Human Development Key Terms
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 3 SUPA Psychology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
biological development
how biological factors like genetics, brain structure, and neurochemistry interact with environmental influences to shape a person's physical, cognitive, and behavioral development from conception through adulthood
2 stage theories of development
piaget
erikson
self-determination theory
people are driven by innate needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness.
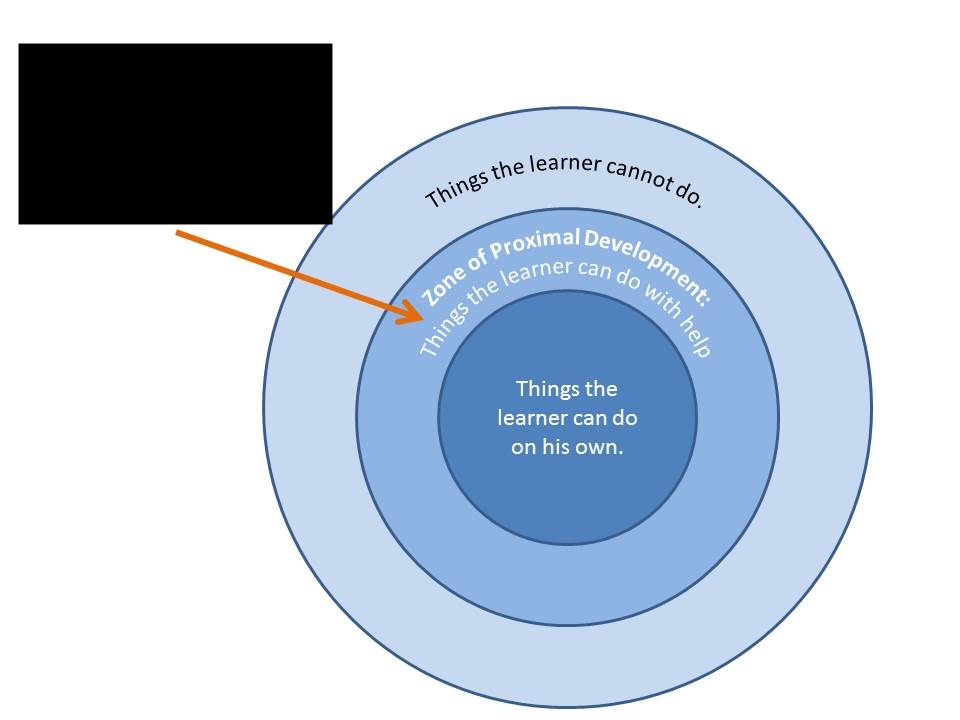
zone of proximal development
the "sweet spot" for learning where a task is challenging but not too difficult, as it's "just right" for developing new skills with support.
heritability
a statistical measure of how much of the variation in a trait within a population is due to genetic differences among individuals
personality traits
Openness
Contentiousness
Extroversion
Agreeableness
Neuroticism
risk factors
conditions or behaviors that increase the likelihood of a negative outcome (ex: mental health problem, academic failure)
protective factors
characteristics that decrease that likelihood or reduce the impact of risk factors, thereby promoting resilience (ex: supportive family relationships)
harlow experiment
infant monkeys preferred a surrogate mother made of cloth for "contact comfort" over a wire surrogate that provided food. this demonstrated that emotional and physical comfort, not just nourishment, are crucial for infant development and attachment.
maslow’s hierarchy of human needs
self-actualization
esteem
love and belonging
safety needs
physiological needs
2 forms of attachment
bowlby
ainsworth
4 types of parenting styles
authoritarian
authoritative
permissive
uninvolved
authoritarian parenting style
strict, high-control style where parents set high demands for obedience but offer little warmth, responsiveness, or negotiation
authoritative parenting style
a balanced approach that combines high expectations with warmth and support, setting clear rules while explaining the reasoning behind them
permissive parenting style
high warmth and low demands, “kids will be kids”
uninvolved parenting style
low responsiveness and low demands, where parents are emotionally distant, provide little guidance or support, and fulfill only basic needs like food and shelter
bowlby & ainsworth say…
the emotional and social development of an infant is profoundly shaped by their relationship with their primary caregivers
piaget
children's intelligence progresses through four distinct, sequential stages: the sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational stages. this development occurs as children actively construct knowledge through interacting with their environment.
erikson
personality develops over a lifetime through eight stages, each with a specific crisis that must be resolved.
infancy (trust vs. mistrust)
early childhood (autonomy vs. shame and doubt)
preschool (initiative vs. guilt)
school age (industry vs. inferiority)
adolescence (identity vs. role confusion)
young adulthood (intimacy vs. isolation)
middle adulthood (generosity vs. stagnation)
maturity (ego integrity vs. despair)