bio lab quiz idk anymore pls help me oh my god why jesus make it stop
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
histology
the microscopic study of animal cells and tissues. also helps us understand how a cell's structure enhances the functionality of tissues and organs.
tissue
collection of cells that have similar structures and functions
organ
collection of different tissues working together for a specific function
epithelial tissues function y examples
Covers both internal and external body structures. Sometimes has a role in absorbing/secreting substances
ex: Simple squamous
Stratified squamous
Simple cuboidal
Simple columnar
connective tissue function y examples
Tissues that specialize in binding and support, protection, internal transport, storage and insulation.
ex: Adipose
Blood
Bone
Dense fibrous
Loose fibrous
Hyaline cartilage
muscle tissue function y examples
Contraction for the purposes of movement
ex: Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth
nervous tissue function y examples
communication
ex: Composed of two classes of cells: neurons and glia
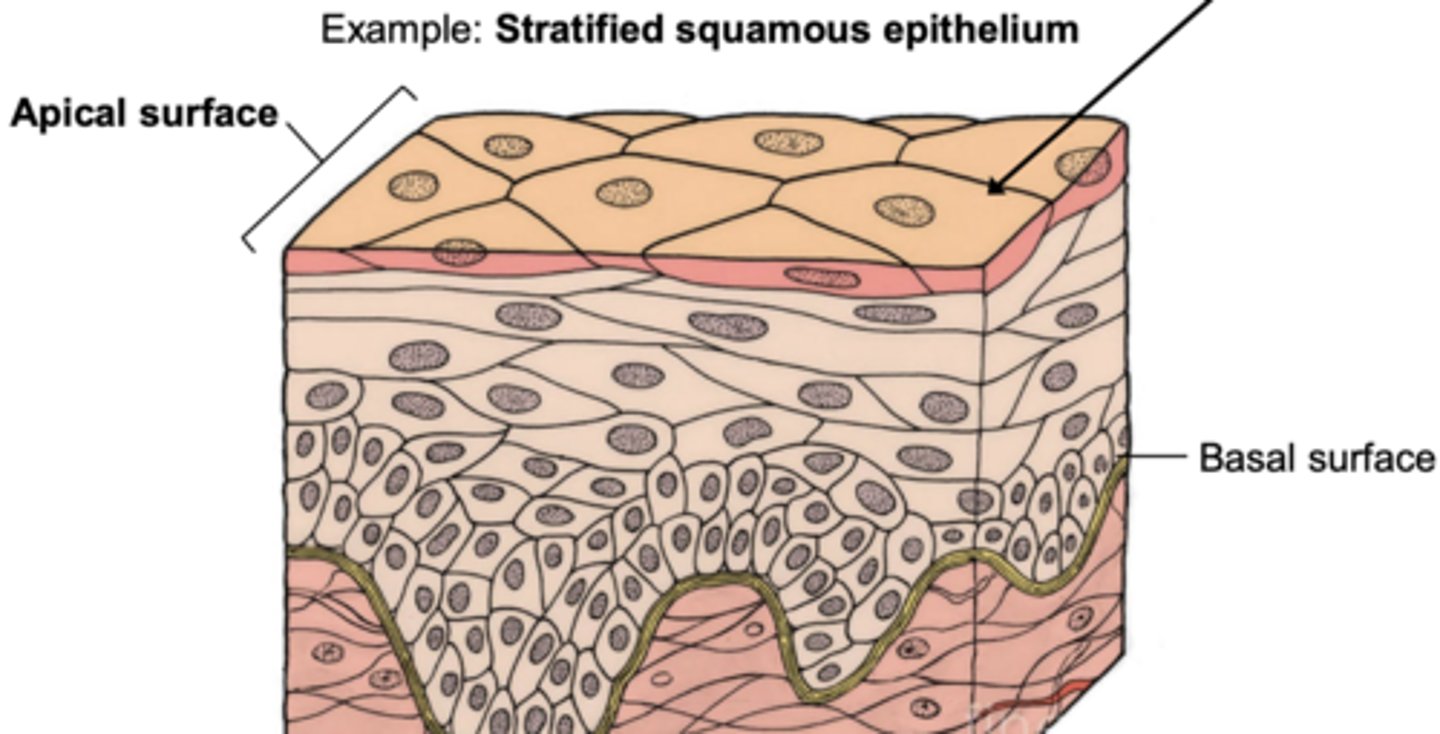
Epithelial tissue (epithelium) forms barriers, coverings, and exchange surfaces. Here, cells are usually tightly joined together, with little or no space in between. what are the characterisics of epithelial tissue?`
• Covers the external body structures (e.g. skin) as well as internal body structures (e.g. intestinal lining)
• Epithelium has two different sides: apical and basal surface
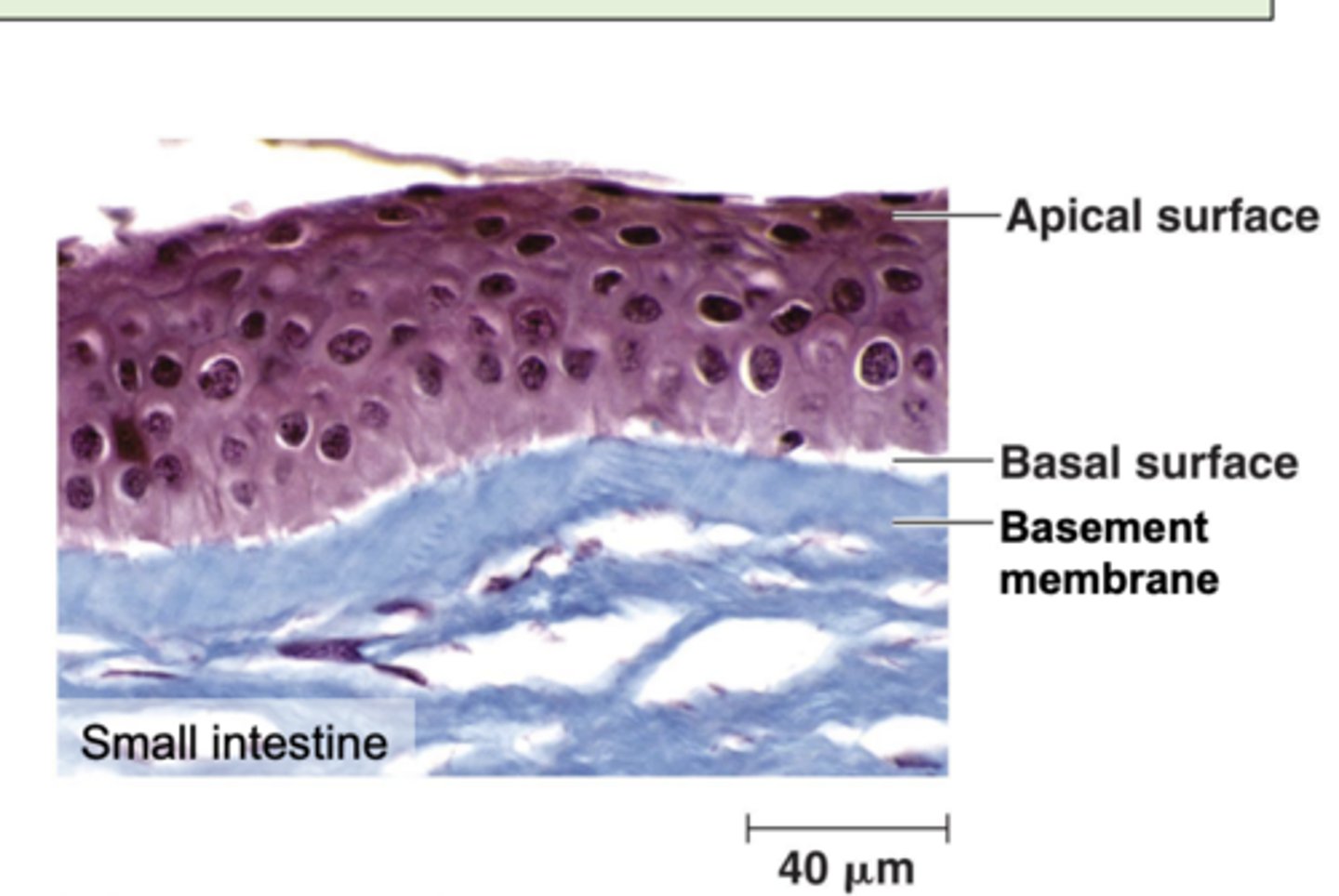
apical surface
outer, exposed surface of organ/tissue
basal surface
opposite to apical, attaches to basement membrane
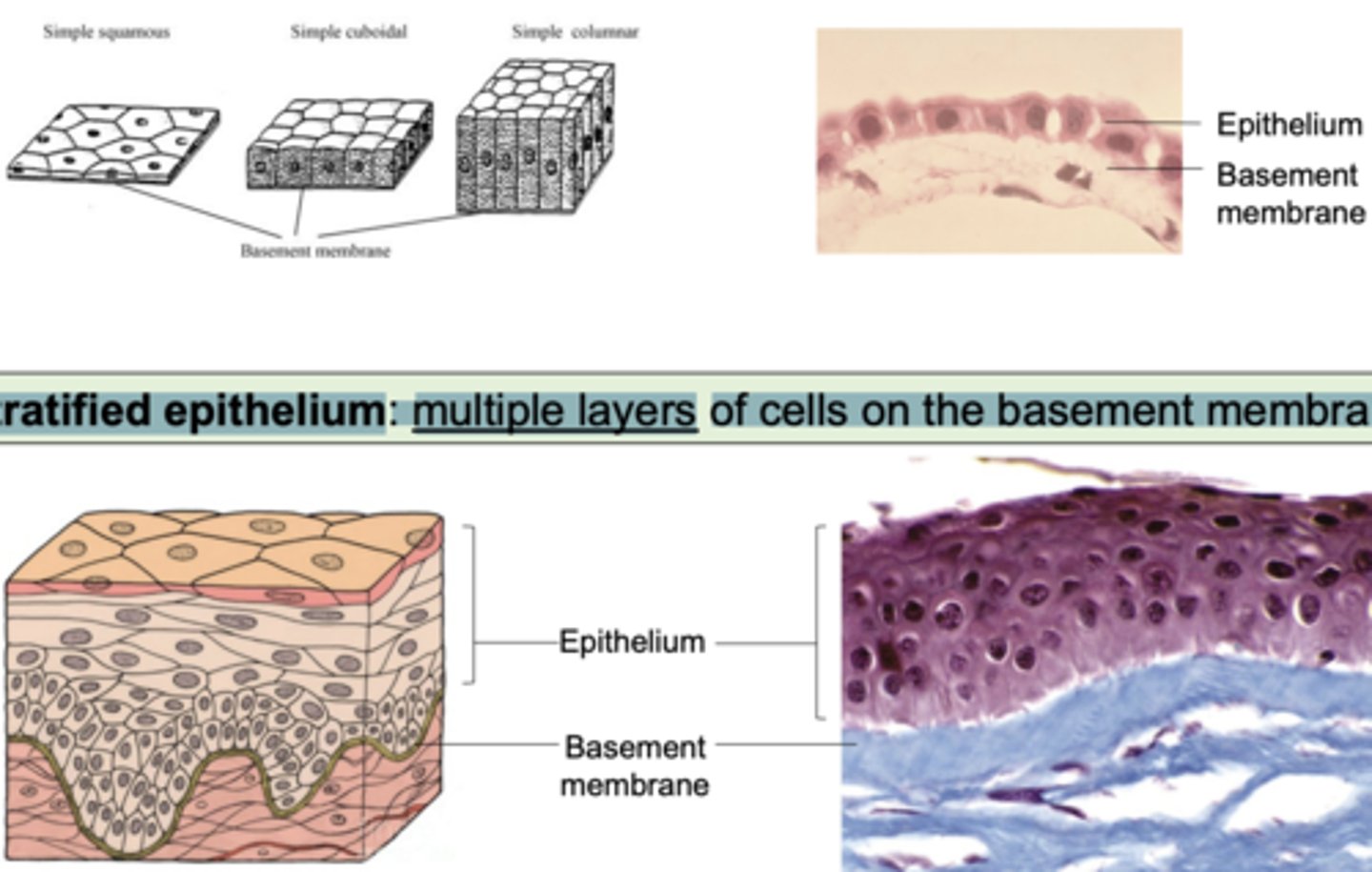
Epithelial tissue arrangement can be simple or stratified. whats the difference
Simple epithelium: single layer of cells on the basement membrane
Stratified epithelium: multiple layers of cells on the basement membrane
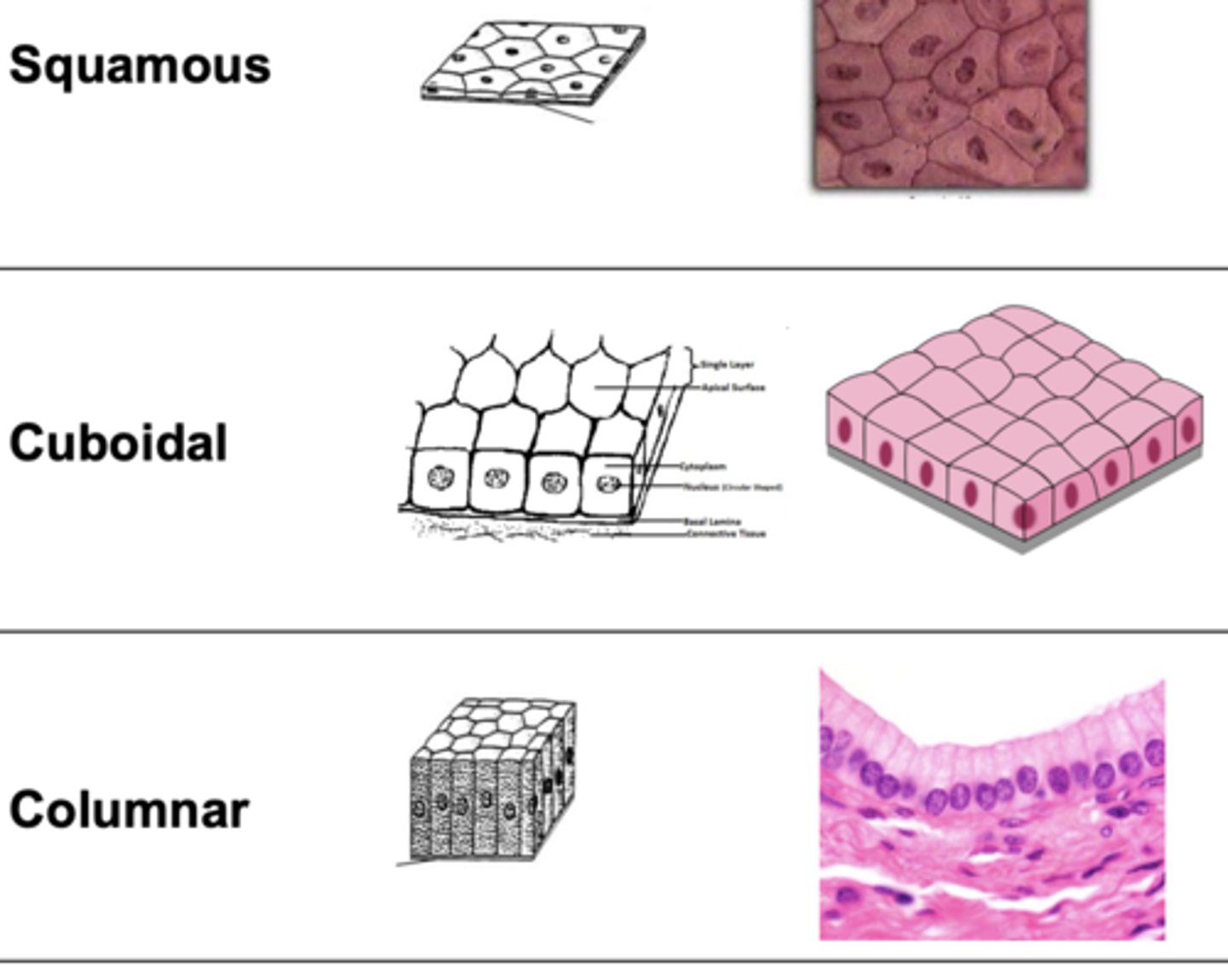
