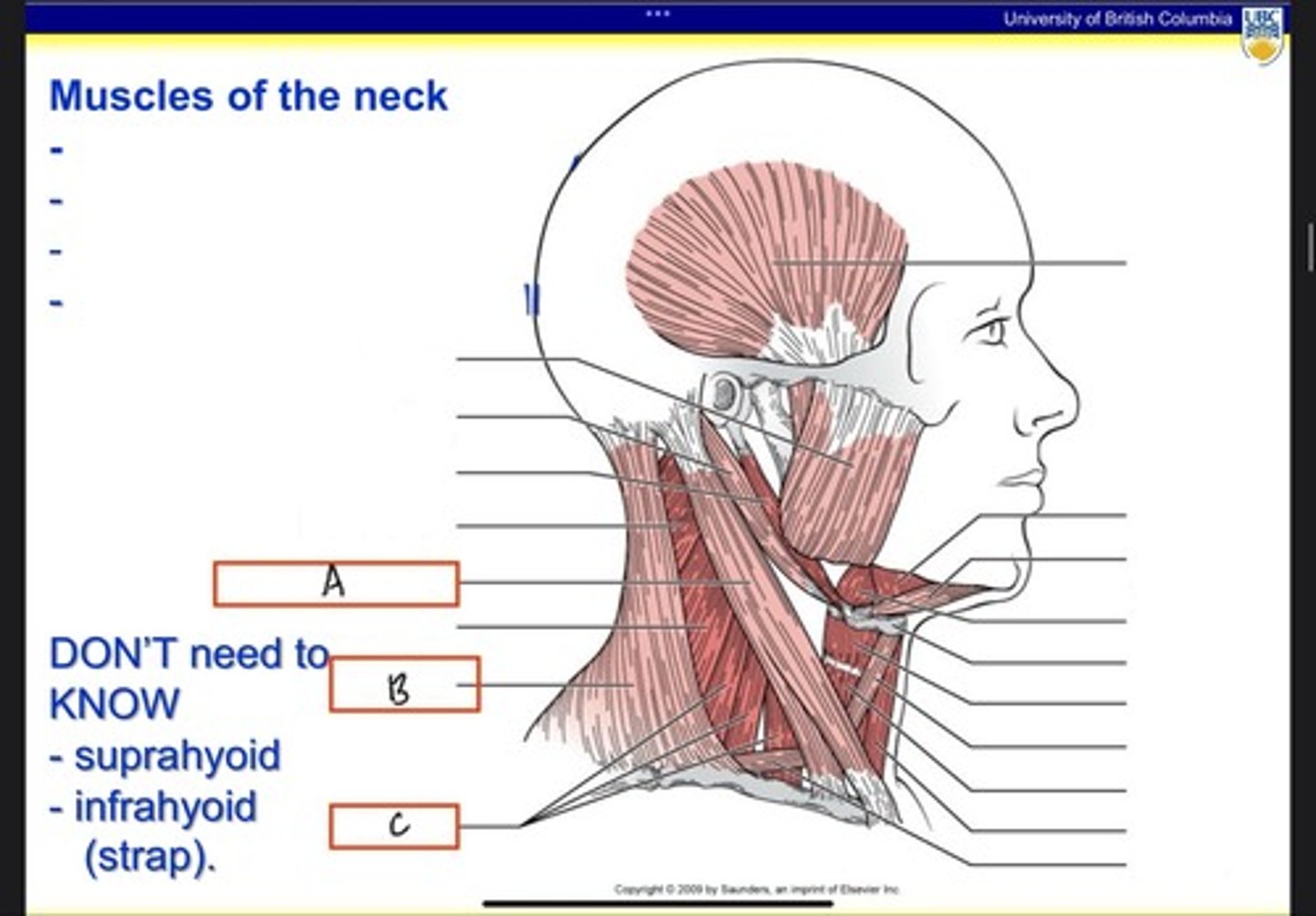
Trapezius
What is B?
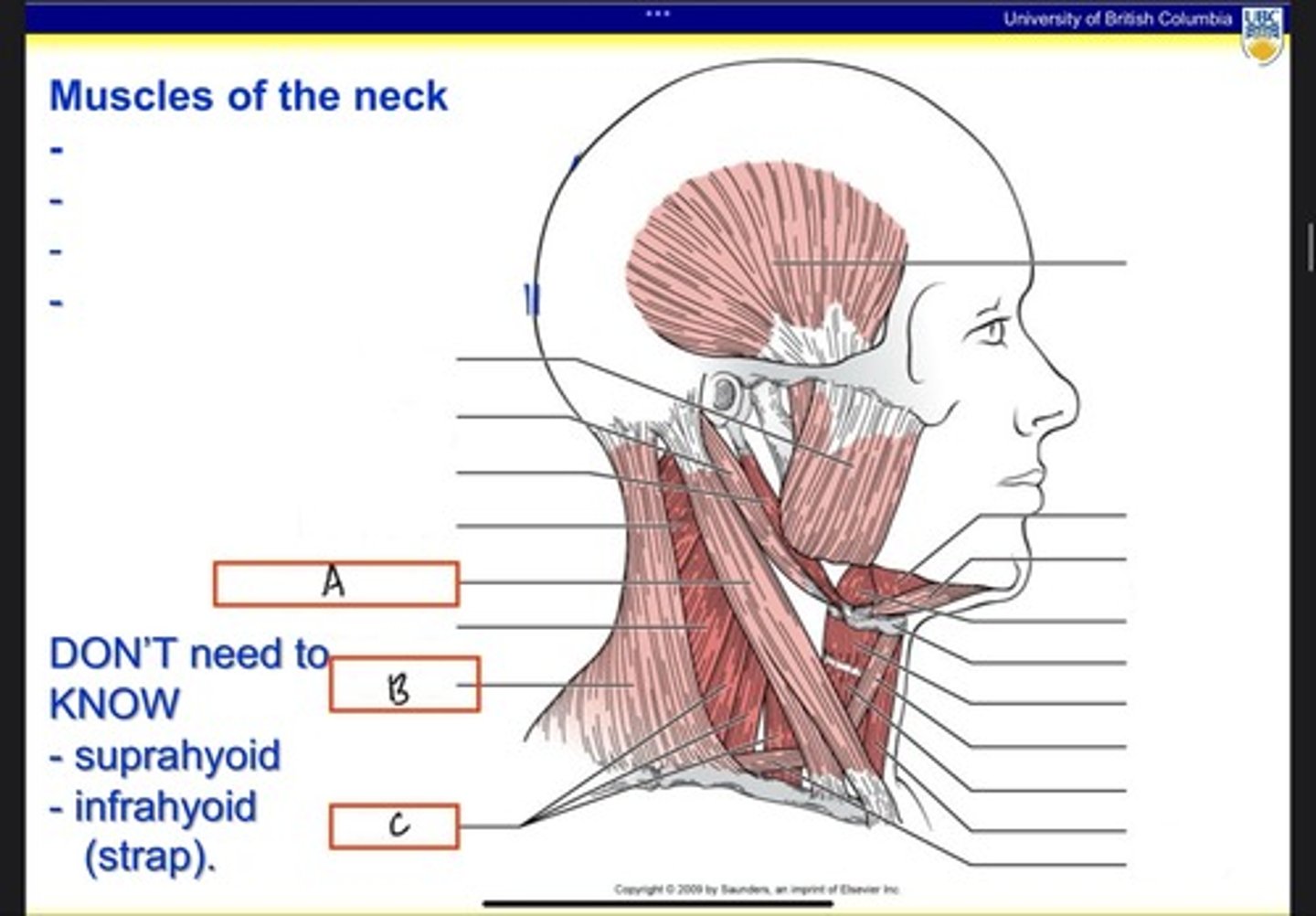
Scalenes
What is C?
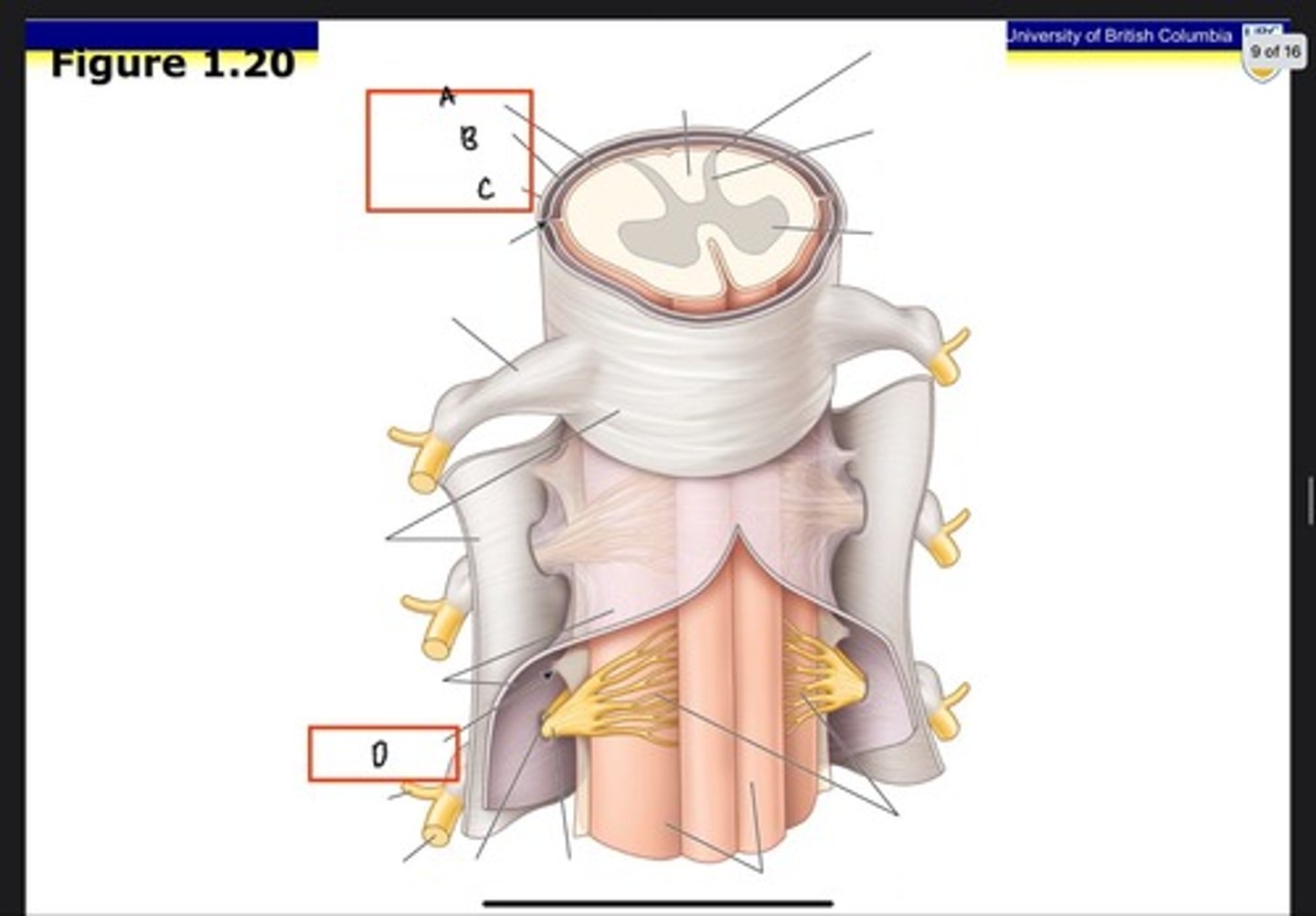
Cervical enlargement
What is A?
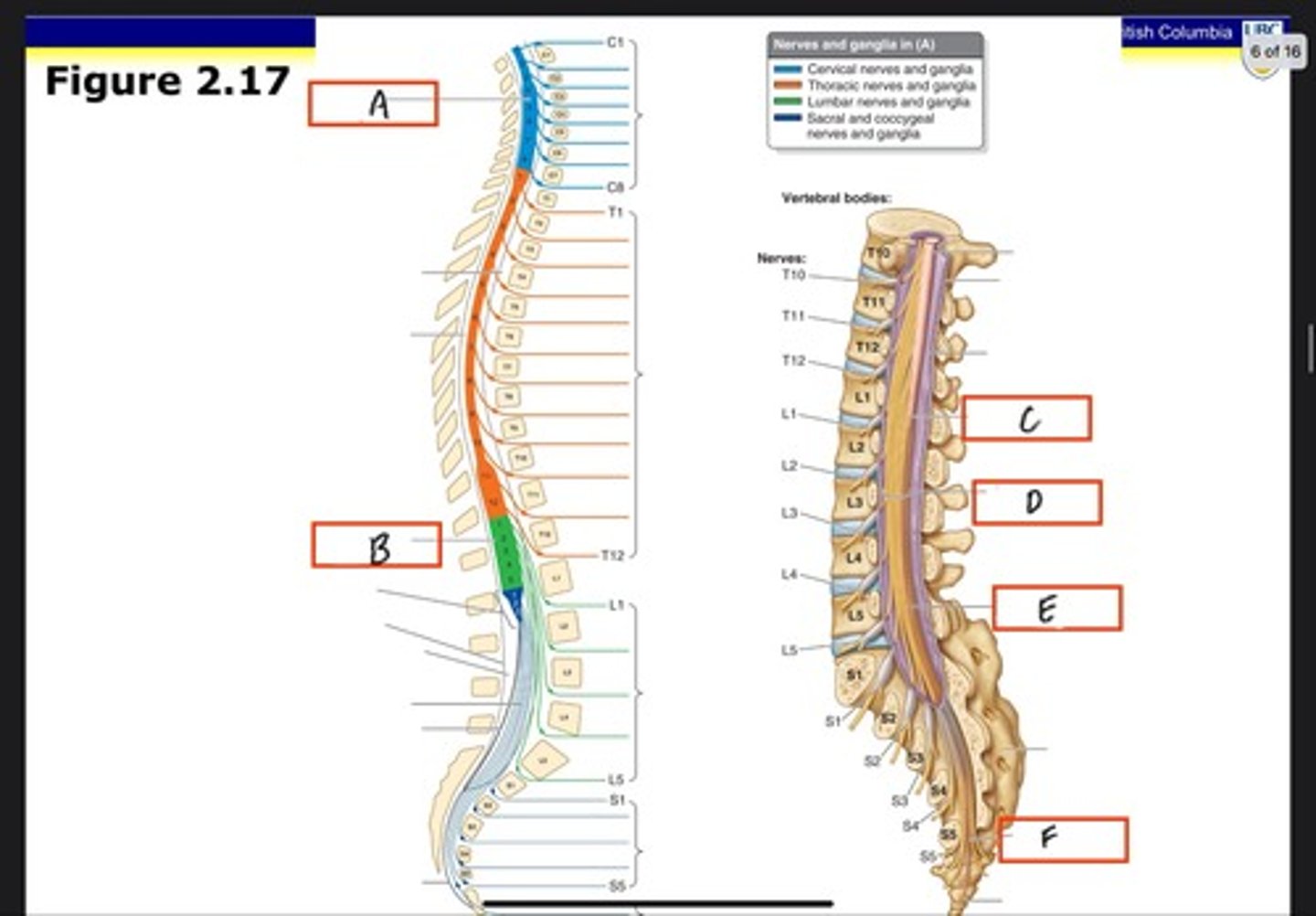
Lumbosacral enlargement
What is B?
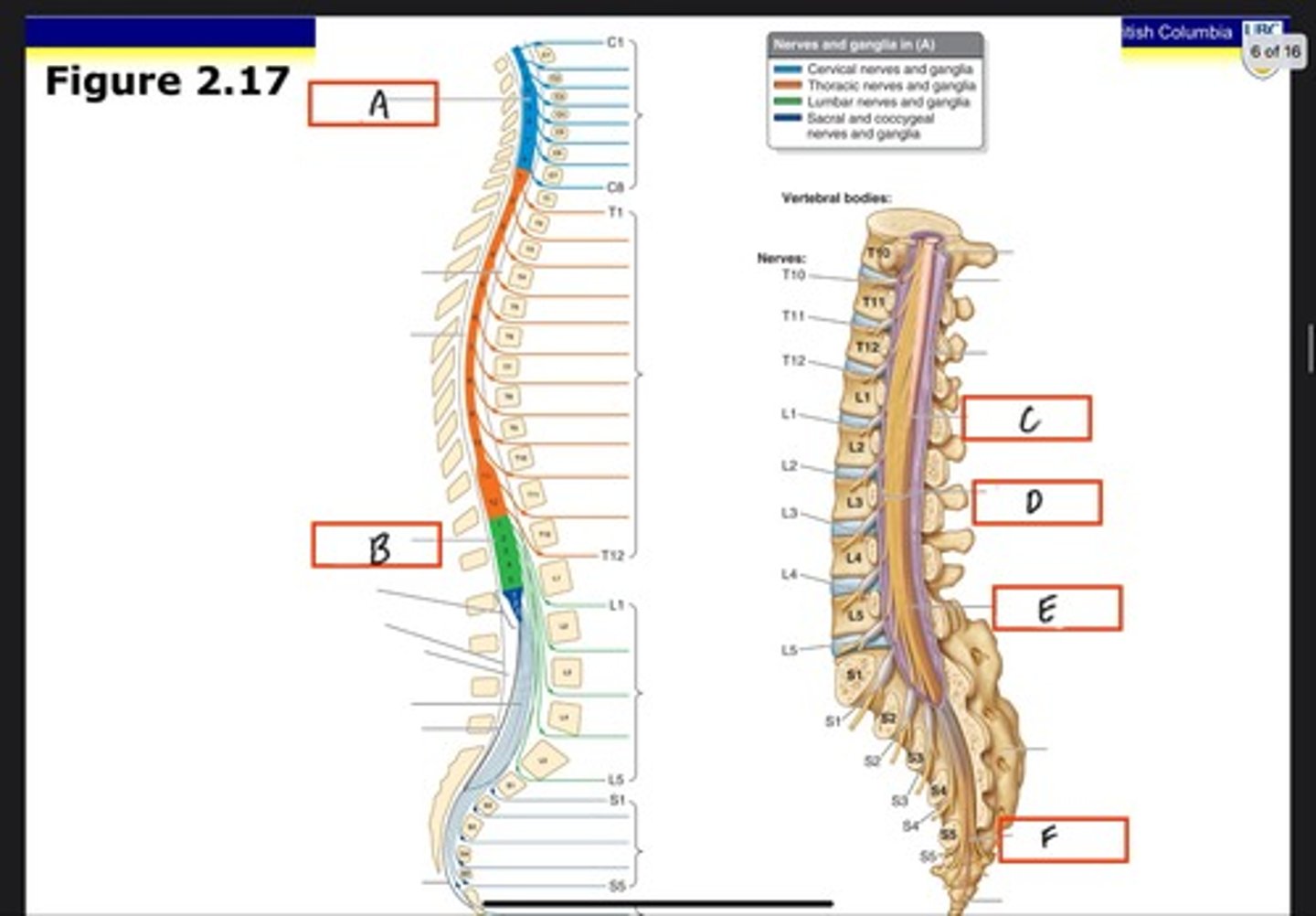
Conus medullaris
What is C?
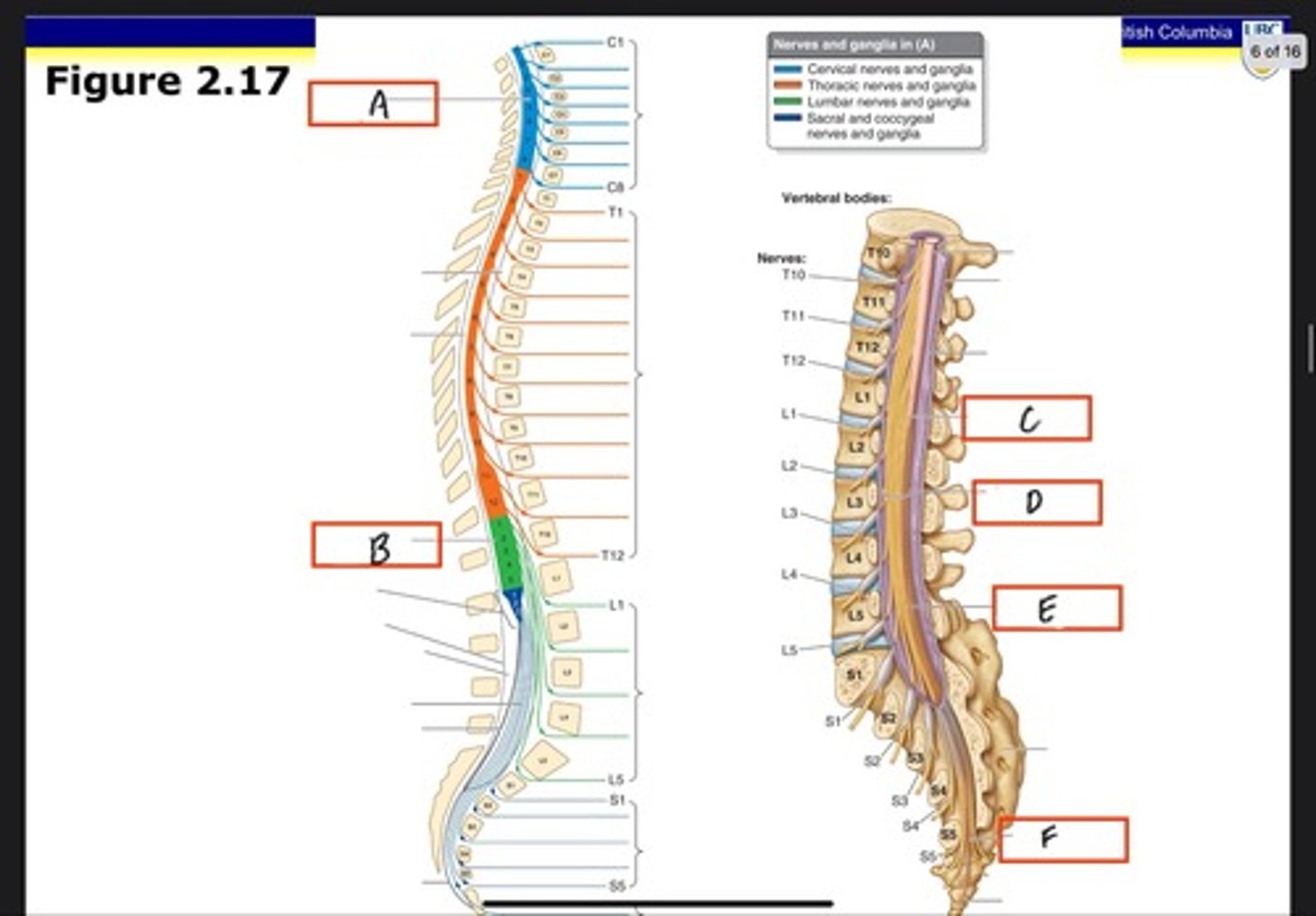
Cauda equina in lumbar cistern
What is D?
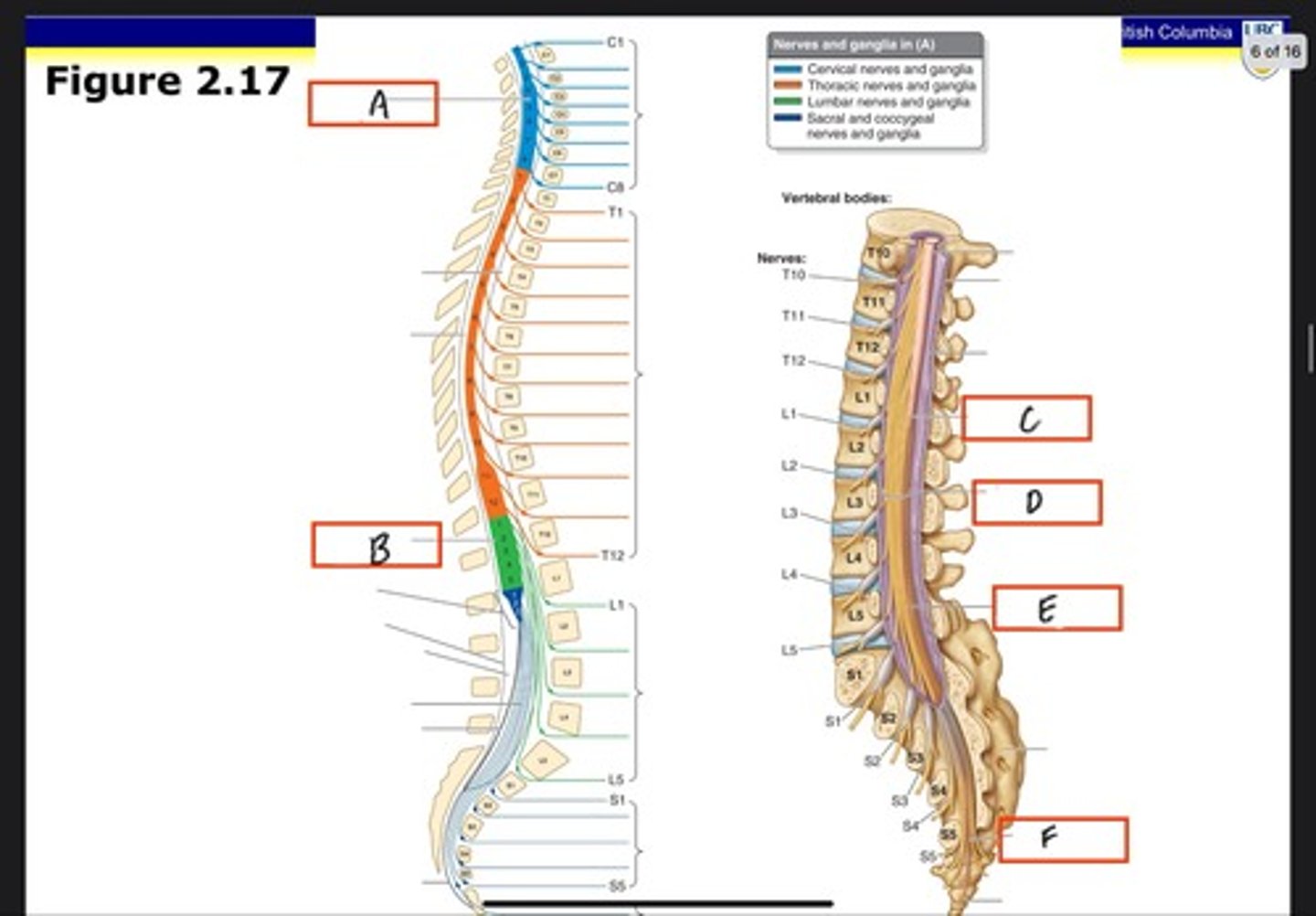
Filum terminale internum
What is E?
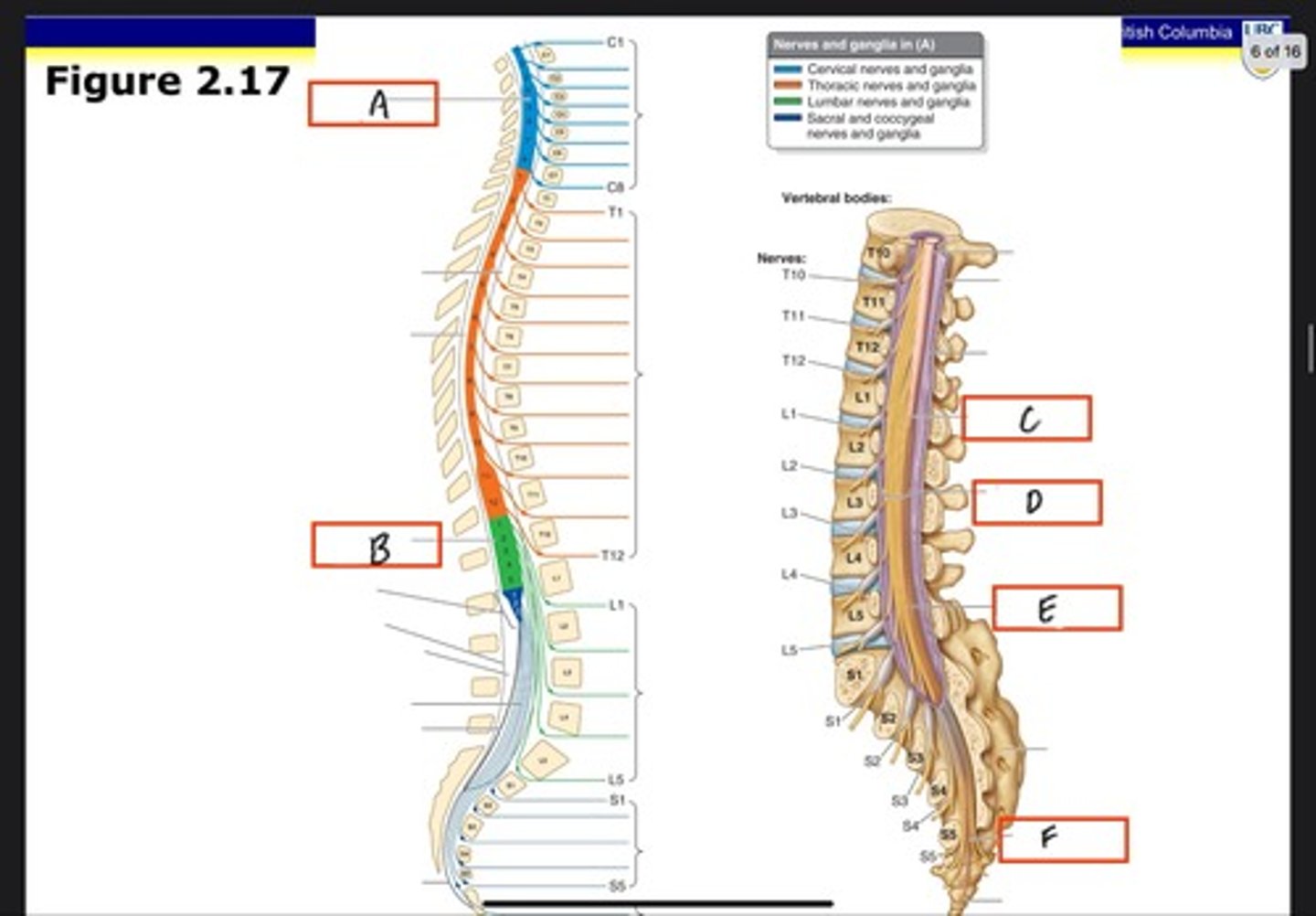
Filum terminale externum
What is F?
