Physio Lect 4 - Resting Membrane Potential
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
______ bring signals to the neuron cell body
dendrites
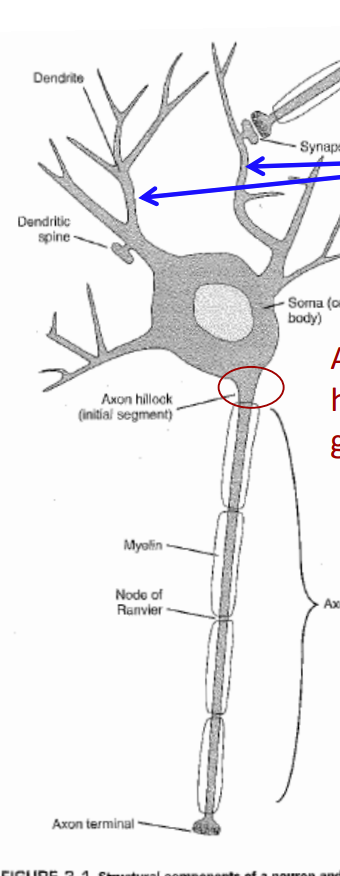
At the initial segment, which is located just beyond the axon hillock, the changes in resting membrane potential result in generation of an ___________
Action potential
What is the name for the cell body?
soma
What sends action potentials (signals) to other cells?
Axons
What is membrane potential?
the voltage difference between the innards of a cell and the ECF (extracellular fluid)
T/F: All living cells have a membrane potential
True
T/F: The inside of cells is more “negative” than the outside of cells
True
At rest, this membrane potential ranges from ______ for some glial cells in the brain to about _____ for red blood cells.
-95 mV
-20 mV
Can ions pass directly through membranes?
NO!
What allows ions to pass through membranes?
Proteins in the membrane (transport proteins)
Are these ions moved passively or actively through membranes?
BOTH!
K+ is ____ inside the cell and ___ outside the cell.
high
low
Na+ is ____ outside the cell and ____ inside the cell.
high
low
What are the two driving forces limiting the diffusion of K+
Chemical driving force (Conc. gradient - more K+ inside cell)
Electrical driving force (more -ve inside cell)
What is Equilibrium Potential?
When outward movement is equal to the inward movement
K+ ions follow concentration gradient from _______to _______the cell, generating an ________flow of positive charges
inside
outside
outward
The ____ Equation is used to calculate the equilibrium potential for K+
Nernst
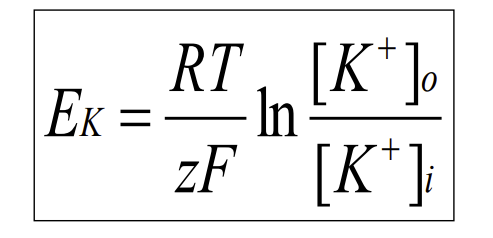
What do each of the variable stand for in this equation?
R = gas constant
T = absolute temperature
z = valence of K+
F = Faraday’s constant
[K+]o = K+ outside cell
[K+]i = K+ inside cell
The calculated membrane potential when NO NET current flow through the ion channel occurs (even if open)
Equilibrium Potential
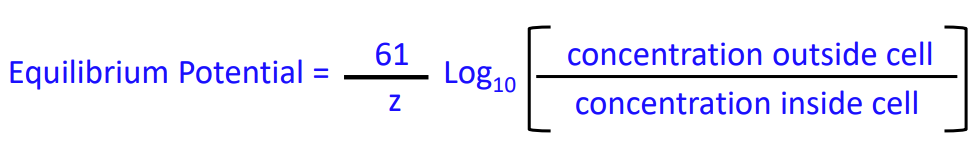
What value of temperature should we use in our equilibrium potential equation?
61
Large anions are ____ inside than outside the cell
Greater
K+ is _____ inside than outside the cell
Greater
Cl- is _______ outside than inside the cell
greater
Na+ is ______ outside than inside the cell
greater
Ca++ is much _____ outside than inside the cell
greater
What is the permeability of K at rest?
1
What is the permeability of Na at rest?
0.04
What is the permeability of Cl at rest?
0.45
What did the Goldman Equation that Hodgkin and Katz used to get the permeability values of K, Na and Cl look like?