what does squamous, cuboidal, y columnar epithelial cell shapes look like
this
In stratified tissues, the tissue is named by the shape of cell on the
apical surface
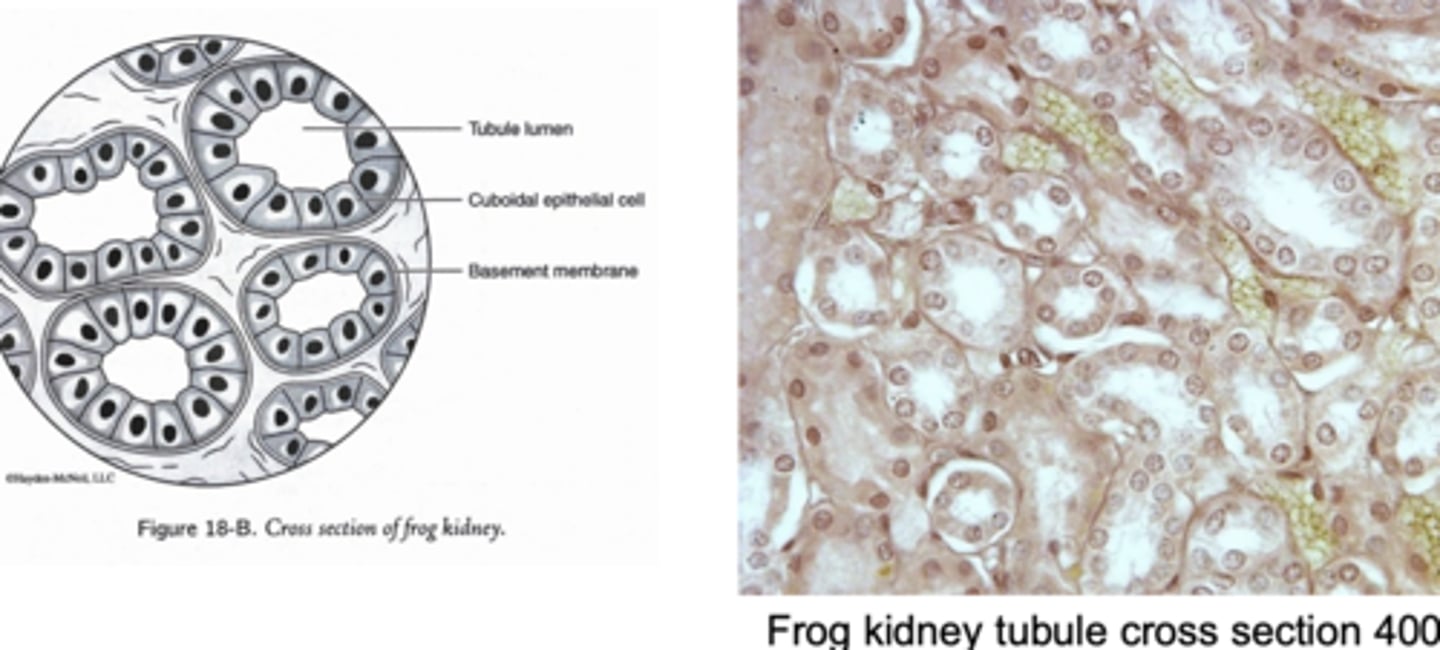
what cell shape do frog kidney tubules have
Simple cuboidal epithelium rolled into a tube
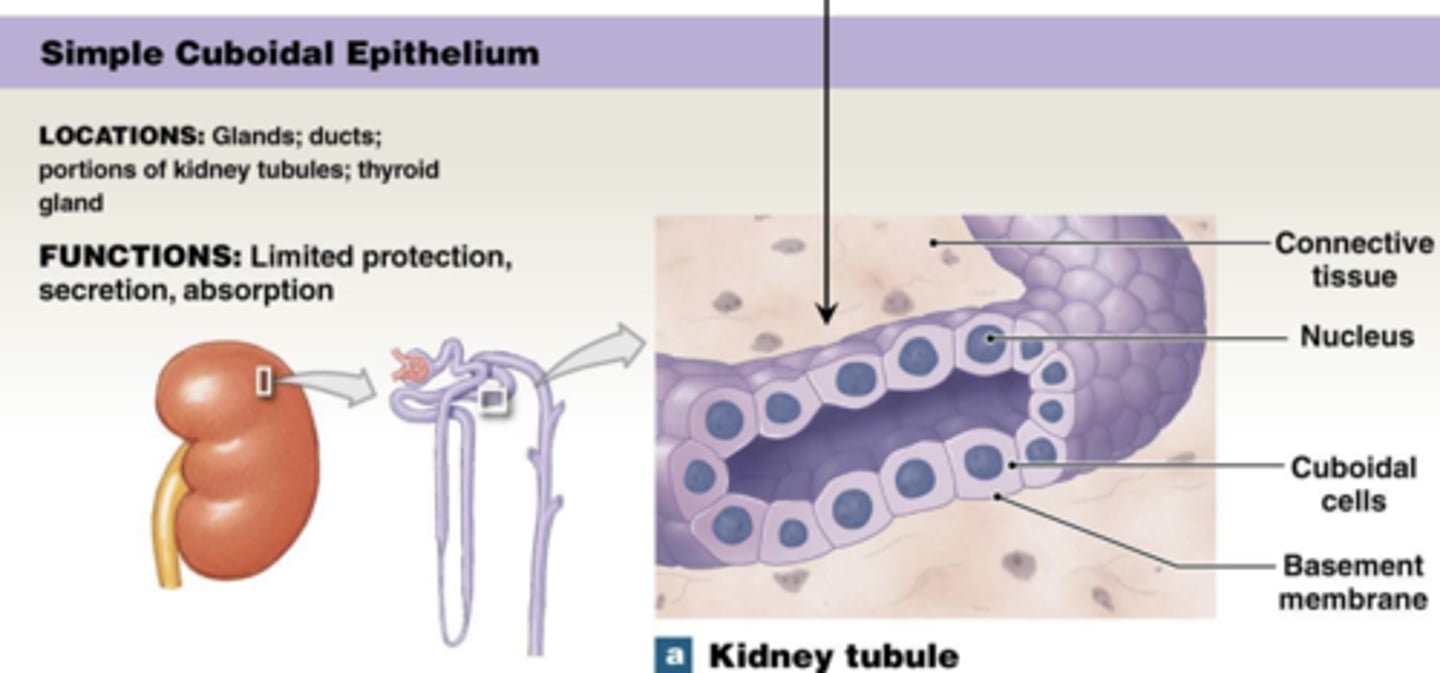
Simple cuboidal epithelium is specialized for _______
secretion and absorption
frog intestinal lining labeled
ok
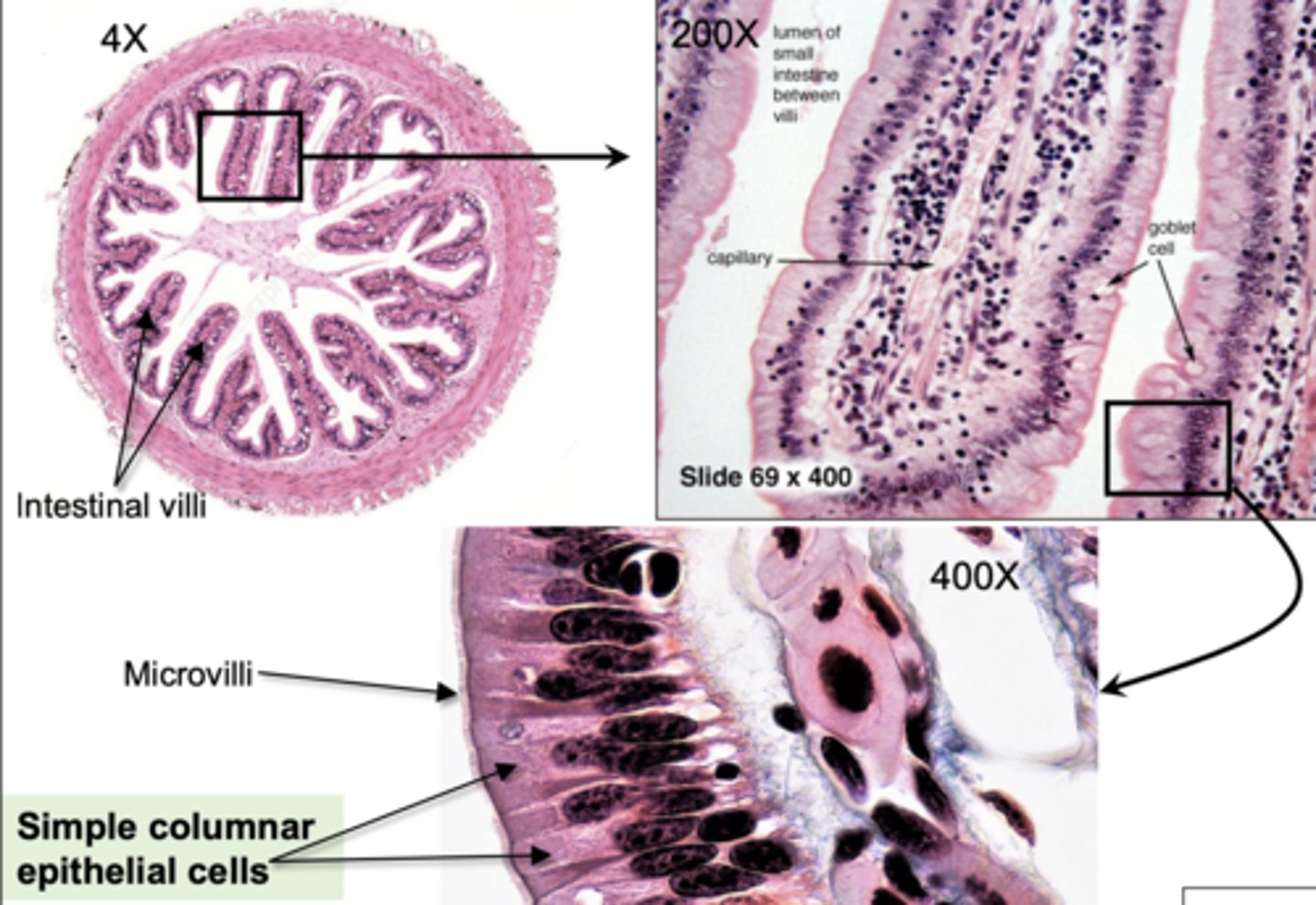
The intestinal lining is structured to maximize surface area for nutrient absorption. what is intestinal villi and microvilli
• Intestinal villi: Finger-like projections of epithelial tissue into the intestinal lumen
• Microvilli: Microscopic membrane protrusions from individual epithelial cells
Connective tissue includes cartilage, bone, blood, and adipose (fat). Here, Cells are generally spaced loosely (not touching one another) within an extracellular matrix that provides structure and flexibility. what is an extracellular matrix
a network of proteins and minerals that may be liquid, semi-solid, or solid
Some connective tissues physically connect other tissues to each other: these include
loose connective tissue
dense connective tissue
ligaments
tendons
Loose connective tissue:
thin mesh scaffolding that binds tissues together
• Dense connective tissue:
dense collagen fiber matrix with high tensile strength (resistance to stretching)
Ligaments
connect bone to bone
Tendons
connect muscle to bone
other connective tissues dont connect anything:
• Cartilage
• Bone
• Blood
• Adipose (fat)
Cartilage tissue provides flexible support in places like the nose and ears. Cartilage matrix contains _________, a protein-carbohydrate complex that gives the cartilage a jelly-like consistency
chondroitin sulfate
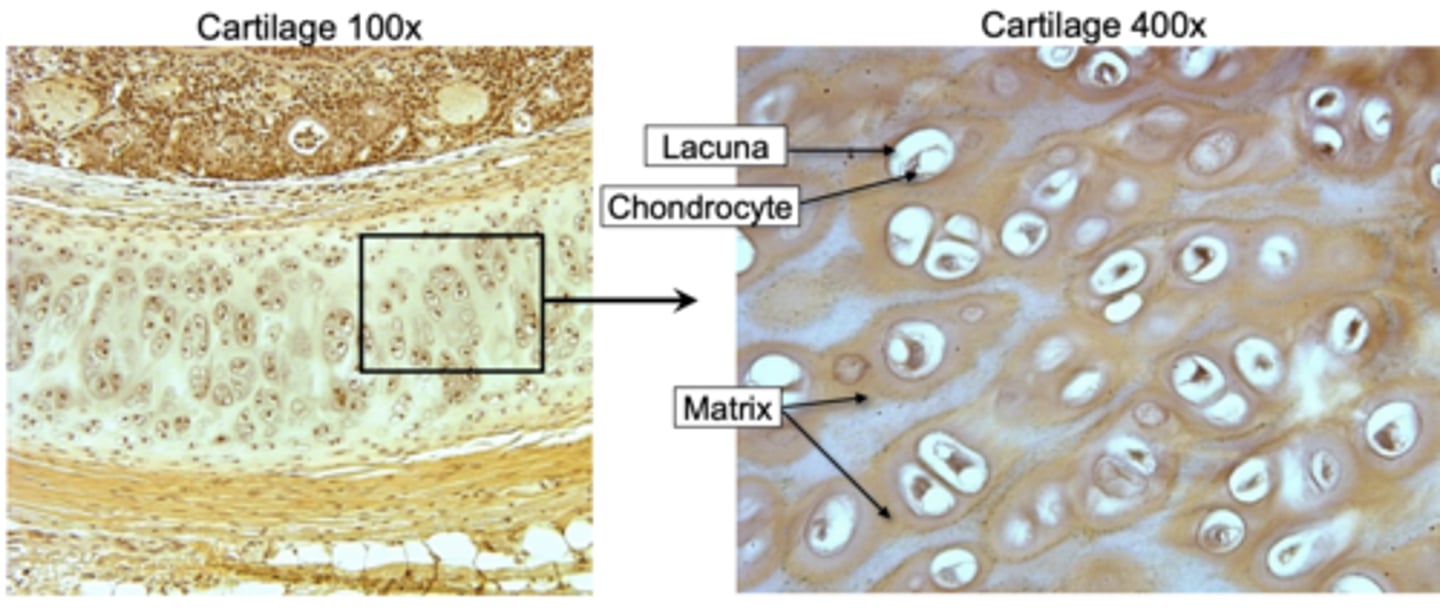
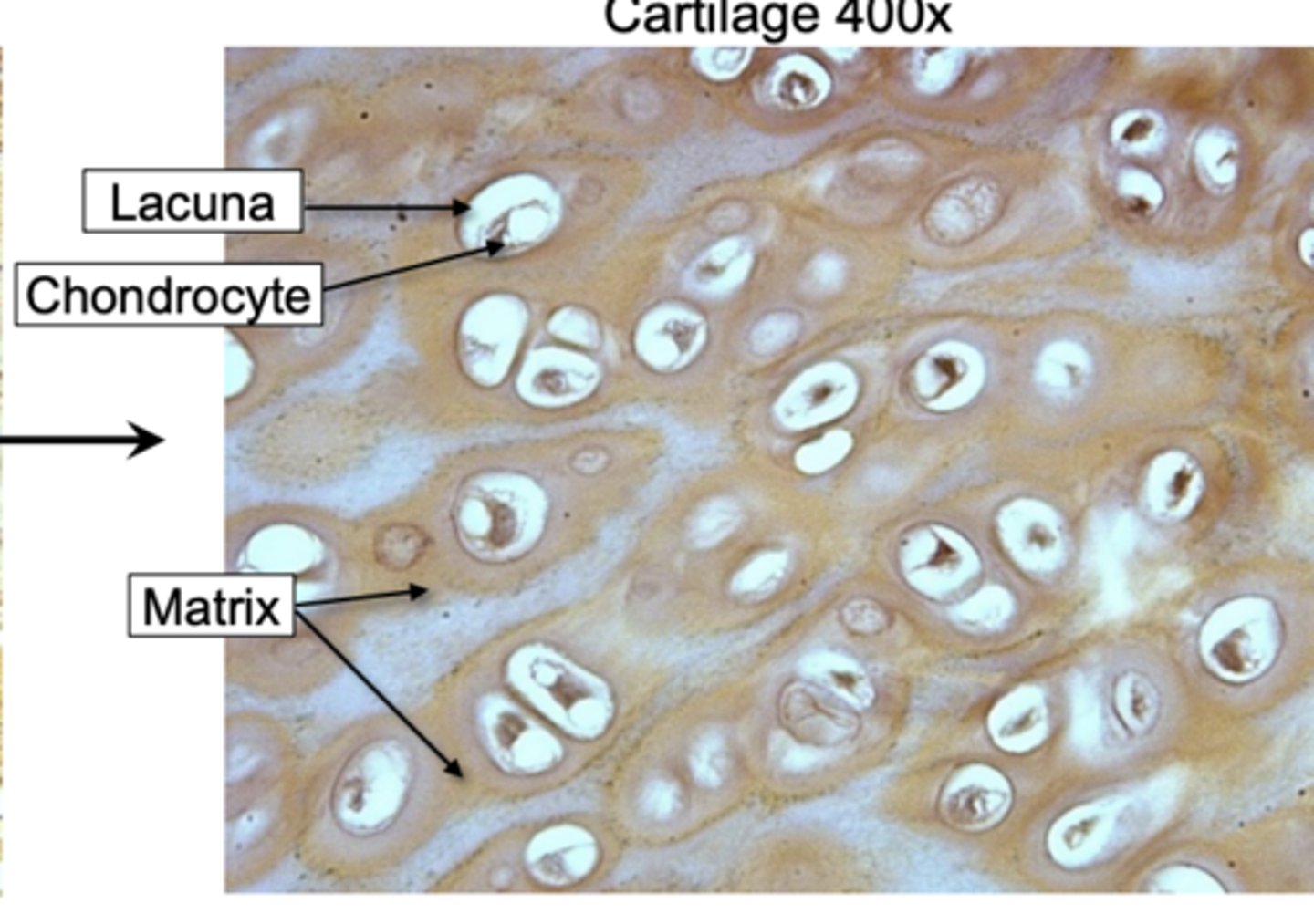
• Chondrocytes:
cells that make up the cartilage tissue
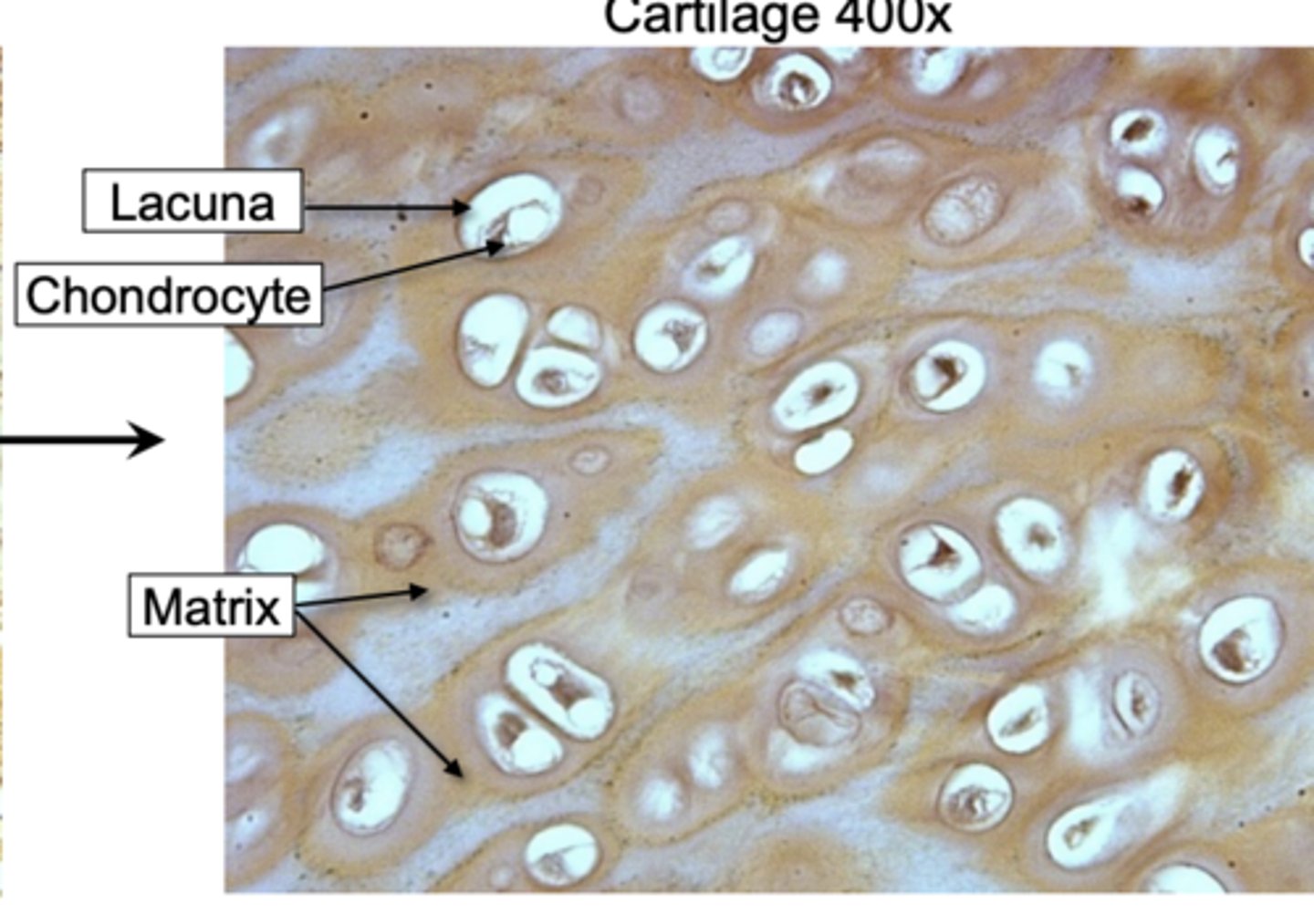