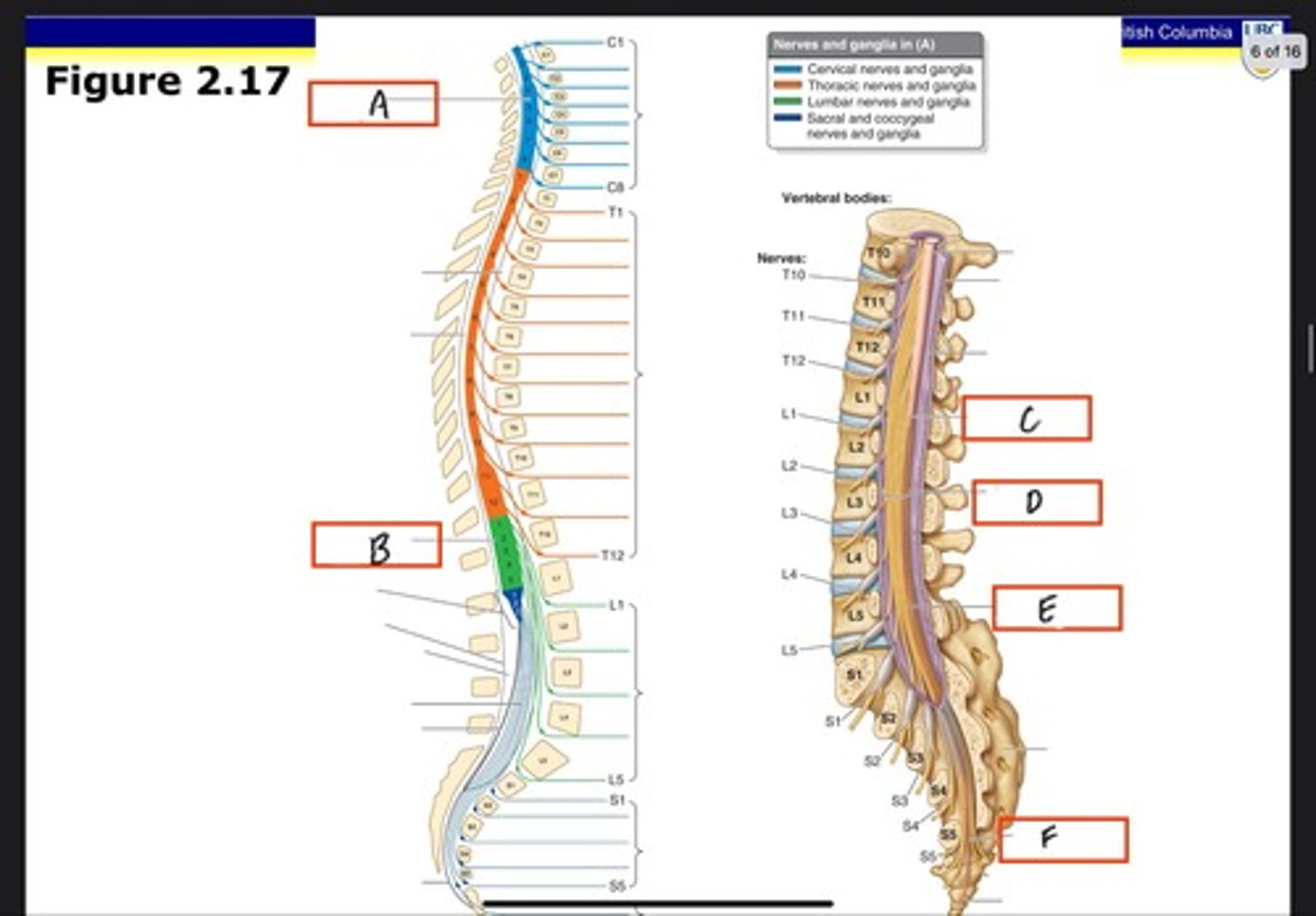
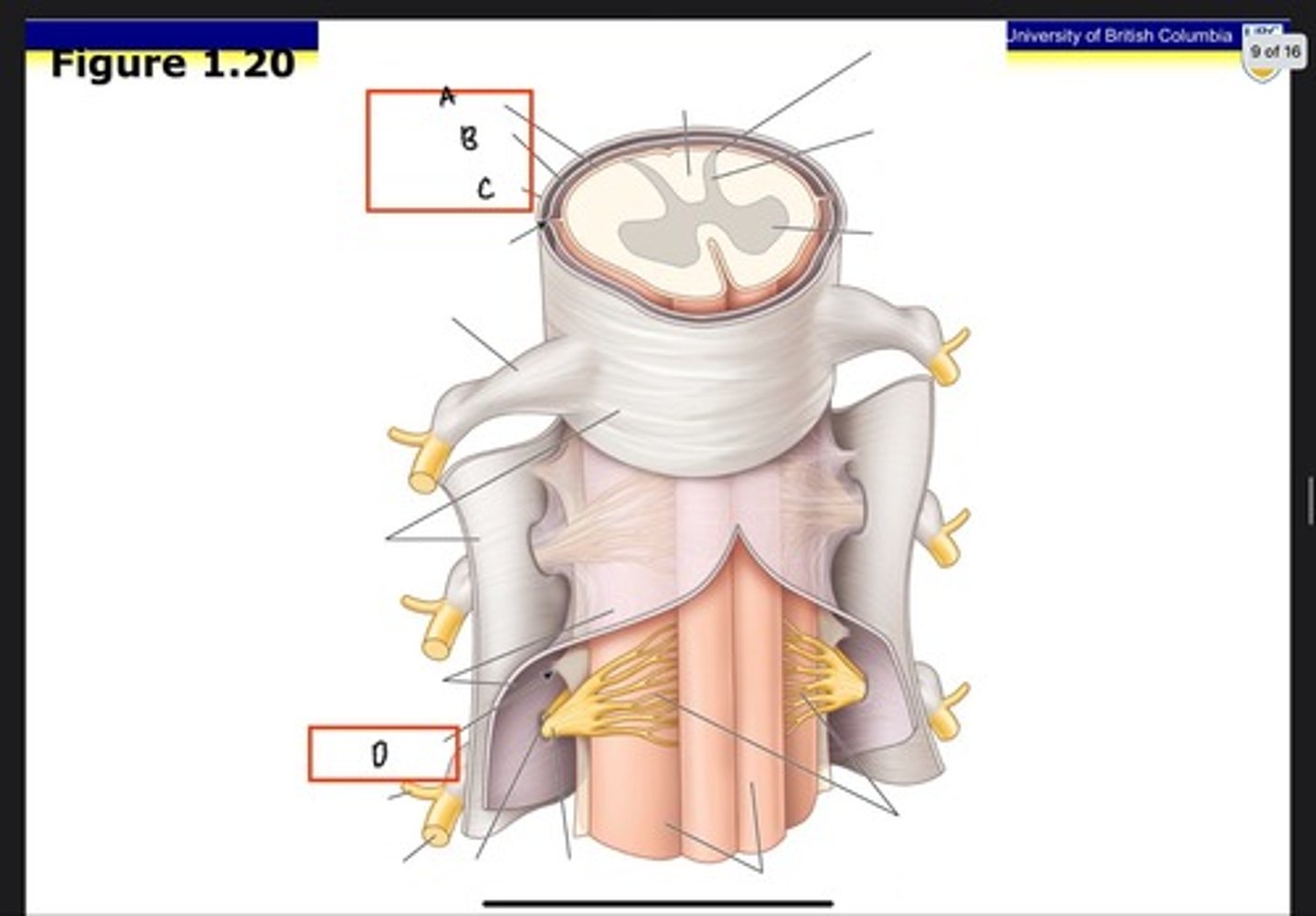
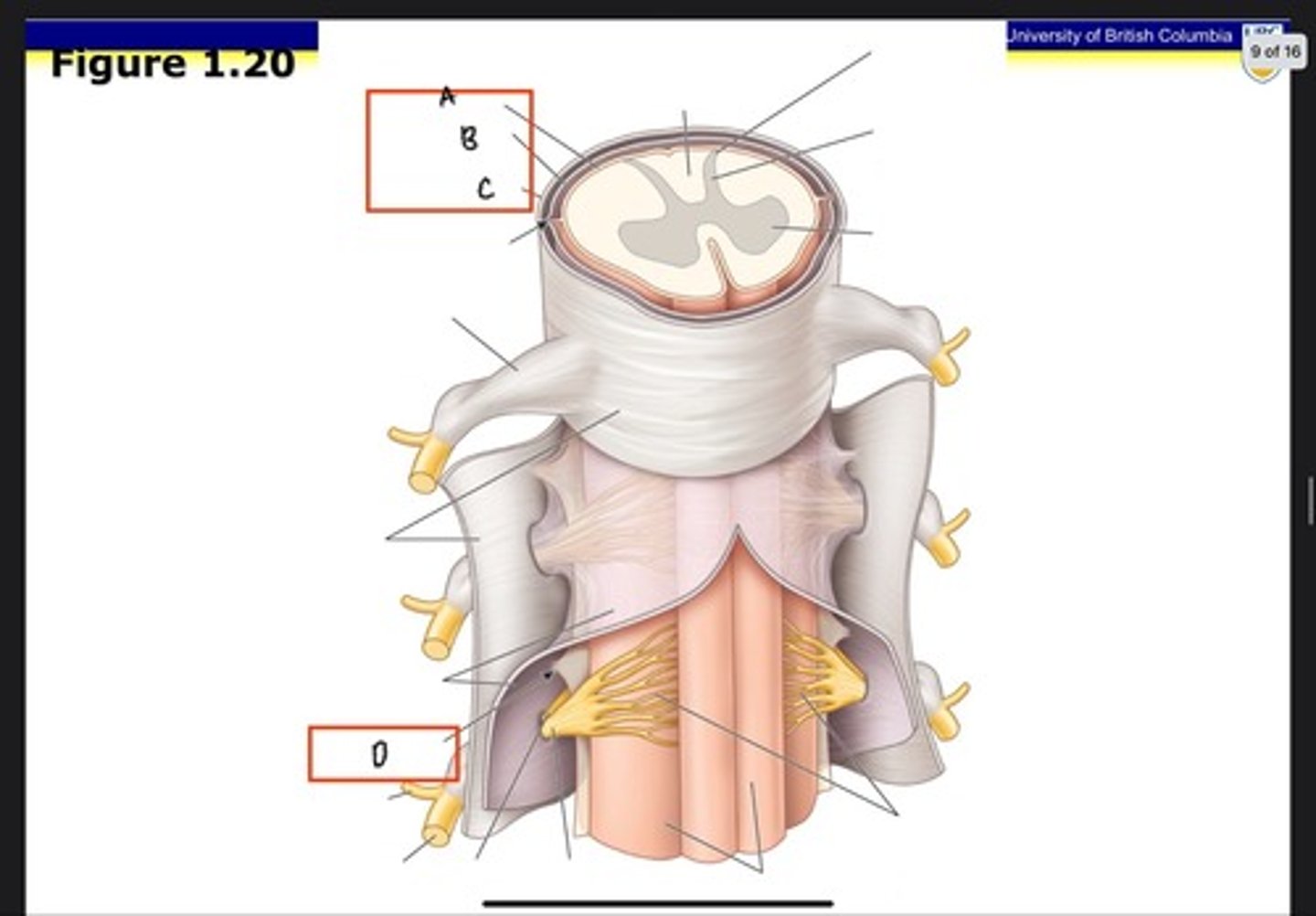
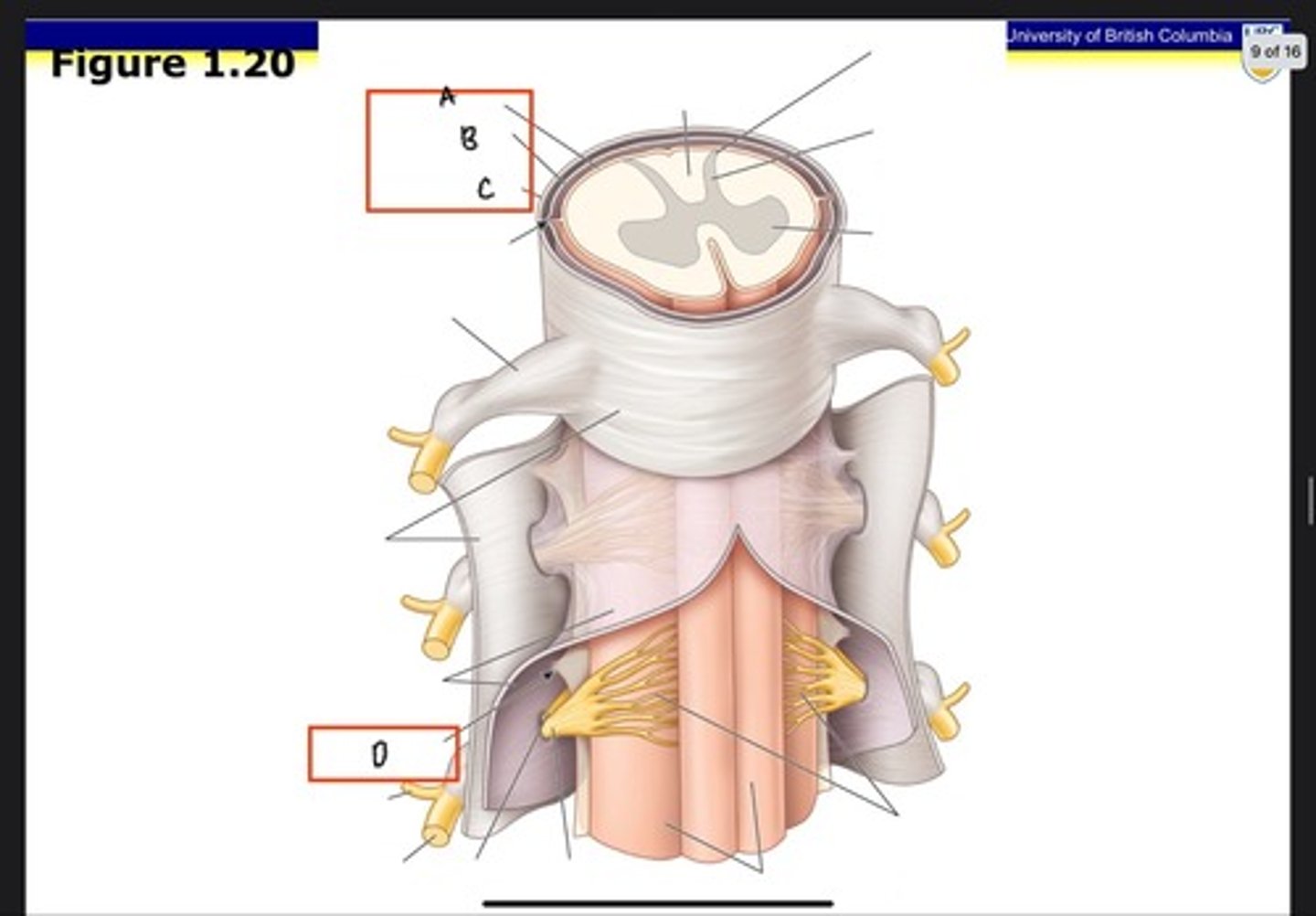
Dura mater
What is A?
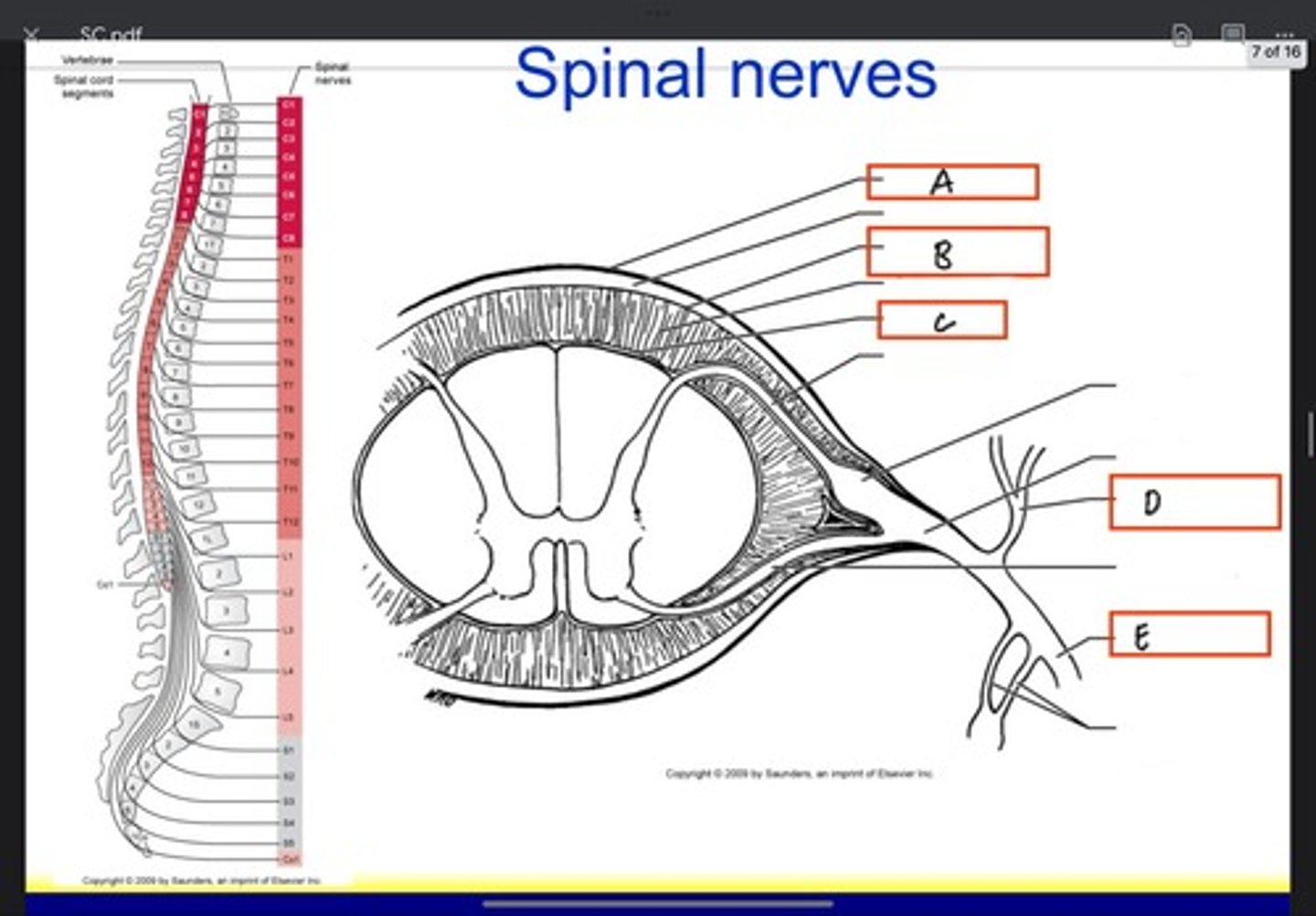
Arachnoid mater
What is B?
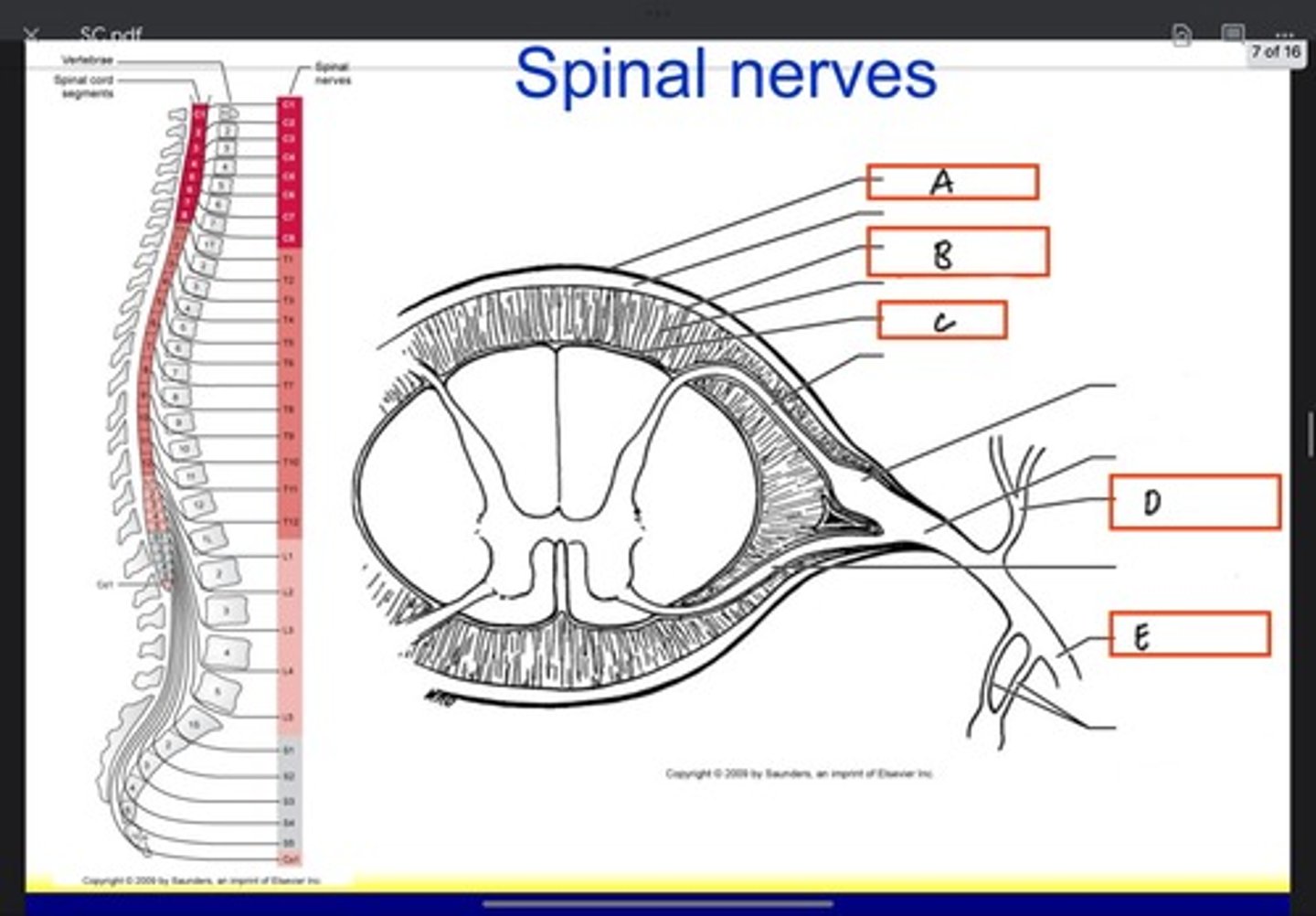
Pia mater
What is C?
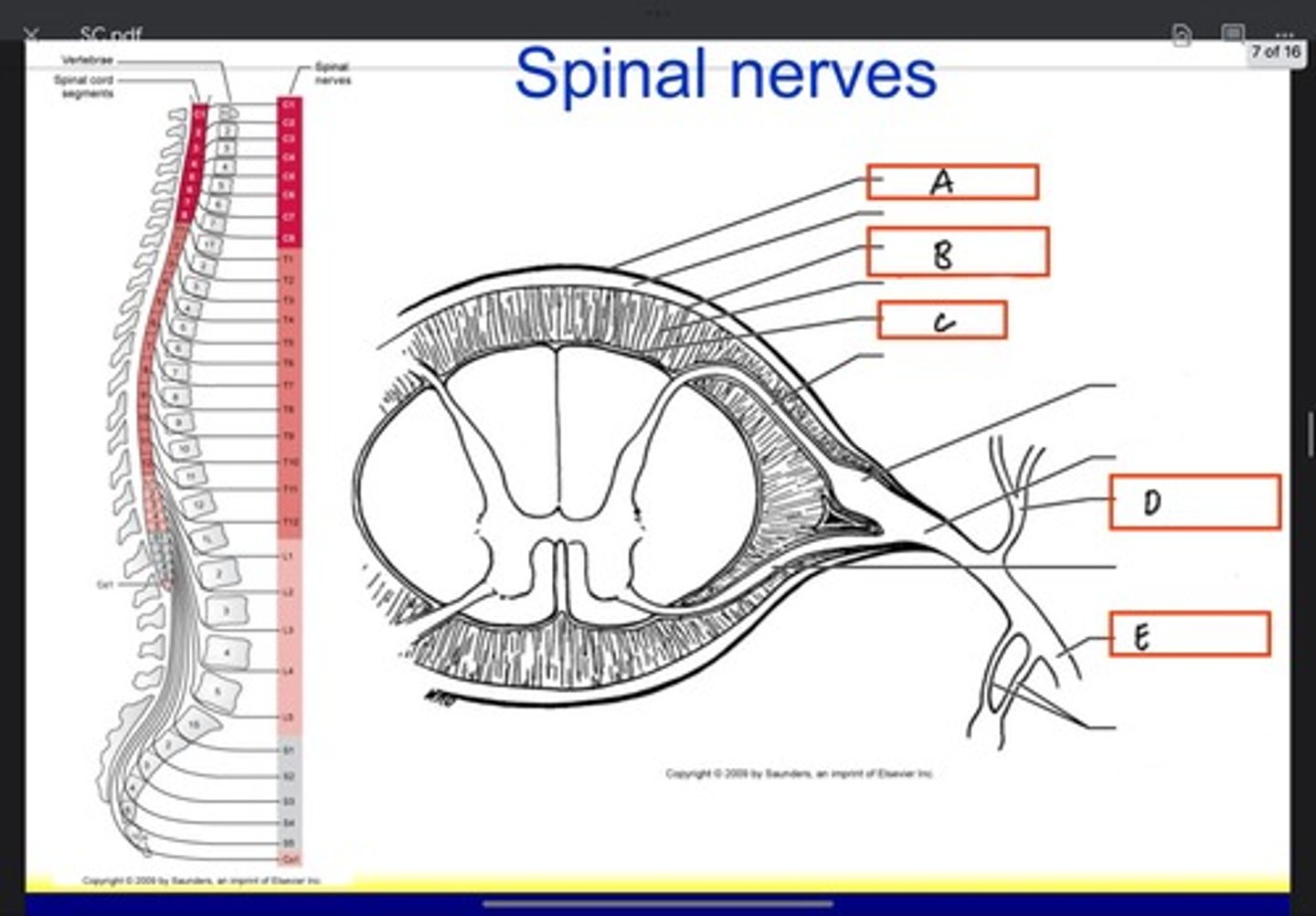
Posterior ramus
What is D?
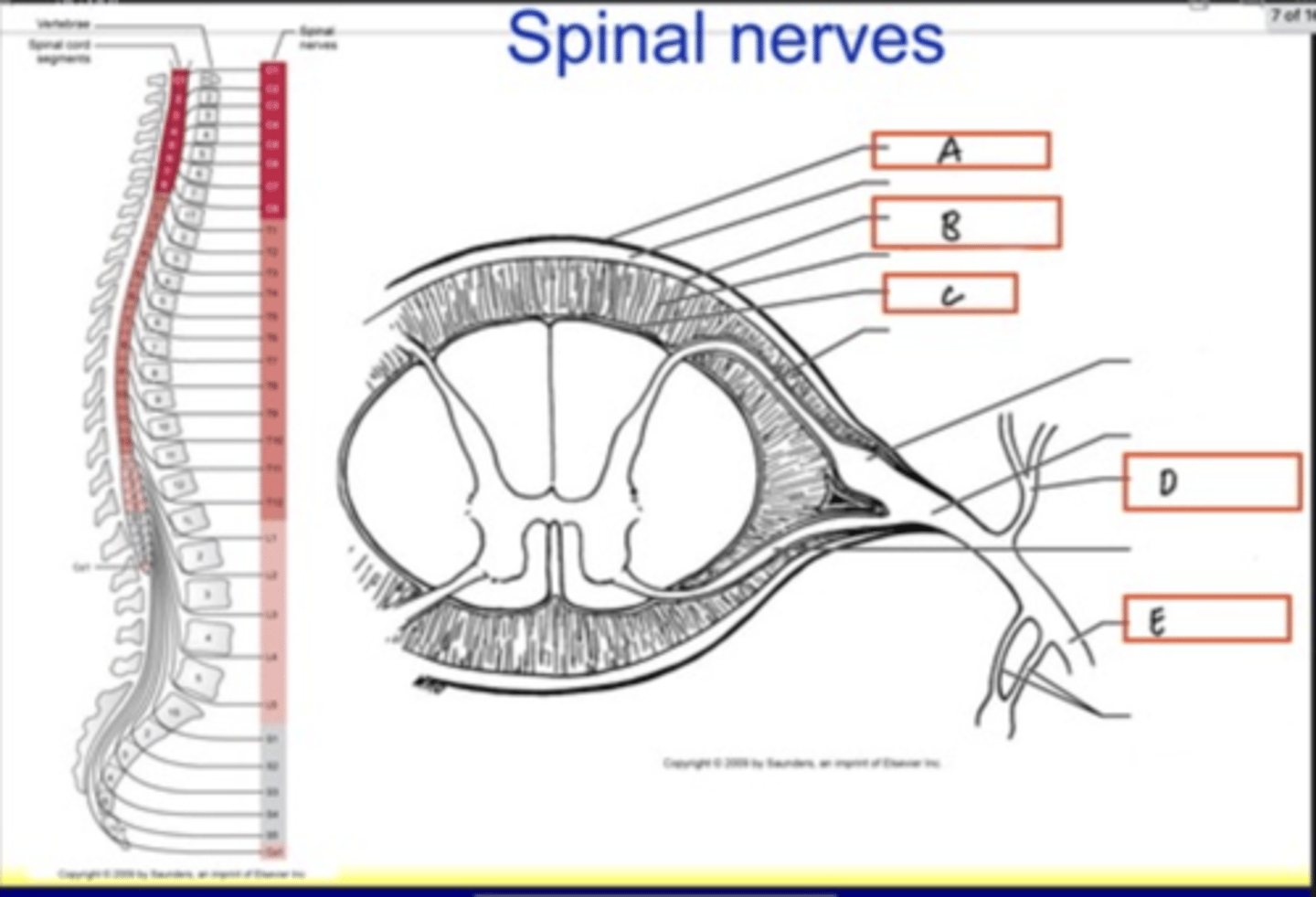
Anterior ramus
What is E?