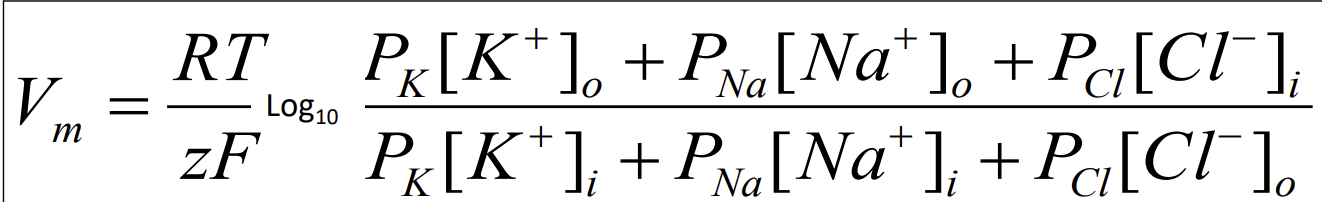
What makes the Na+ - K+ pump (ATPase) so important?
maintains membrane potential
What do we draw equilibrium potential as on a membrane potential vs time plot? And for the net driving force?
Horizontal bar
Arrow
If the membrane potential (Vm) is different than the equilibrium potential (Ex) for an ion and a channel opens allowing the ion to move across the membrane, then…
the ion will flow down its electrochemical gradient to reach equilibrium potential
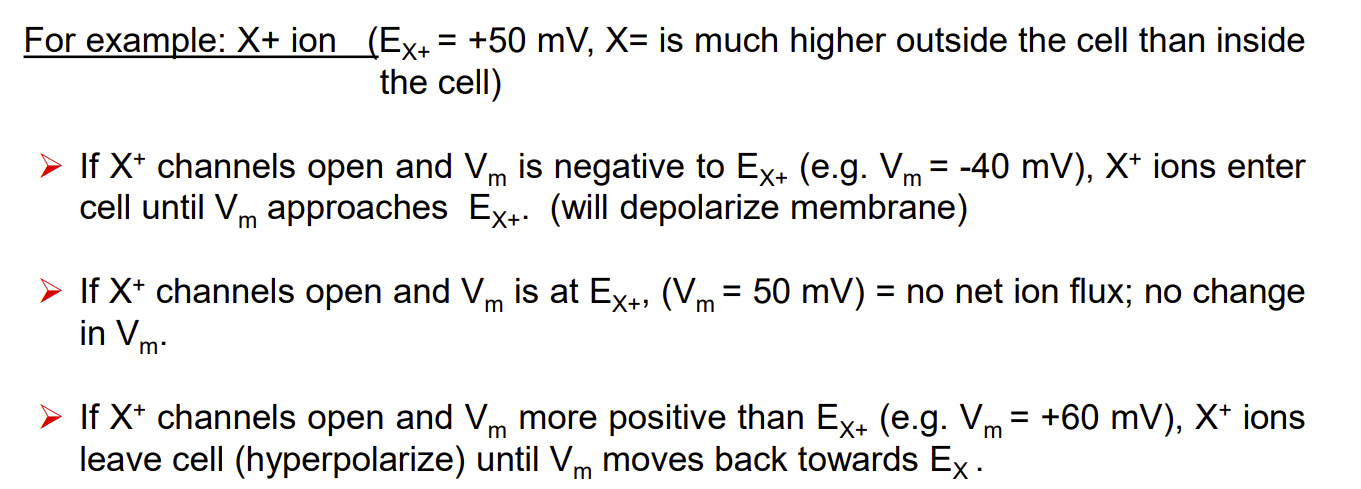
Electric current flowing into and out of the cell is carried by either ___ charged ions (____) and ___ charged ions (______). Whenever there is a net flow of cations/anions into or out of the cell, the charge separation across the resting membrane is disturbed
+ve
cations
-ve
anions
What is the equilibrium potential of Na+?