• Lacunae:
spaces within the extracellular matrix where chondrocytes reside
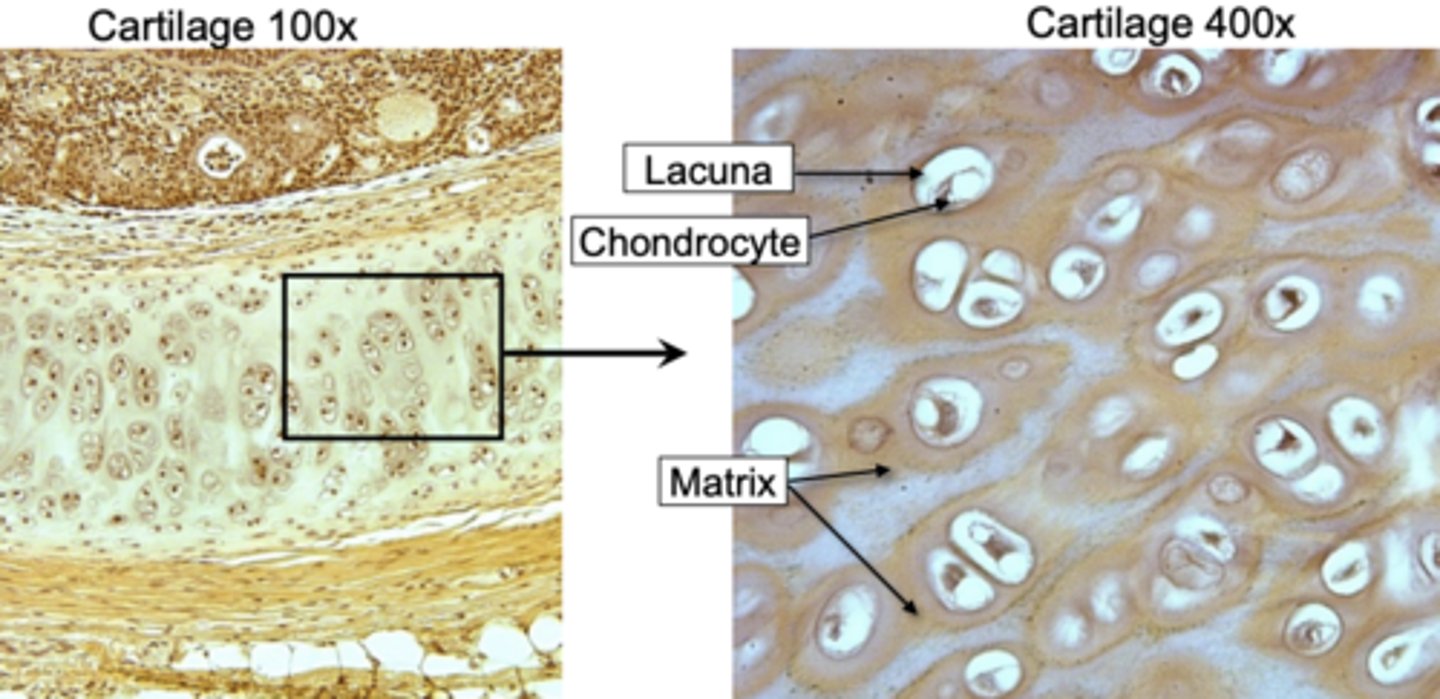
Cartilage matrix contains _________, a protein-carbohydrate complex that gives the cartilage a jelly-like consistency
chondroitin sulfate
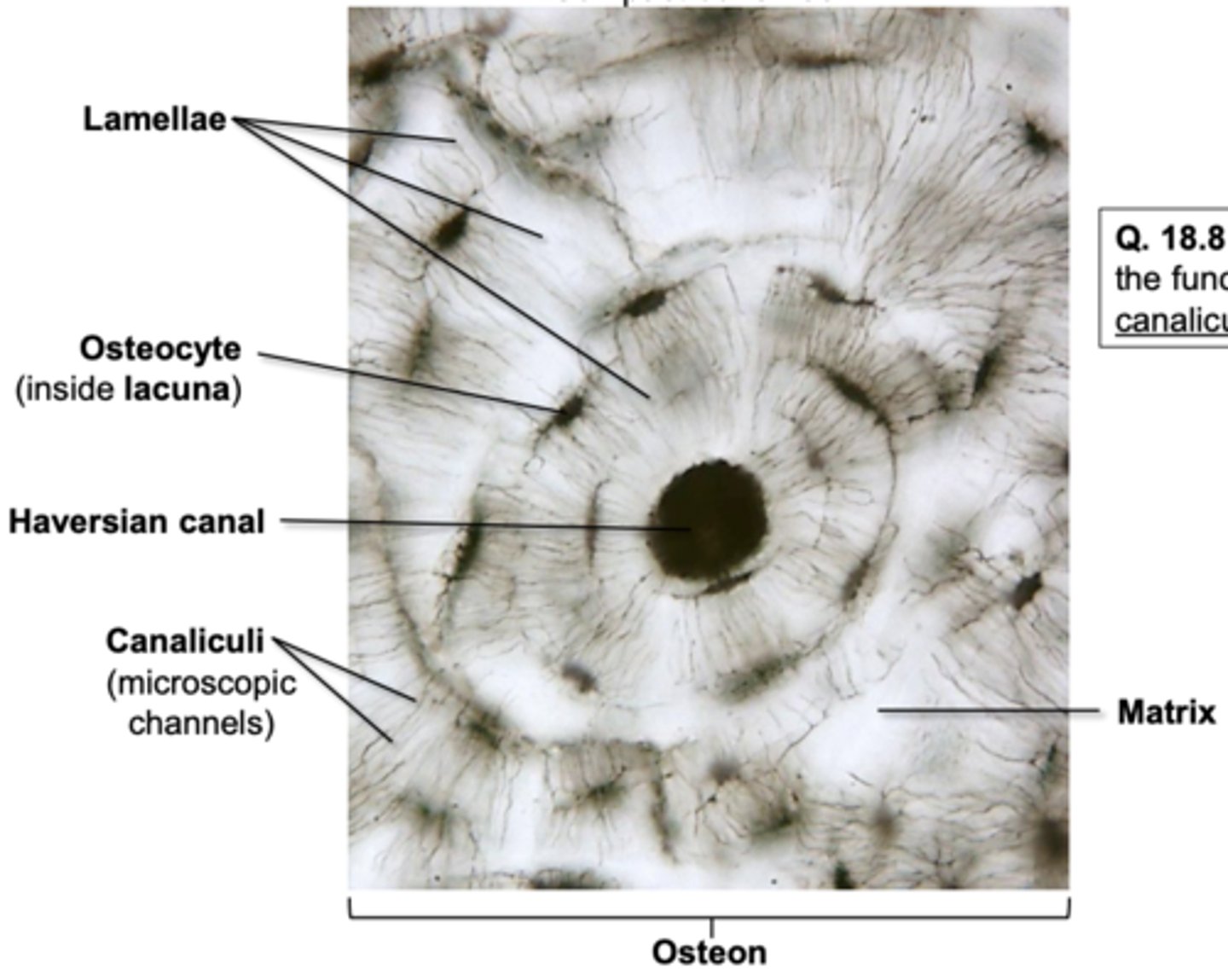
Bone matrix:
contains calcium, magnesium, and phosphate to make it solid
• Osteocytes:
bone cells
• Lacunae:
spaces in the matrix where chondrocytes reside
• Haversian canals:
tubes in the matrix for nerves and blood vessels to run through
• Lamellae:
layers of matrix arranged in concentric circles
• Canaliculi:
thin channels in the matrix connecting the lacunae and Haversian canal
• Osteon:
a unit of bone; consists of one Haversian canal and its associated lamellae
Can you label the connective tissue: bone?
yes, i can label the connective tissue bone
blood is composed of blood plasma, erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets. what is blood plasma
, a fluid matrix
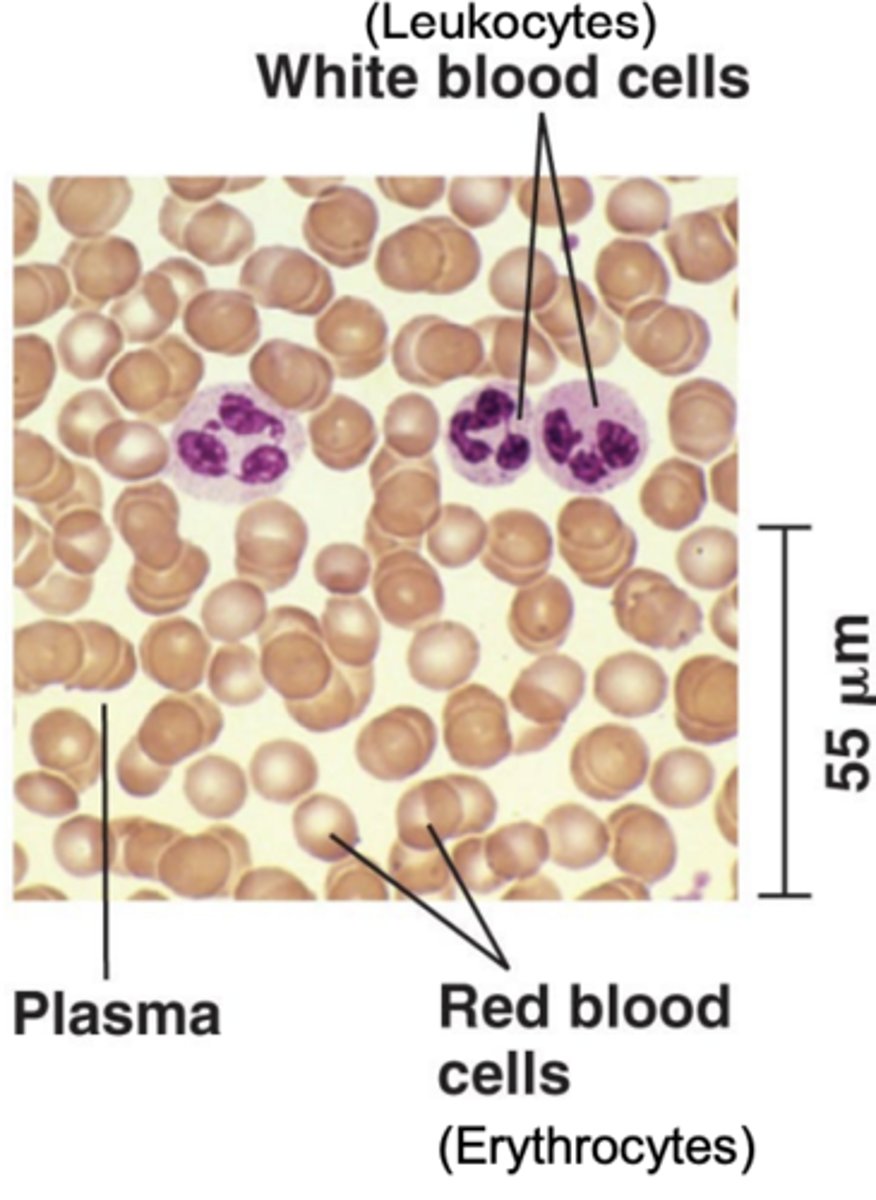
• Erythrocytes: \
red blood cells that contain hemoglobin and carry O2
• Leukocytes:
white blood cells that are involved in immunity
• Platelets:
cellular fragments involved in clotting
can u label the connective tissue of blood?
yes, i can label the connective tissue of blood
adipose is another connective tissue. what does adipose do
stores energy in the form of fat. It also helps to cushion and insulate the body.
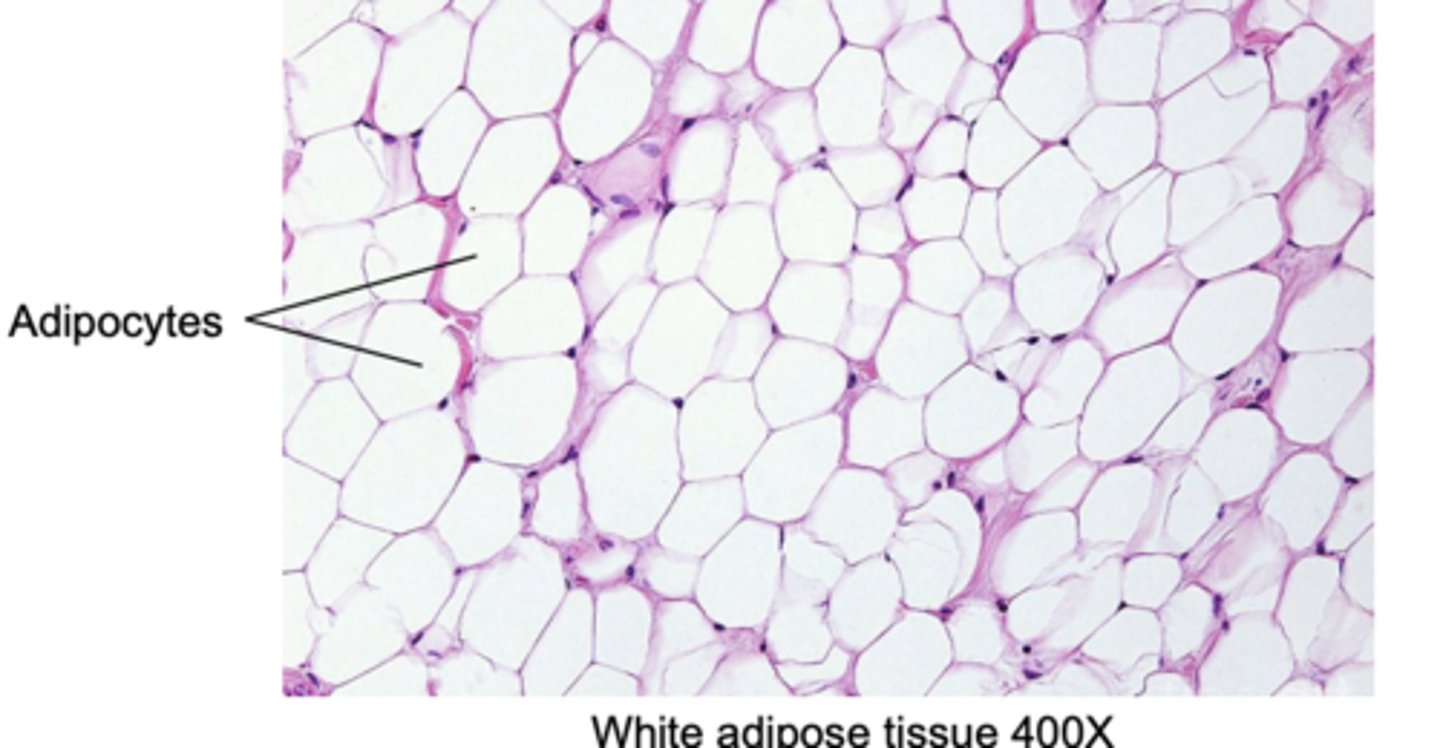
muscle tissue consists of
long cells (muscle fibers) that are specialized to contract in response to nerve signals.
3 types of muscle tissue
skeletal muscle
smooth muscle
cardiac muscle
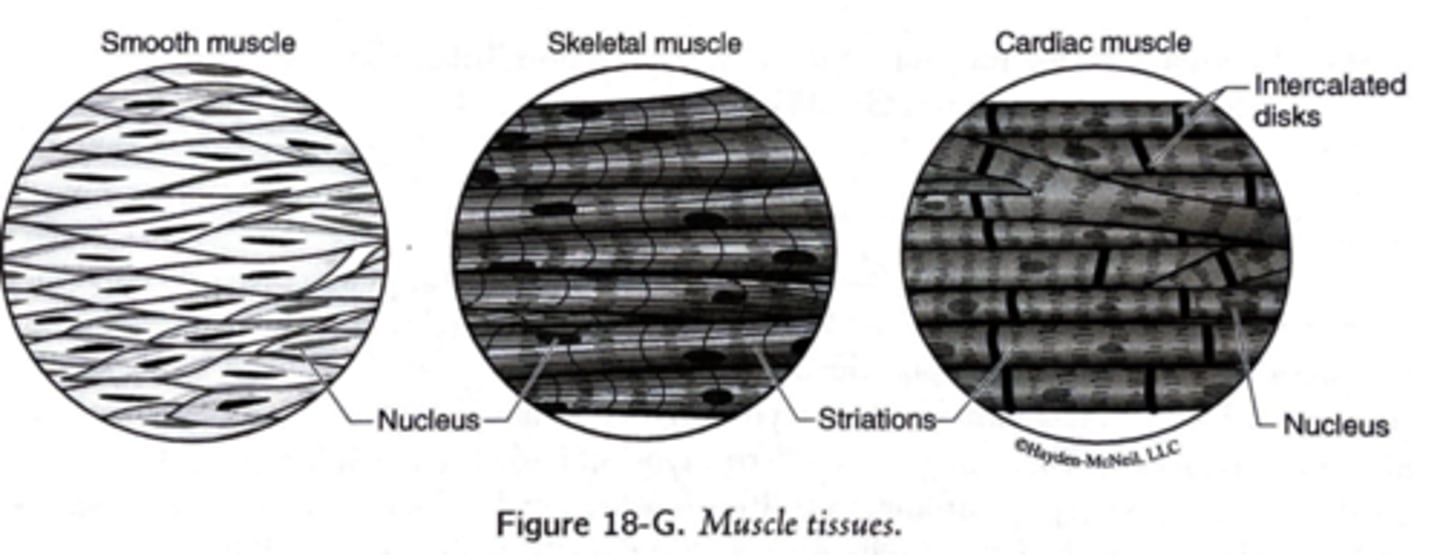
skeletal muscle
striated muscle, is responsible for voluntary movement of the skeleton.
smooth muscle
not striated and is responsible for involuntary movement of internal organs.
cardiac muscle
responsible for contraction of the heart; it is a striated and involuntary muscle.