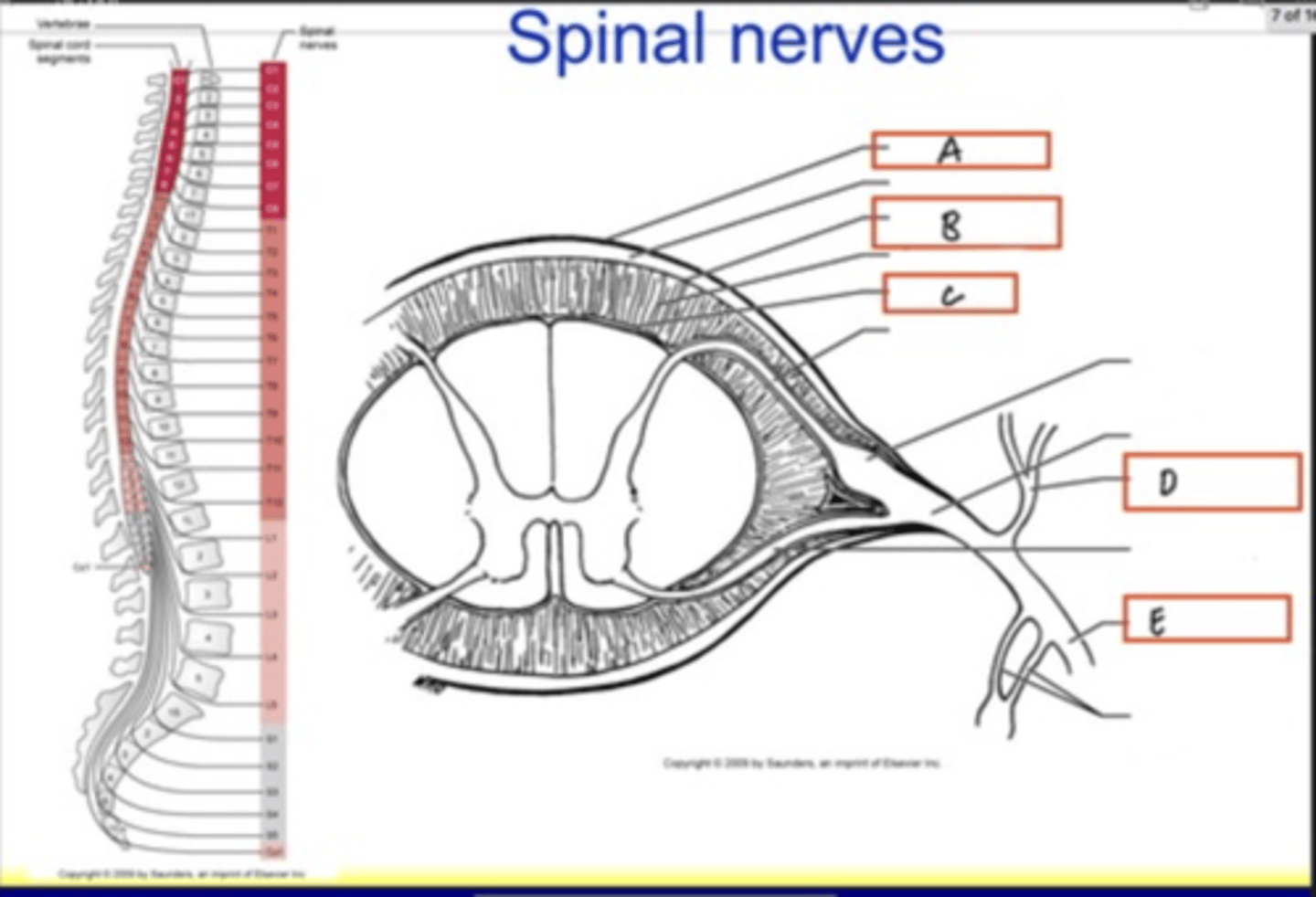
Denticulate ligament
What is A?
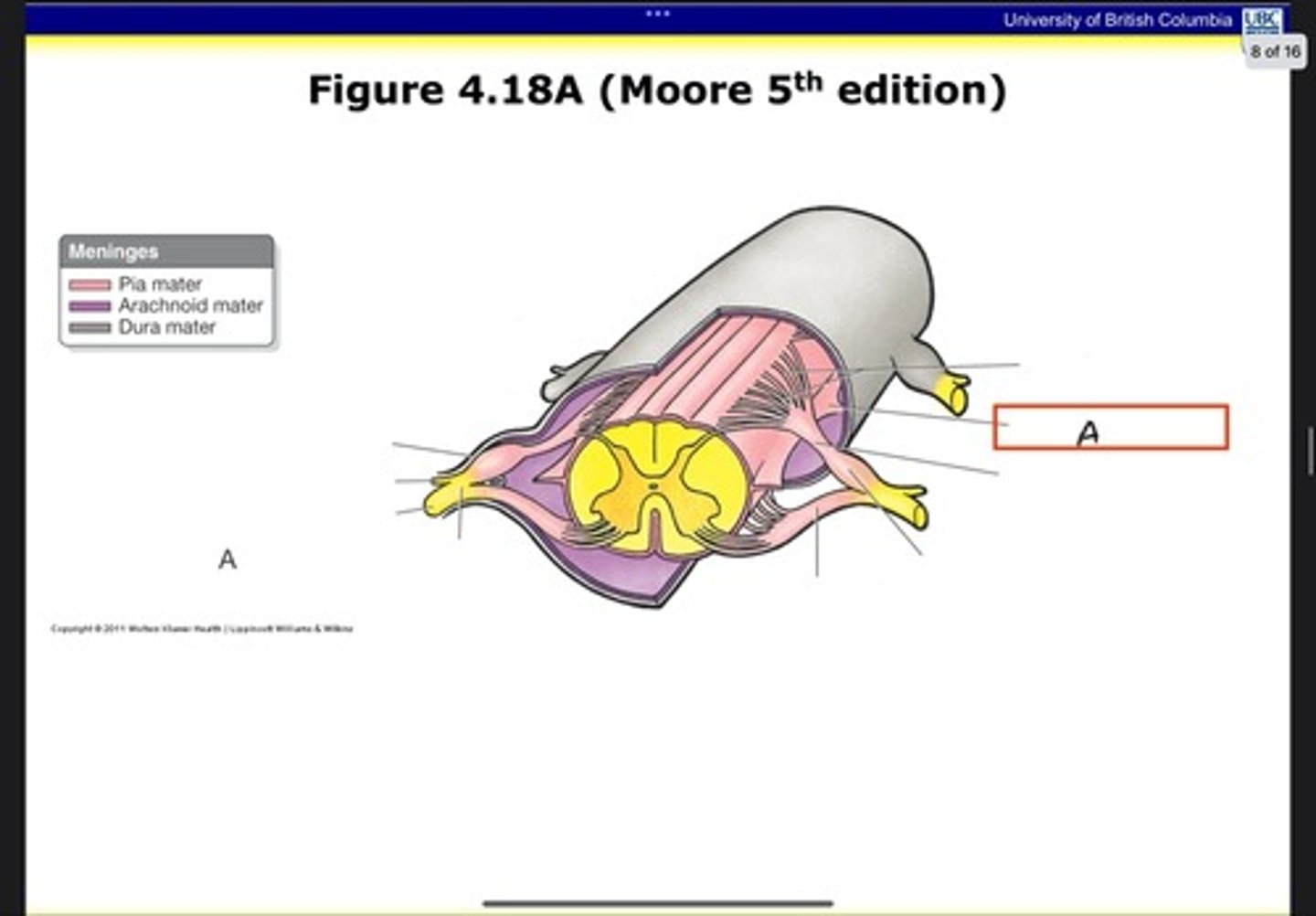
Pia mater
What is A?
Arachnoid mater
What is B?
Dura mater
What is C?
Denticulate ligament
What is D?
CSF in subarachnoid space
What is A?
Denticulate ligament (pia mater)
What is B?
Denticulate ligament
What is C?
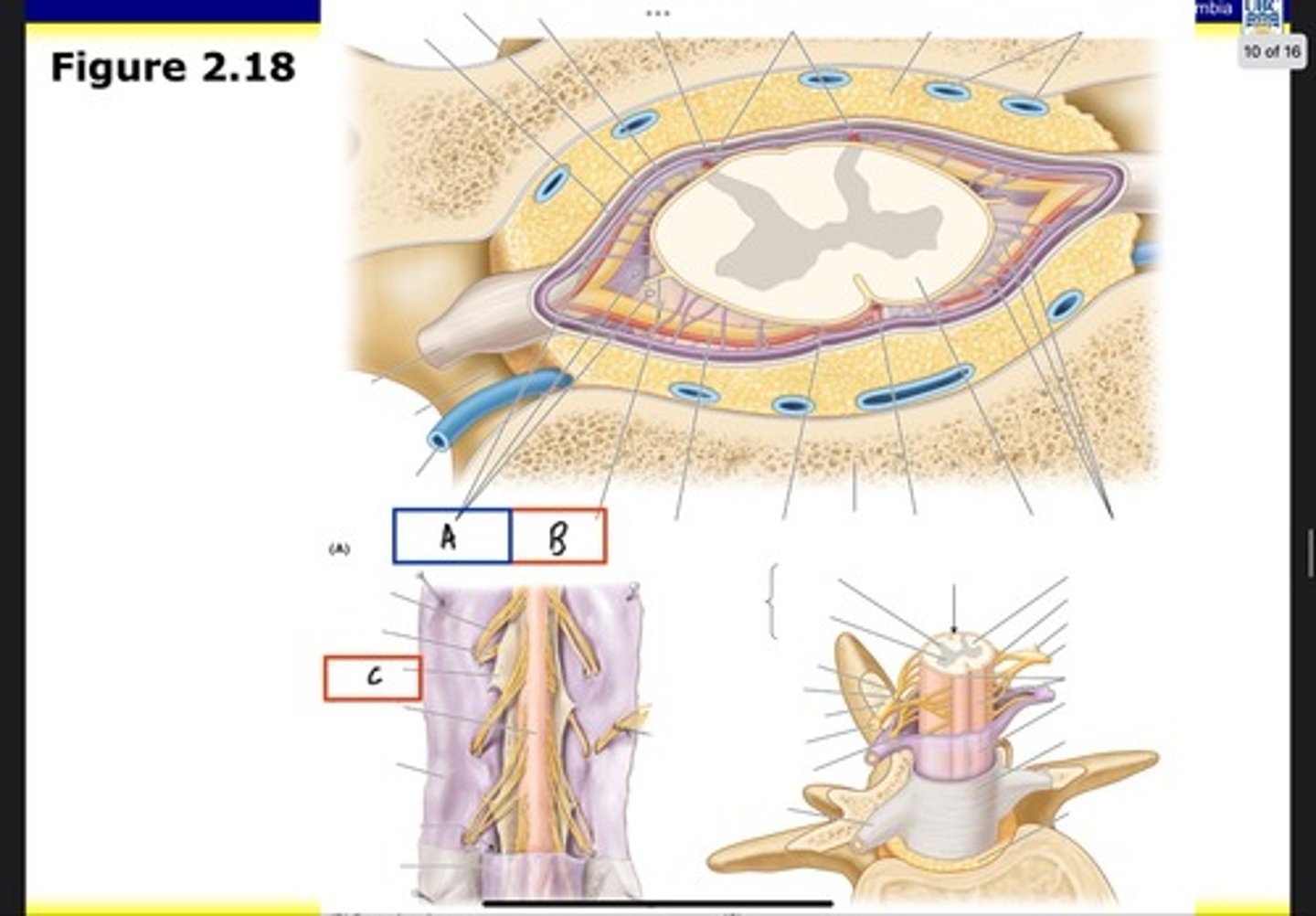
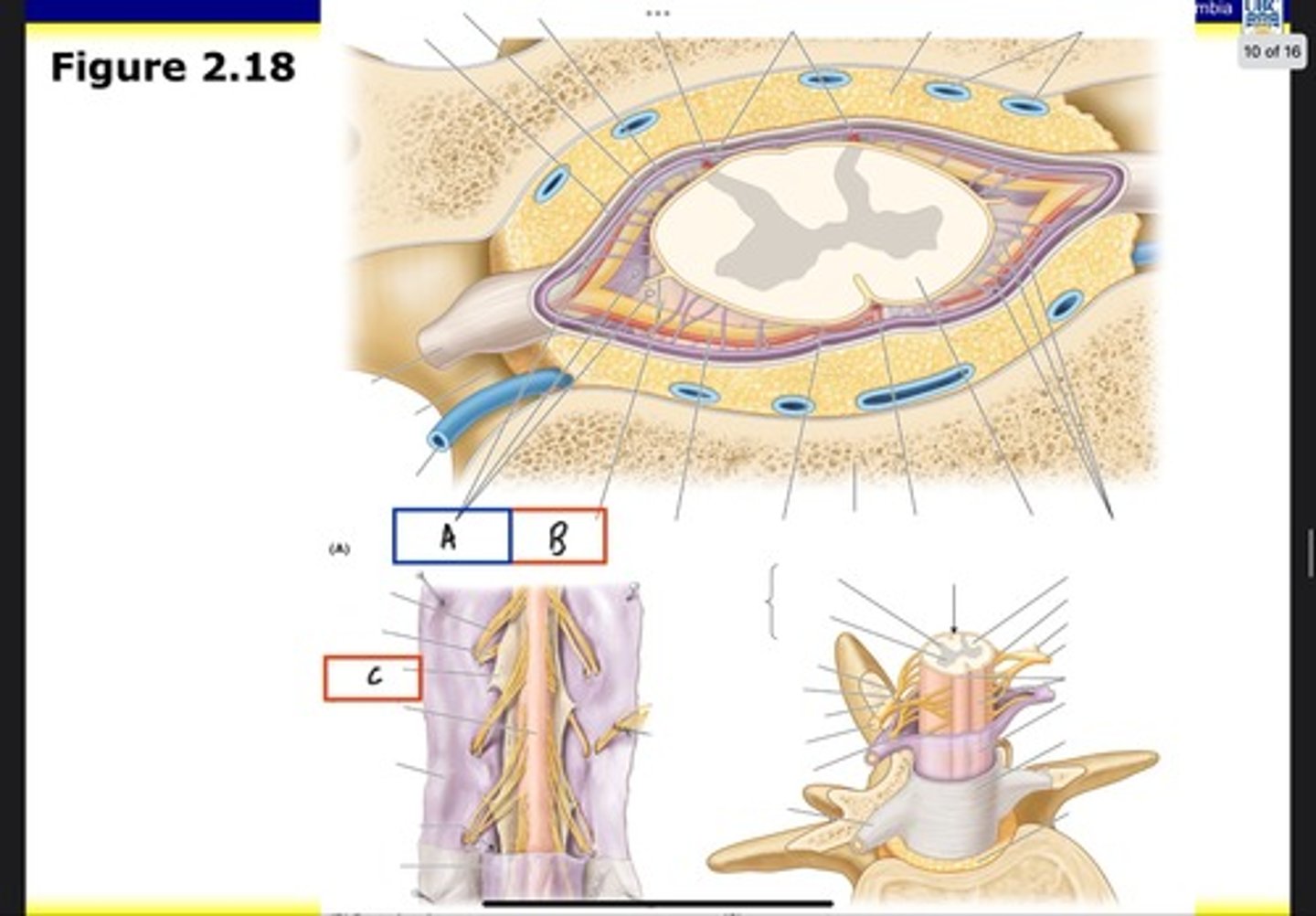
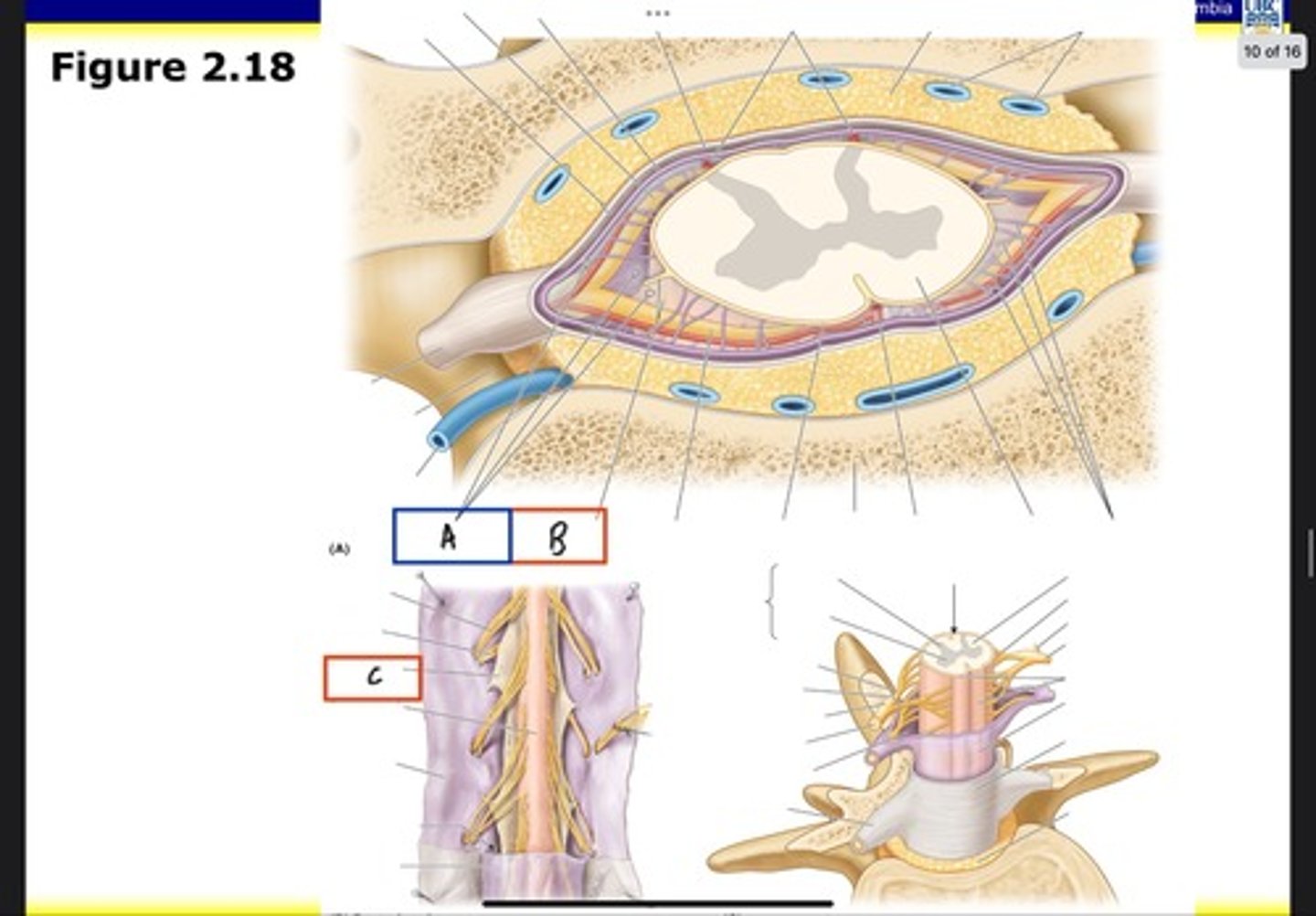
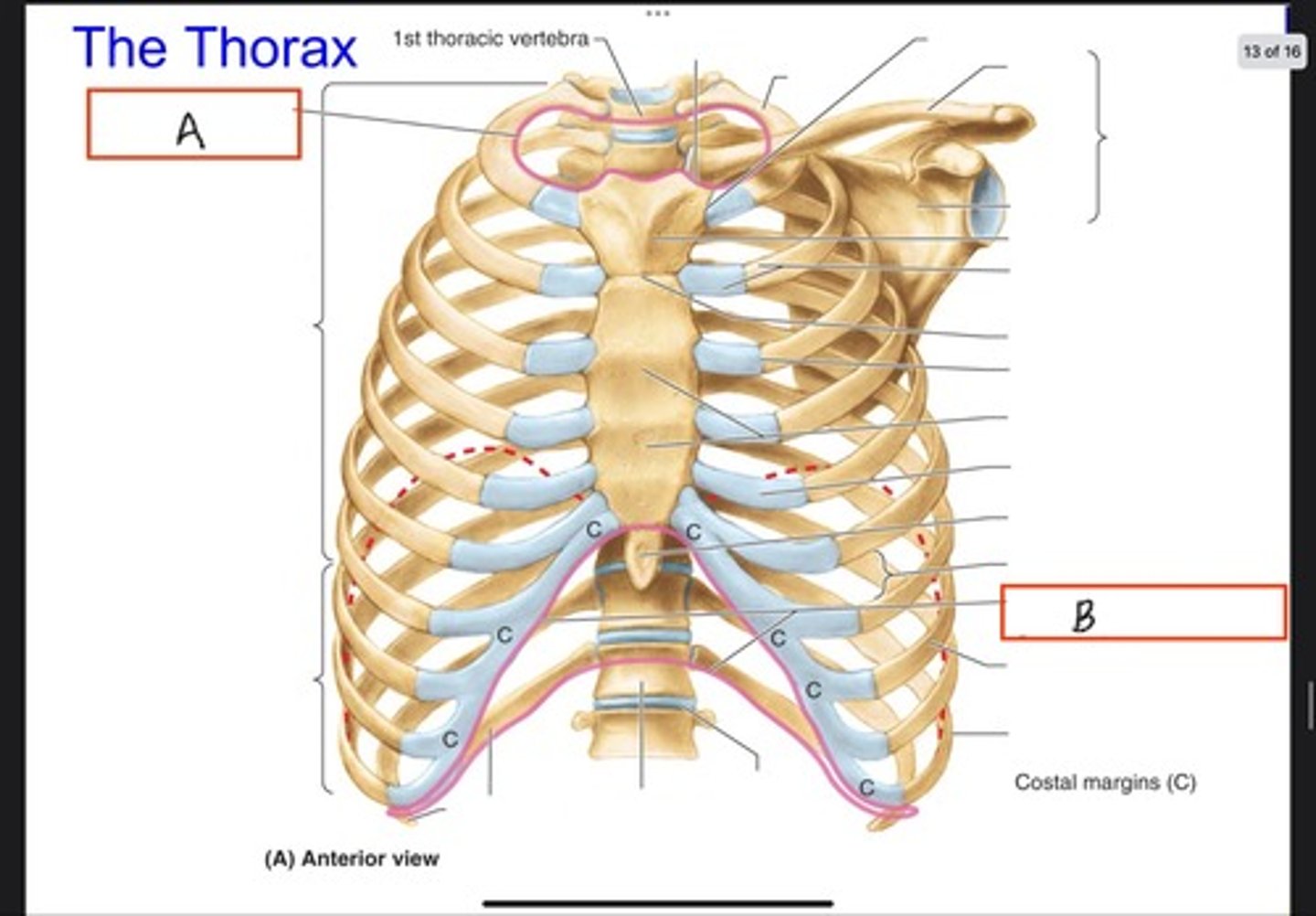
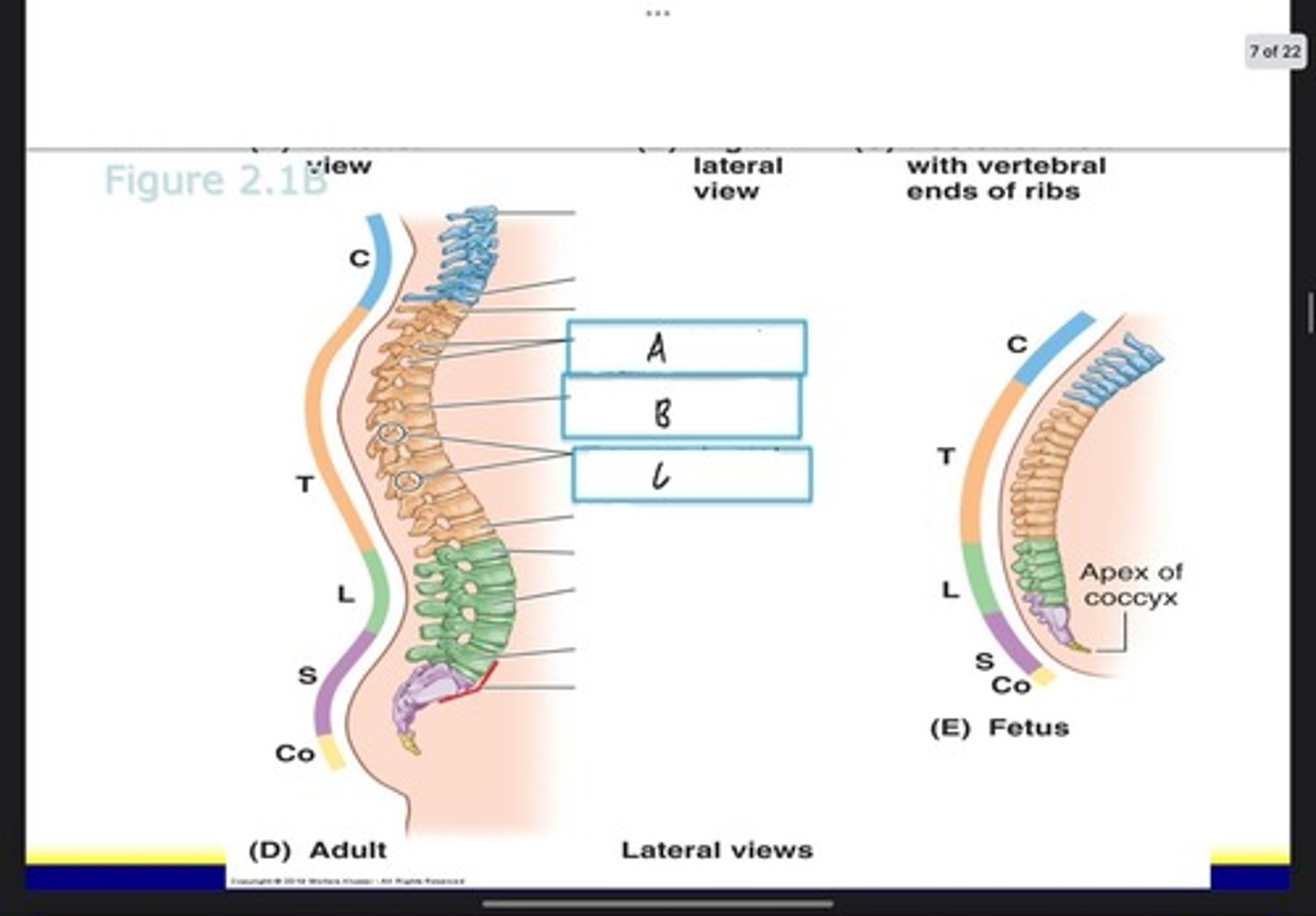
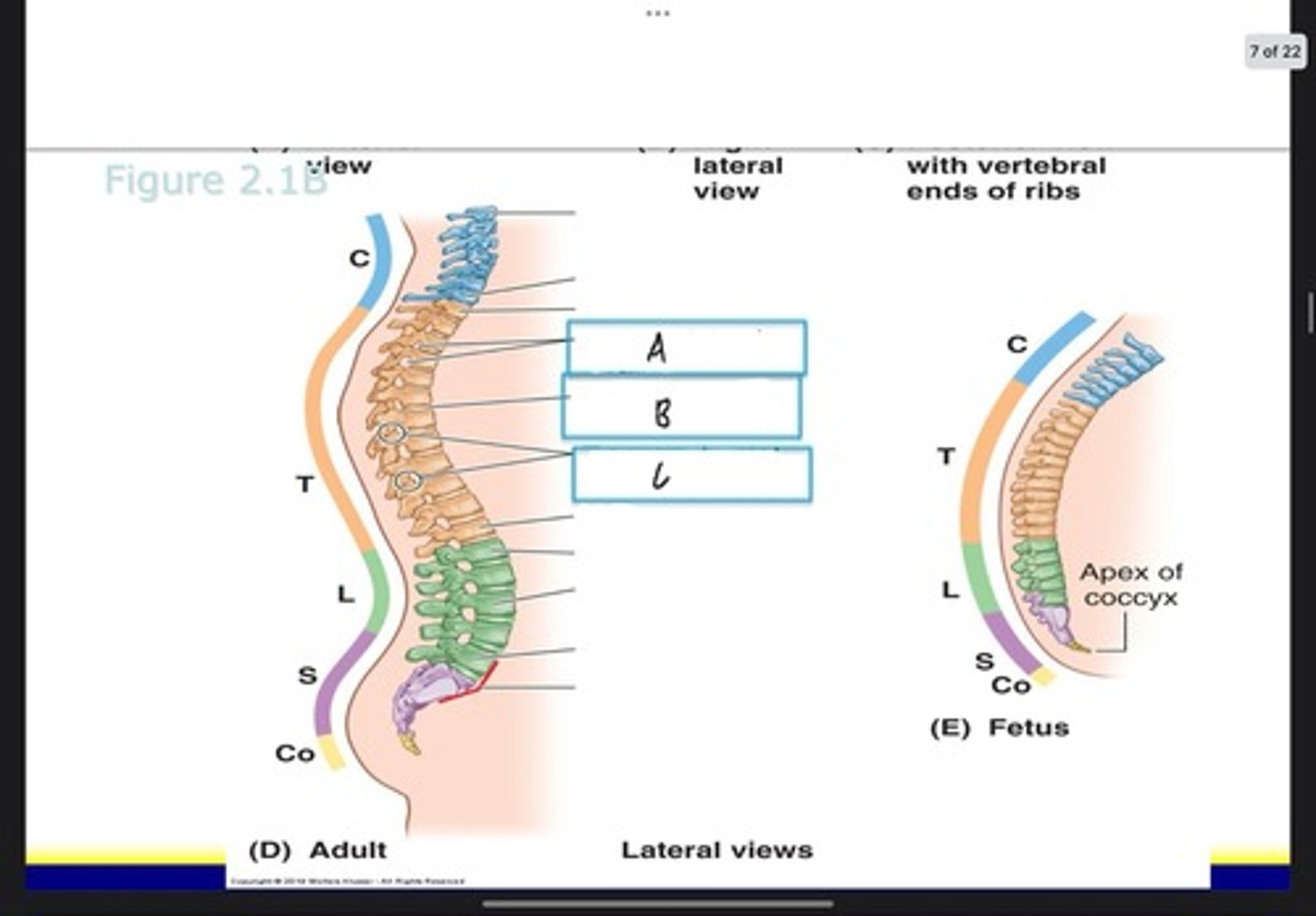
Superior thoracic aperture (pink line)
What is A?