+67
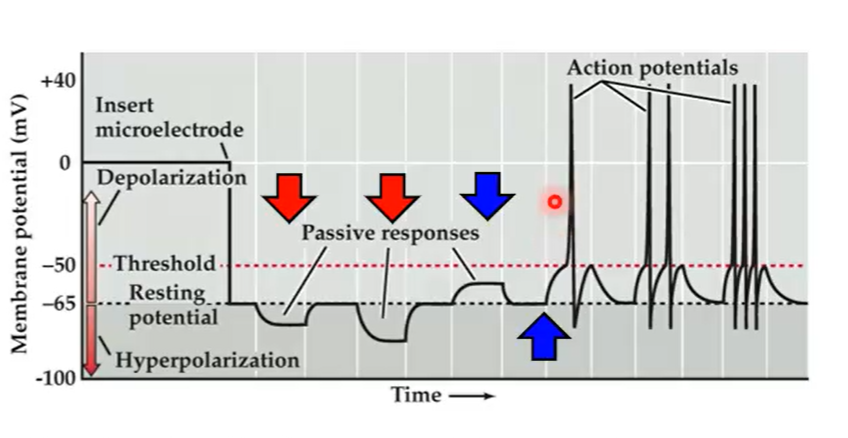
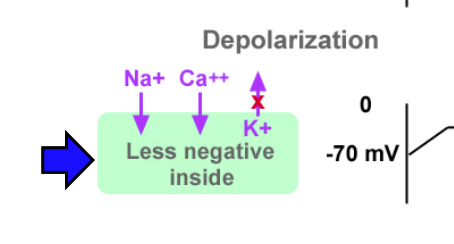
What is depolarization?
when you allow positively charged ions to flow into the cell, causing the potential to move up towards zero and be less negative.
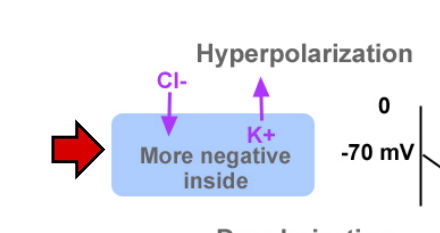
An increase in permeability to K+ (EK+ = -95 mV) and Cl- (ECl-=-89 mV skeletal muscle), by increasing channels that carry these ions, results in ________
hyperpolarization
An increase in permeability to Na+ (ENa+ = +67 mV) and Ca++ (Eca++ = =123 mV) by increasing channels that carry these ions or decreasing outward leak of K+ (EK+ = -95 mV) by inhibiting K+ channels results in ________
depolarization
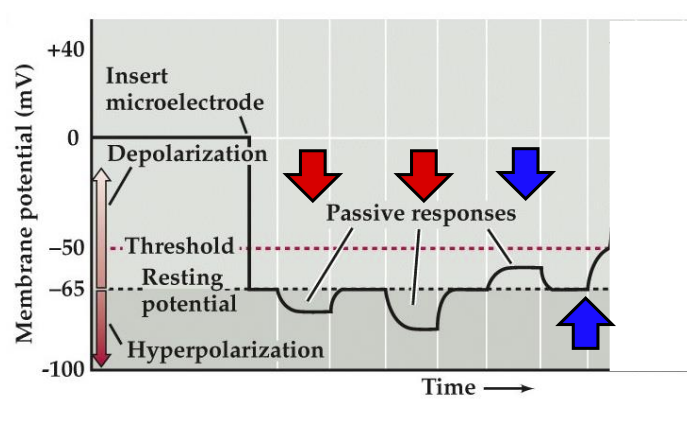
What color arrows demonstrate hyperpolarization?
red
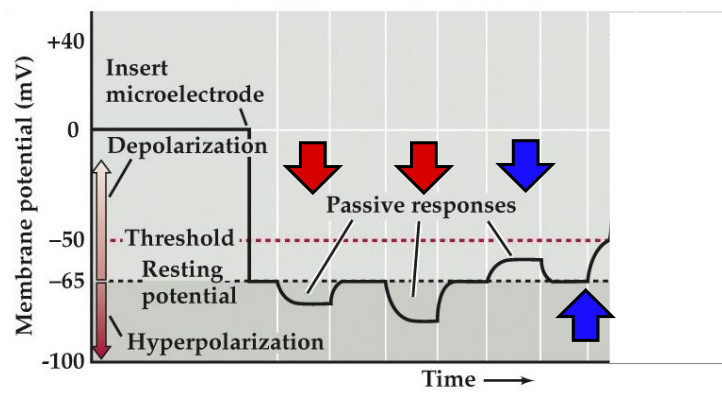
What color arrows demonstrate depolarization?
blue
If the membrane potential gets to a certain point and we depolarize enough, what can happen?
we can get an action potential