Skeletal muscle moves the skeleton. During development, its cells fuse into large muscle fibers that contain _______. Most of the fiber consists of contractile proteins (actin and myosin) that are arranged to produce visible _________ (stripes).
multiple nuclei, striations
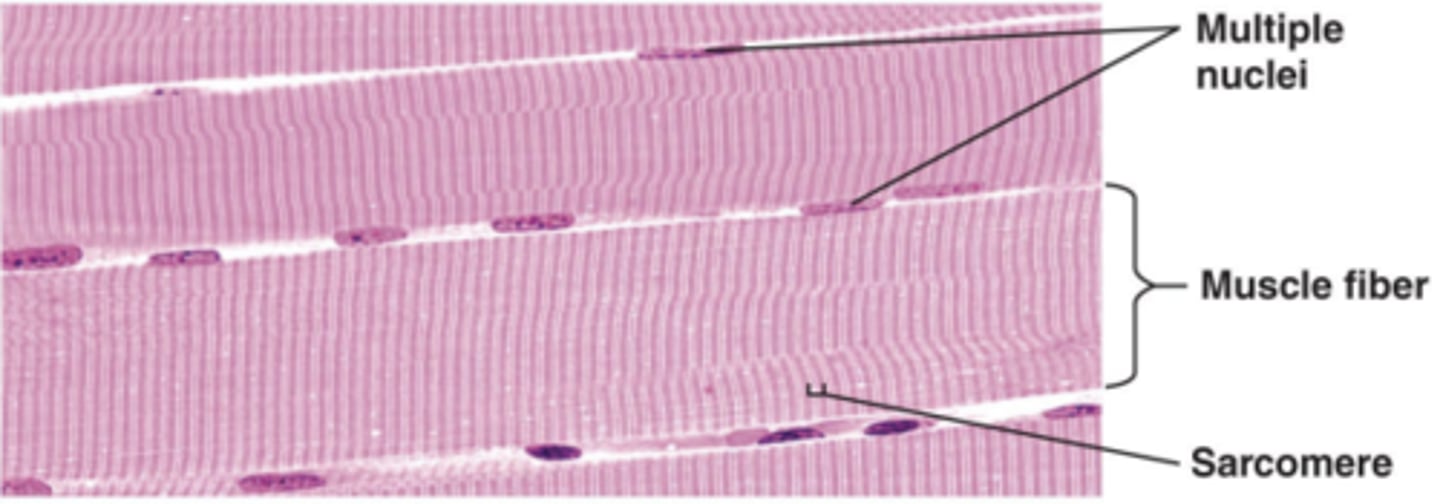
what are striations
visible perpendicular stripes from the sarcomeres
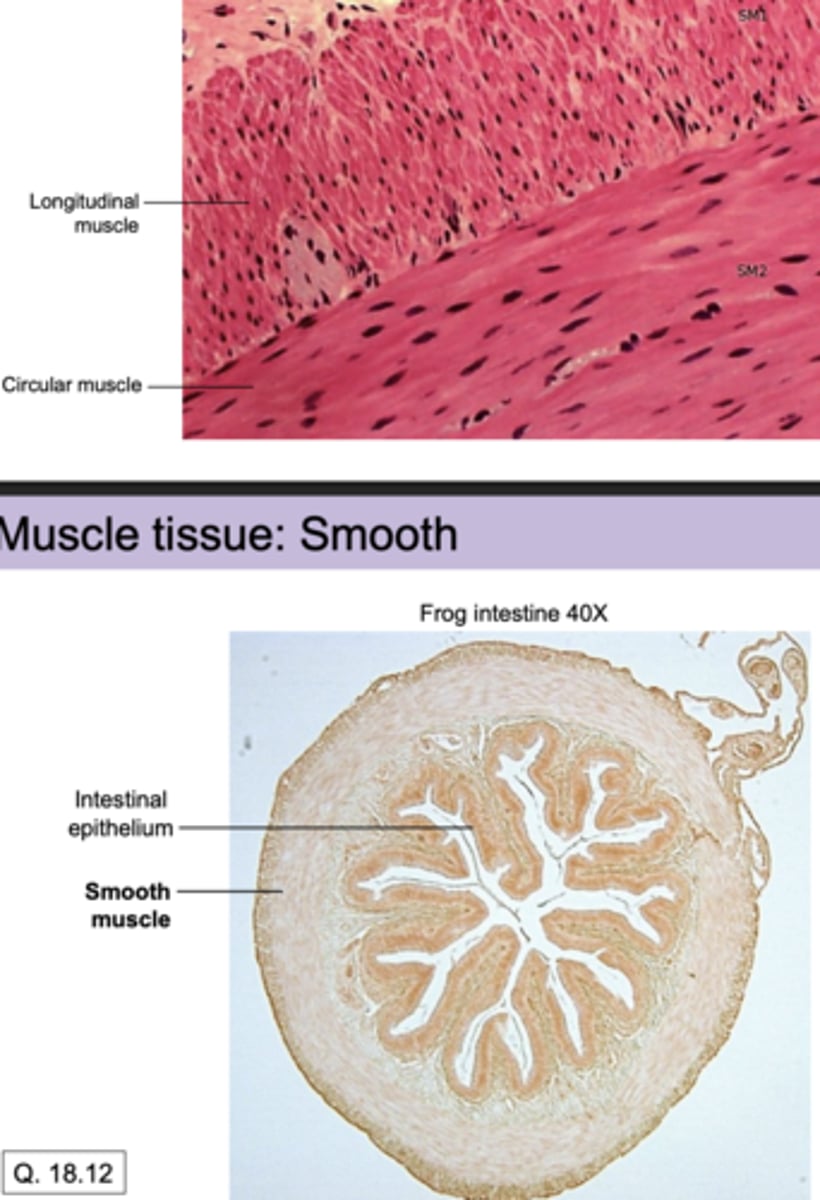
Smooth muscle contracts around internal organs for involuntary movement (e.g. in the walls of blood vessels or intestines). Not striated. Can you label a cross section?
yes, i can label a cross section
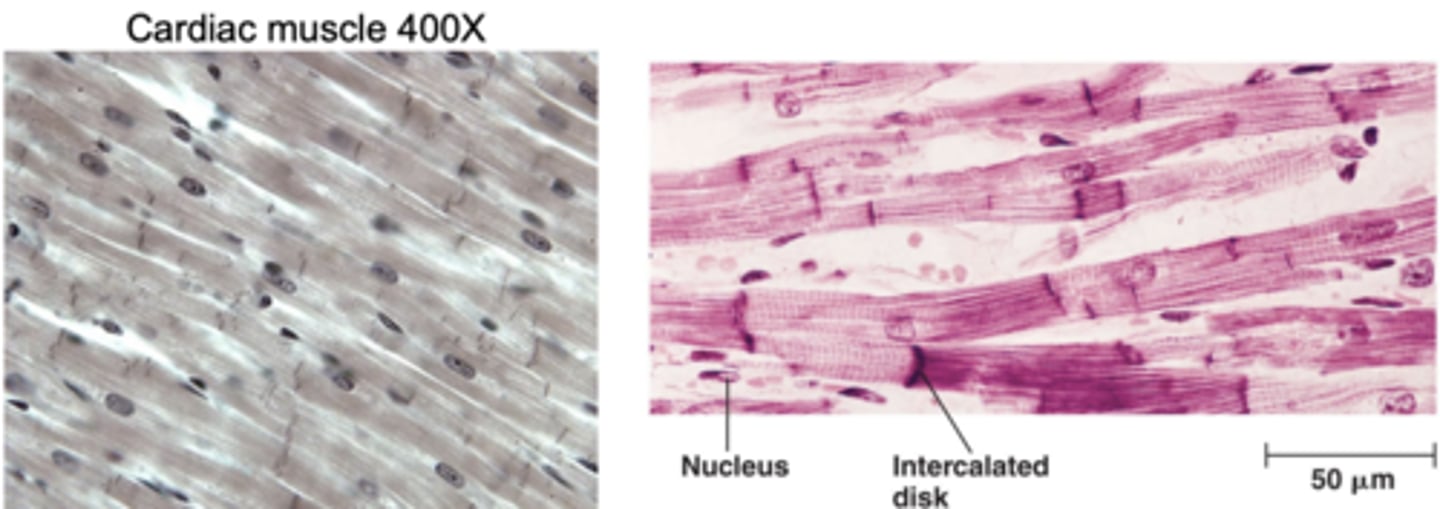
Cardiac muscle is responsible for heart contractions. what are characteristics of cardiac muscle?
• Straited, but less obvious than in skeletal muscle
• Branched cells, each with a single nucleus
• Numerous connections between cells
• Intercalated discs: connections between two cardiac muscle cells to allow for rapid communication between cells
Nervous tissue transmits signals to and from
different parts of the body to collect sensory information and coordinate action
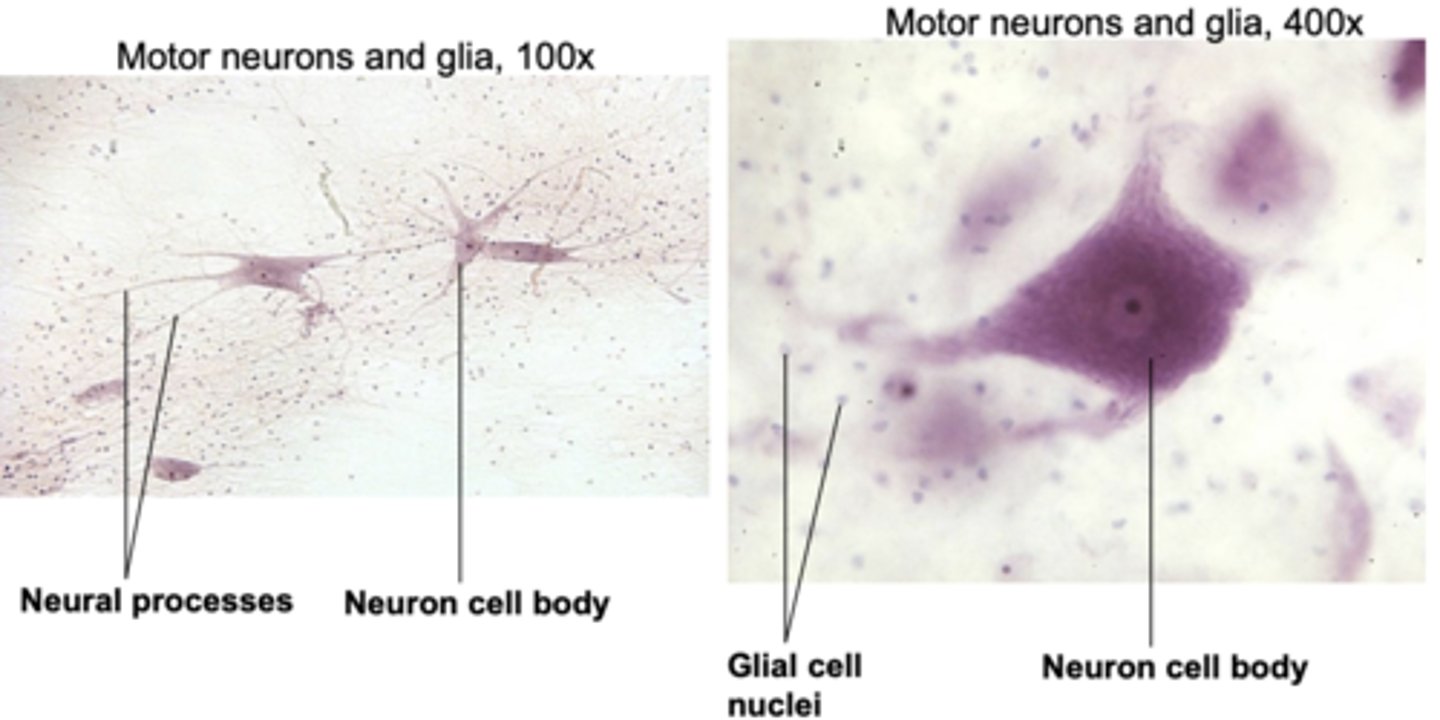
Nervous tissue consists of two types of cells:
neurons and glial cells
Neurons send and receive electrochemical signals. Each one has:
cell body, axon, dendrites
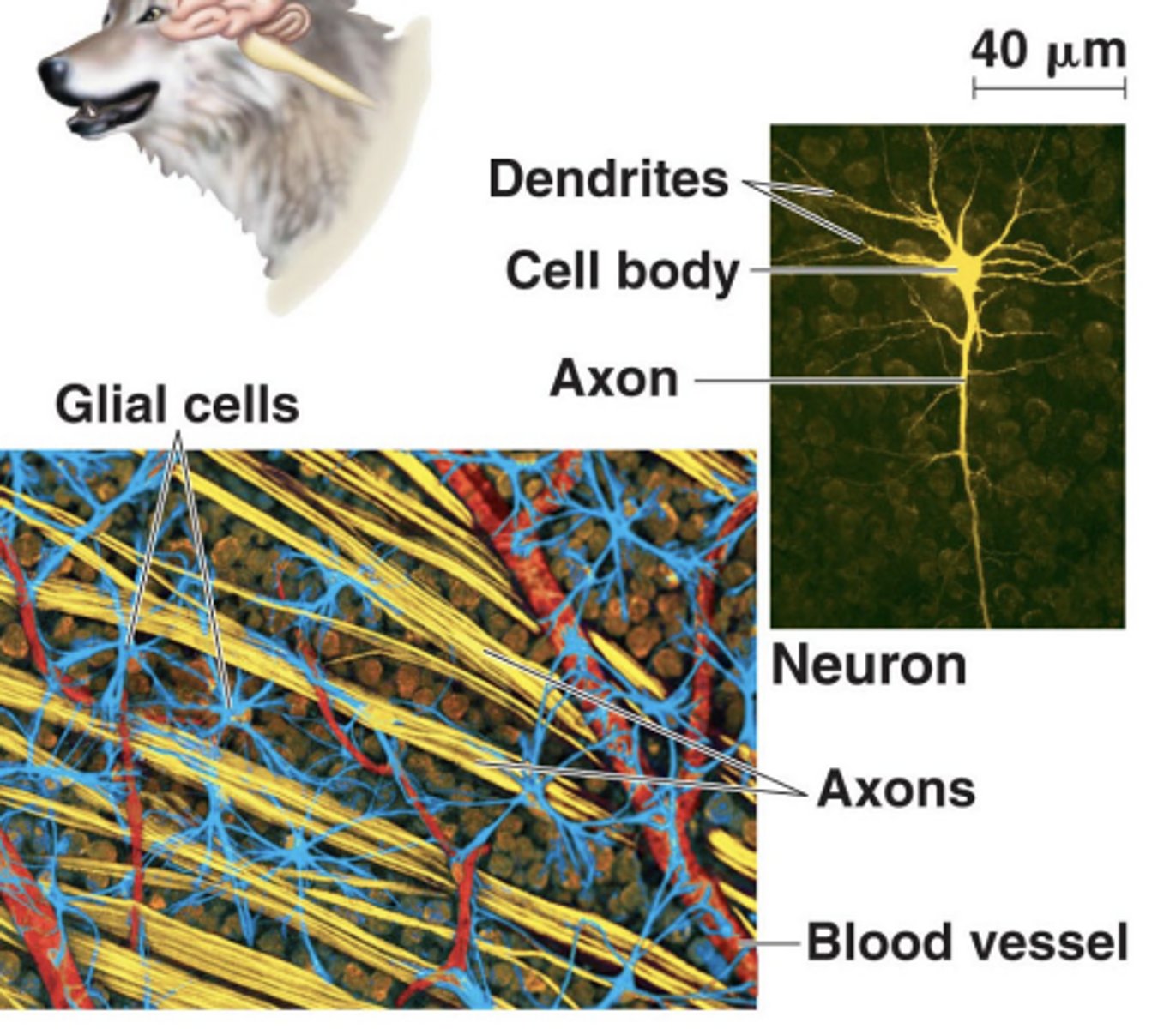
• Cell body (soma)
contains the nucleus
• Axon
a long projection that sends signals
• Dendrites
several branched extension that receive signals
• Glial cells (glia) provide
structural and nutritional support to neurons
Neurons are highly diverse in both .
shape and function
Axons and dendrites together are called
neural processes.
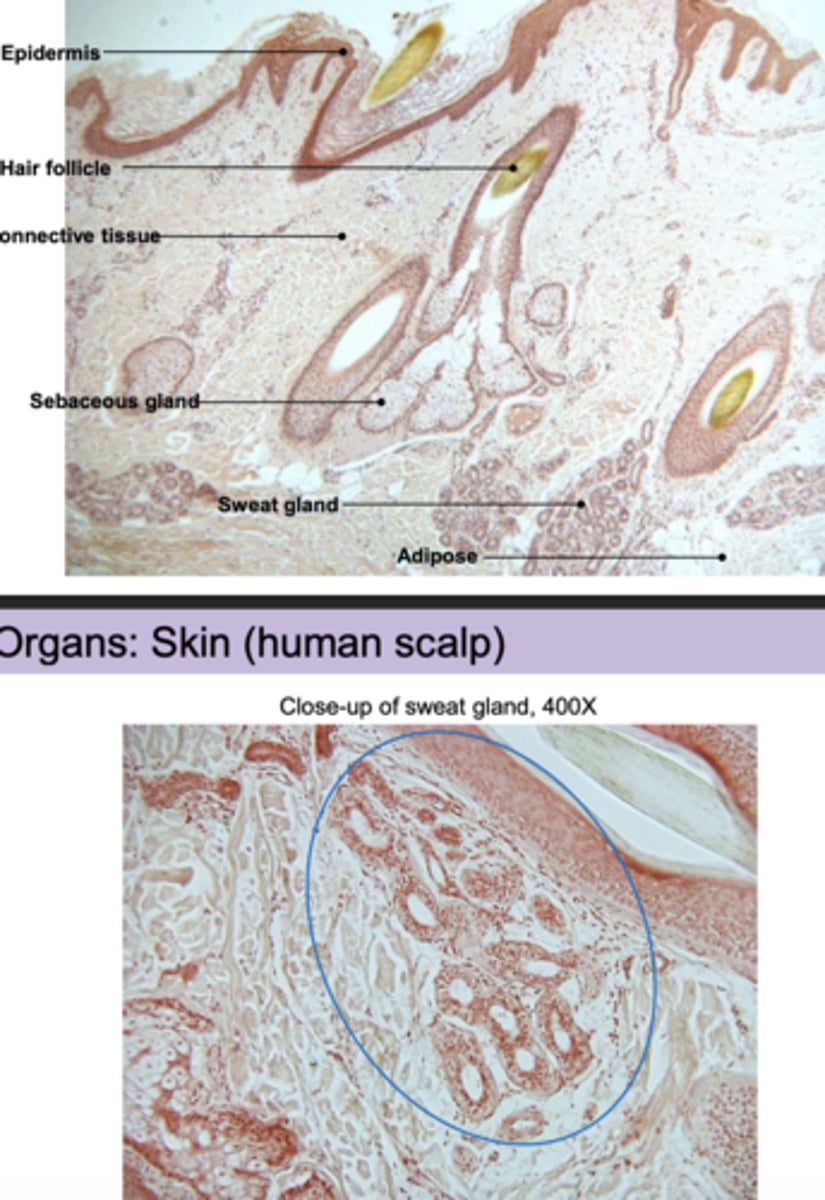
Organs are
collections of different tissues that work as a functional unit.
human skin layers include the
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
epidermis characteristics
-Stratified squamous
epithelium
• Keratinized outer layer
dermis characteristics
• Hair follicles
• Sebaceous glands
• Sweat glands
• Nerves, blood vessels
hypodermis (subcutaneous) characteristics
• Adipose (fat) tissue
can you label the organs:skin (Human scalp)?