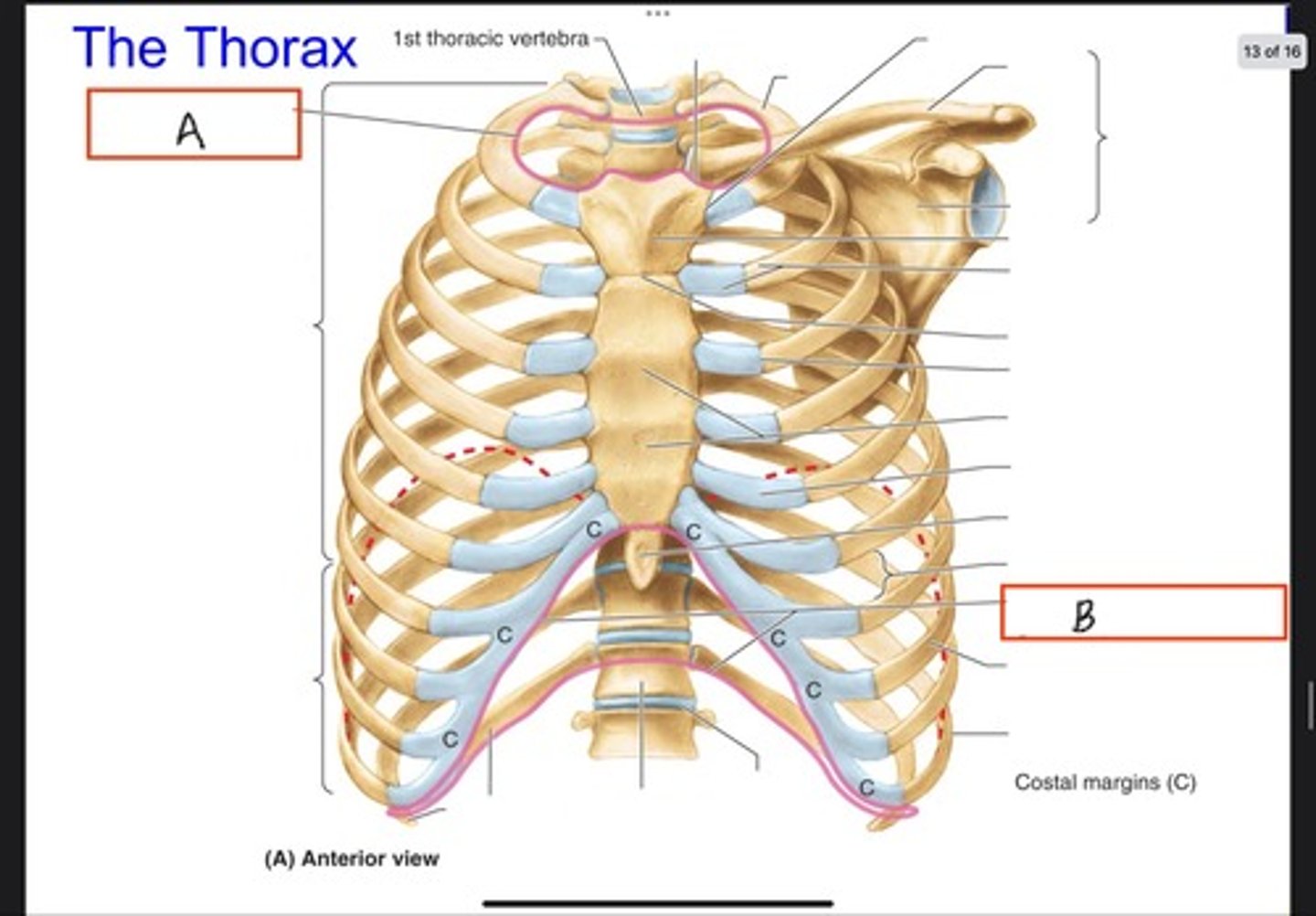
Inferior thoracic aperture (pink line)
What is B?
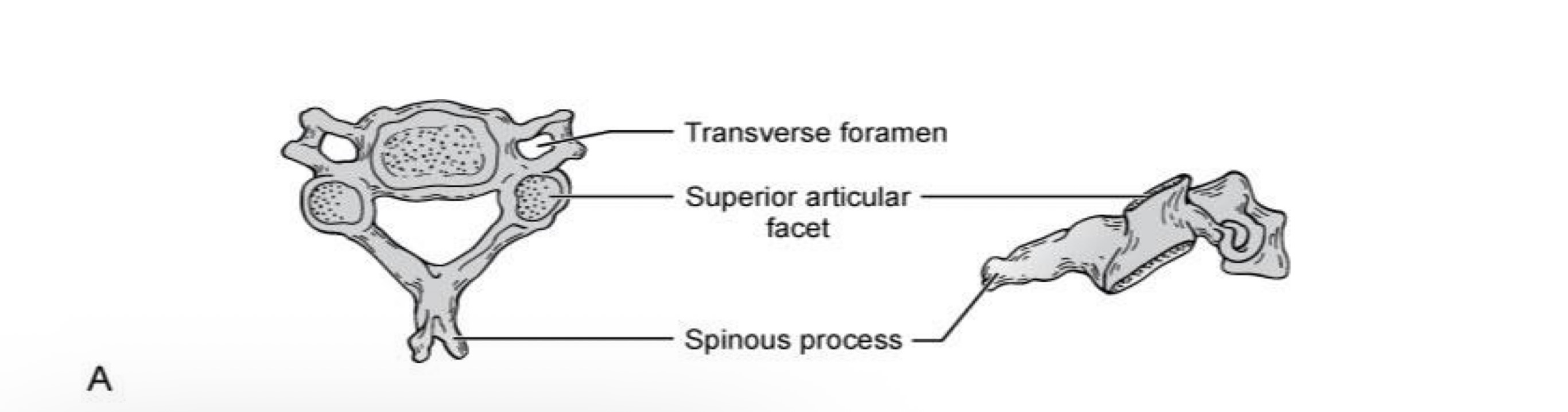
Superior articular facet
What is A?
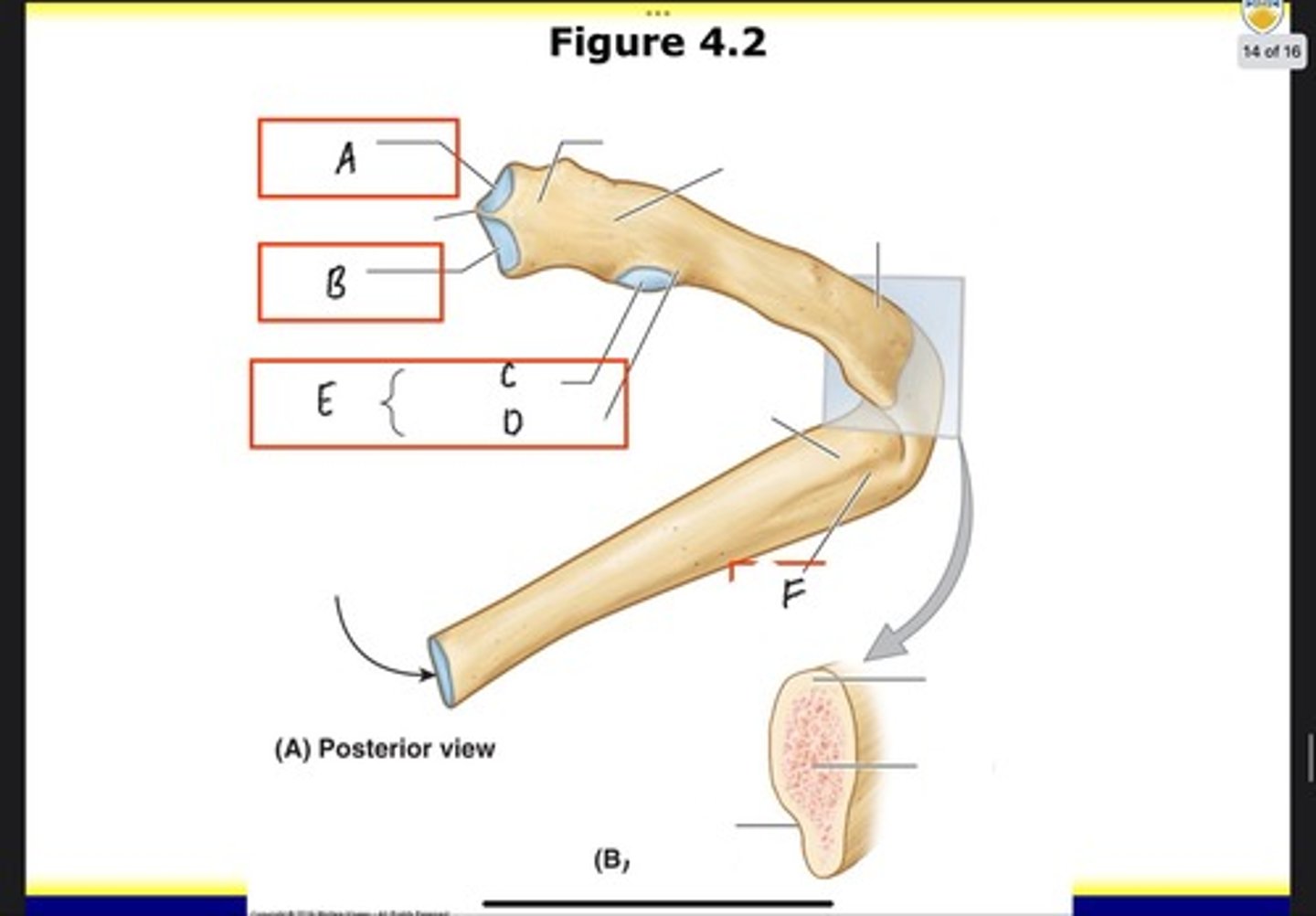
Inferior articular facet
What is B?
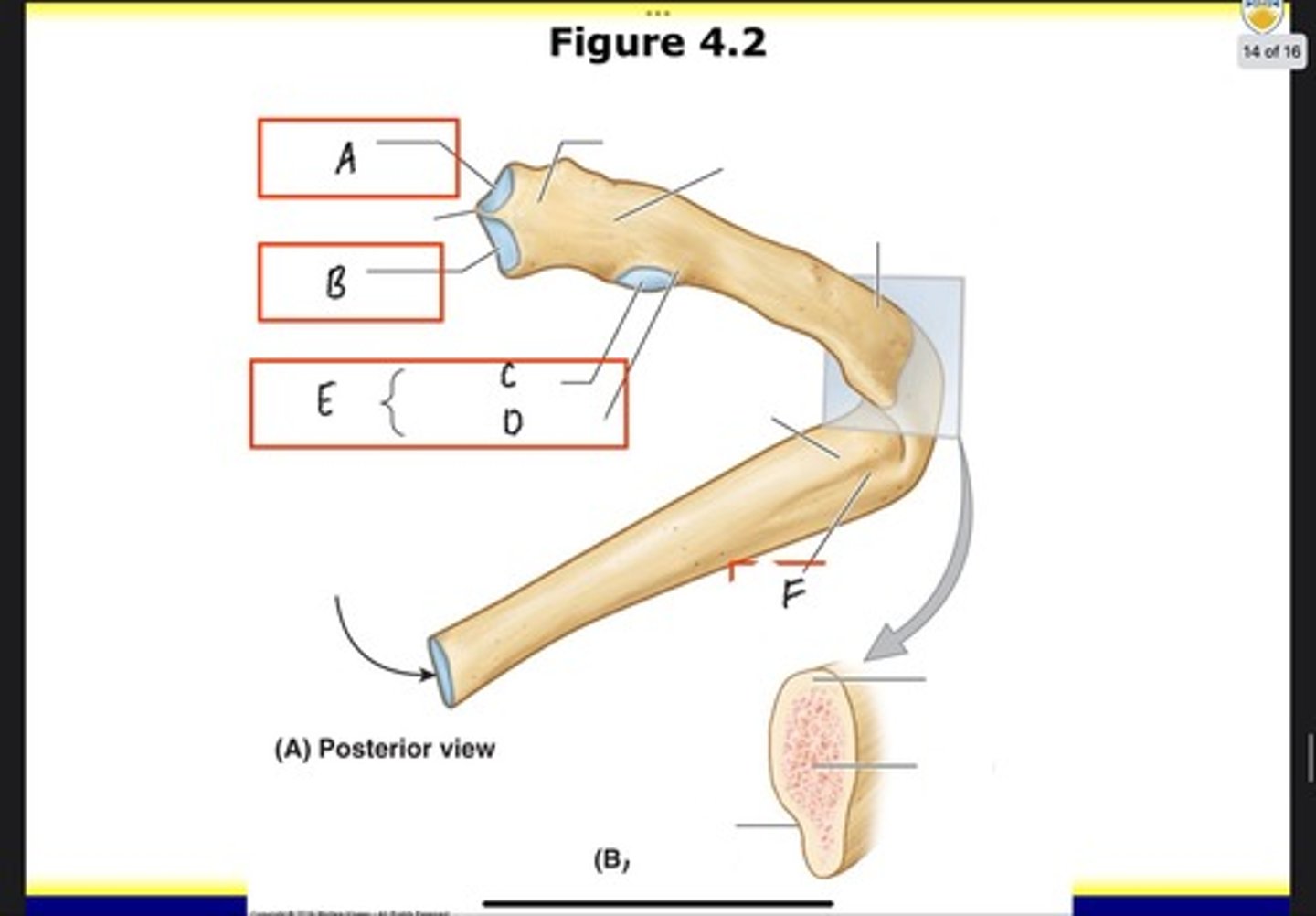
Articular part of tubercle
What is C?
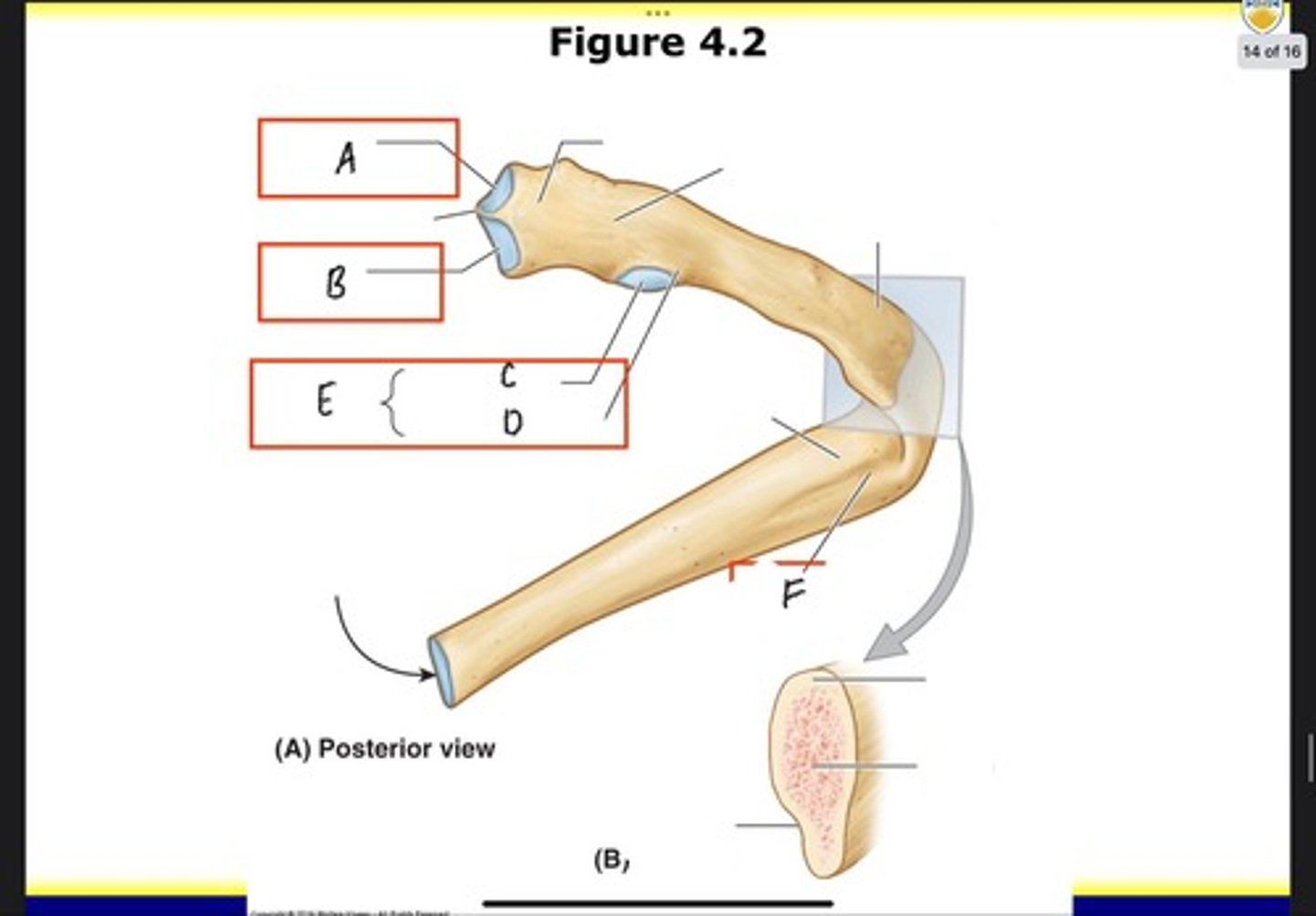
Nonarticular part of tubercle
What is D?
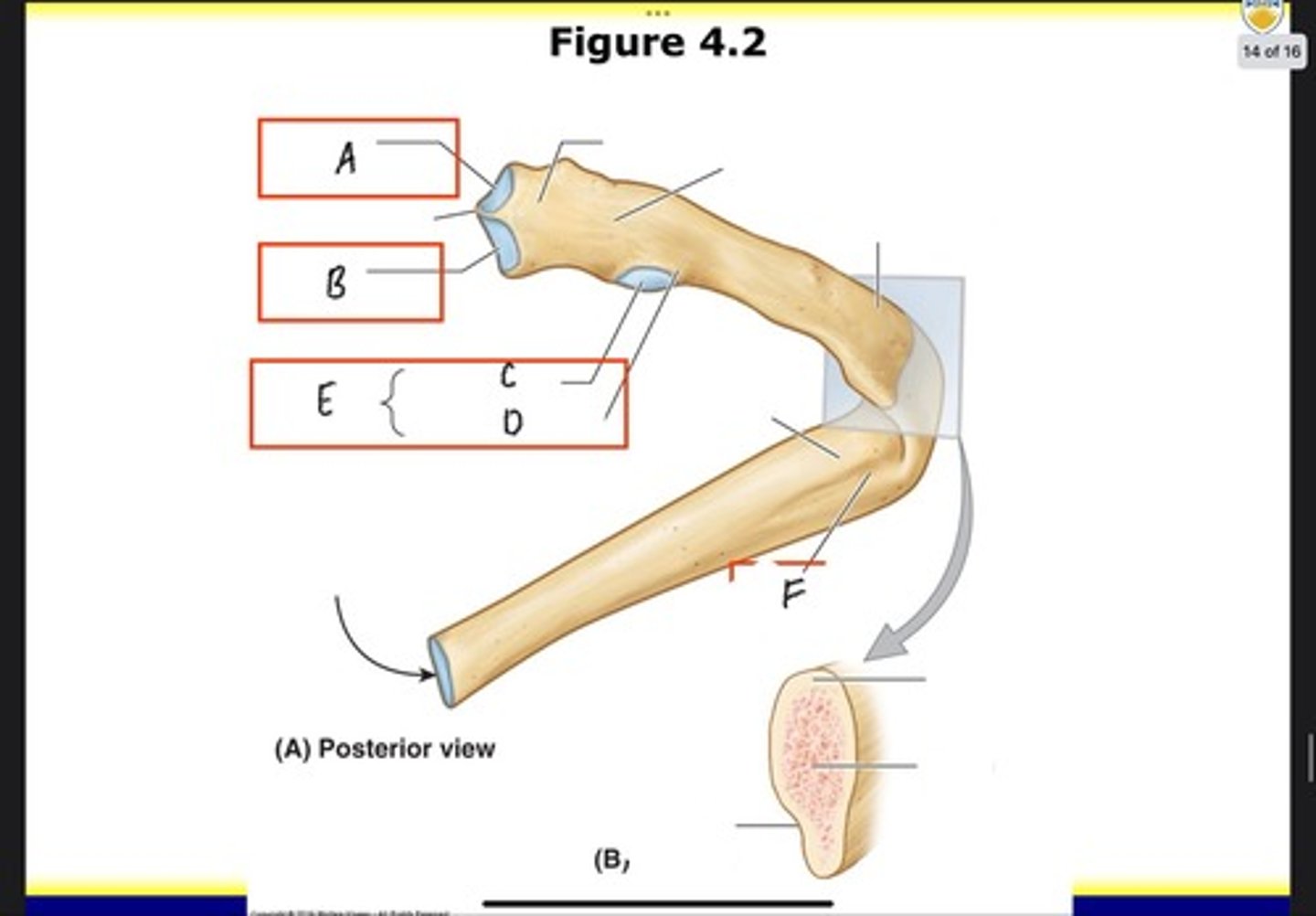
Tubercle
What is E?
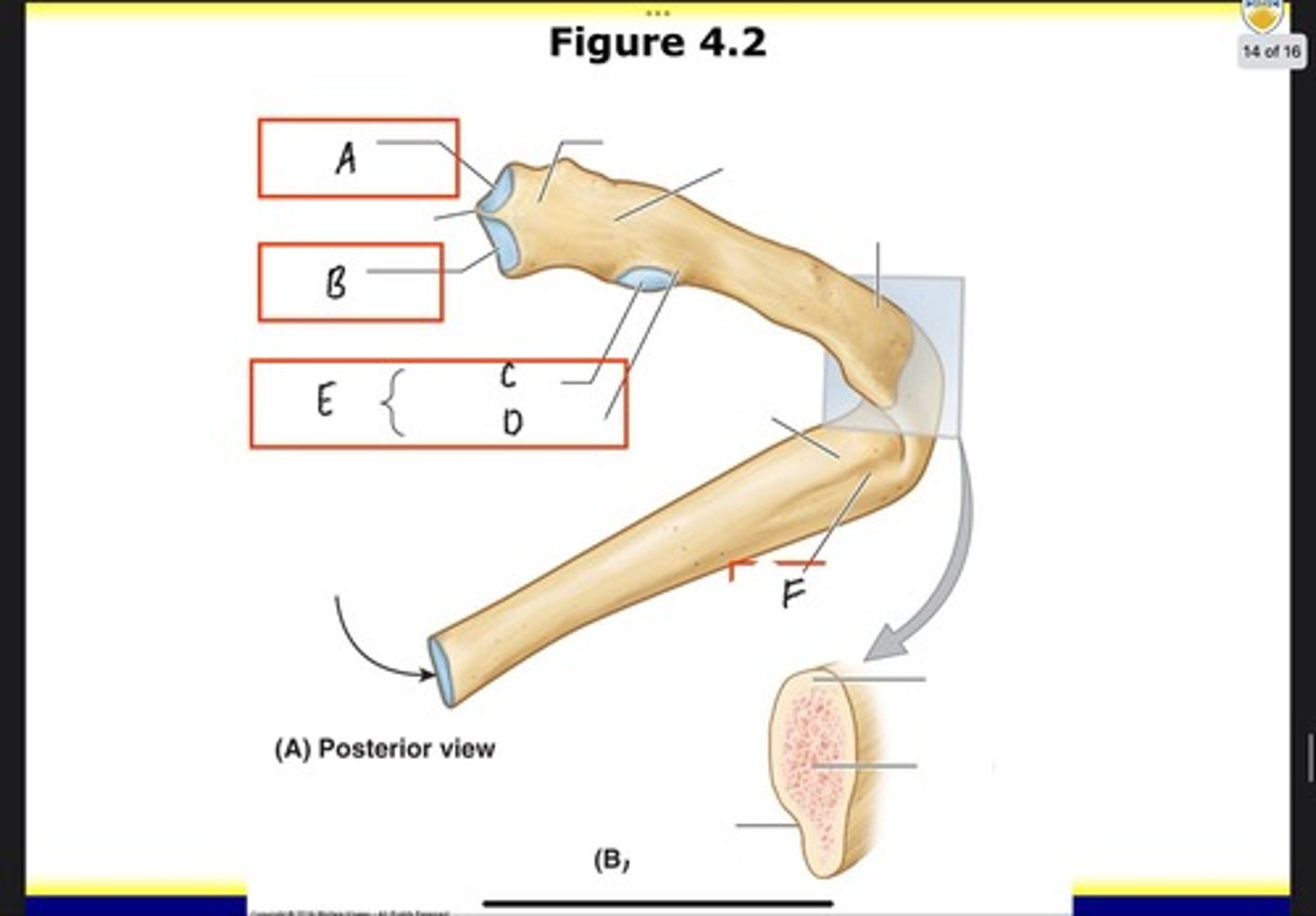
Costal groove
What is F?
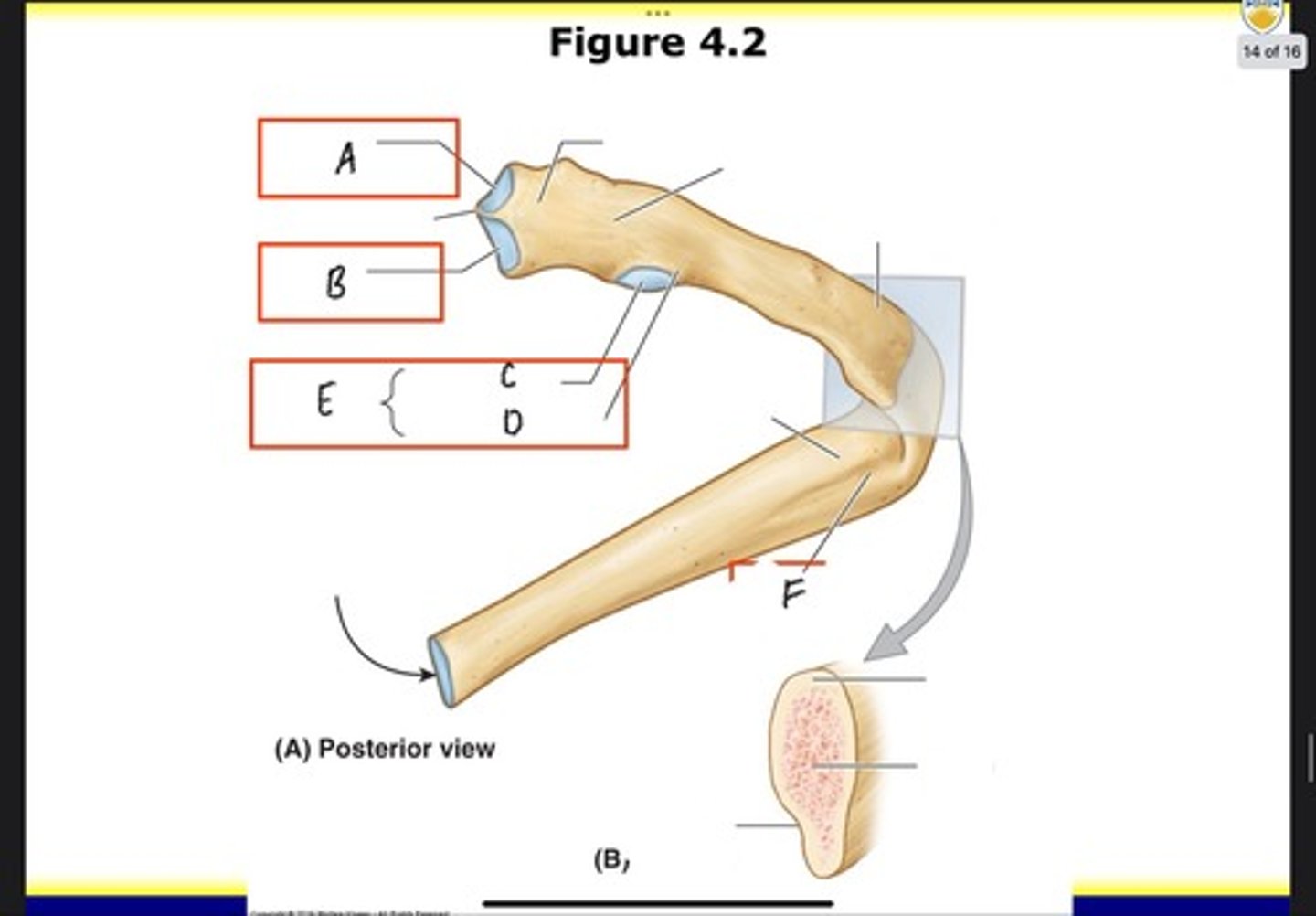
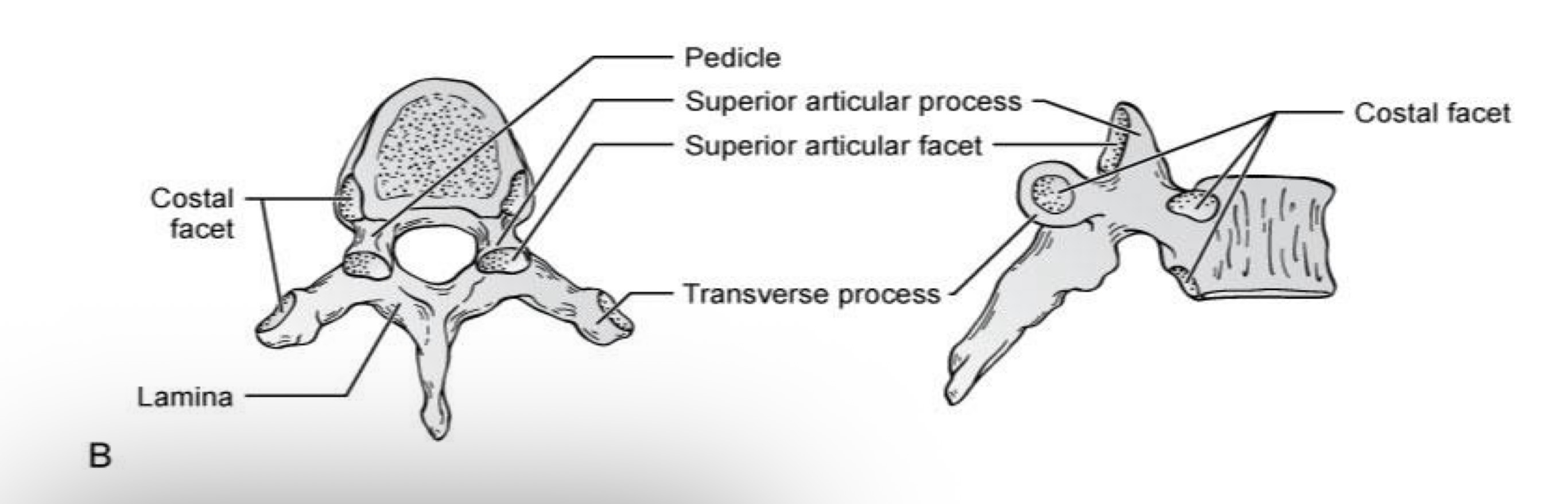
Costovertebral joints
What is A?
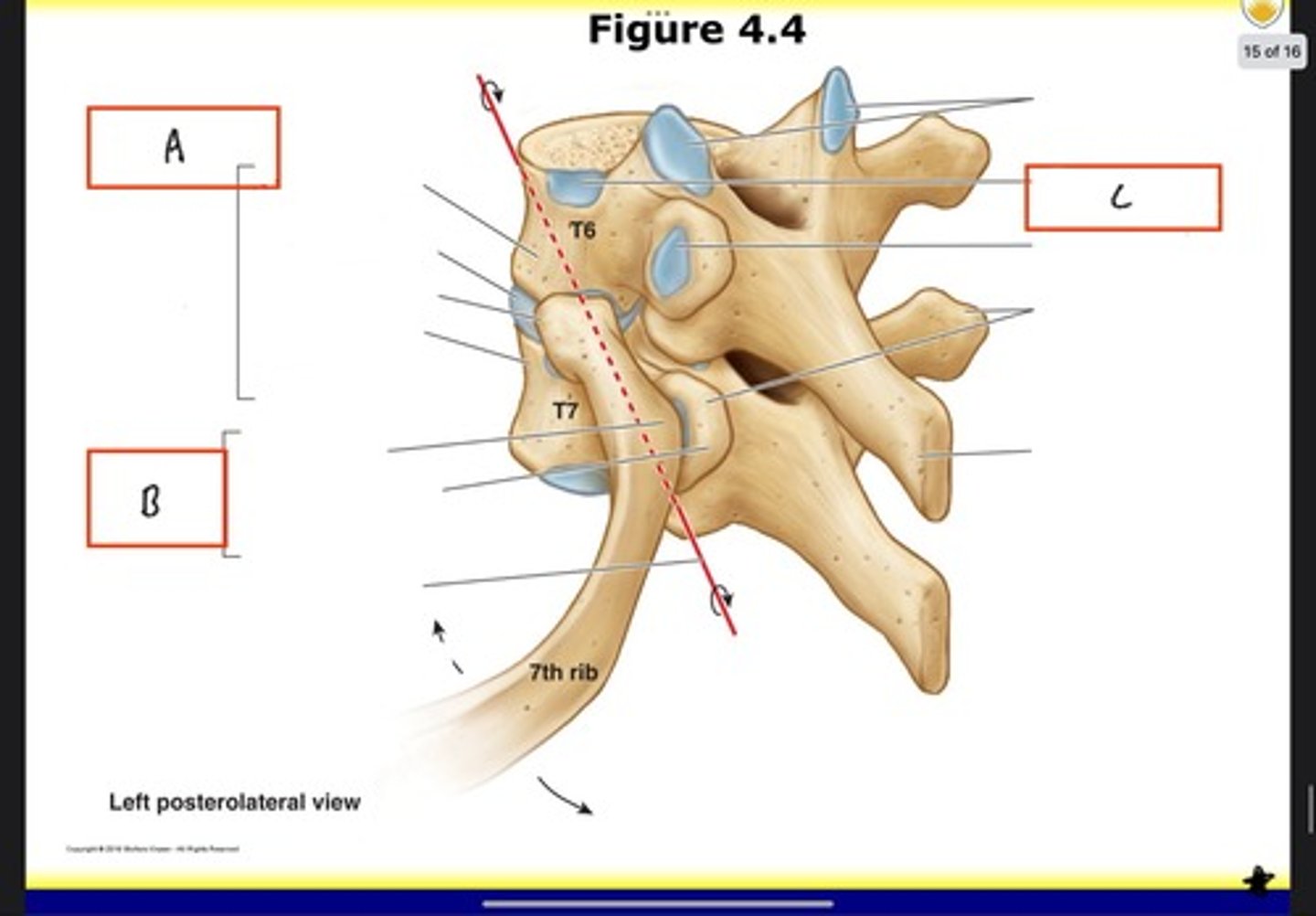
Costotransverse joint
What is B?
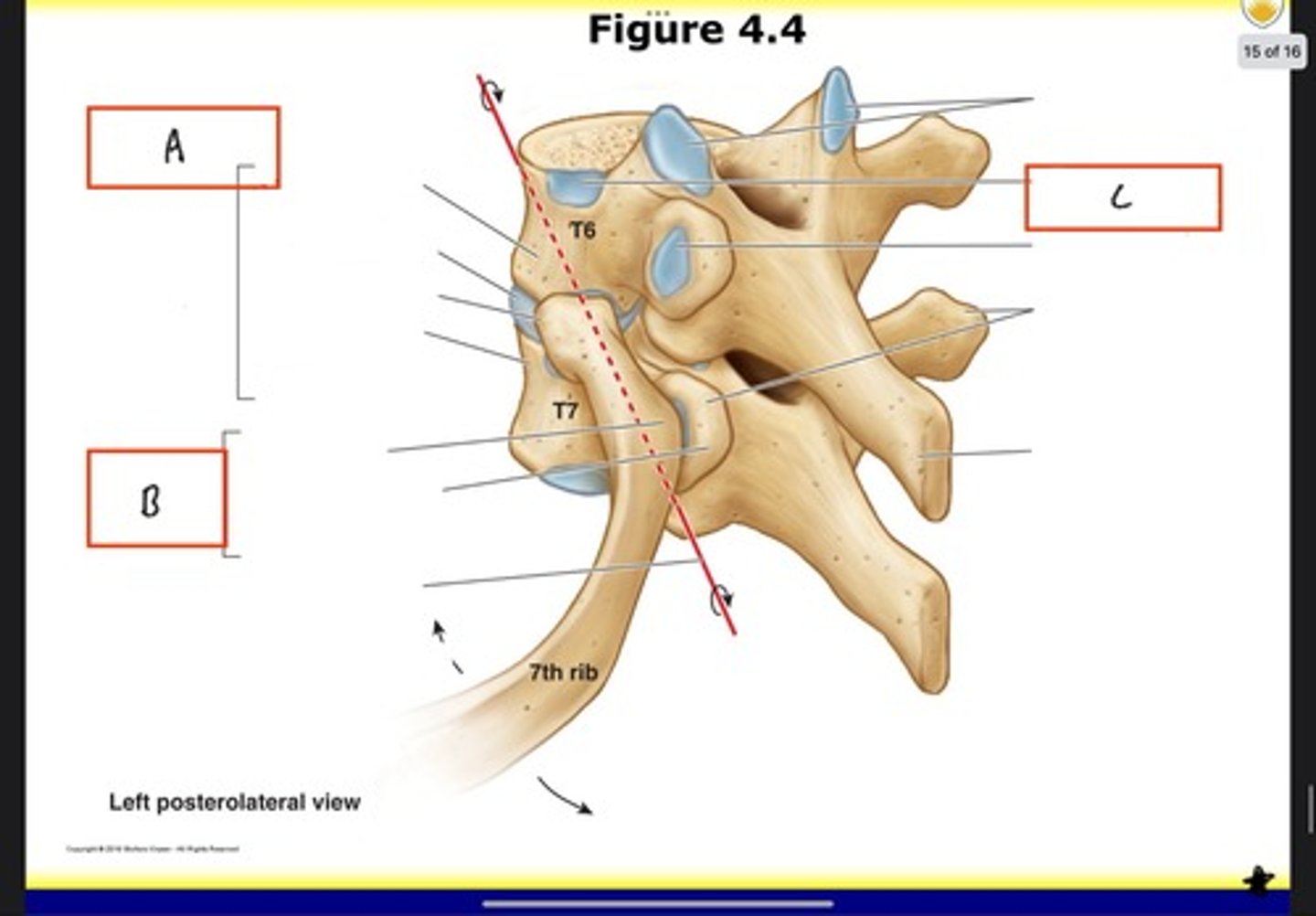
Costal demifacet for head of the 6th rib
What is C?
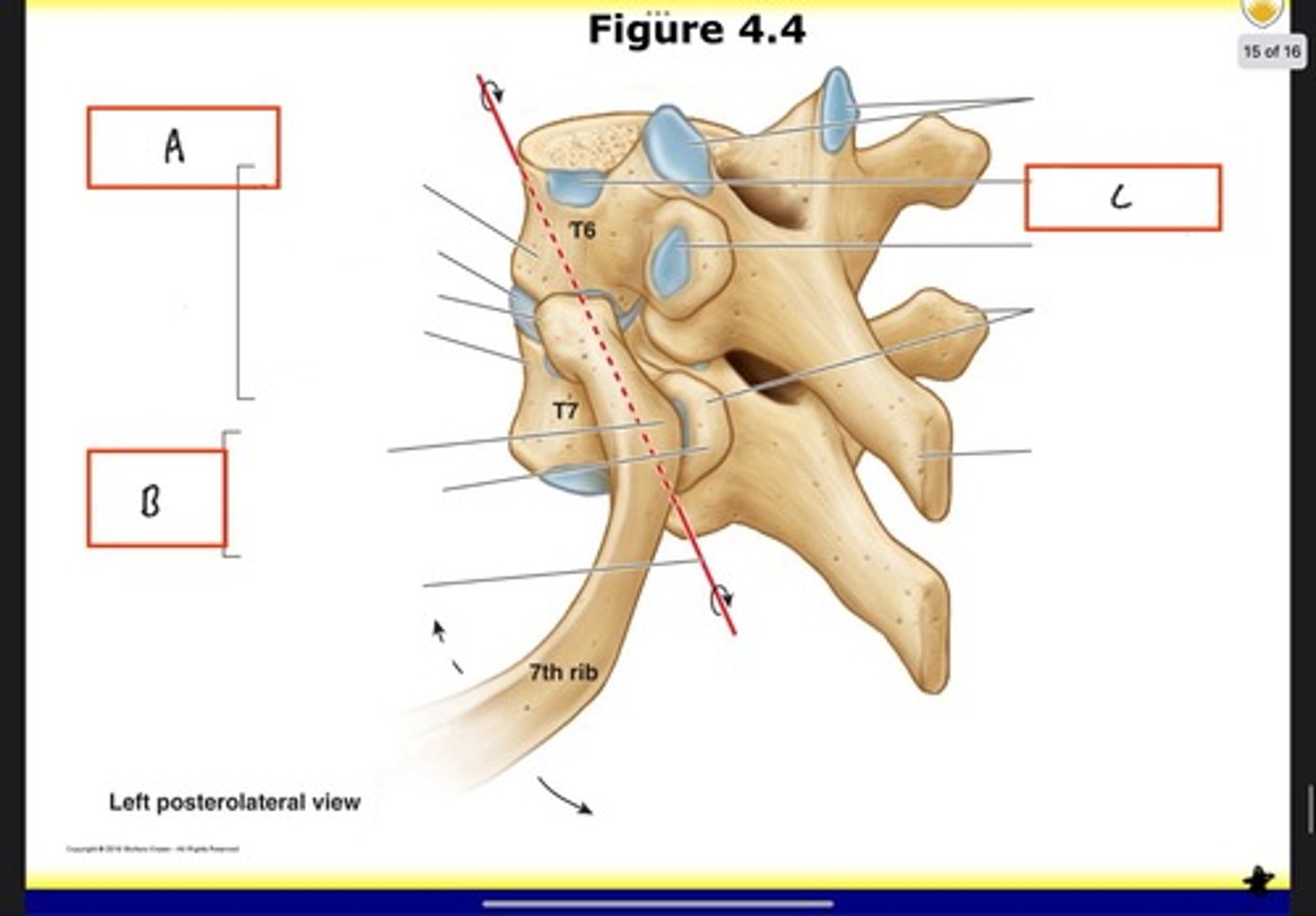
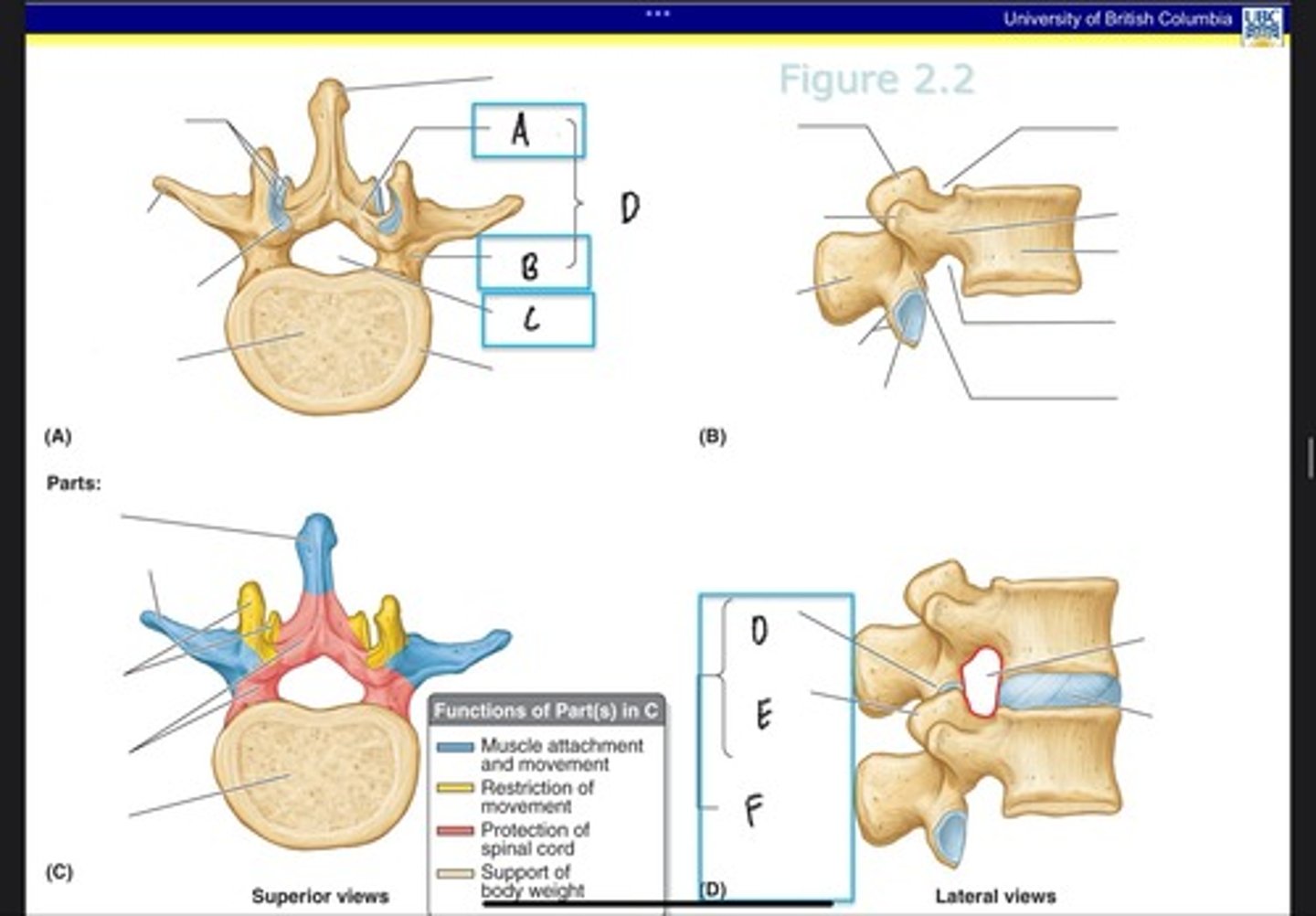
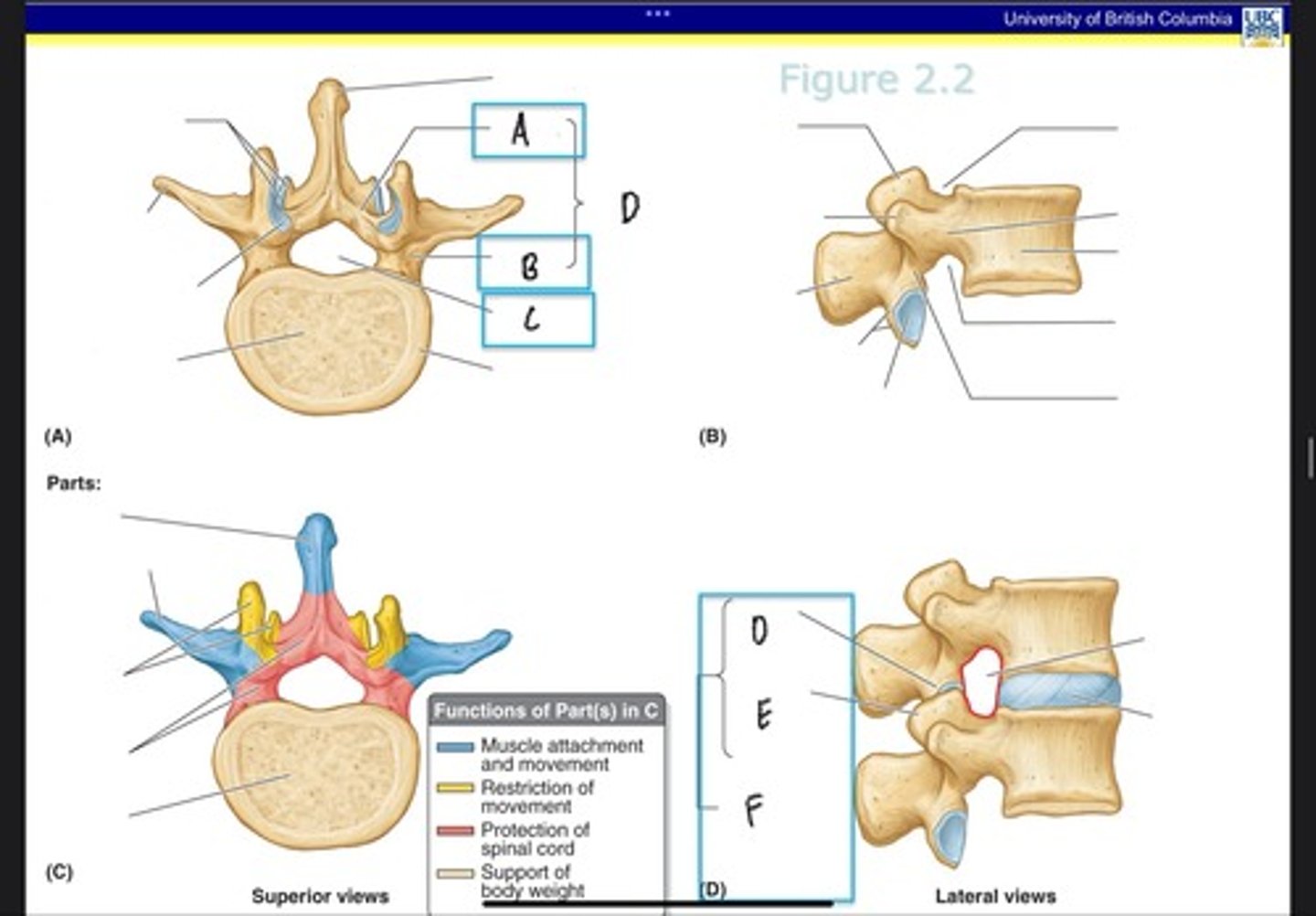
Intervertebral foramina
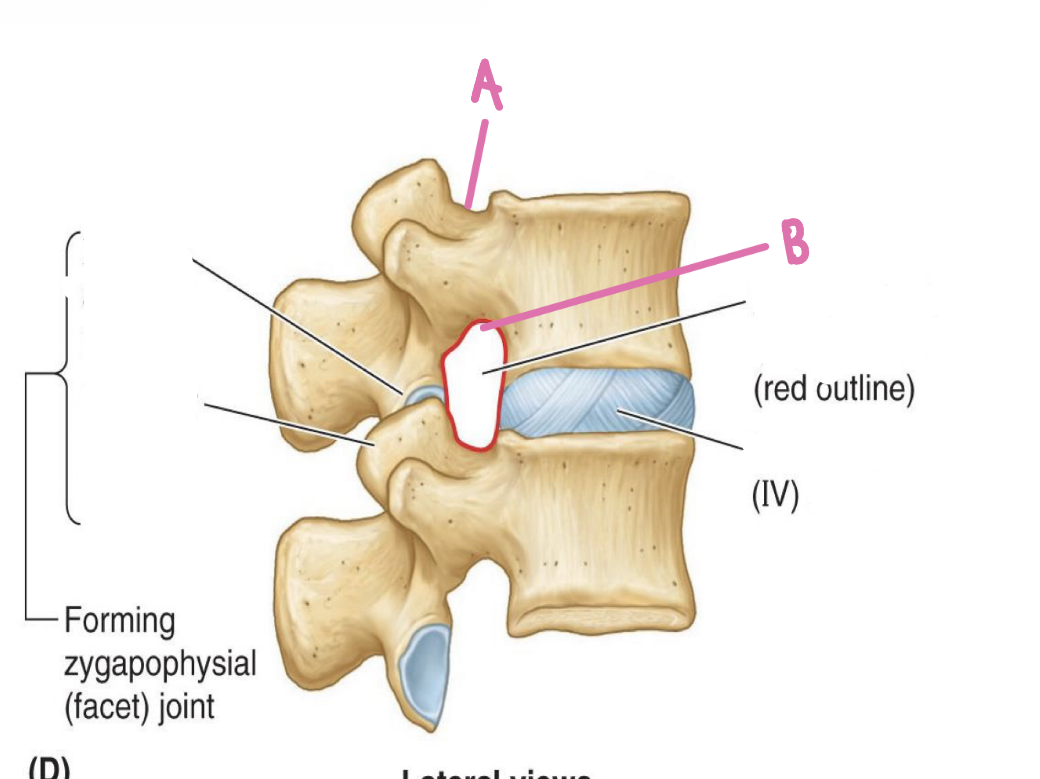
What is A?
Intervertebral discs
What is B?
Zygapophysial joints
What is C?
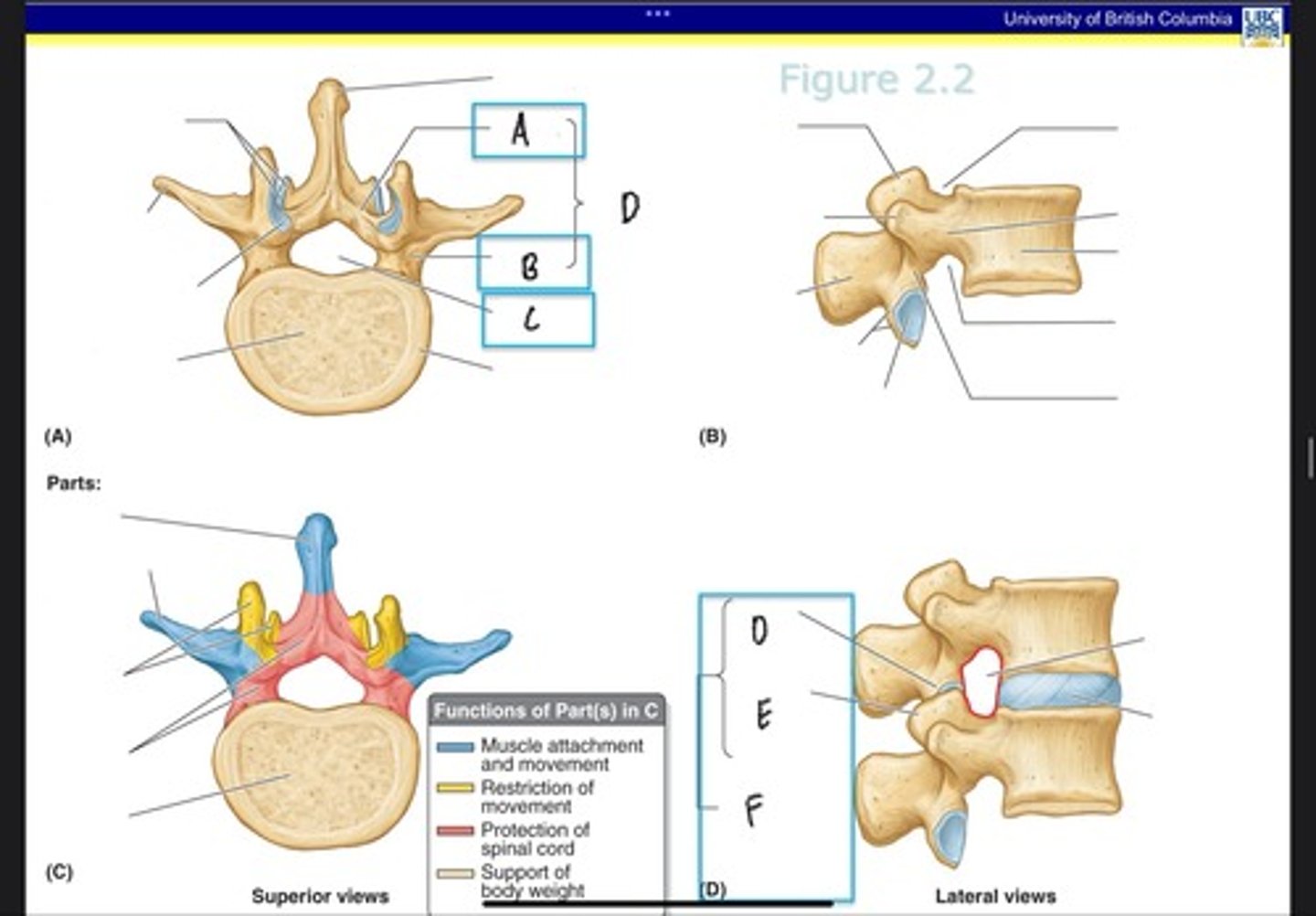
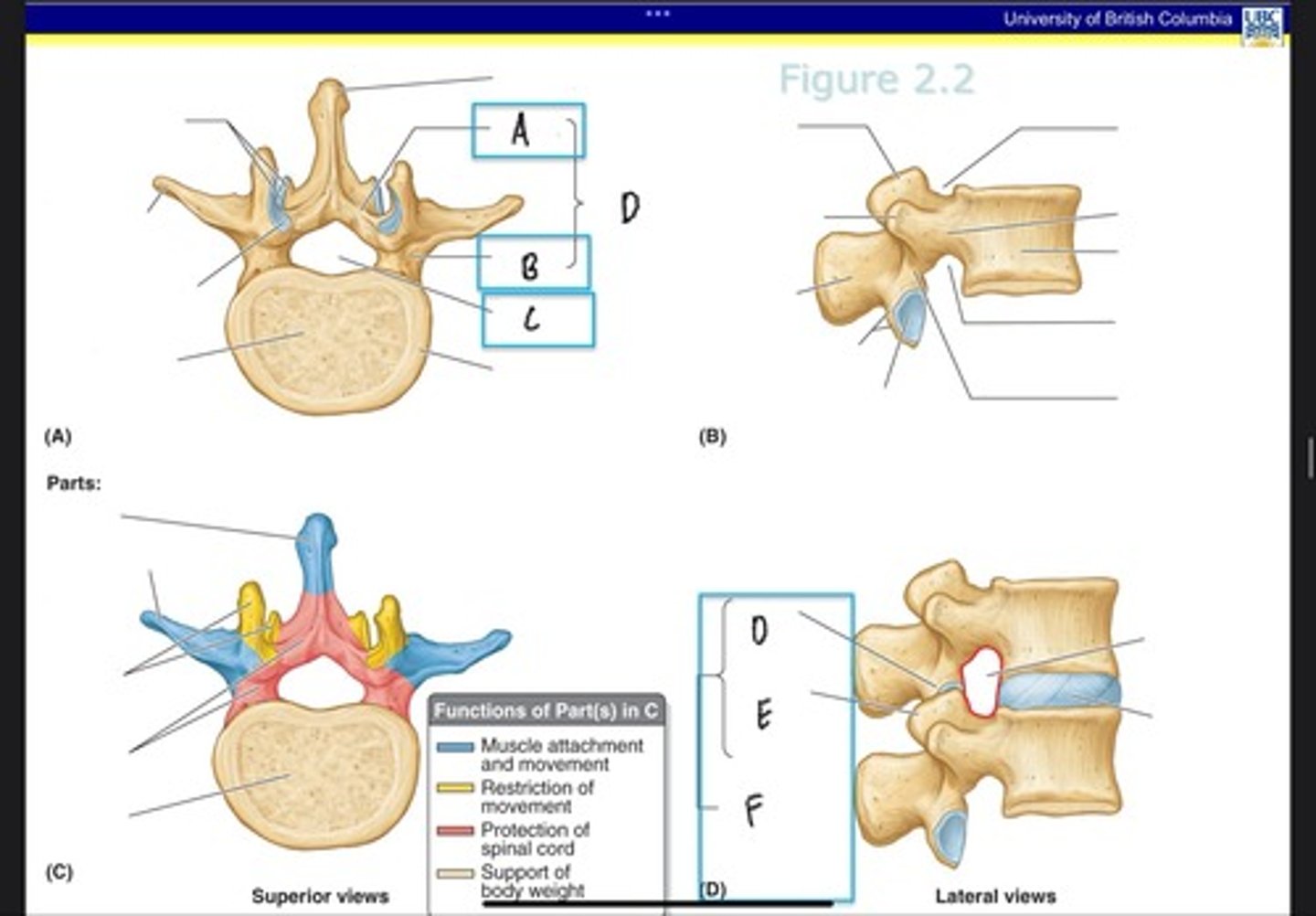
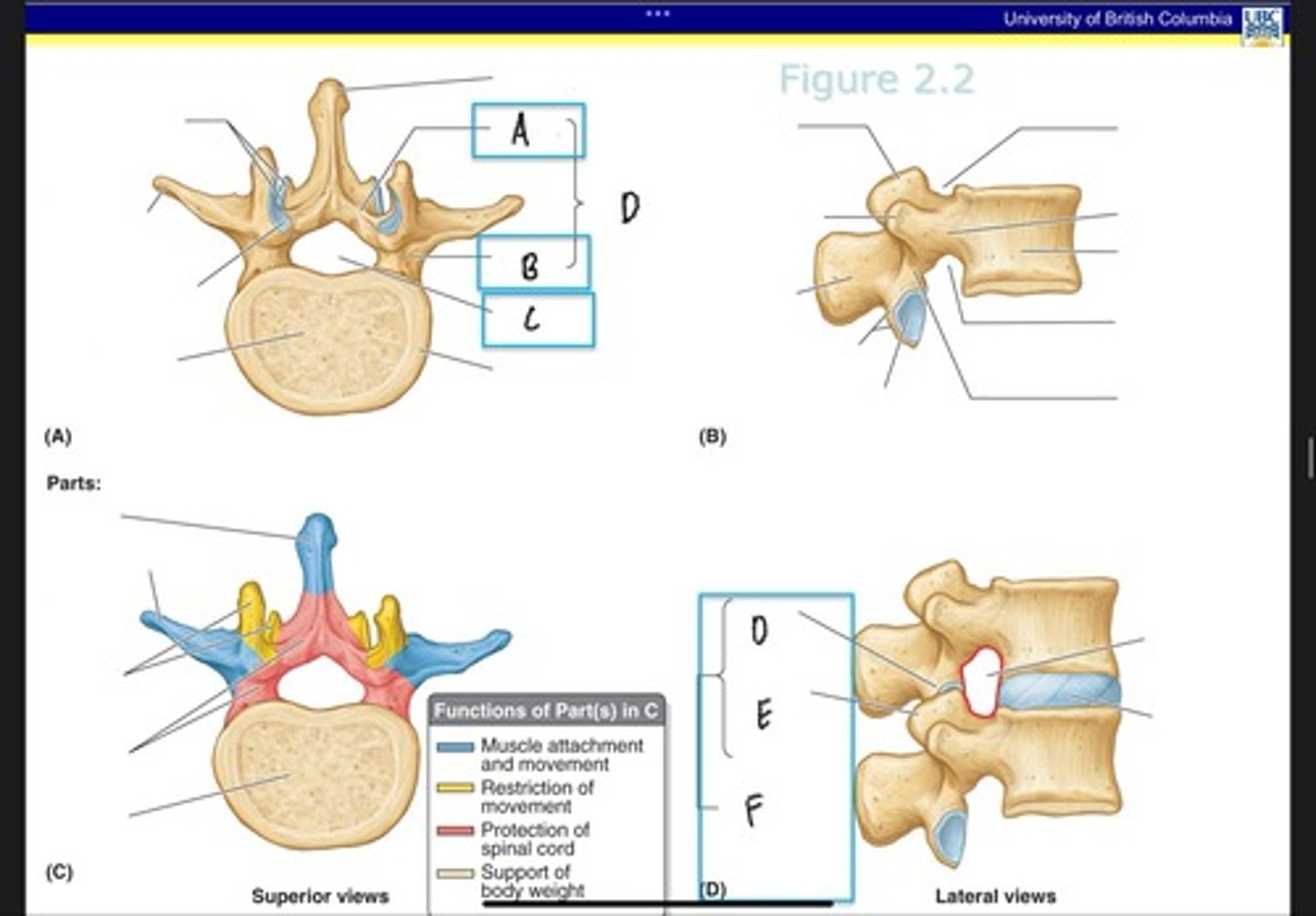
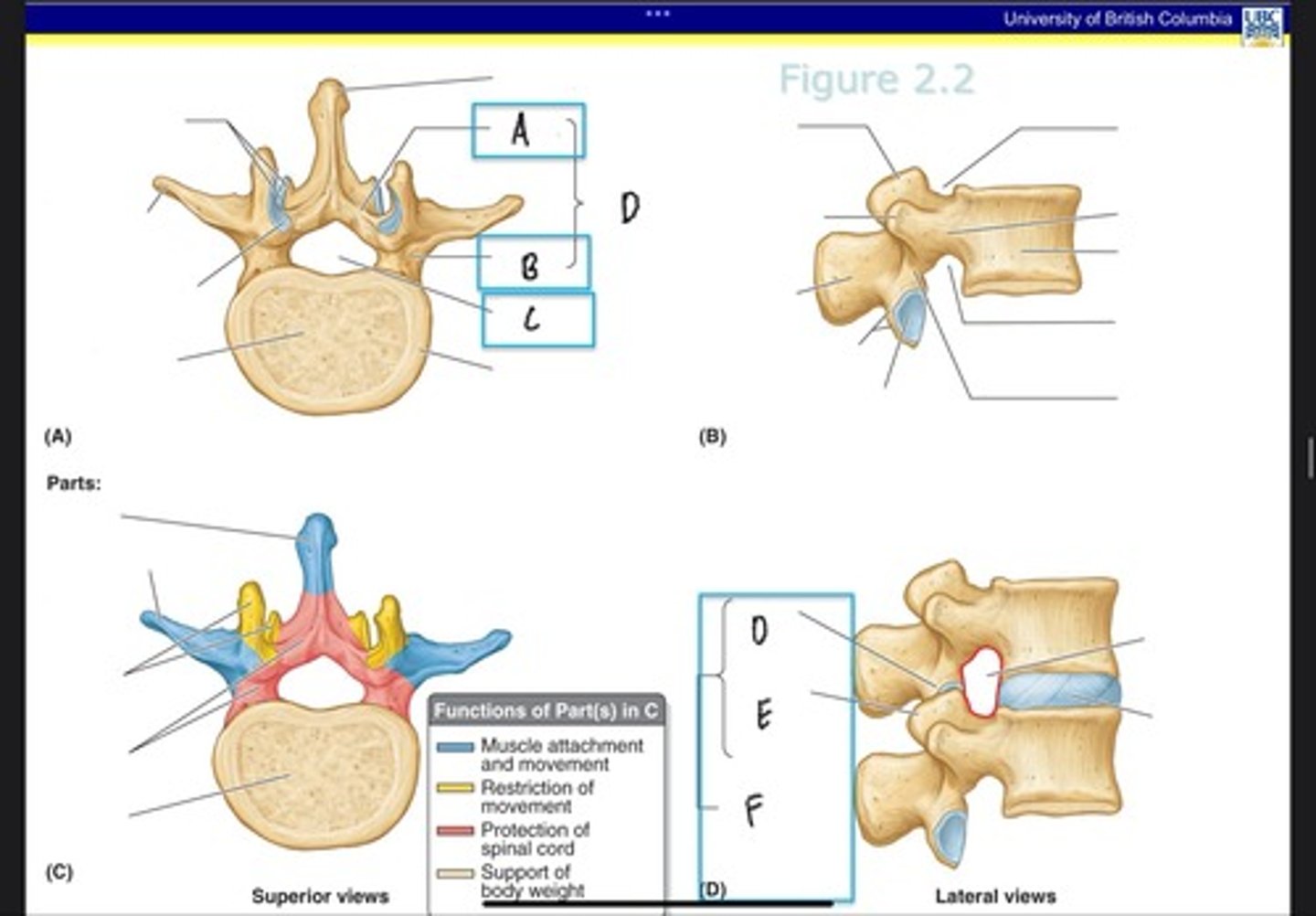
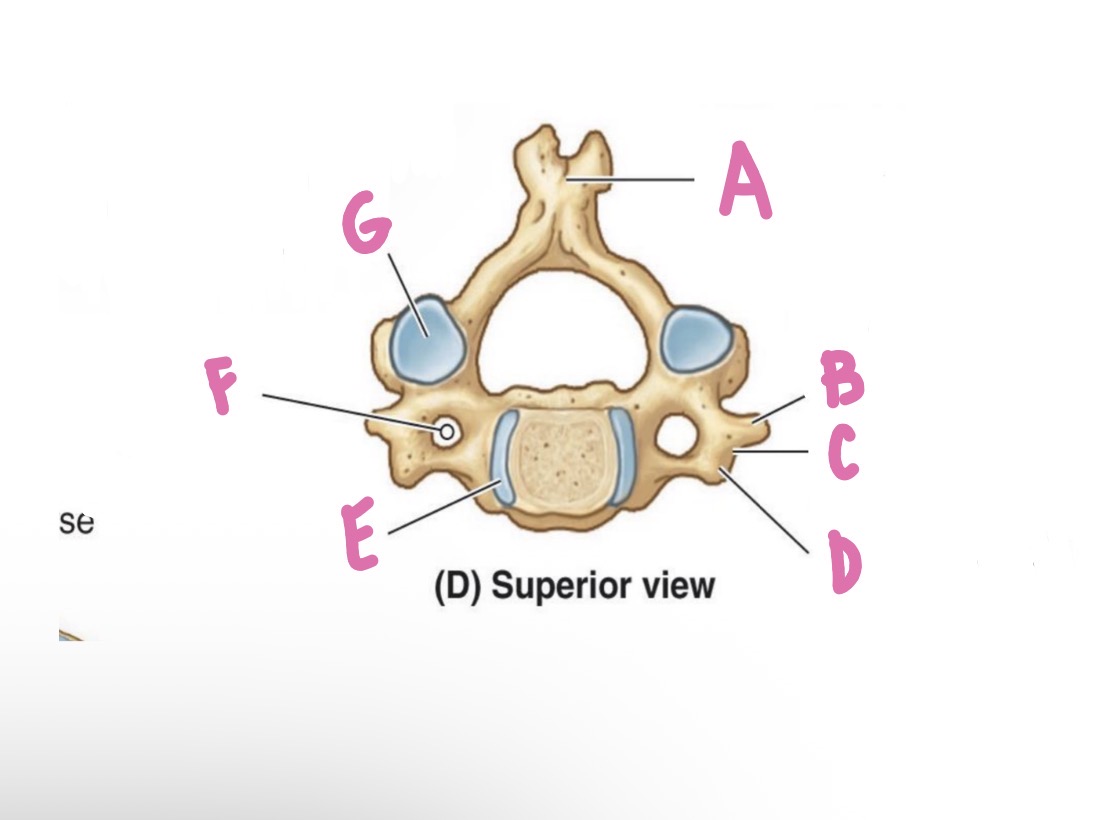