yes, i can label the human scalp
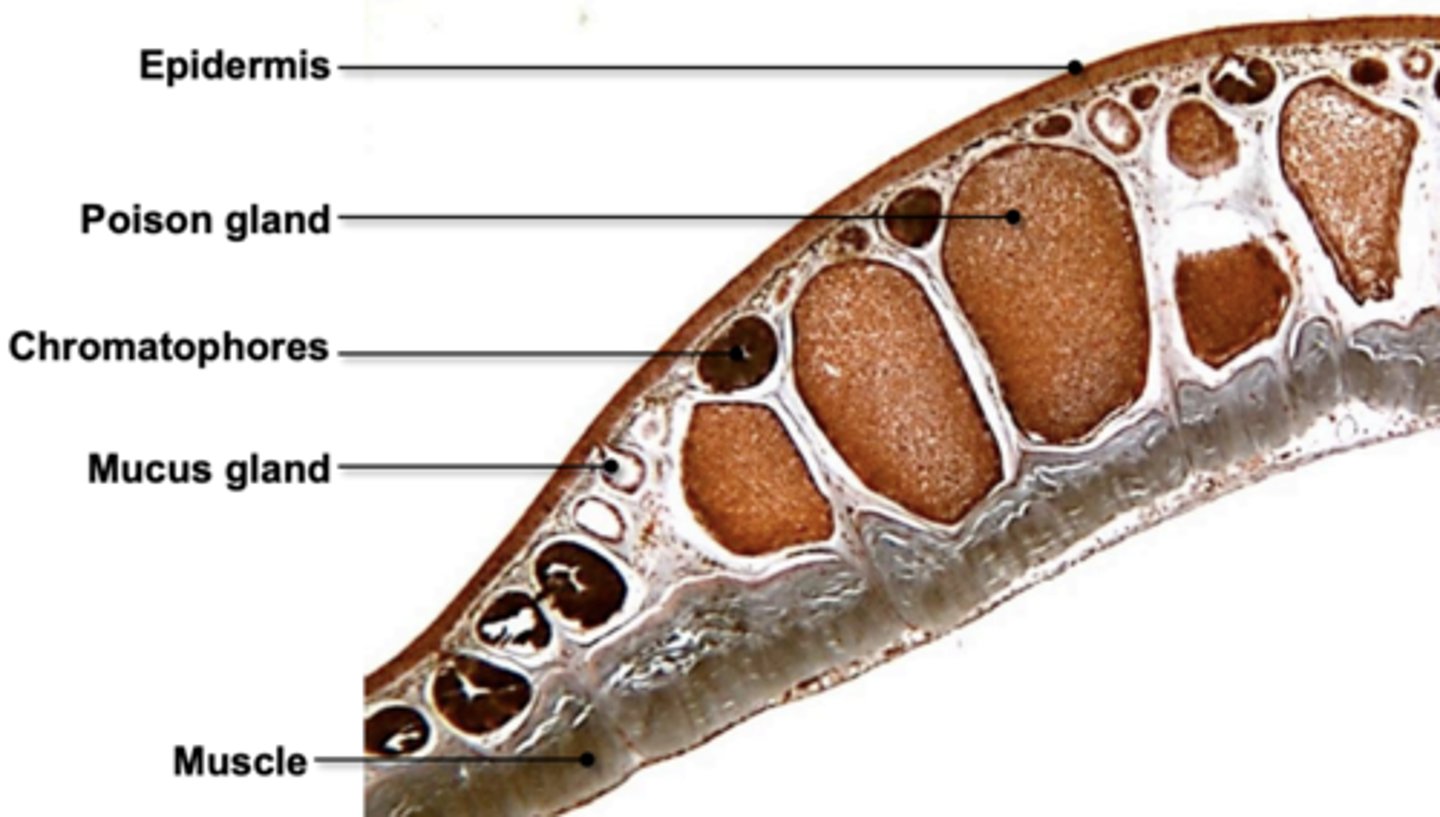
in the organs: skin (frog), they have an epidermis and a dermis. what is included in these
Epidermis: Stratified squamous epithelium
Dermis: Chromatophores
(pigmented cells)
• Mucus glands
• Poison glands
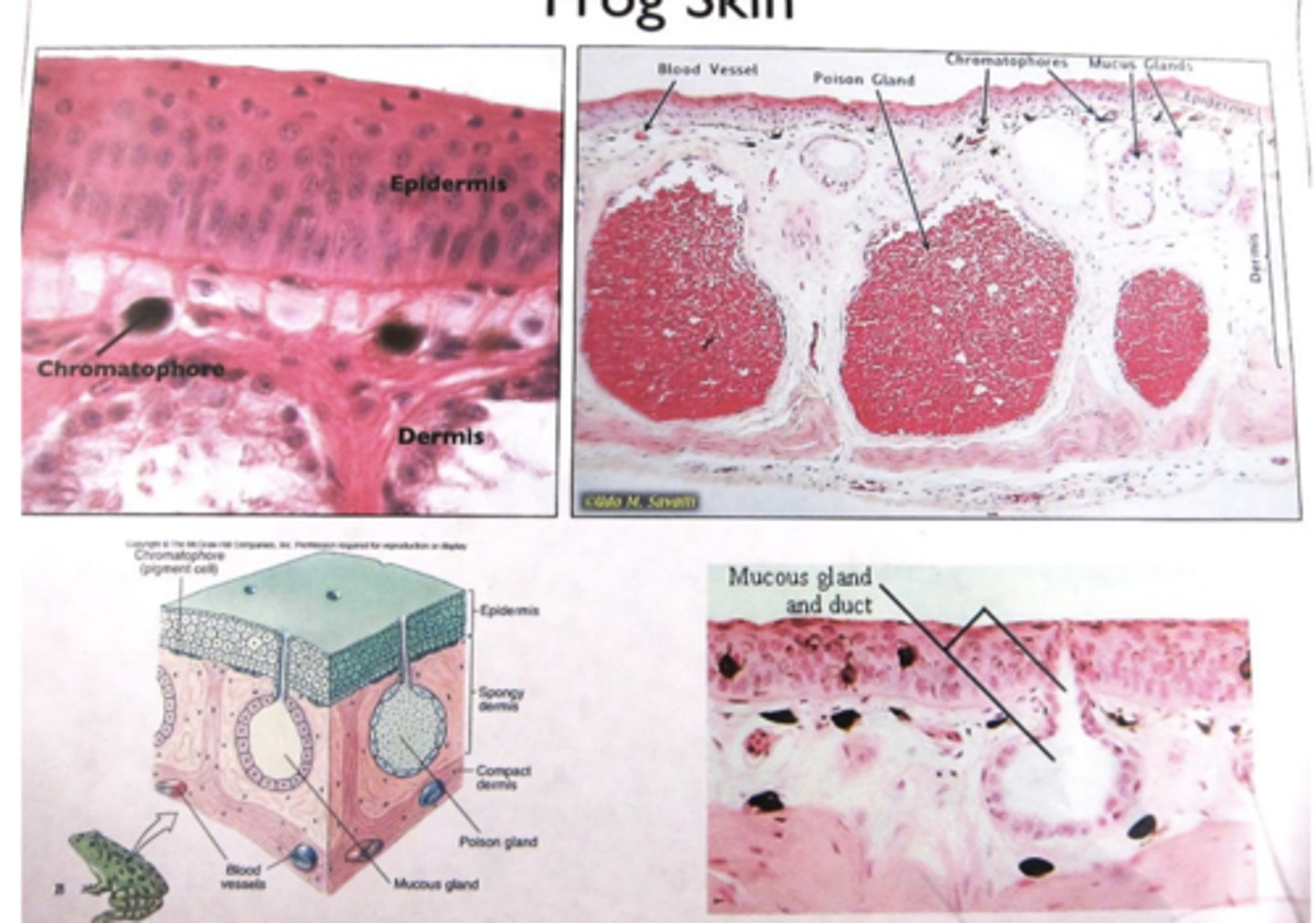
CAN U label frog skin
yes i can label frog skin
frogs and toads phylum, subphylum, and class
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Amphibia
frogs develop w metamorphosis. what is a tadpole?
frog larva
frogs must live close to water. why?
• Most frogs go through an aquatic larval stage (tadpole), followed by metamorphosis into a semi-aquatic terrestrial adult.
• Amphibians have a very limited ability to conserve body water.
• Amphibians primarily use their skin as a respiratory surface, so they must stay moist.
vertebrates (frog and humans) have an endoskeleton (internal skeleton). what are the characteristics of an endoskeleton
• Allows for much larger growth compared to exoskeletons
• Protects the internal organs
• Serves as a support structure for muscles to attach to
• Has great flexibility and mobility due to the large number of separate bones
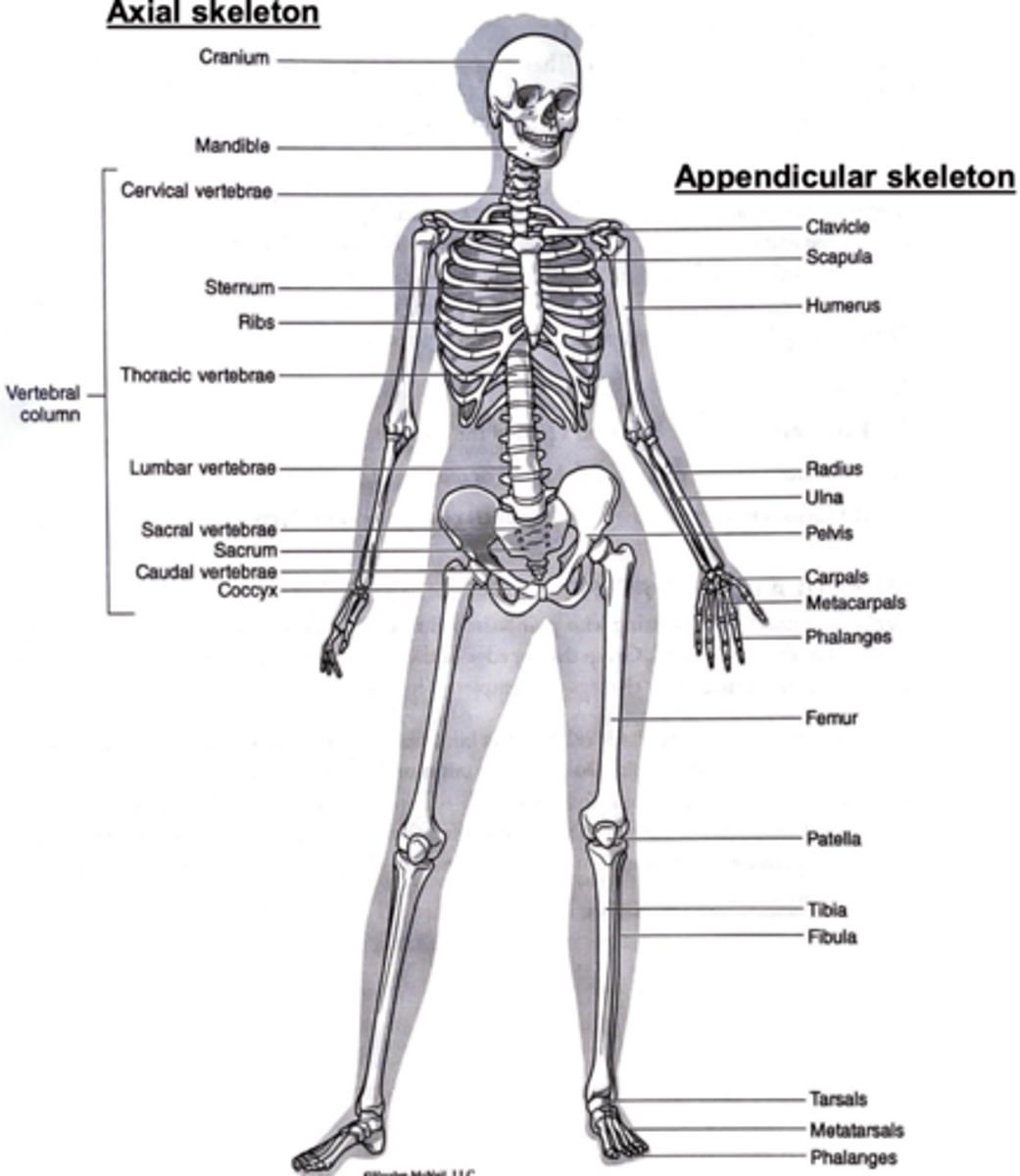
axial skeleton has...
skull, vertebral column, sternum/ribs
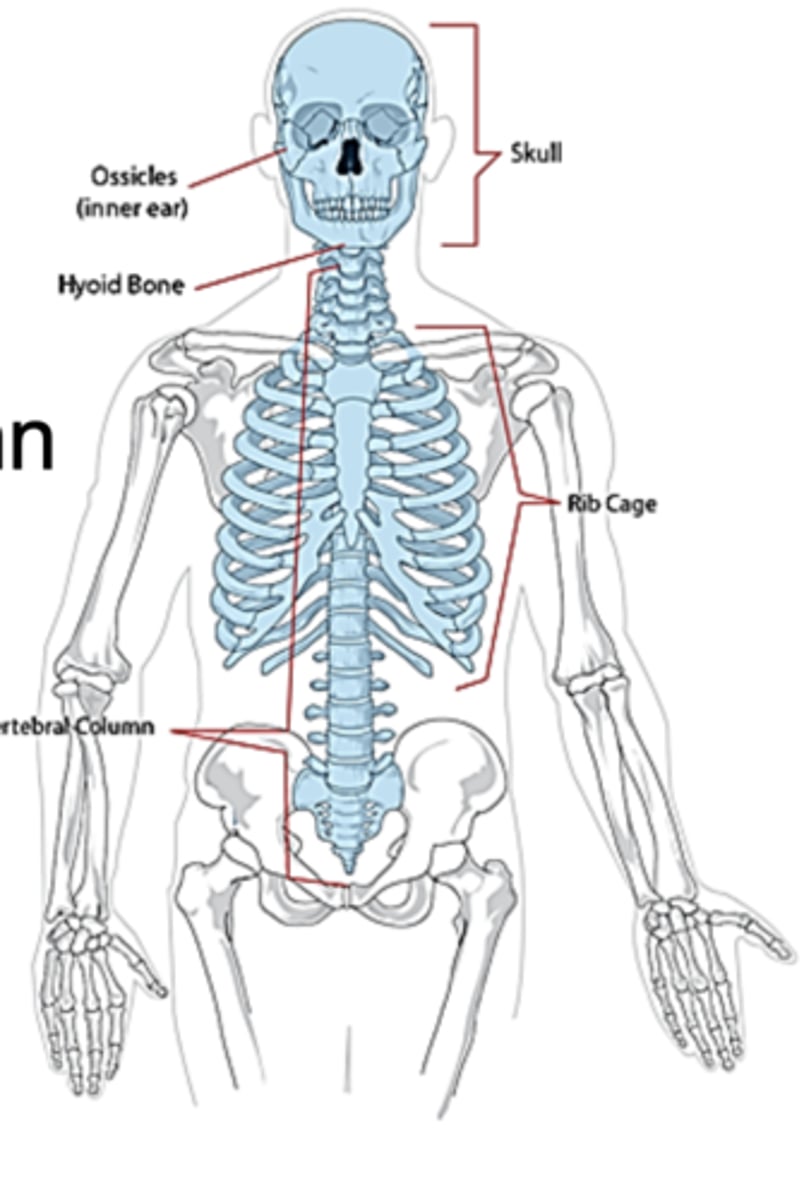
Appendicular skeleton has...
• Shoulder girdle
• Pelvic girdle
• Limbs
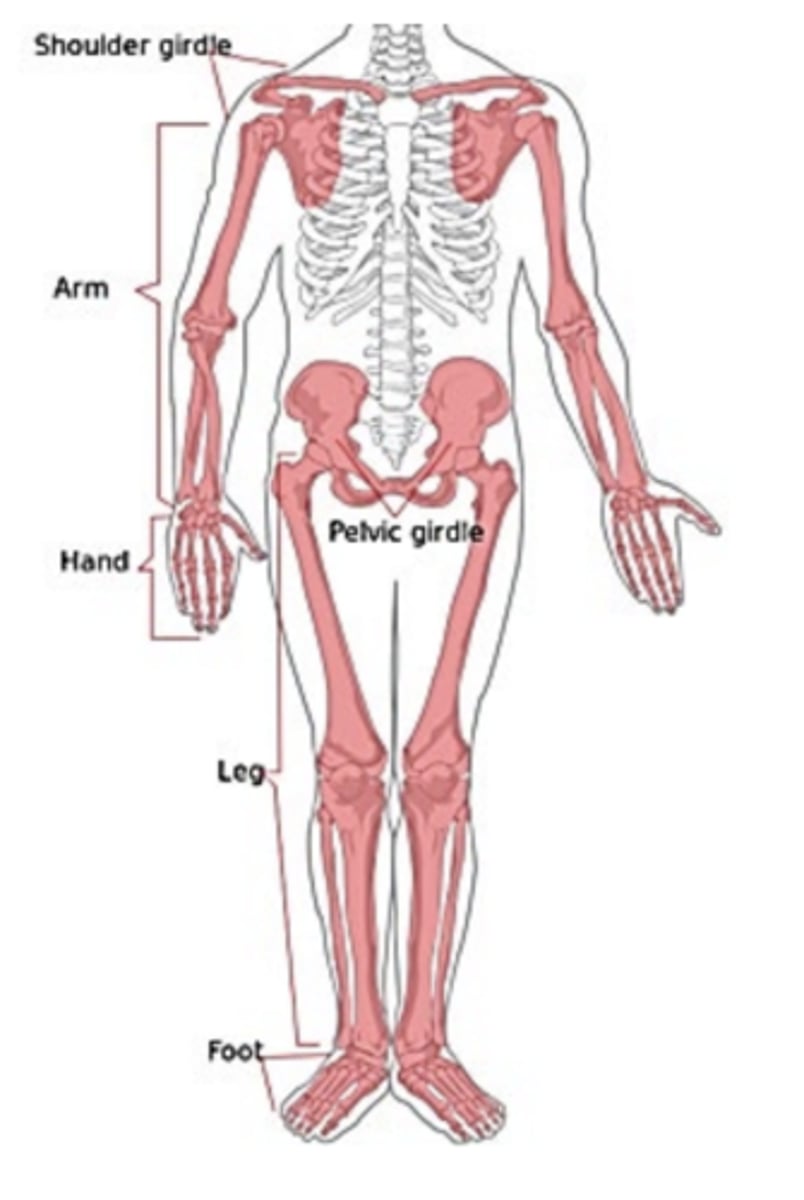
you must know the human skeletal anatomy
okay ill try
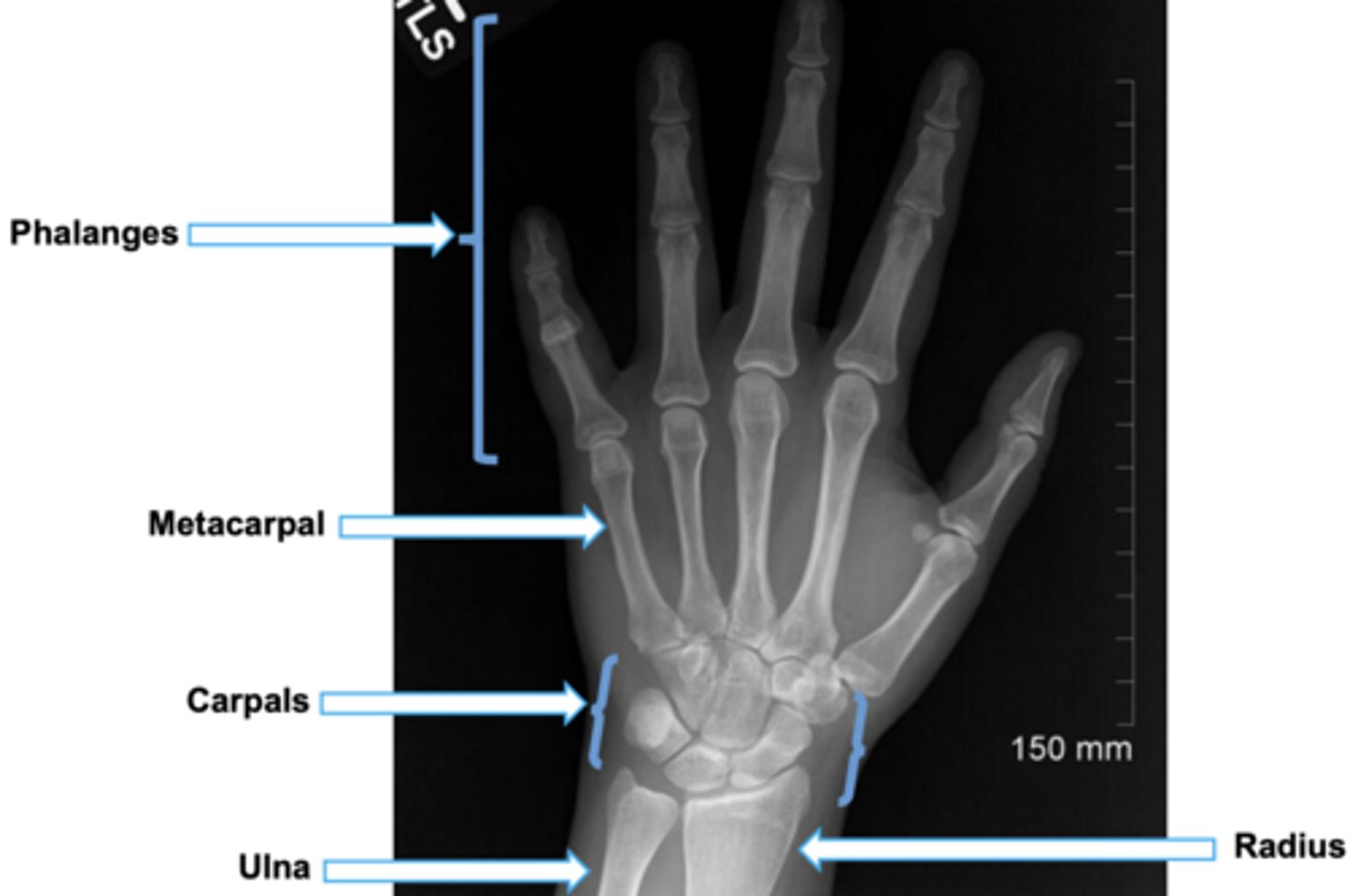
do u know the human hand anatomy??