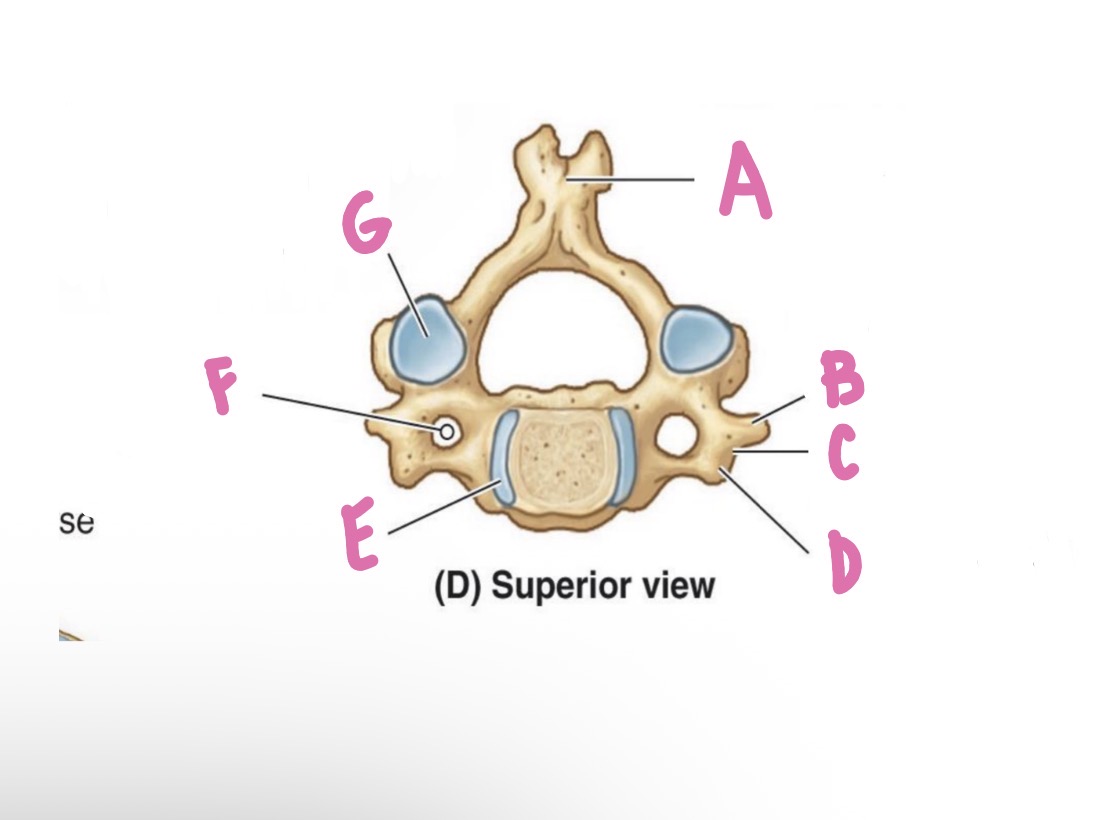
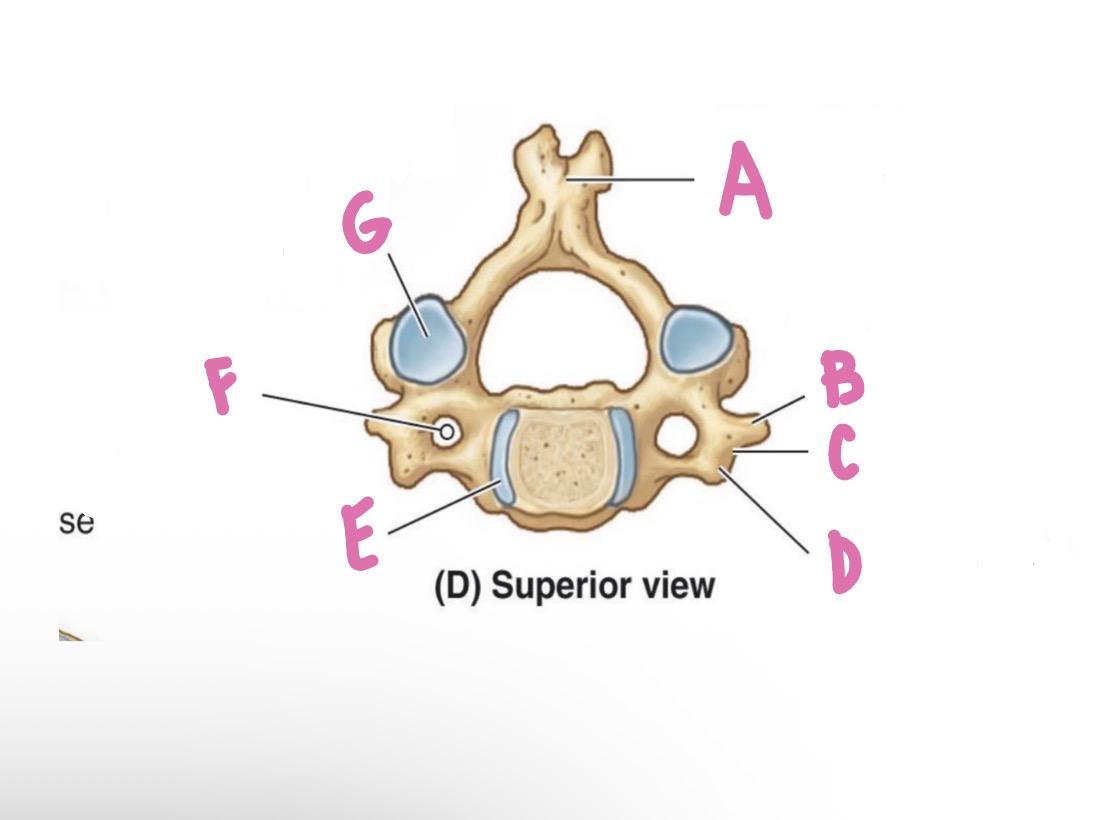
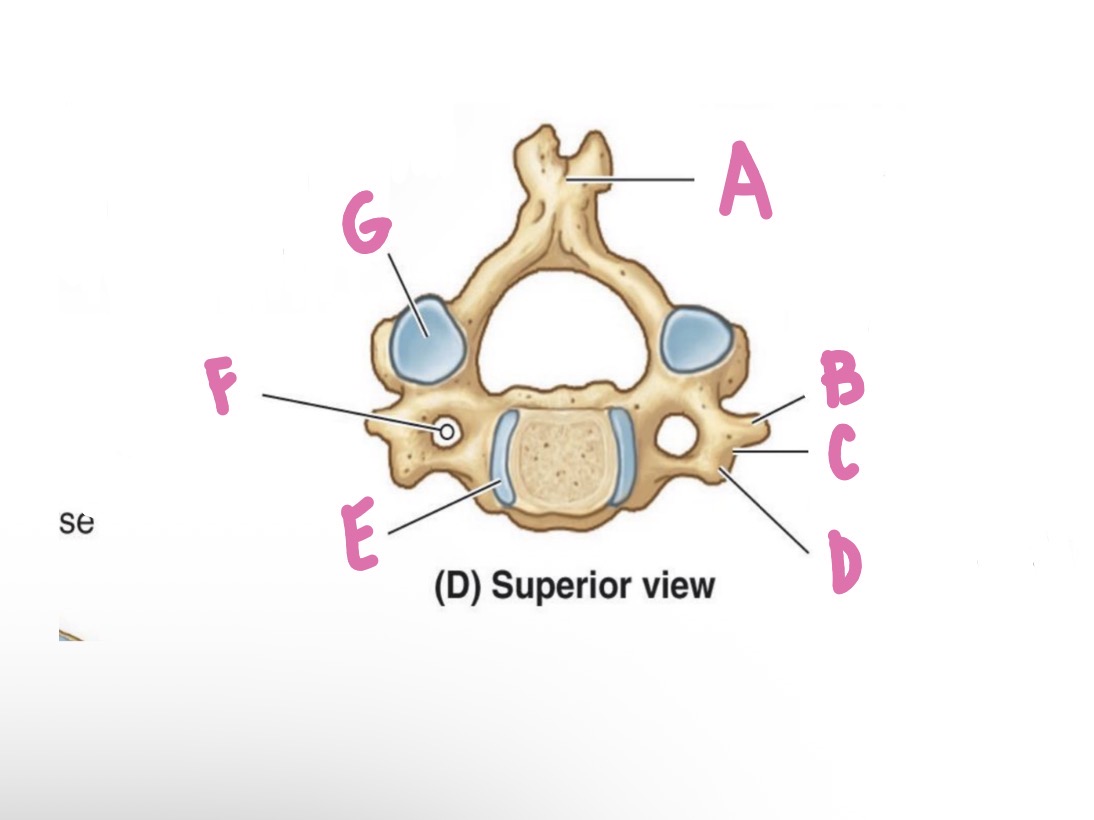
Lamina
What is A?
Pedicle
What is B?
Vertebral foramen
What is C?
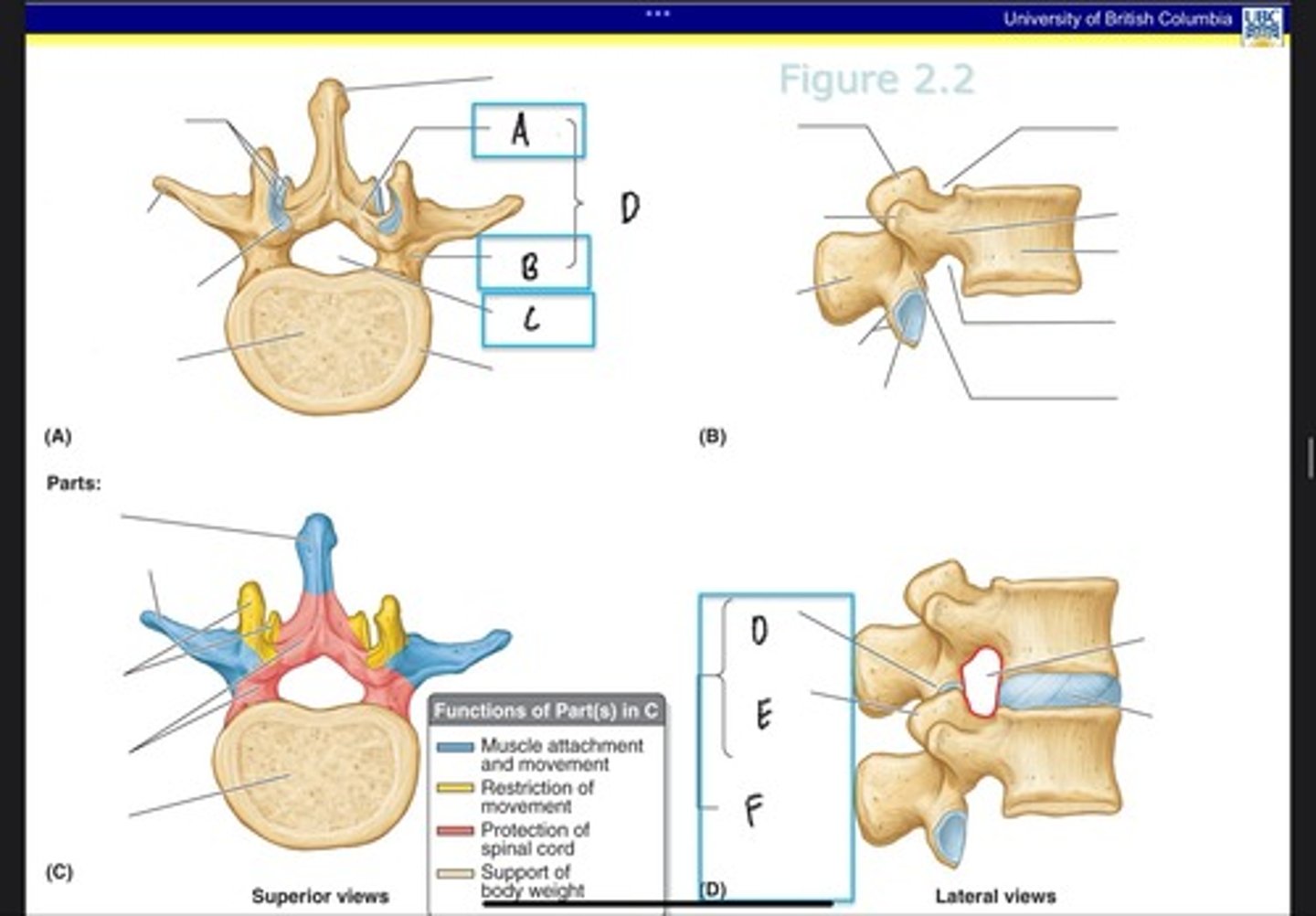
Vertebral arch
What is D? (Top)
Inferior articular process
What is D? (Bottom)
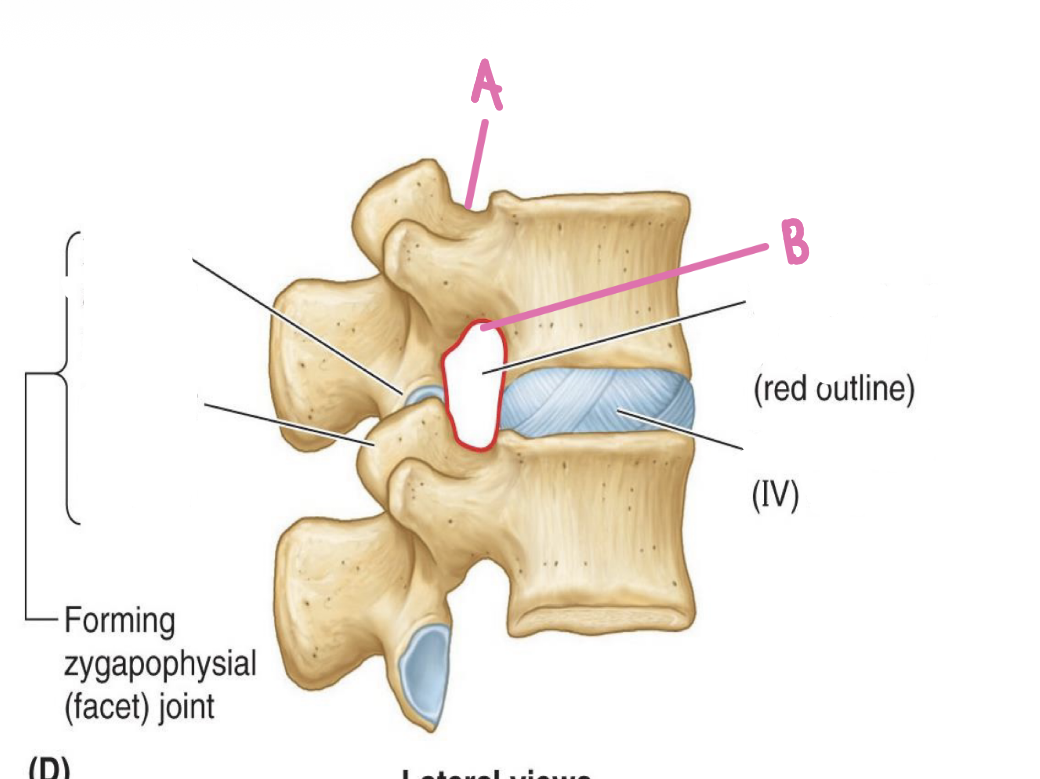
Superior articular process
What is E?
Forming zygapophysial (facet) joint
What is F?
Ligamentum flavum
What is A?
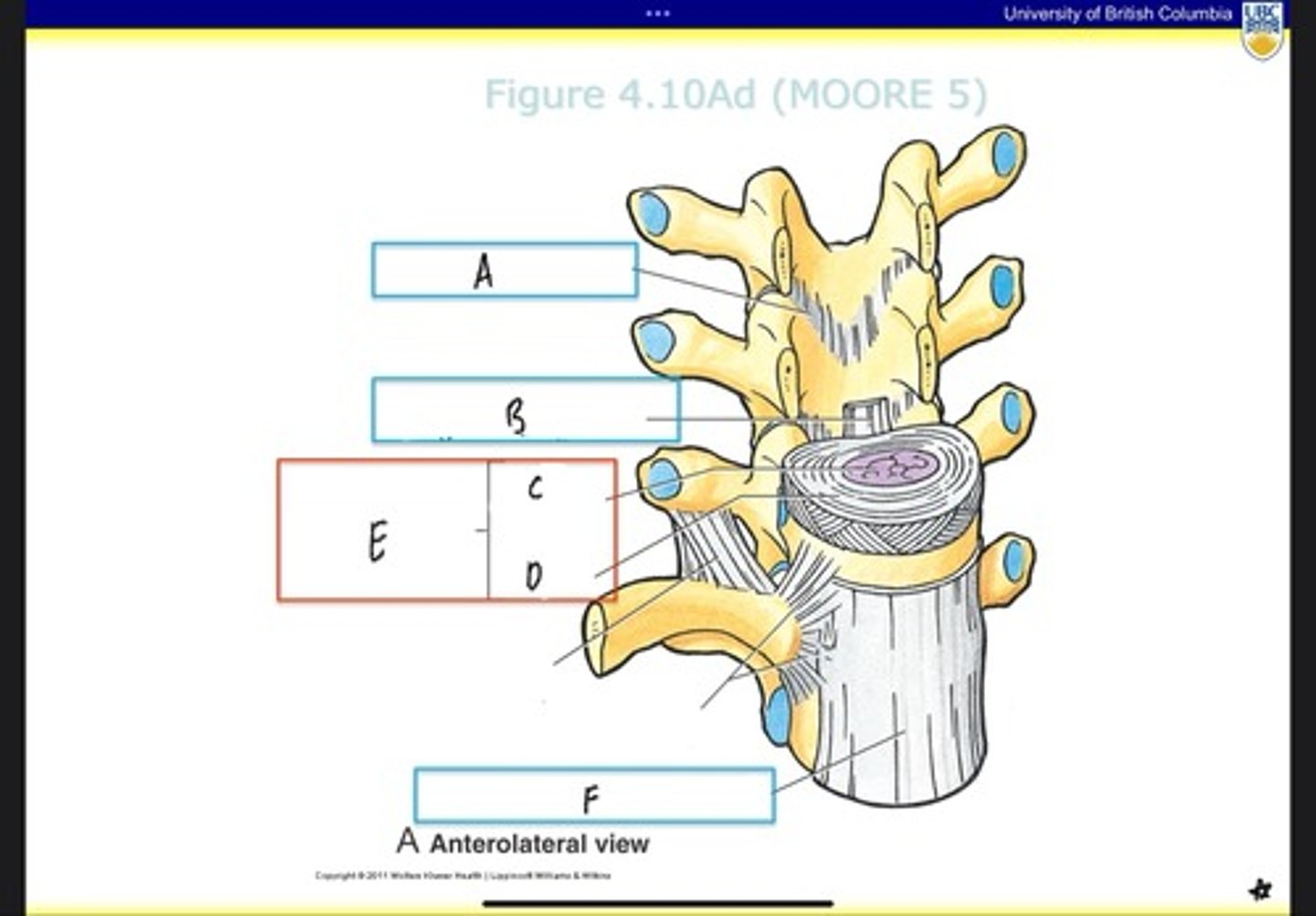
Posterior longitudinal ligament
What is B?
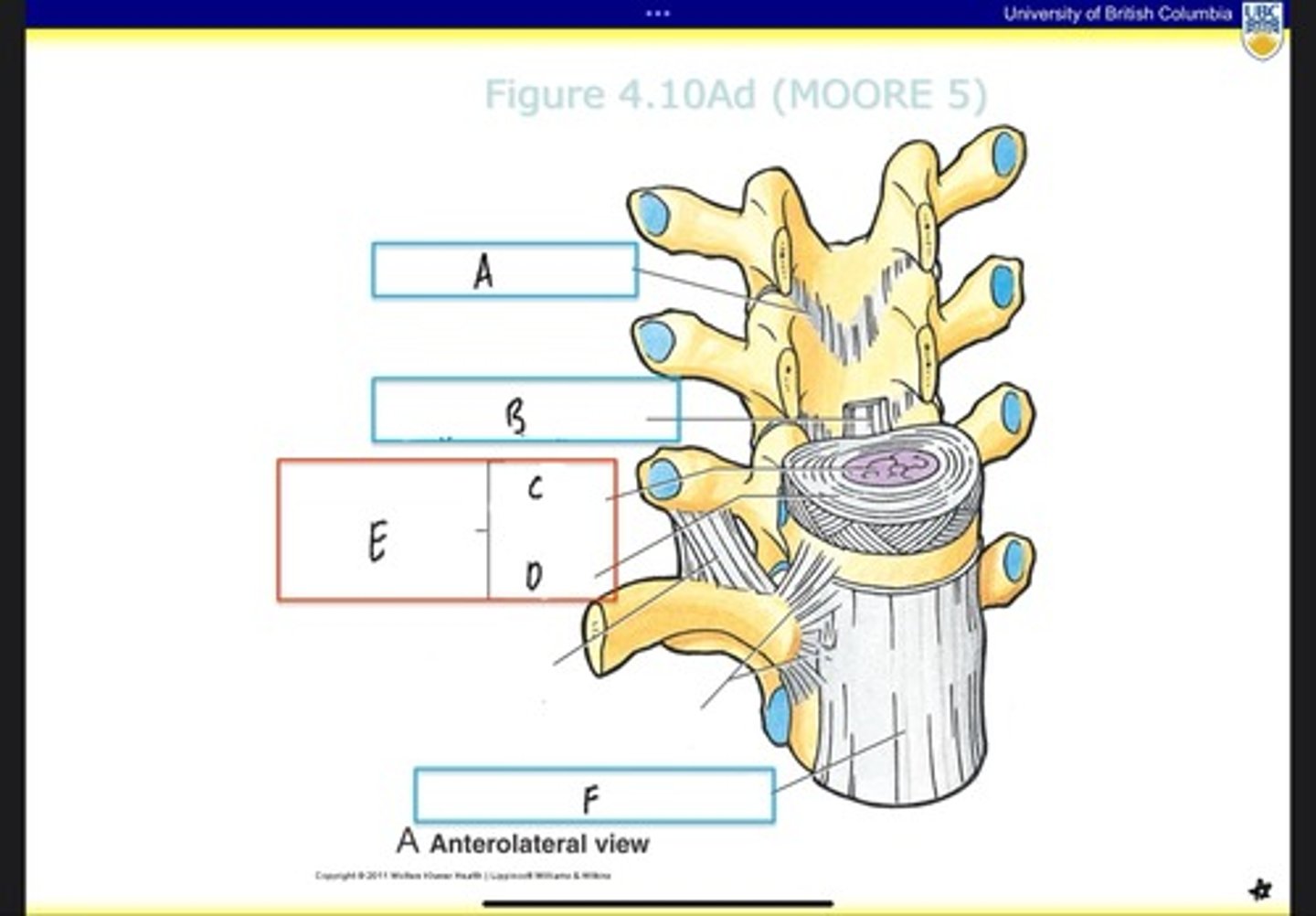
Nucleus pulposus
What is C?
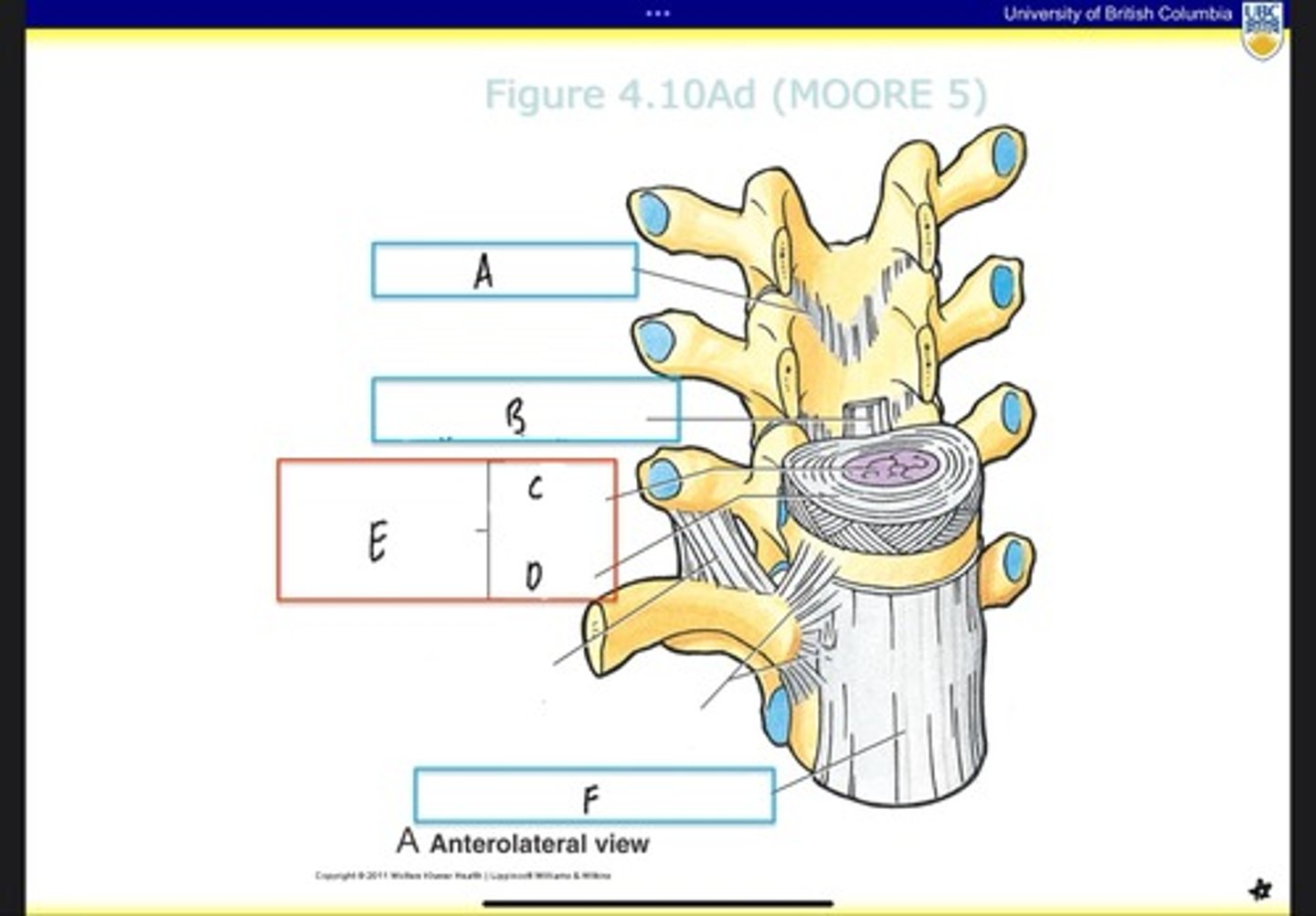
Anulus fibrosus
What is D?
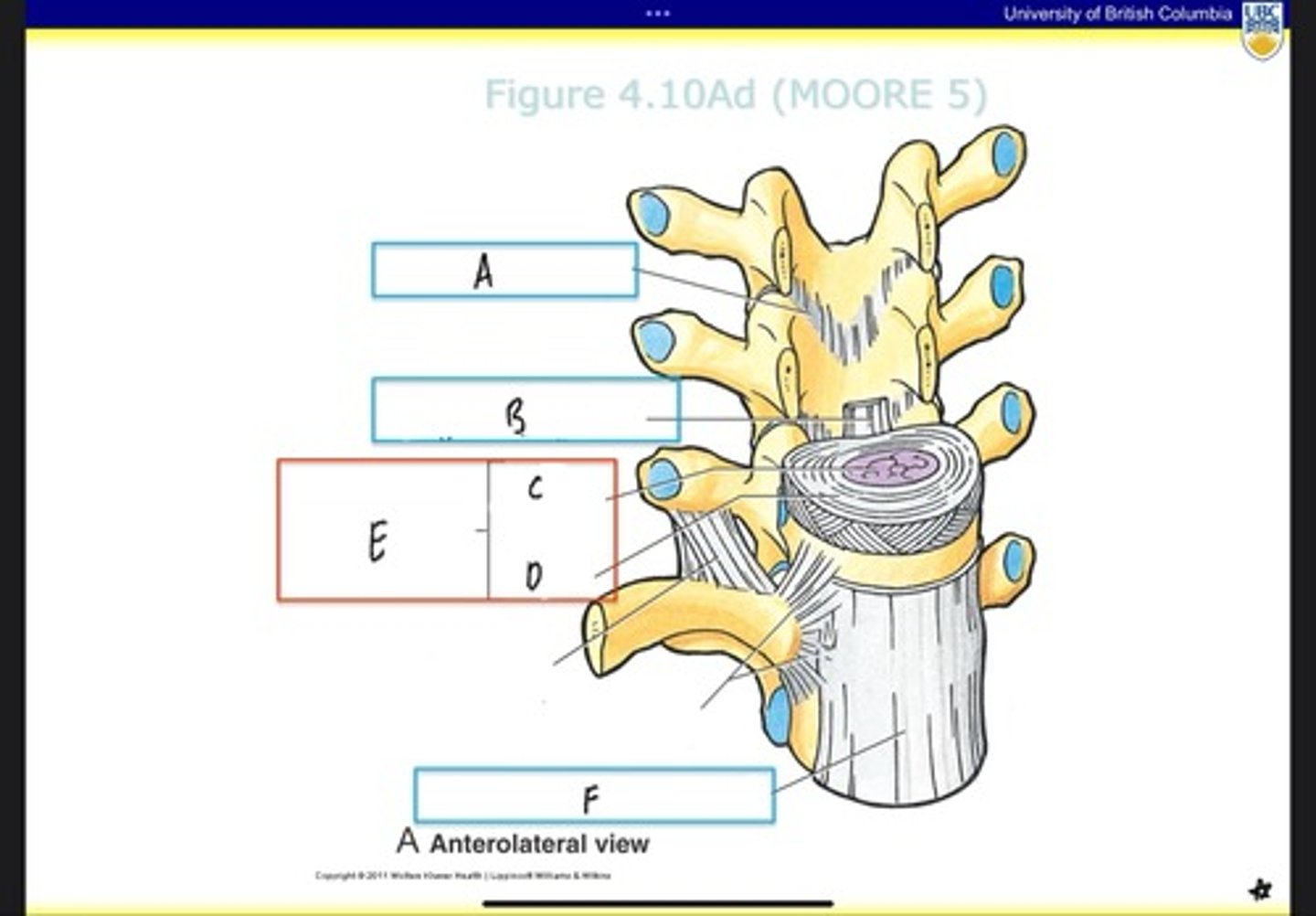
Intervertebral disc
What is E?
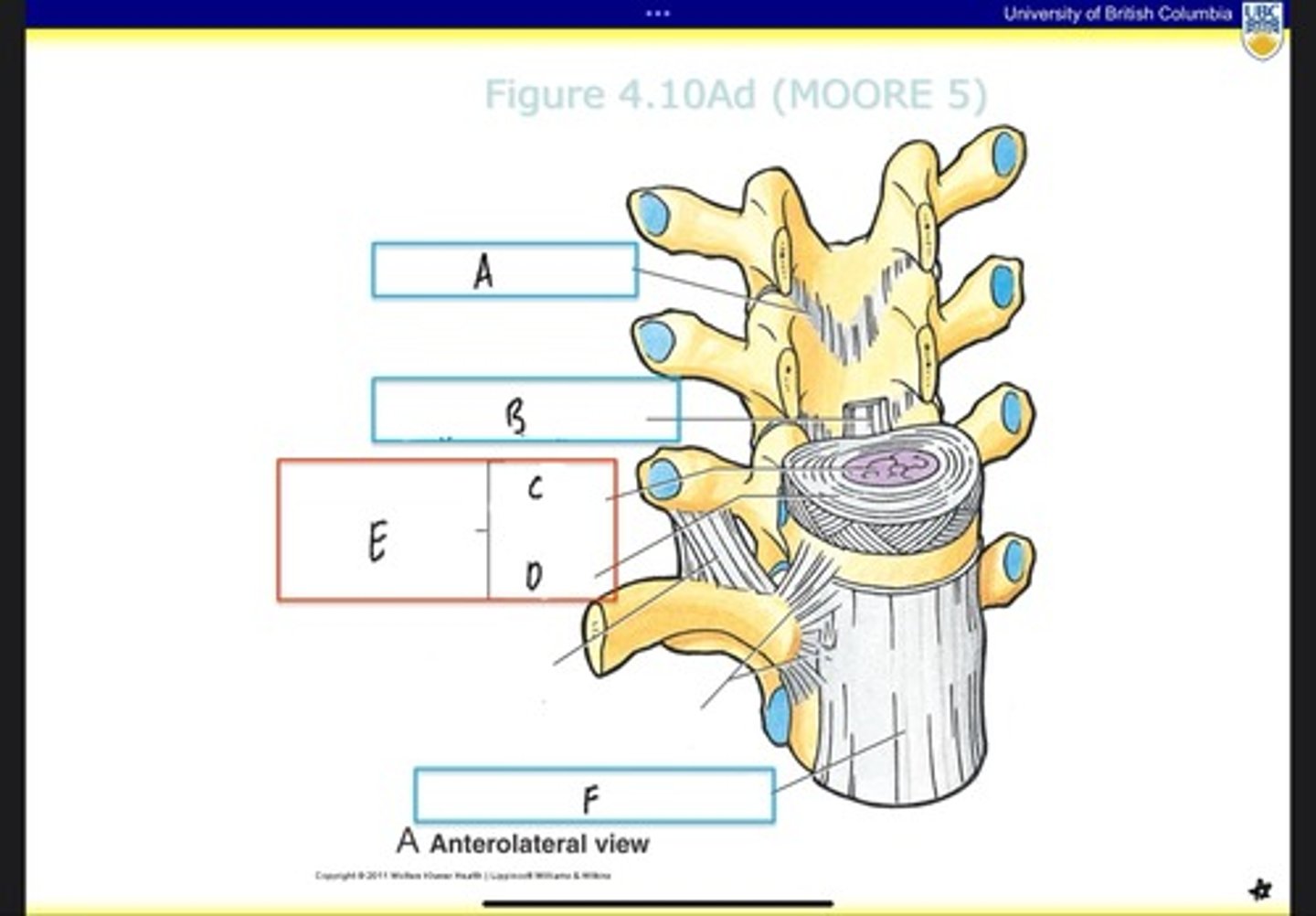
Anterior longitudinal ligament
What is F?
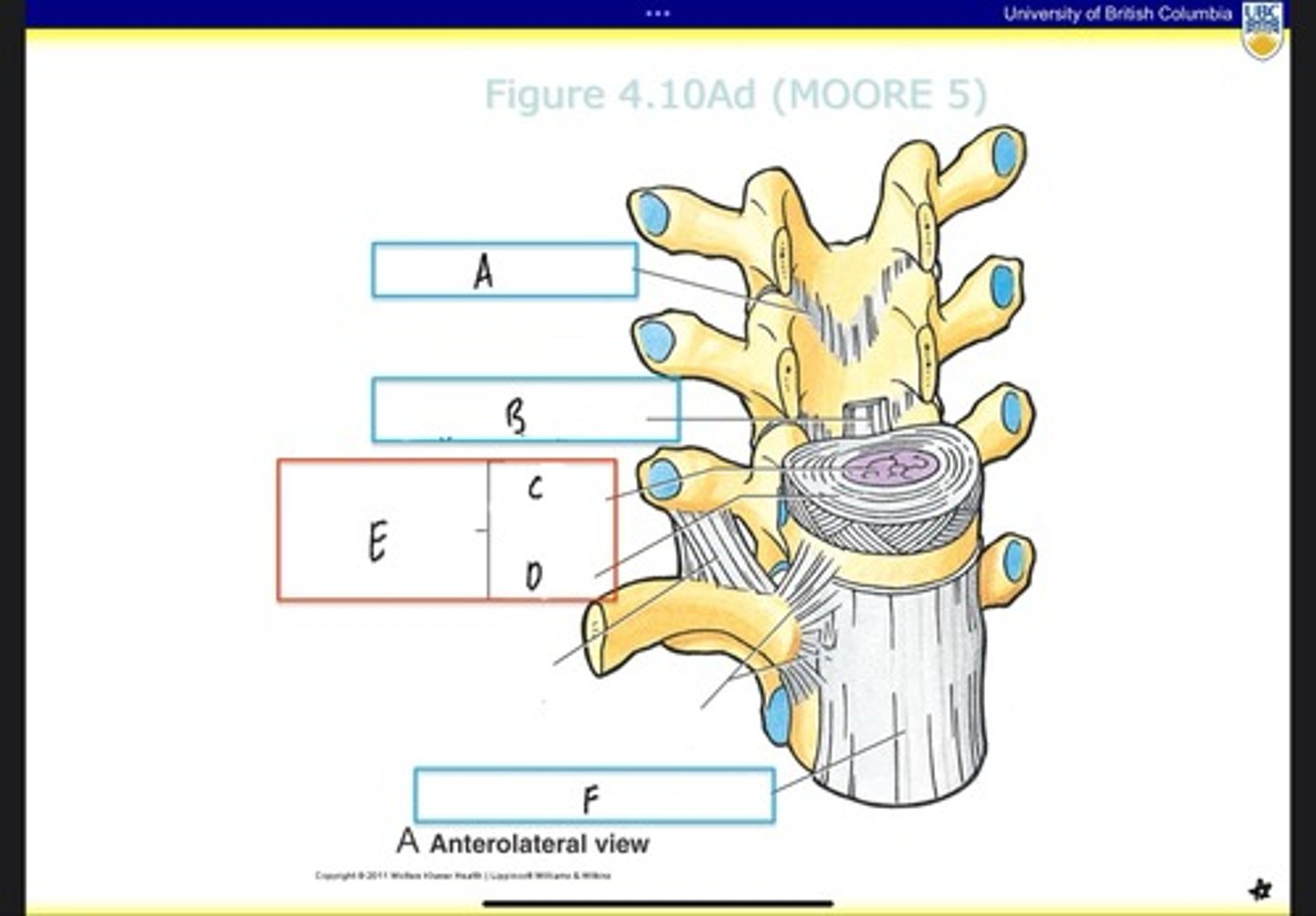
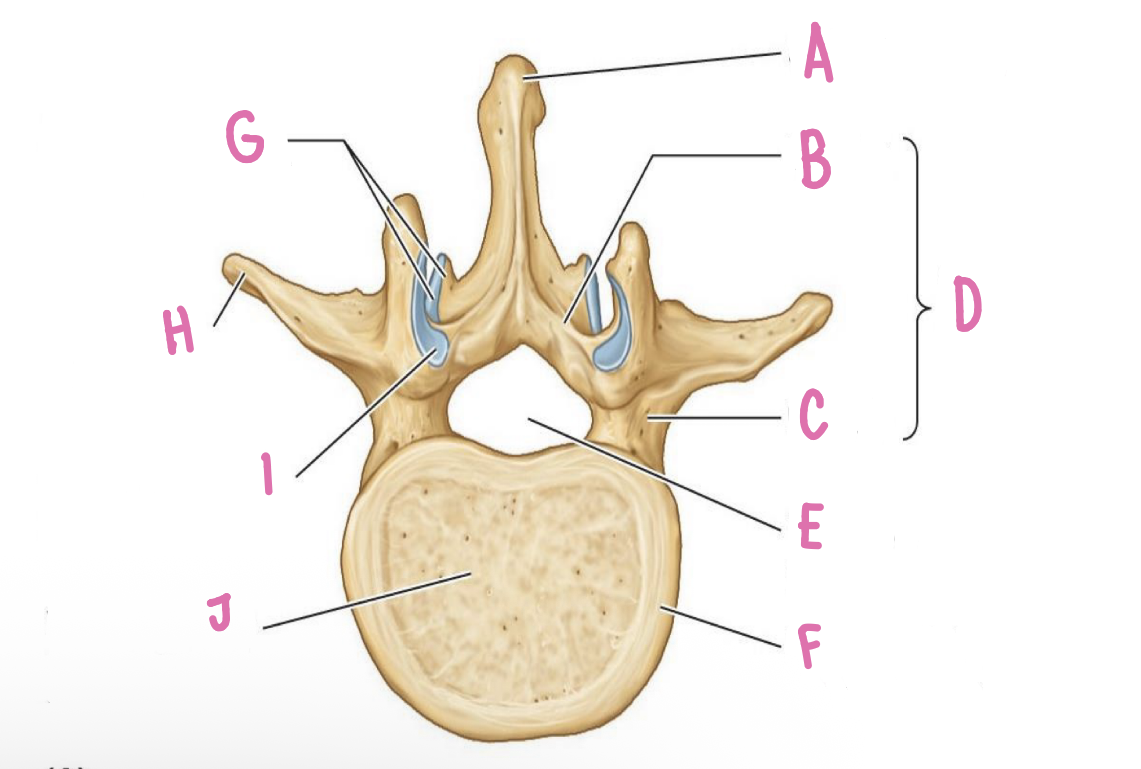
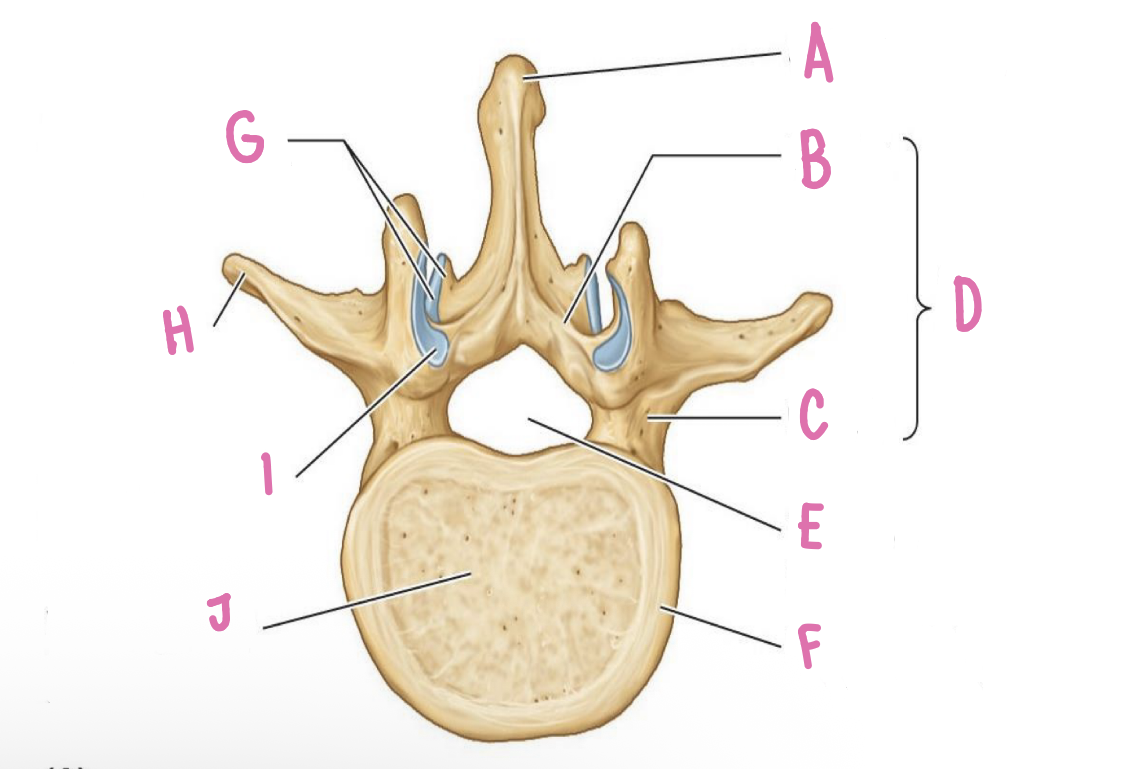
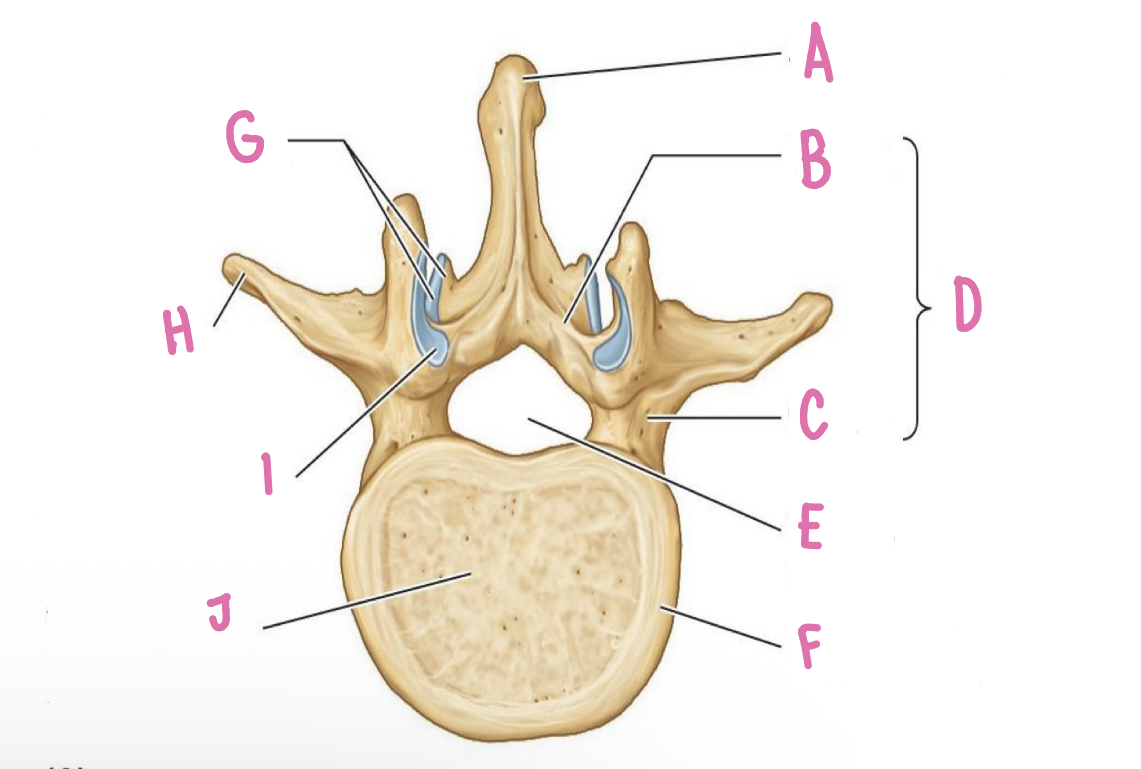
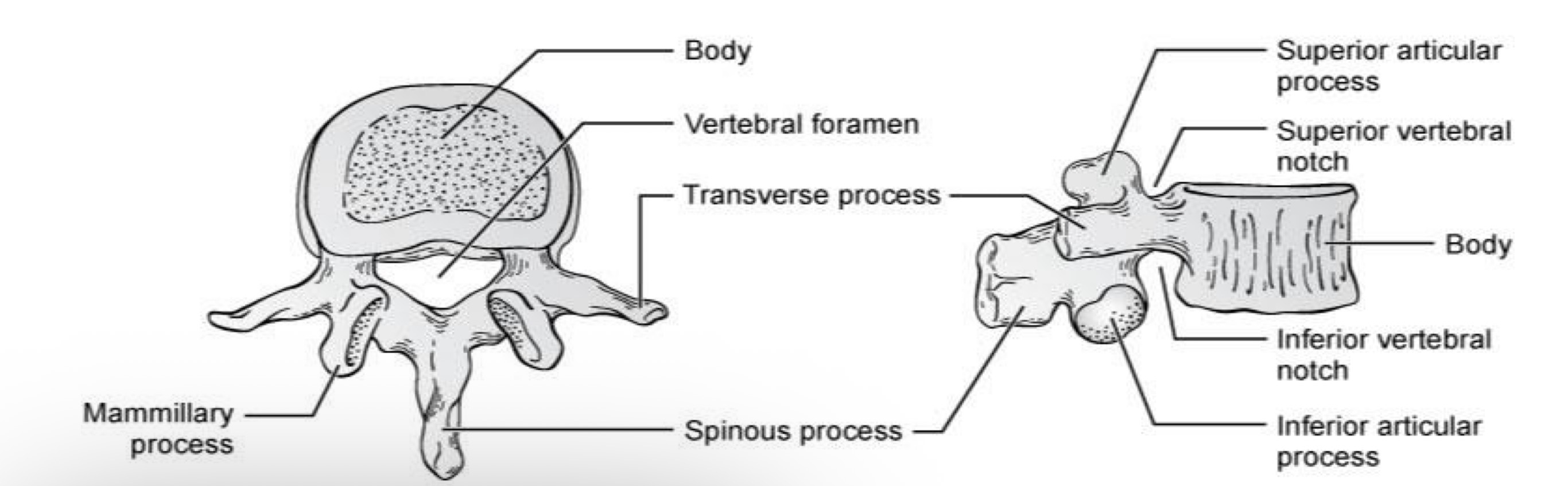
transverse proccess
what is H?
vertebral body
what is J?
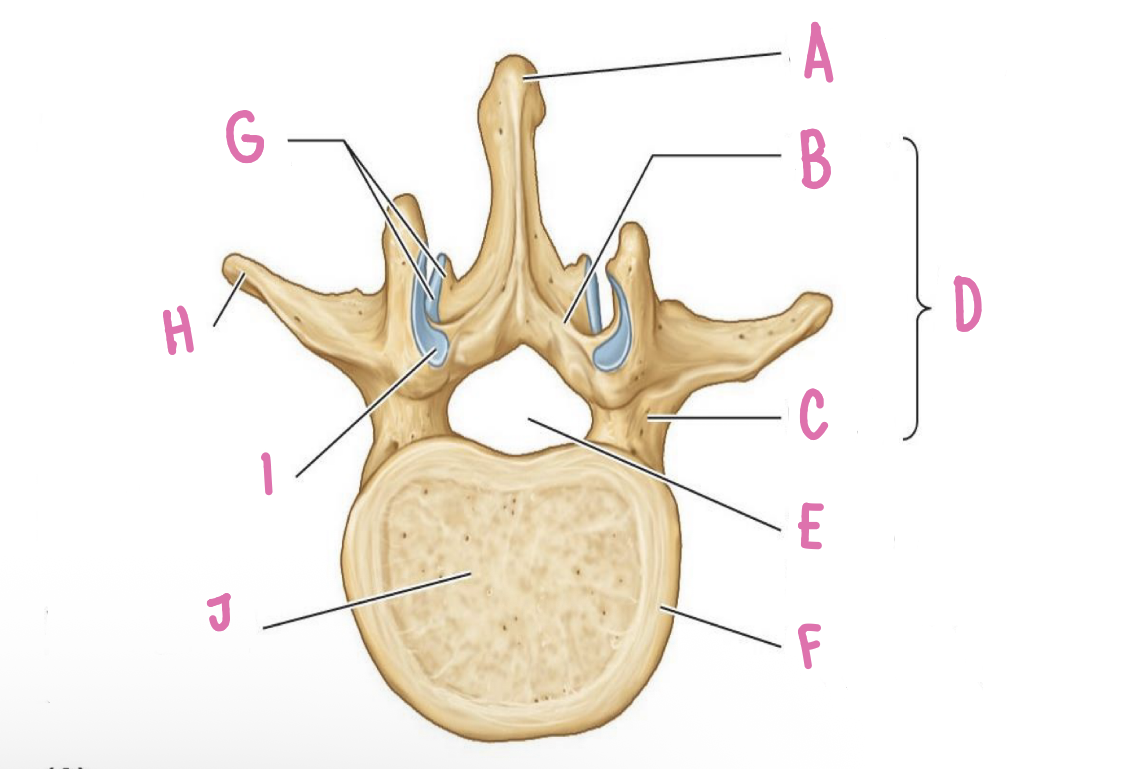
epiphysial rim
what is F?
inferior articular process/facet
what is G?
superior vertebral notch
what is A?
inferior vertebral notch
what is B?
Groove for spinal nerve
What is C?
vertebral foramina\
what is F?
spinal process
what is A?
uncus of body
What is E?
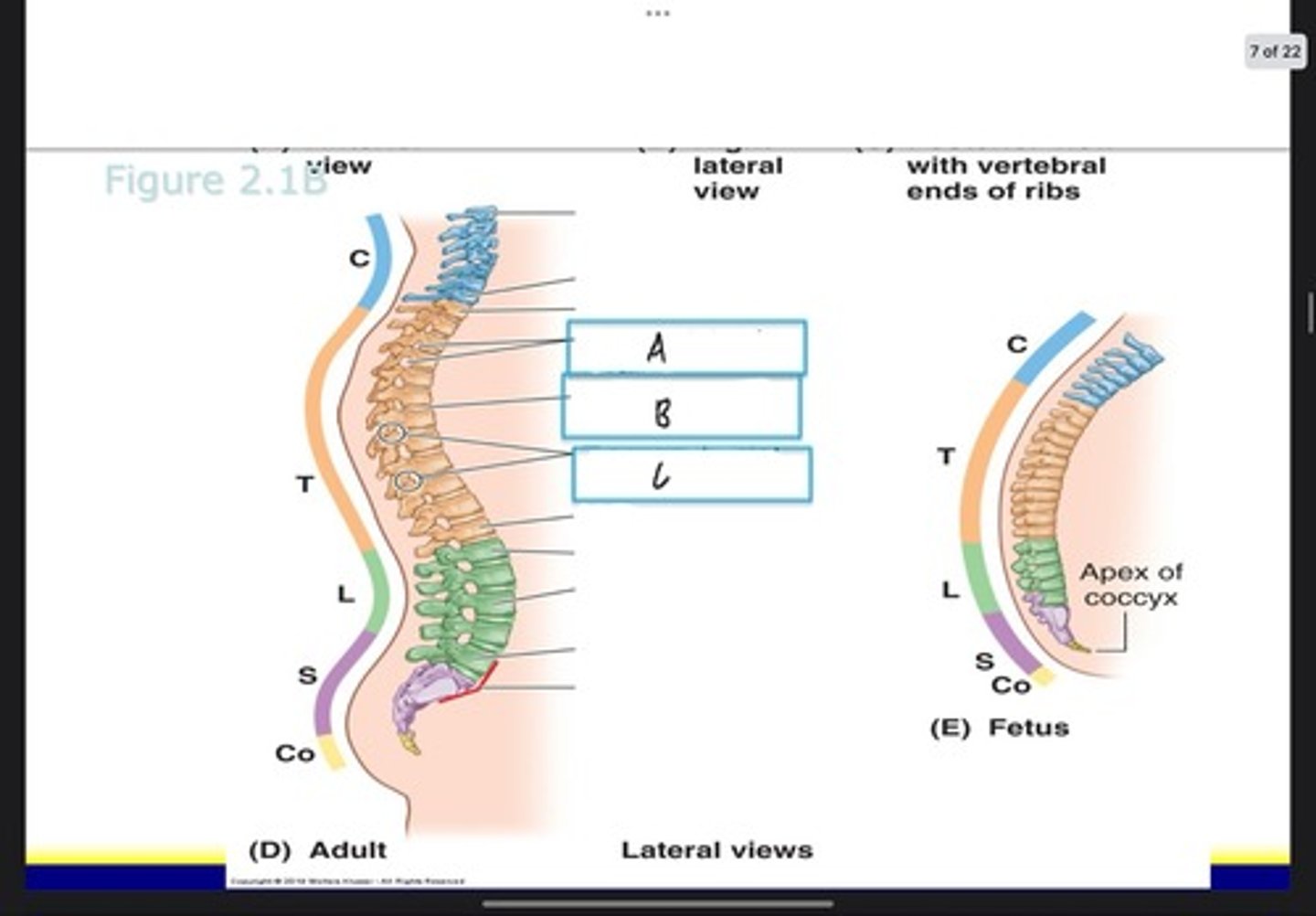
Cervical
What type of vertebrae is this?
thoracic
What type of vertebrae is this?
lumbar
What type of vertebrae is this?