yes, ik the human hand anatomy
u must know the frog skeletal anatomy
ok ik the frog skeletal anatomy
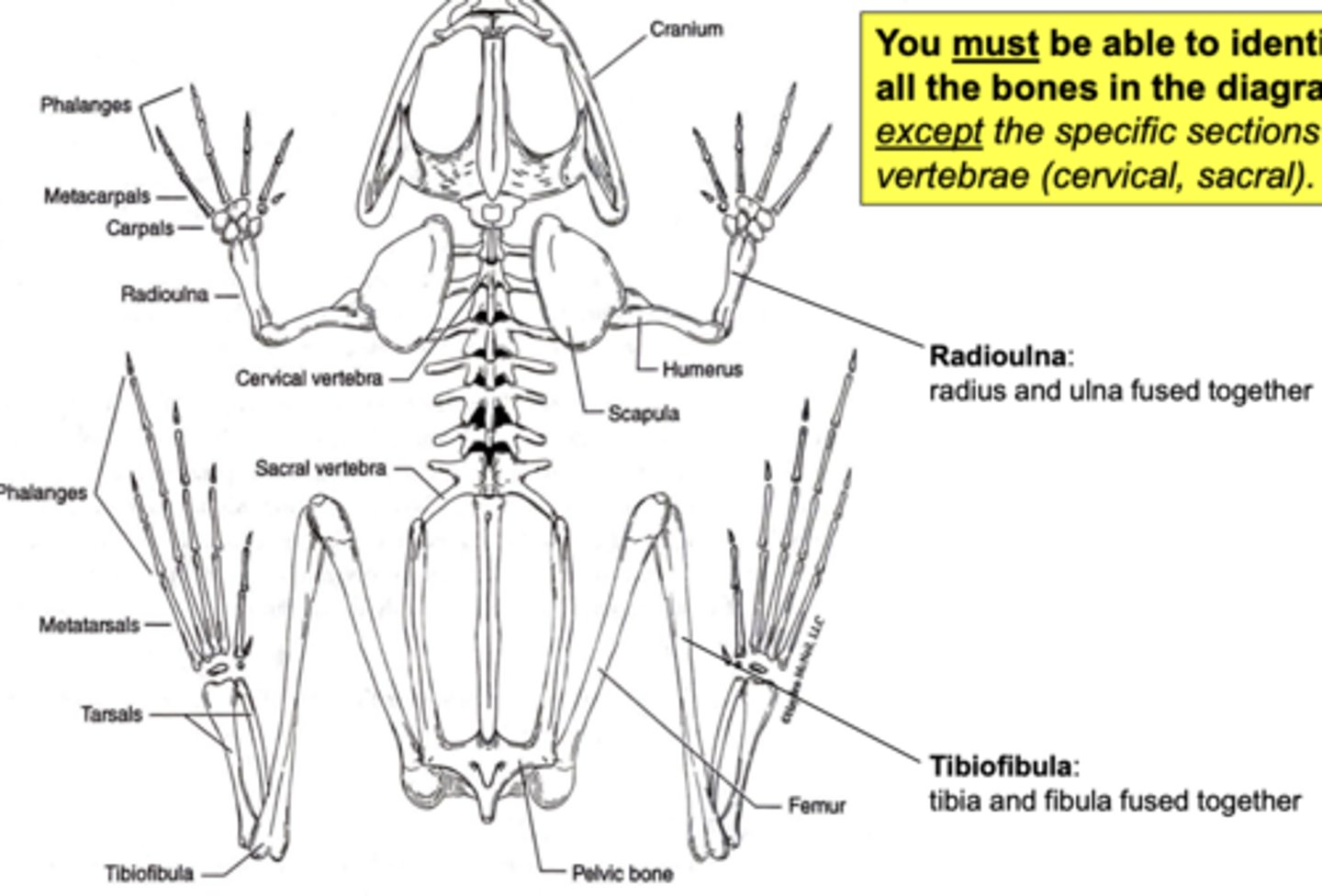
radioulna and tibiofibula
radius and ulna fused together, tibia and fibula fused together
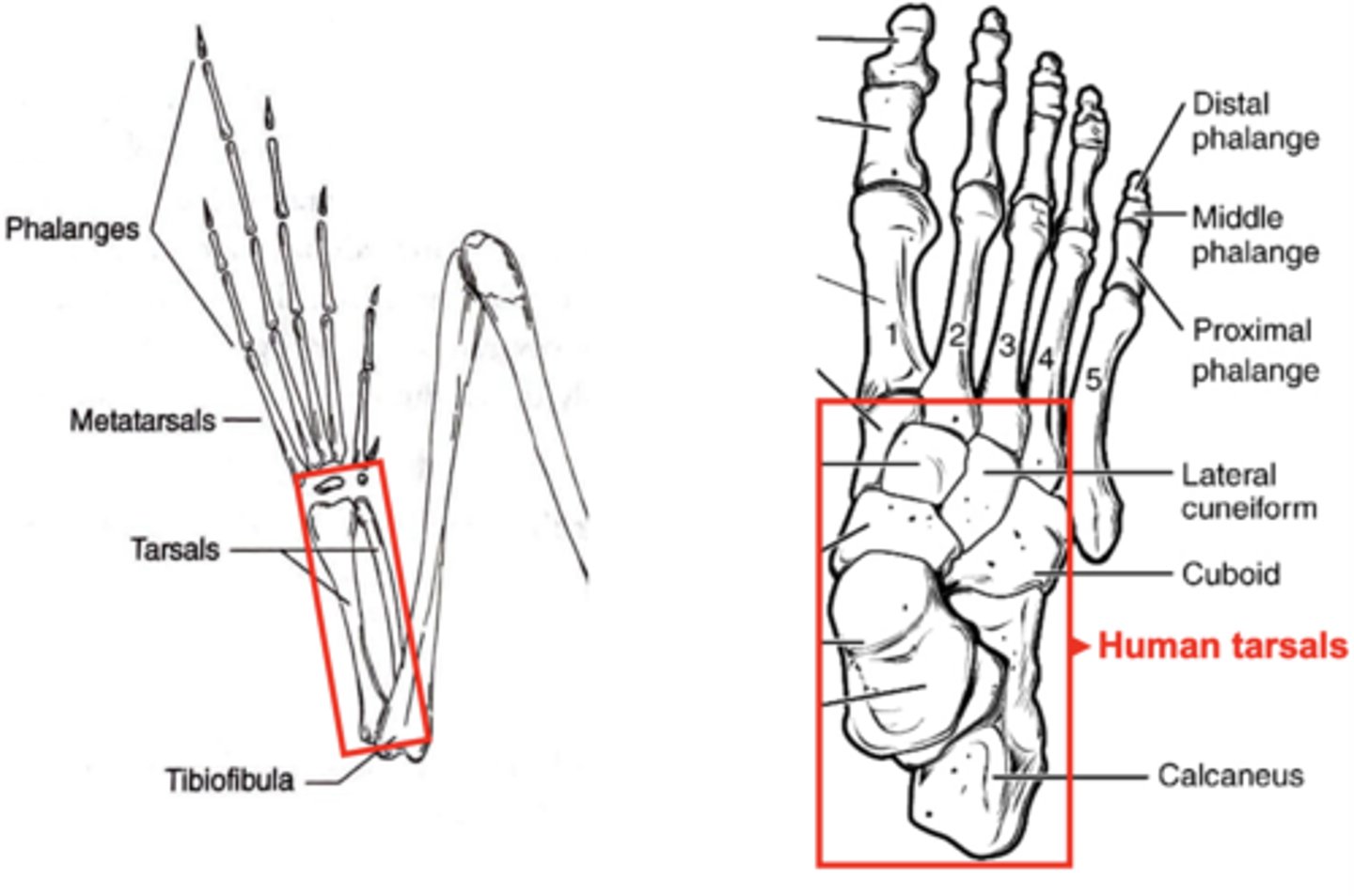
frogs vs human tarsals..who has bigger ones
humans do
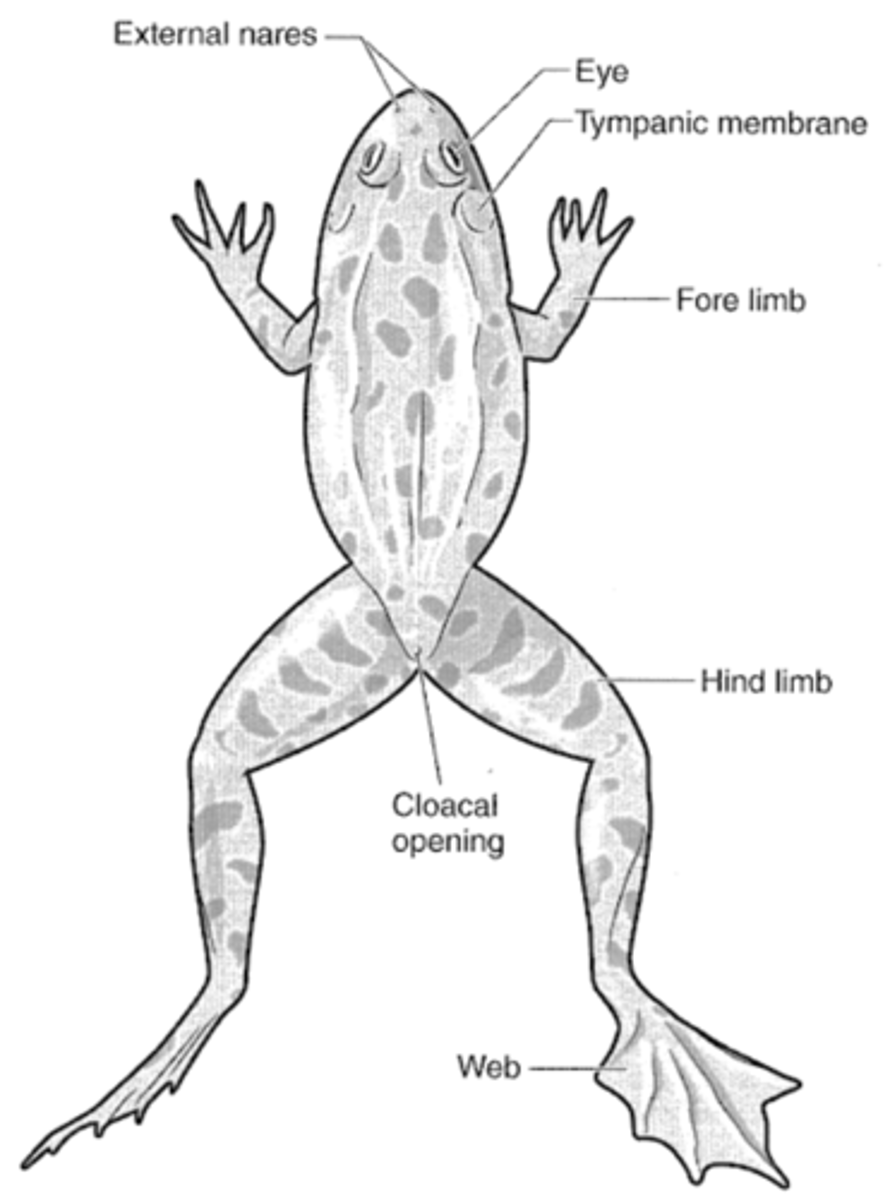
can u point out these structures on a frogs external anatomy?
Eyes
External nares (nostrils)
Tympanic membrane (eardrum)
Cloacal opening (for digestive, urinary, and genital tract discharge)
Webbed feet
yes, i can point out these structures
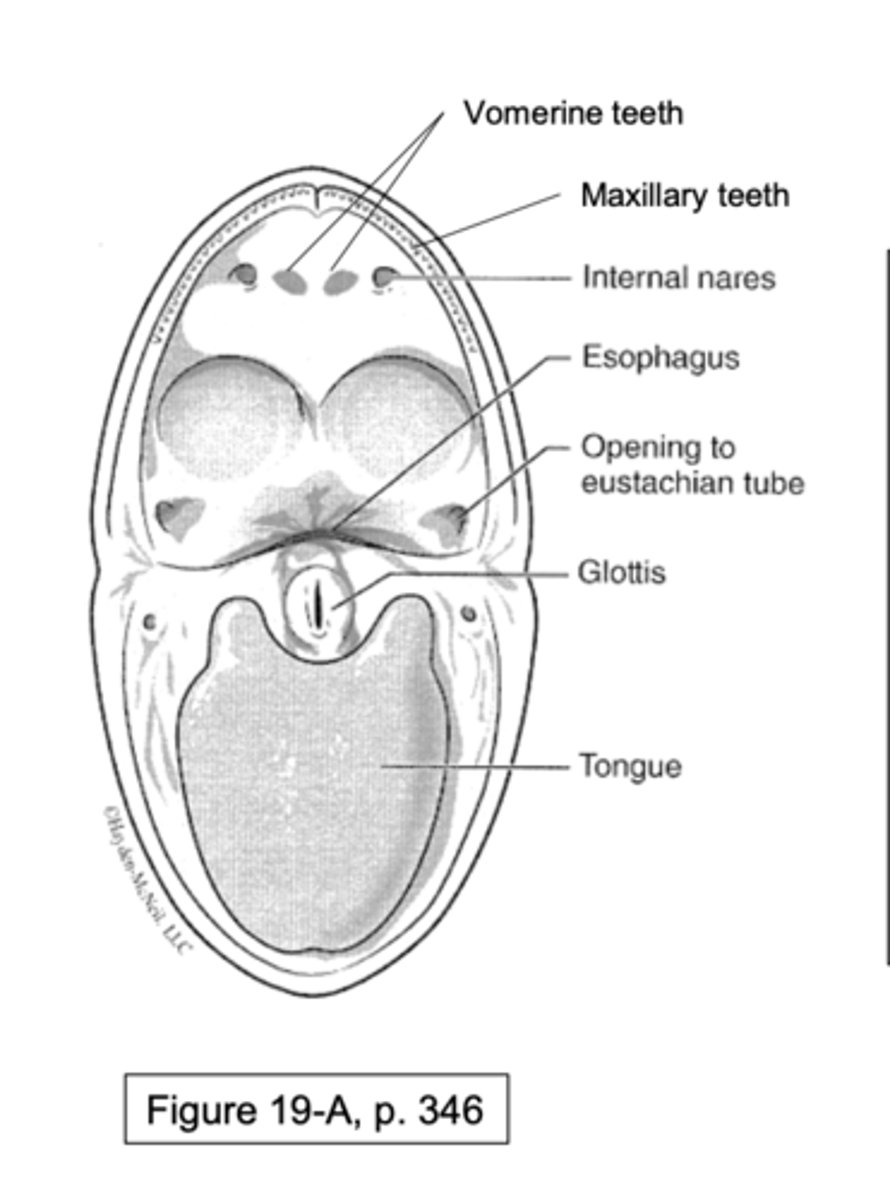
can u point out these structures on a frog oral cavity?
Vomerine teeth
Maxillary teeth
Internal nares (connect to external)
Eustachian tube opening (connects to ear under tympanic membrane)
Esophagus
Glottis (opening to lungs, keeps food out)
Tongue
yes, i can see structures on a frog oral cavity
frog tongue characteristics
Tongue is elastic and located near the front of the mouth
• Saliva is a two-state fluid (liquid and viscous) that instantly can change during prey capture
Muscles are arranged in opposing pairs: what does this mean
one muscle moves a bone in one direction, and an opposing muscle moves it in the opposite direction.
flexor
causes bending at joint
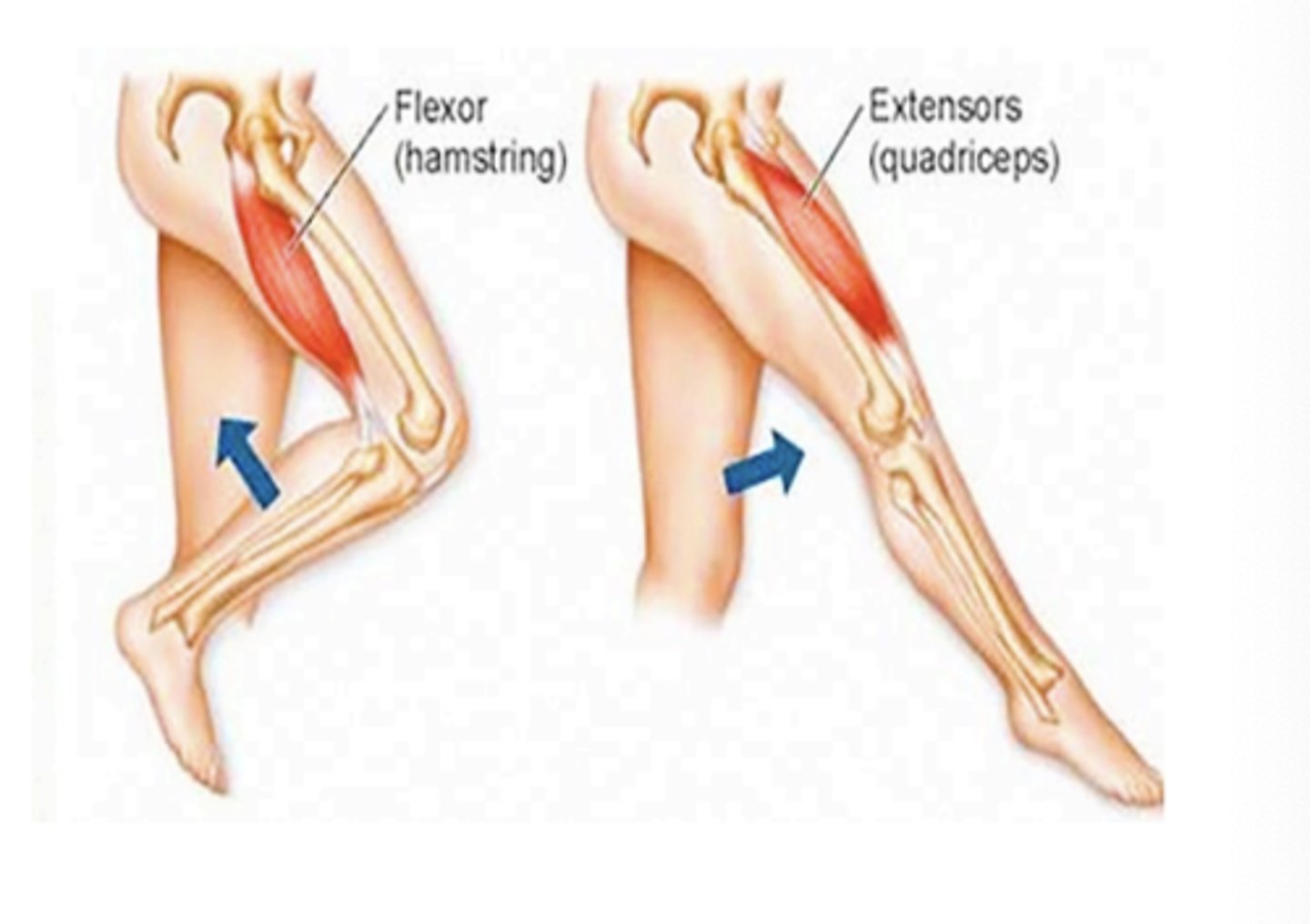
extensor
straightens or extends joint
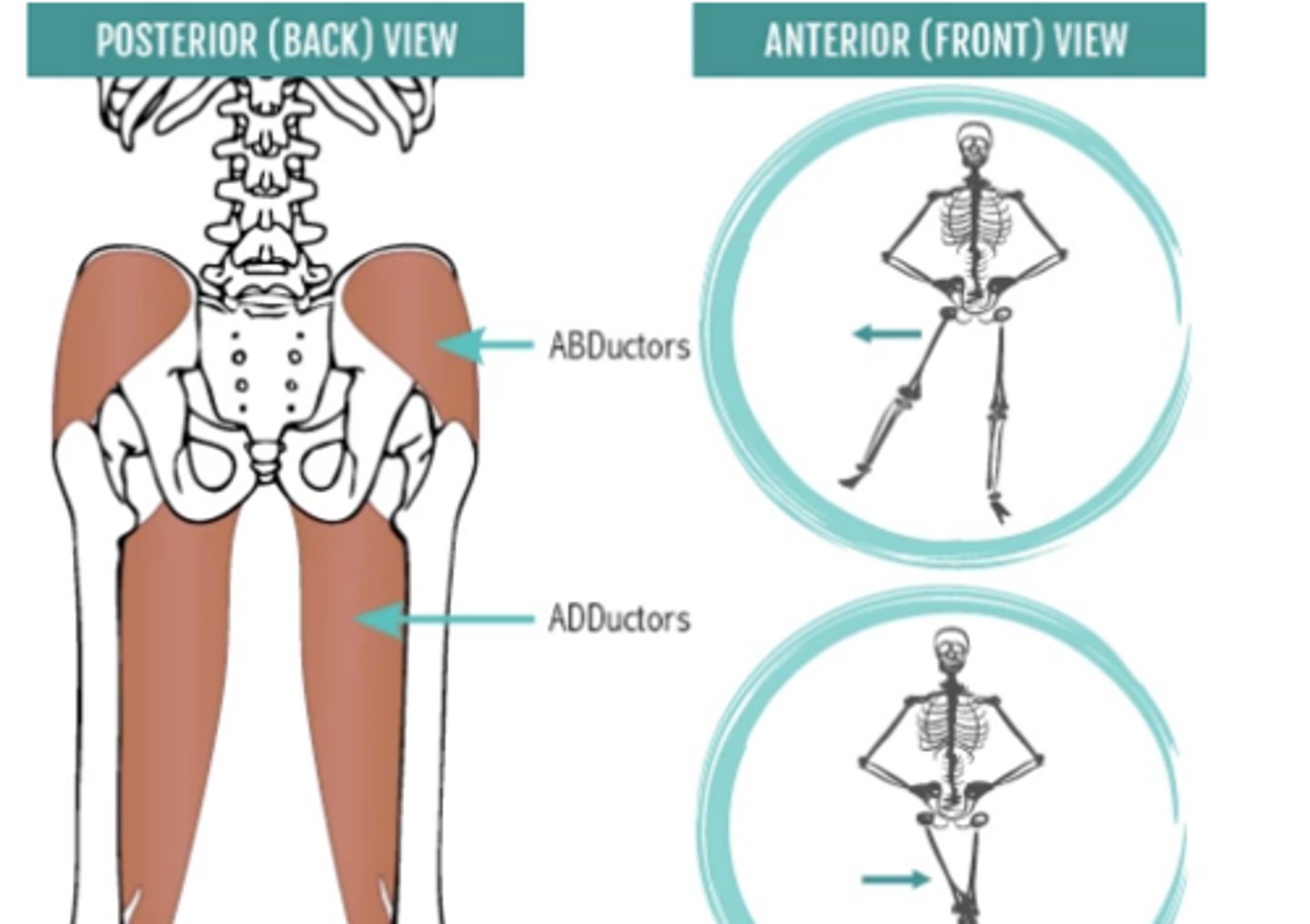
adductor vs abductor
Adductor - moves a body part toward the midline
Abductor - moves a body part away from the midline
flexors and extensors control bending at the ___
knee
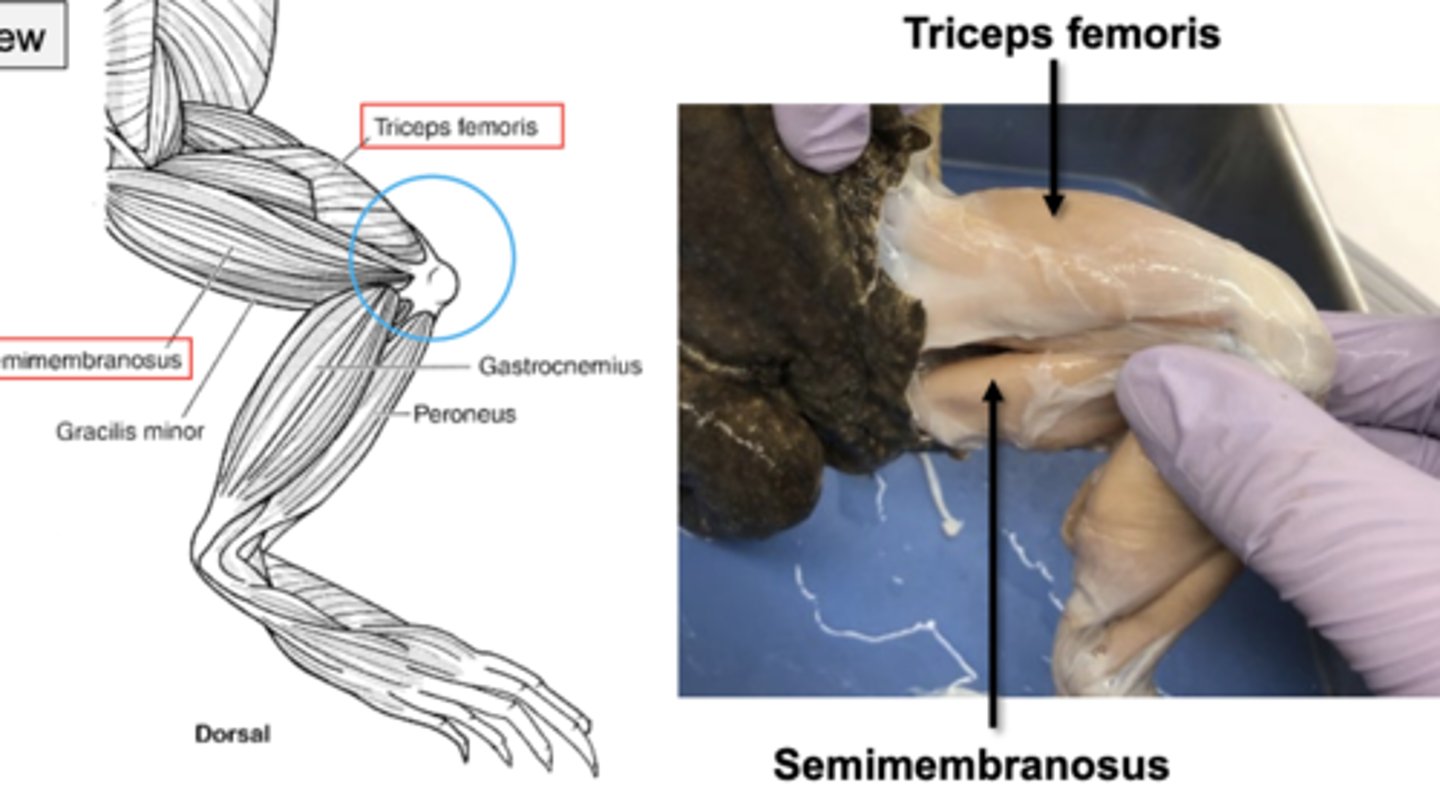
upper leg muscles have triceps femoris and semimembranosus (opposing movements at knee joint). this is at the dorsal view. which one flexes and which one extends
triceps femoris extends, semimembranosus flexes
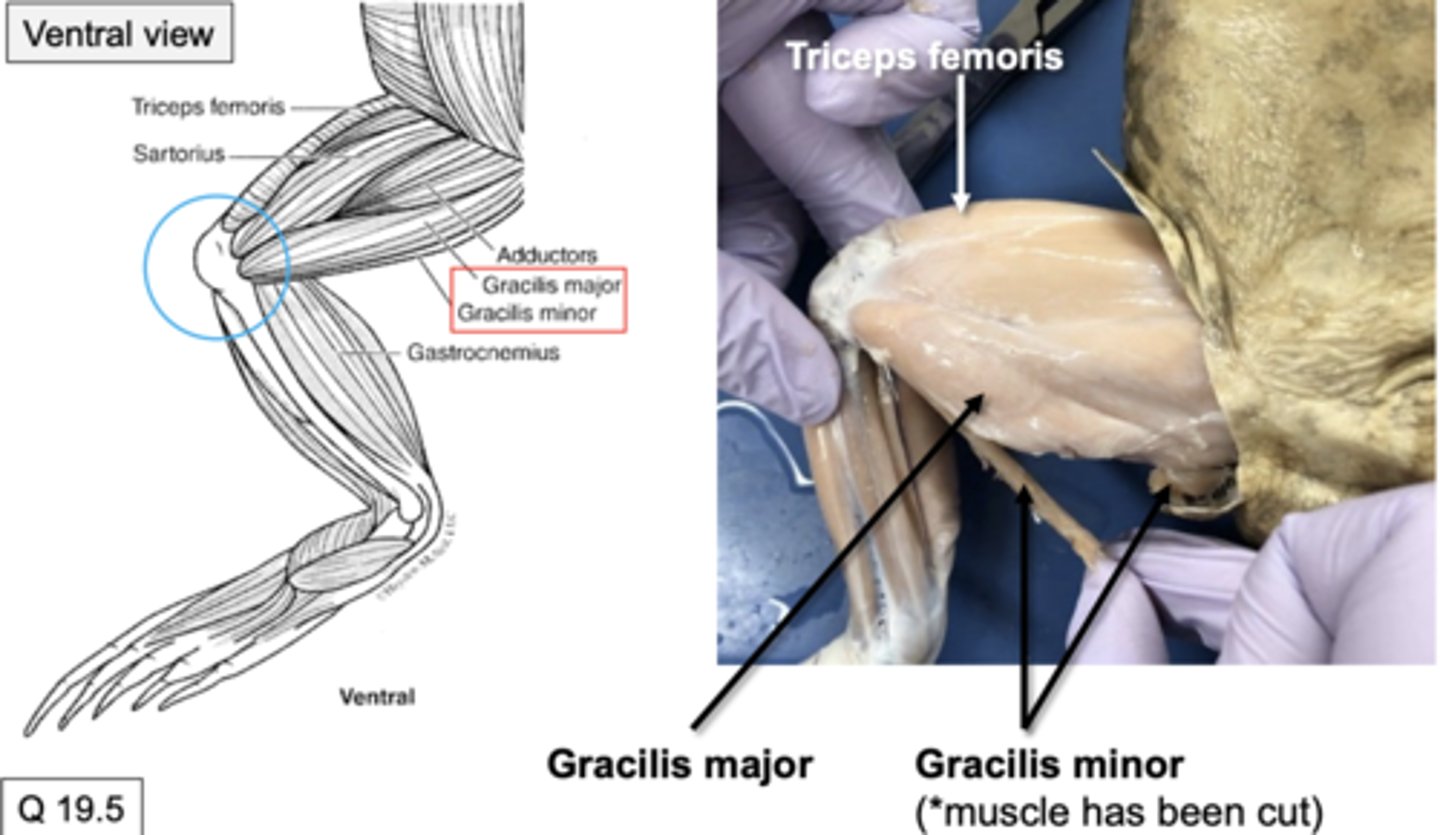
upper leg muscles also have gracilis major and gracilis minor (Flexion at the knee joint) (ventral side). do these muscles flex or extend
they flex at the knee joint
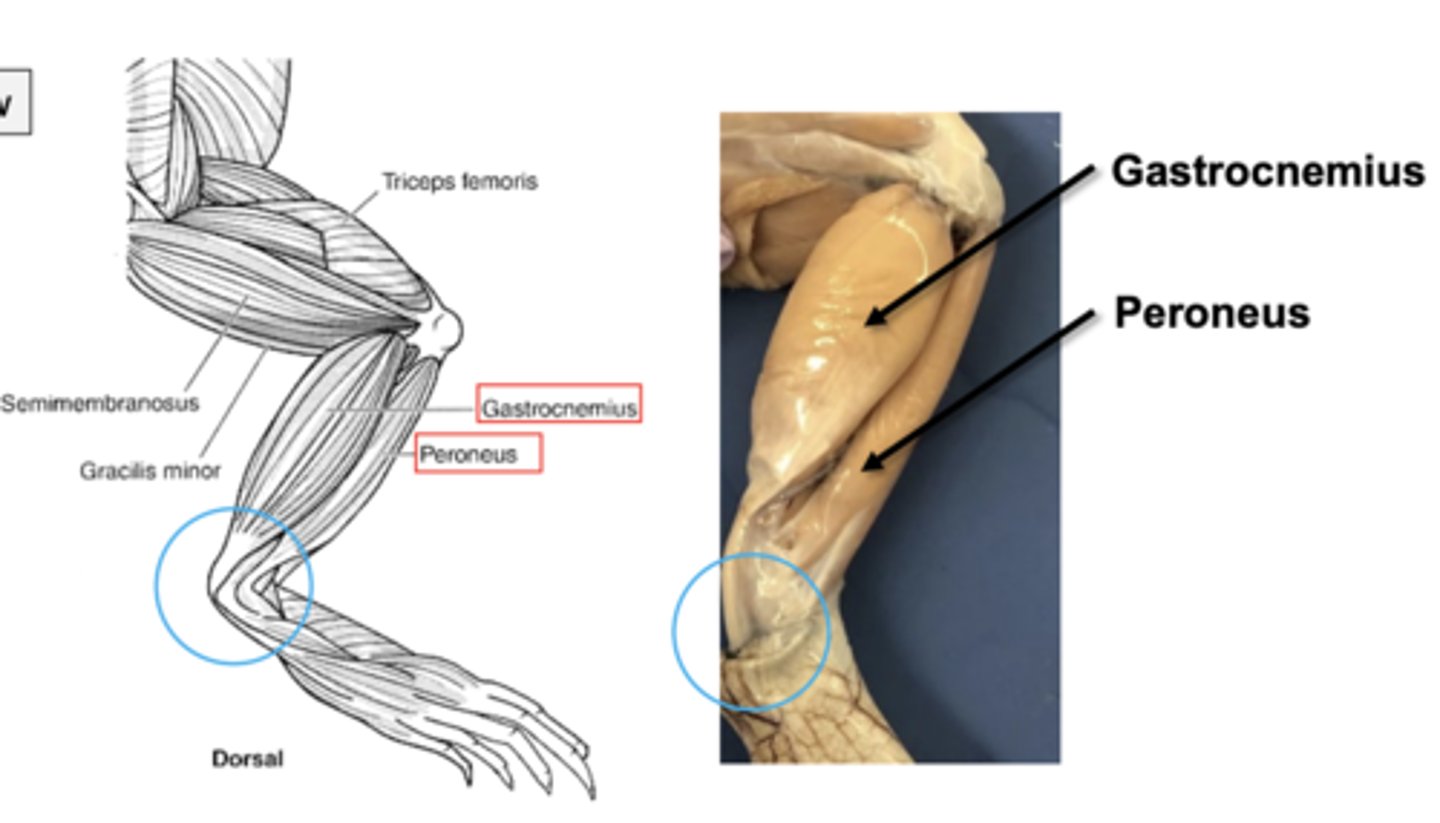
lower leg muscles include gastrocnemius and peroneus. which one is a flexor and which is an extensor???