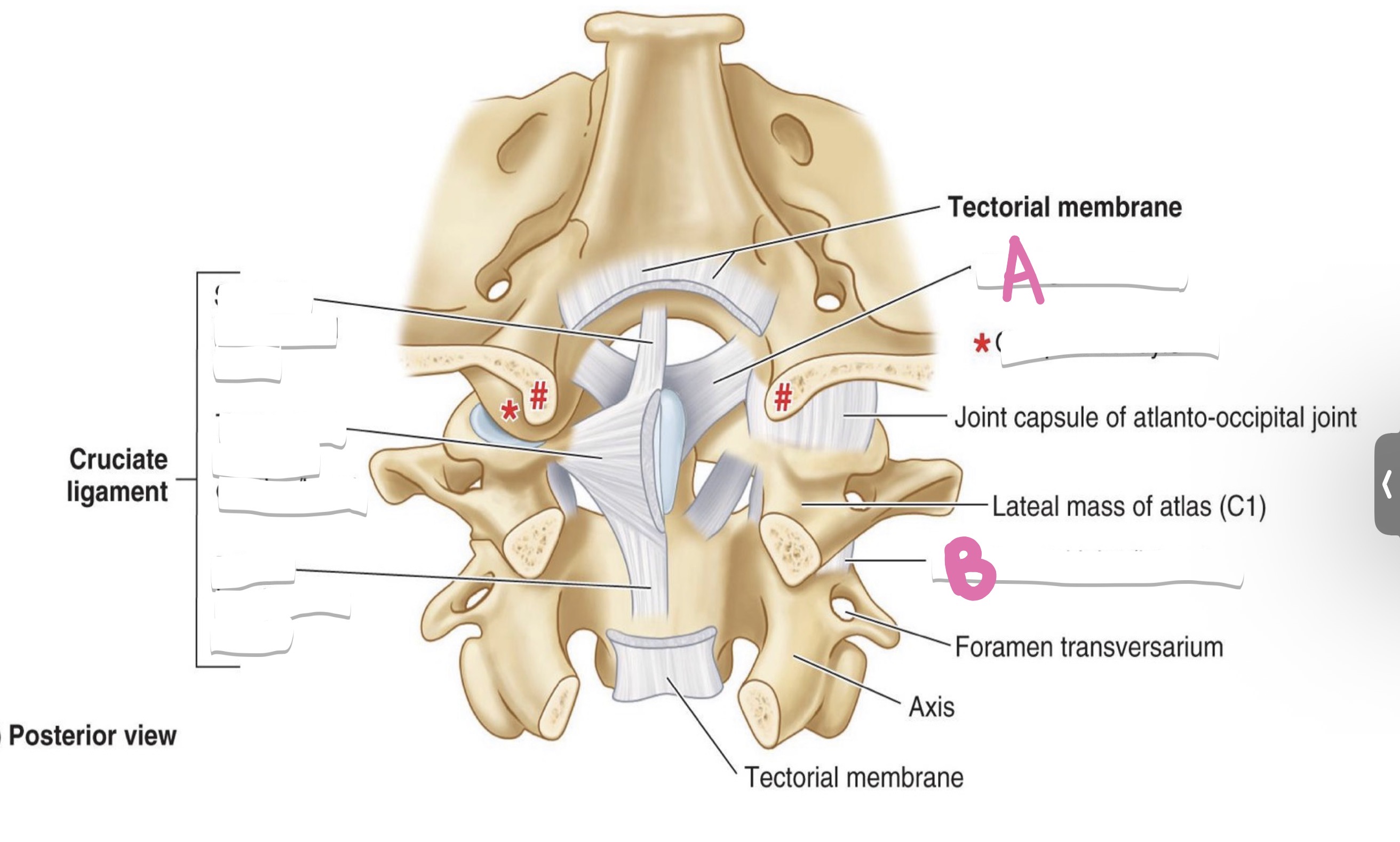
median atlanto-axial joint
what is A?
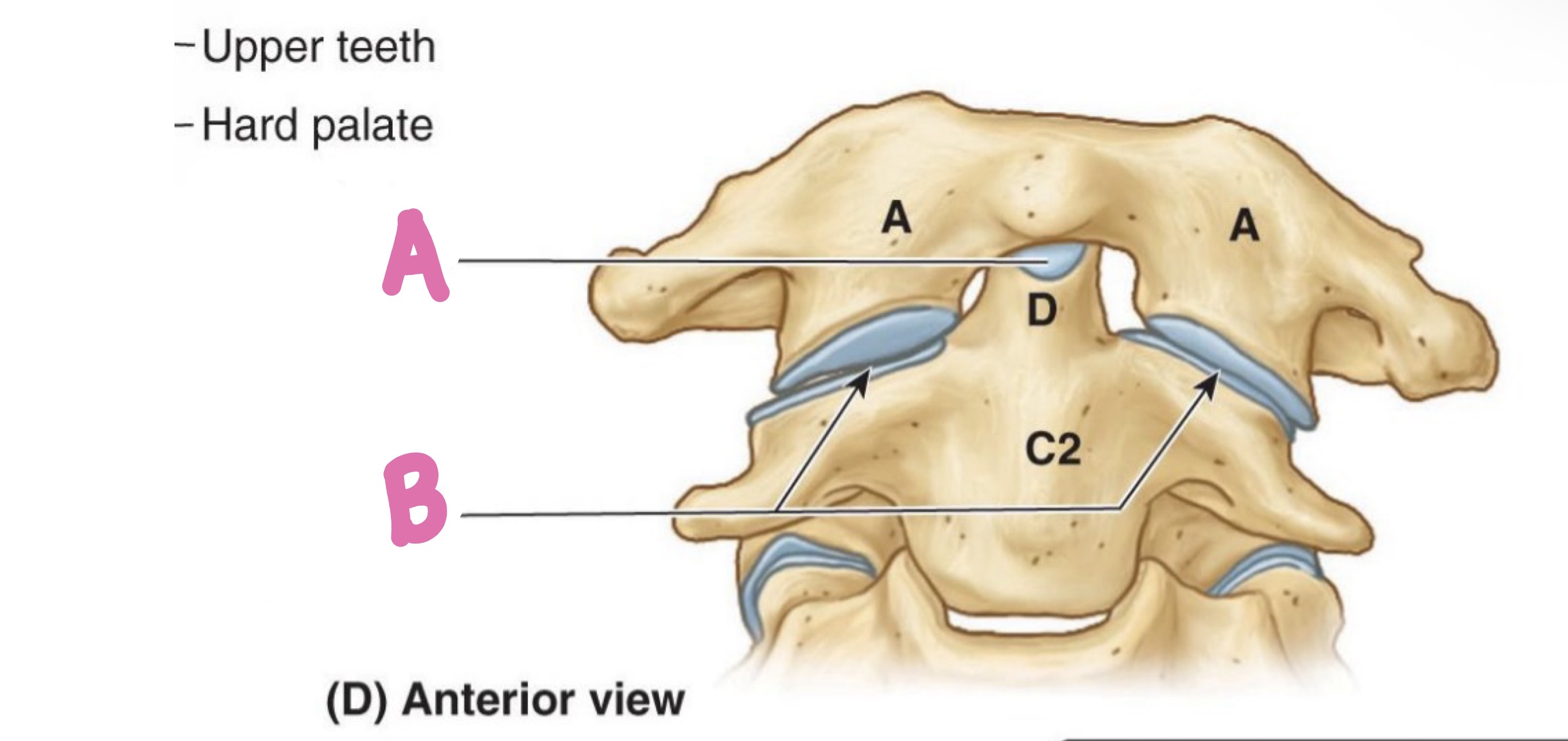
lateral atlanto-axial joint
what is b?
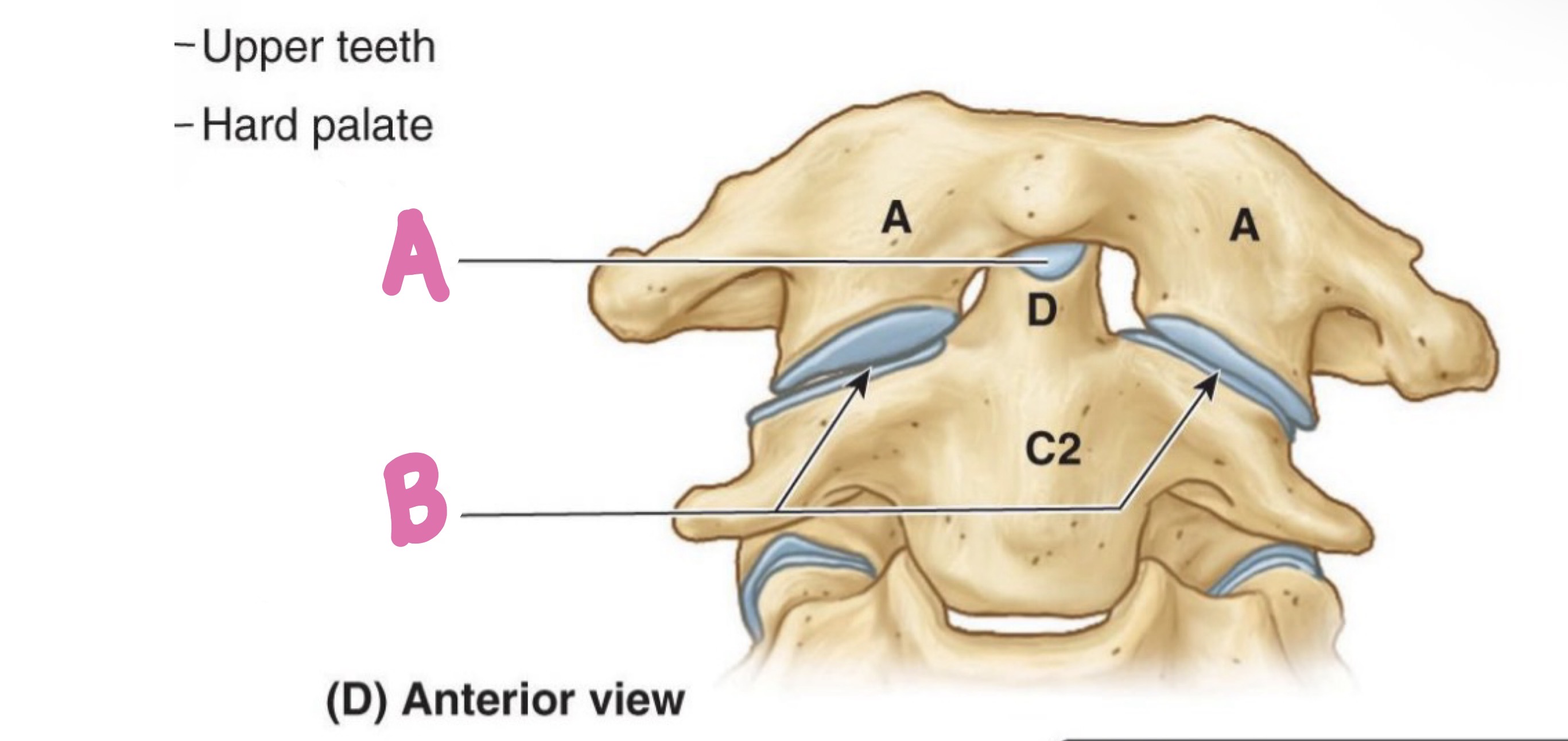
Atlanto-occipital joint
What sits on A and B?
Transverse ligament of atlas
What is C?
nuchal ligament
what is A?
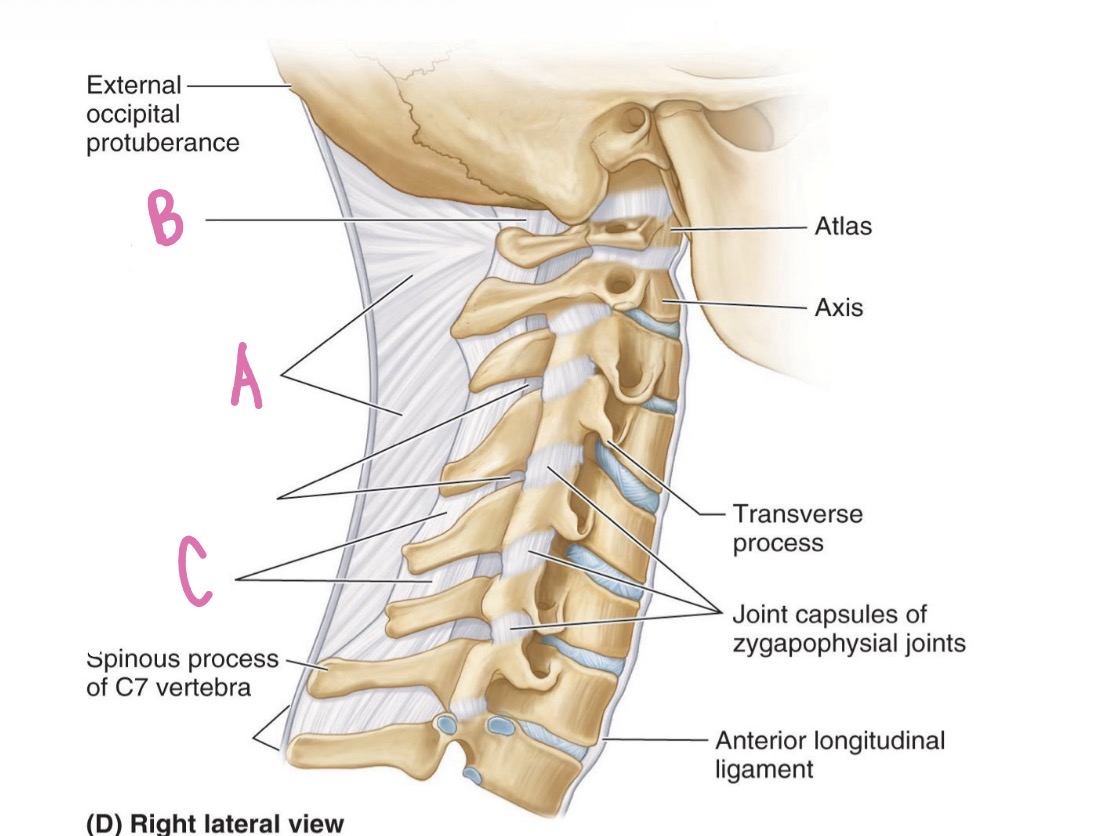
posterior atlanto-occipital membrane
what is B?
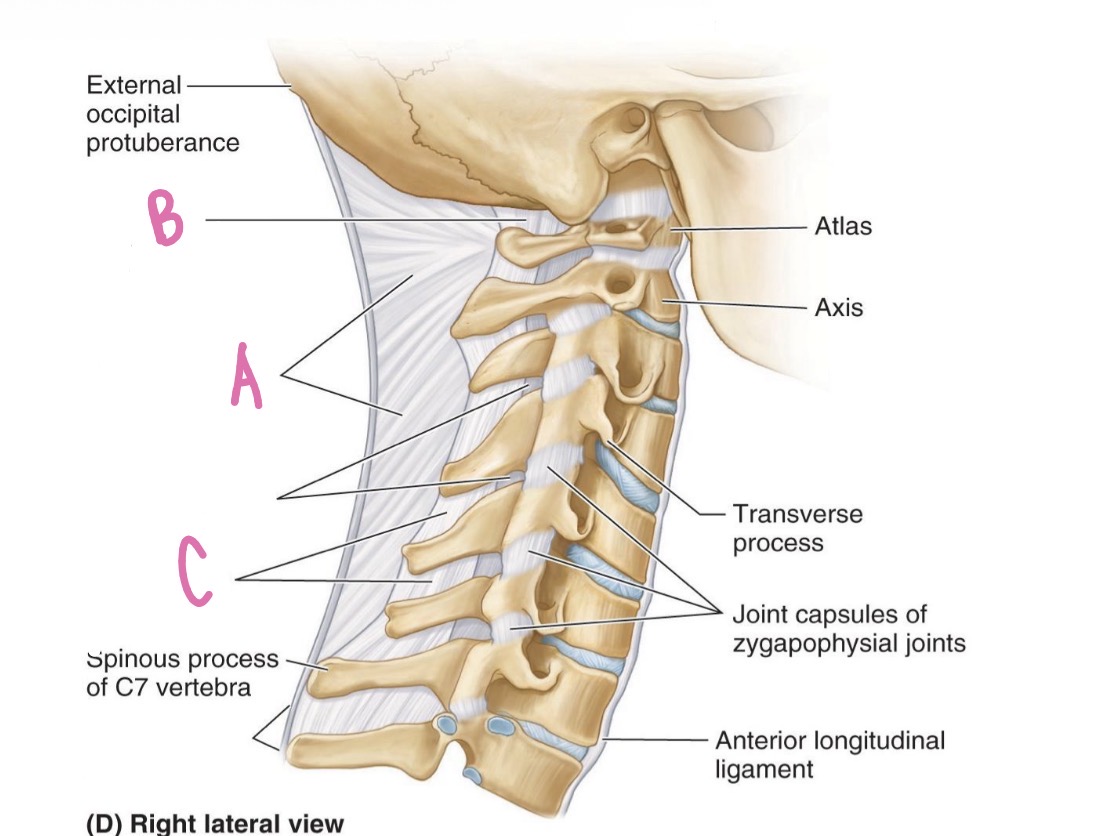
interspinous ligaments
What is C?
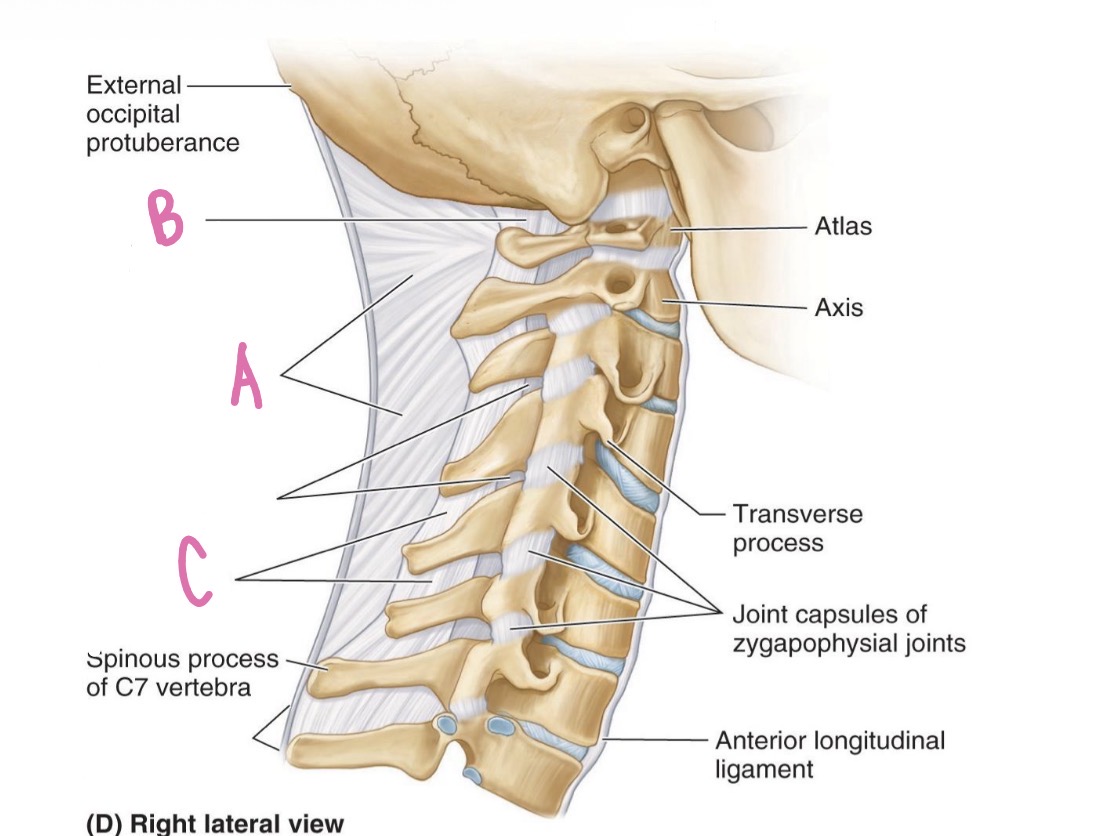
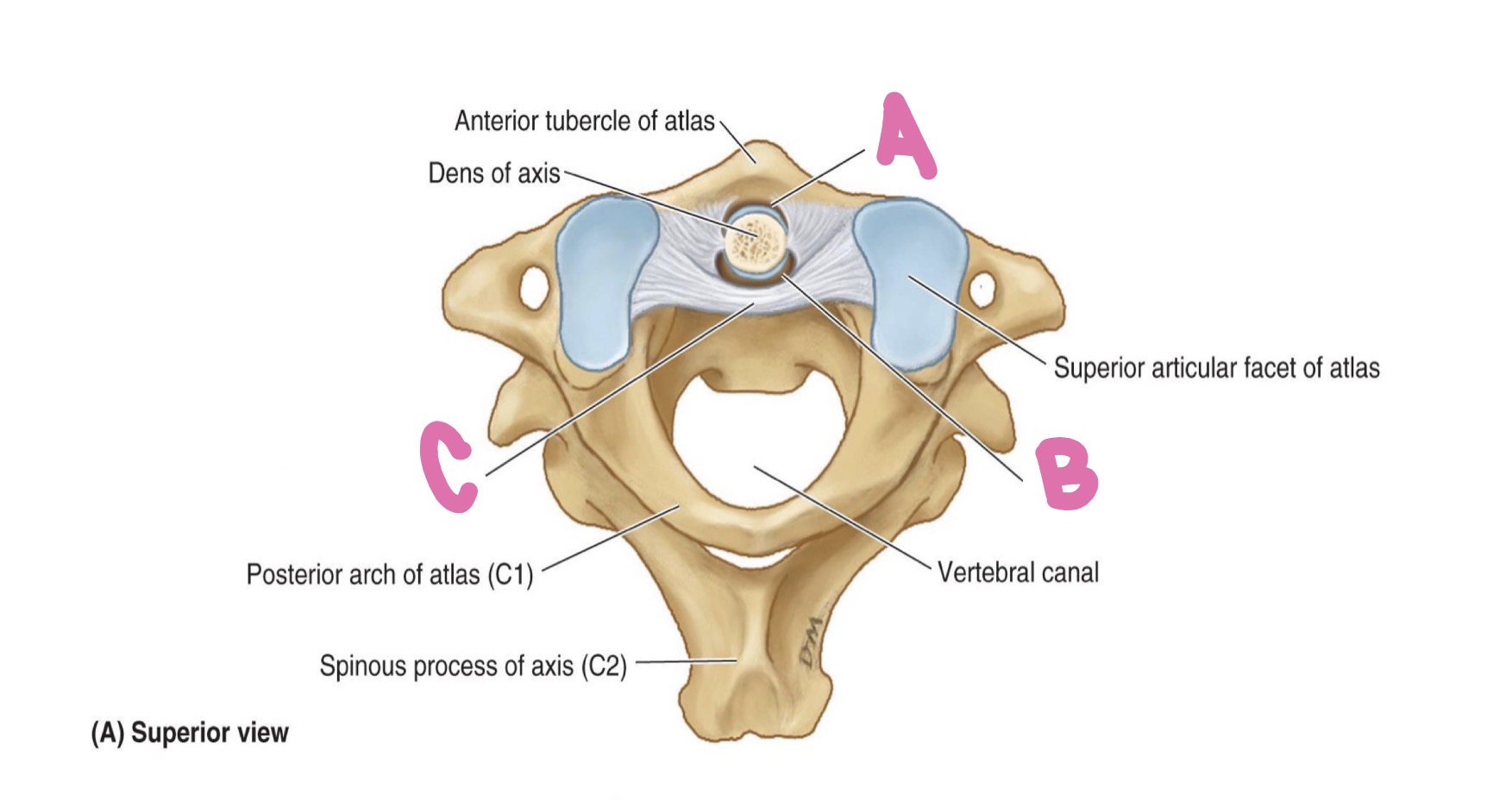
alar ligament
what is A?
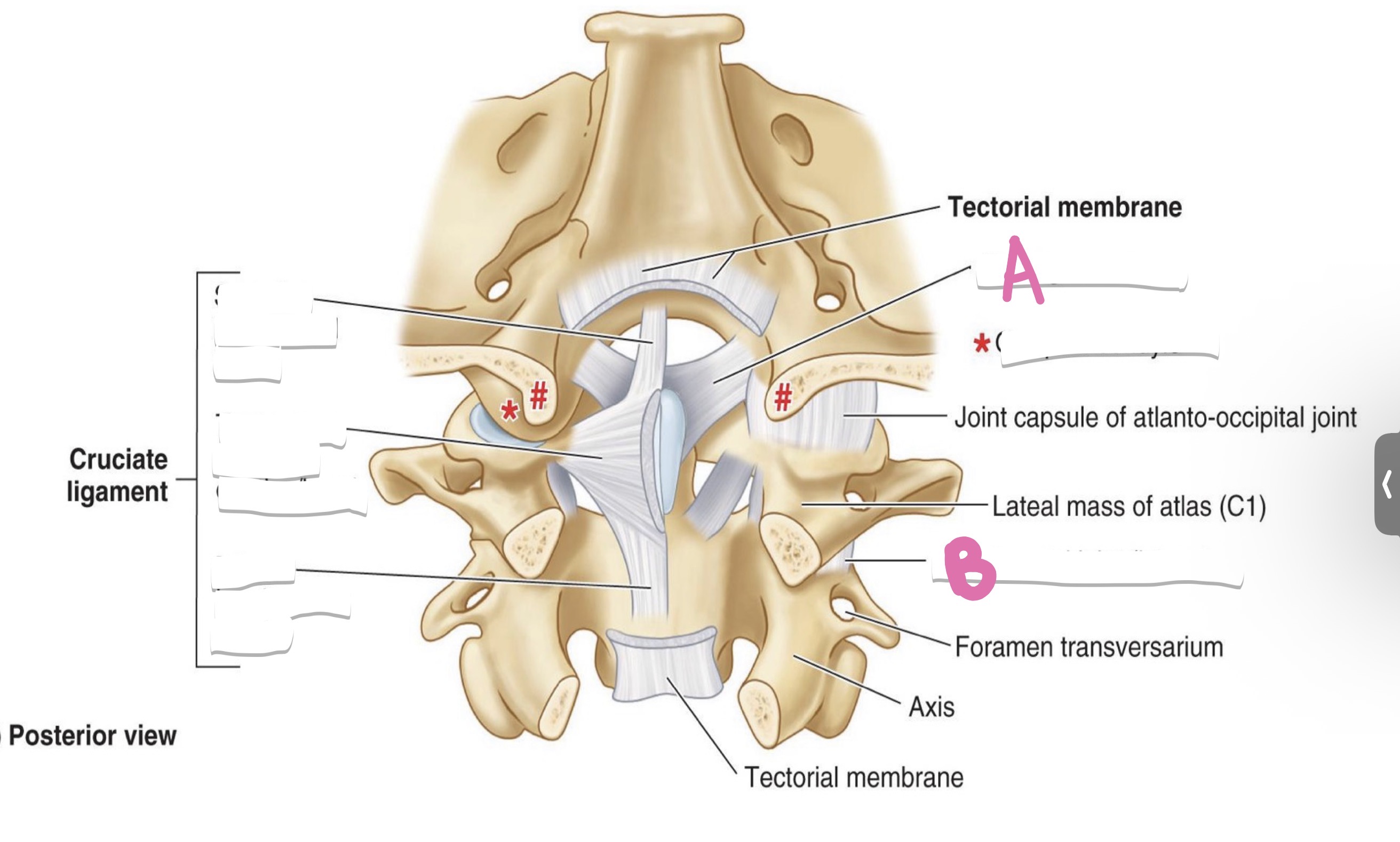
atlanto-axial joint
what is B?
7
How many cervical vertebrae?
12
How many thoracic vertebrae?
5
How many lumbar vertebrae?
5
How many sacrum vertebrae?
lamina to lamina
Origin and attachment of ligamenta flava
Bind laminae together, resist separation, preserve posture, assist with straightening the column afterflexing
Function of ligamenta flava
Between spine processes
Origin and attachment of interspinous ligaments
Prevents excessive forward flexion and sliding motion between vertebrae
Function of interspinous ligament
Tip to tip of spinous process
Origin and attachment of supraspinous ligament
Nuchal ligament from c7 to base of skull
What does the supraspinous ligament merge into?
Intervertebral disks
Attachment of posterior longitudinal ligament
Prevents hyperflexion
Function of posterior longitudinal ligament
Prevents hyper extension
Function of anterior longitudinal ligament
Resists extreme flexion
Function of supraspinous ligament
Connects vertebral bodies
Attachments of anterior longitudinal ligament
Neck of a rib to underside of the transverse process of the vertebrae above it
Attachment of superior costotransverse ligament
Stability to thoracic cage, ensuring rib expansion is controlled for respiration
Function of costotransverse ligaments
Connects tubercle of rib to transverse costal facet
Attachments of lateral costotransverse ligament
Head of rib to both vertebral bodies and interveterbral discs
Attachments of radiate ligament
Between transverse process
Attachments of intertransverse ligaments
Limit lateral flexion of spine
Function of intertransvere ligaments
foramen magnum and vertebral arch of C1
attachments of posterior/anterior atlanto-occipital membrane
connect C1 and cranium
function of posterior/anterior atlanto-occipital membrane
external occipital protuberance to spinous process of cervical vertebrae
attachements of nuchal ligament
limit forward flexion of head
function of nuchal ligament
attachments of apical ligament of dens
function of apical ligament of dens