flexor: peroneus
extensor: gastrocnemius
in frog hindlimb muscles, adductor muscles move thigh towards the midline. which upper leg muscles are included in this
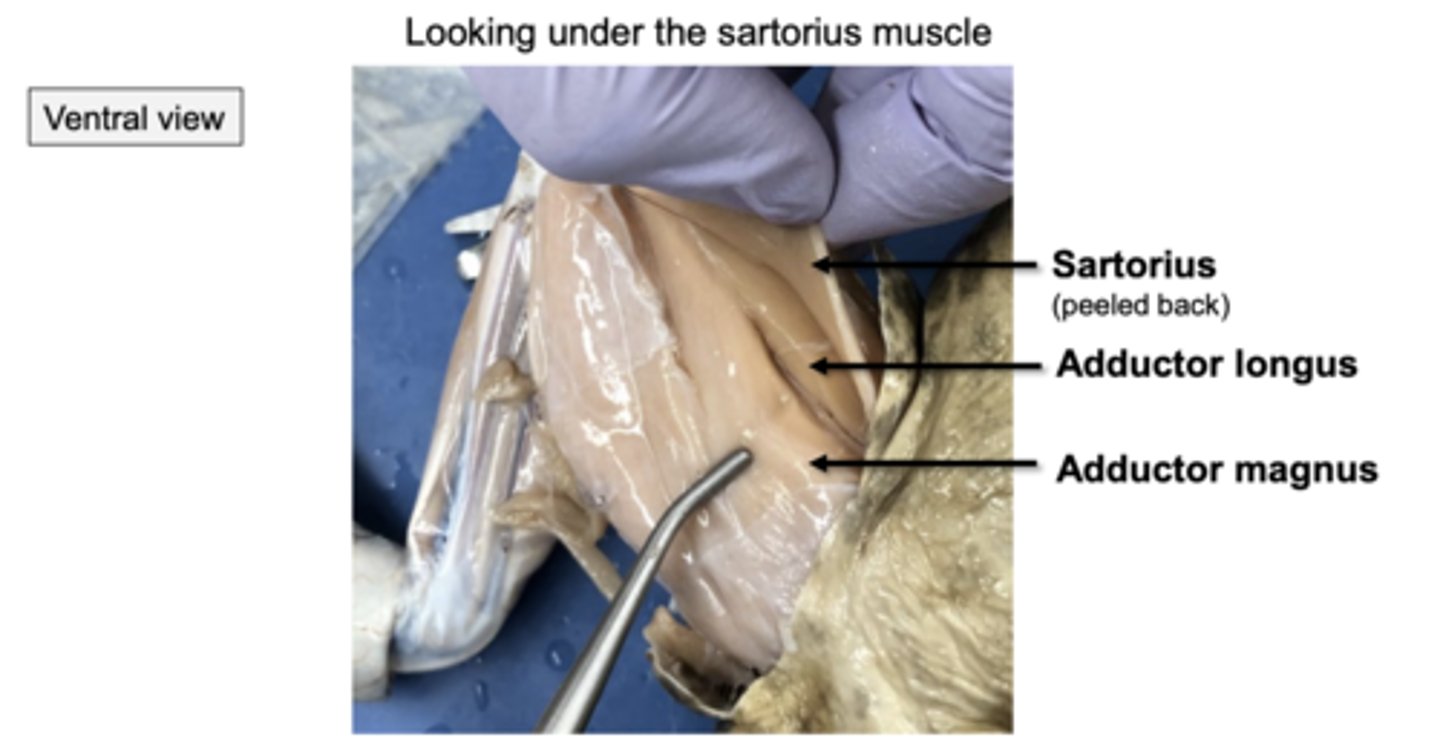
adductor longus, adductor magnus, and sartorius (ribbon like muscle)
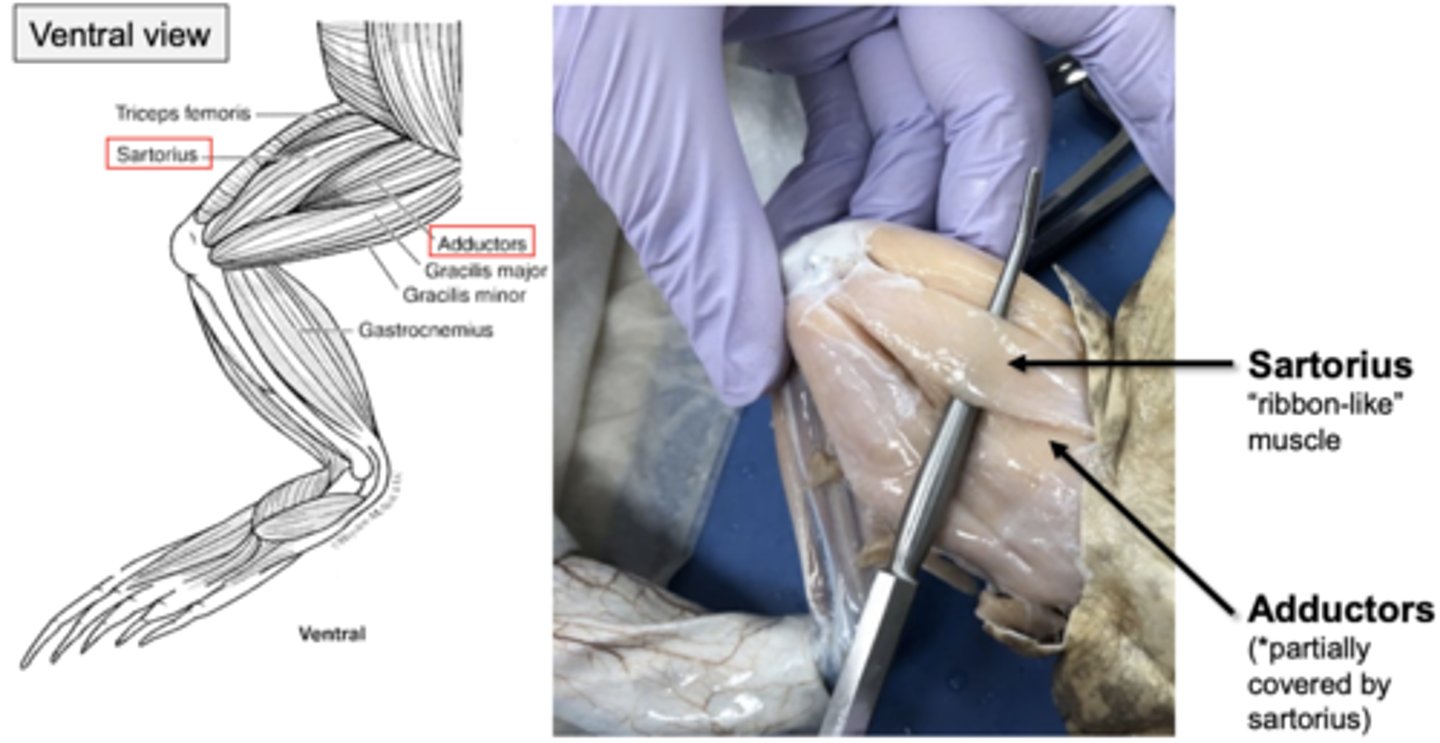
what do the adductor longus, adductor magnus, and sartorius muscles look like in ventral view?
this is what they look like in ventral view
Coelom:
Body cavity
Peritoneum:
Layer of epithelium that lines the internal body cavity
Mesenteries:
Sheets of epithelium that extend from the dorsal body wall to the organs to stabilize them
Pericardium:
Sac containing the heart
do u know the frogs internal anatomy?
yes ik the frogs internal anatomy
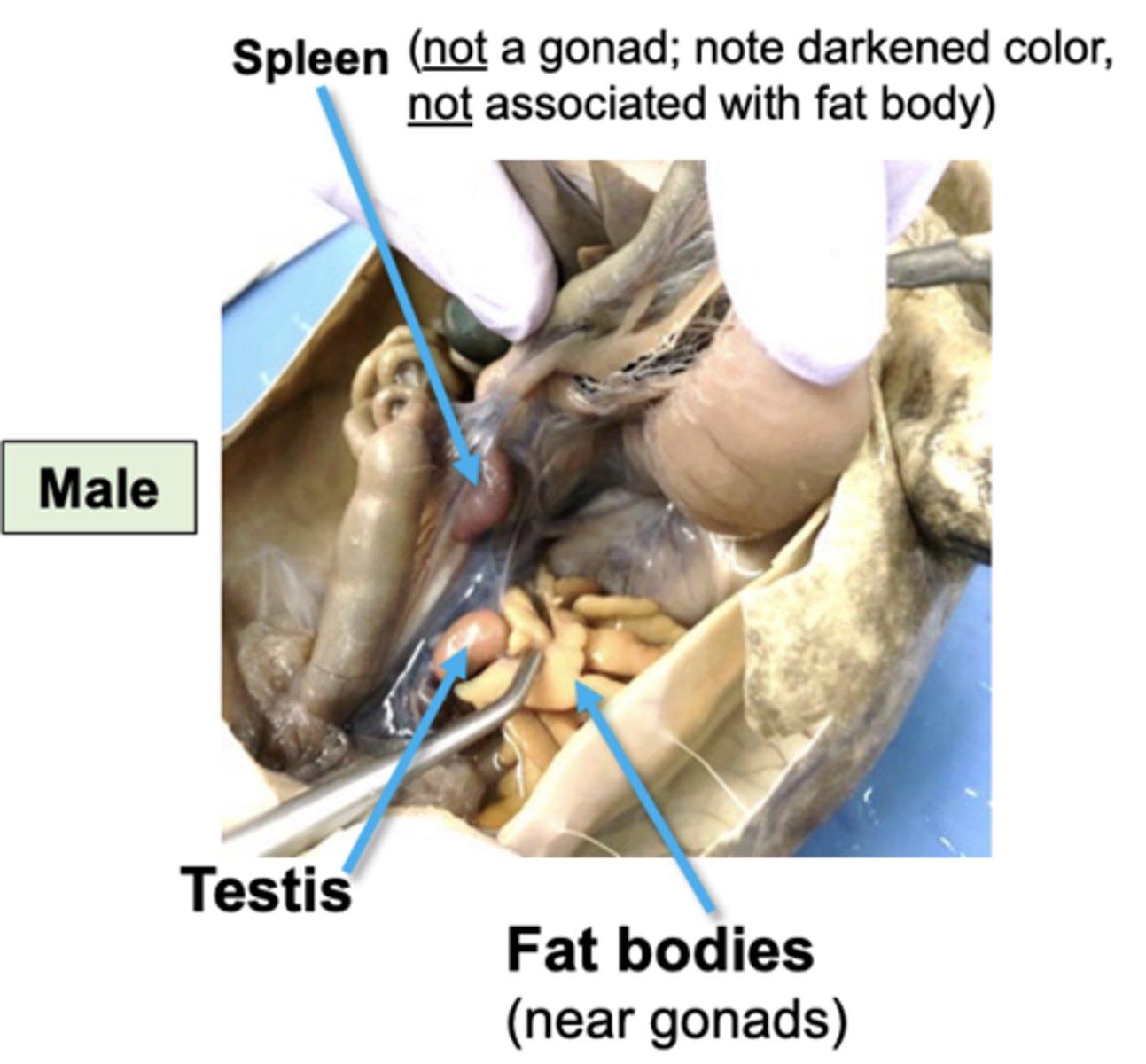
what do male testes look like
testes look like this
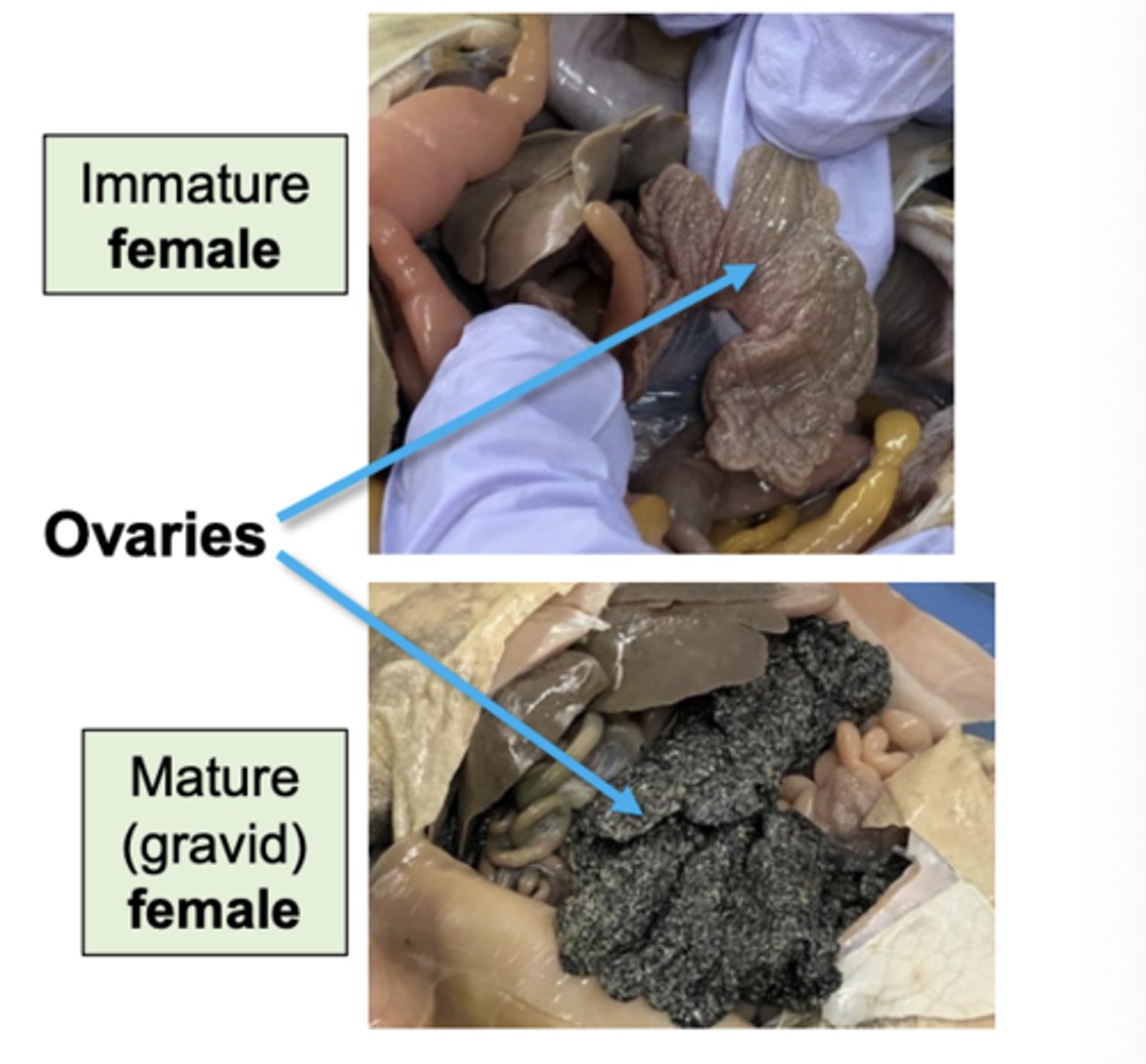
what do female ovaries look like
female ovaries look like this
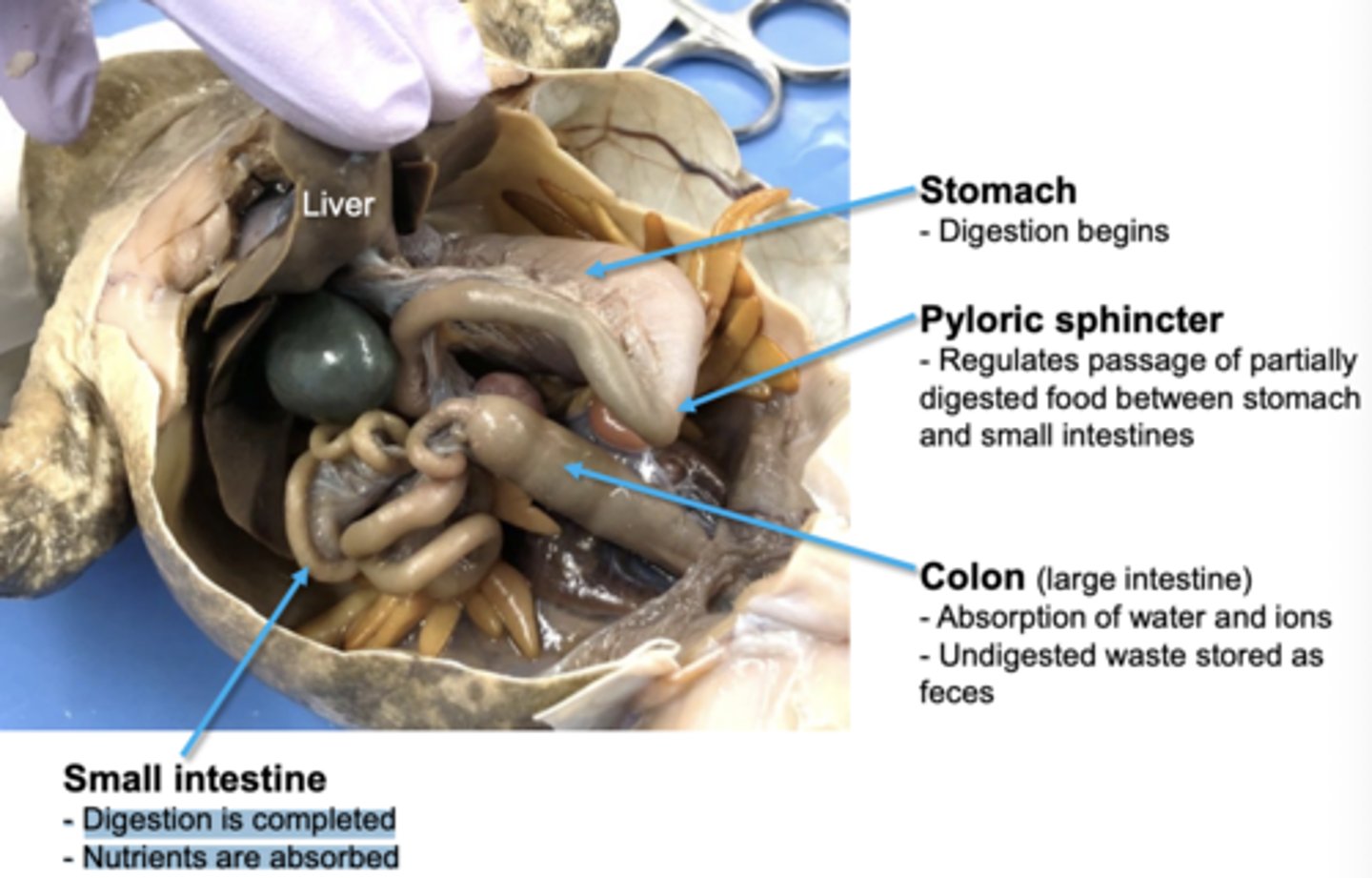
what are the main organs of the frog digestive system
stomach, pyloric sphincter, small intestine, colon