Week 4: Enzymes:Regulation, and Mechanisms L5-6, Enzyme Assays and Michaelis-Menten Kinetics
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What are enzymes?
Complex biological molecules that are primarily or entirely protein, acting as biological catalysts.
How do enzymes function in chemical reactions?
They alter the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the reaction.
What determines the stereospecificity of an enzyme?
The shape of the enzyme.
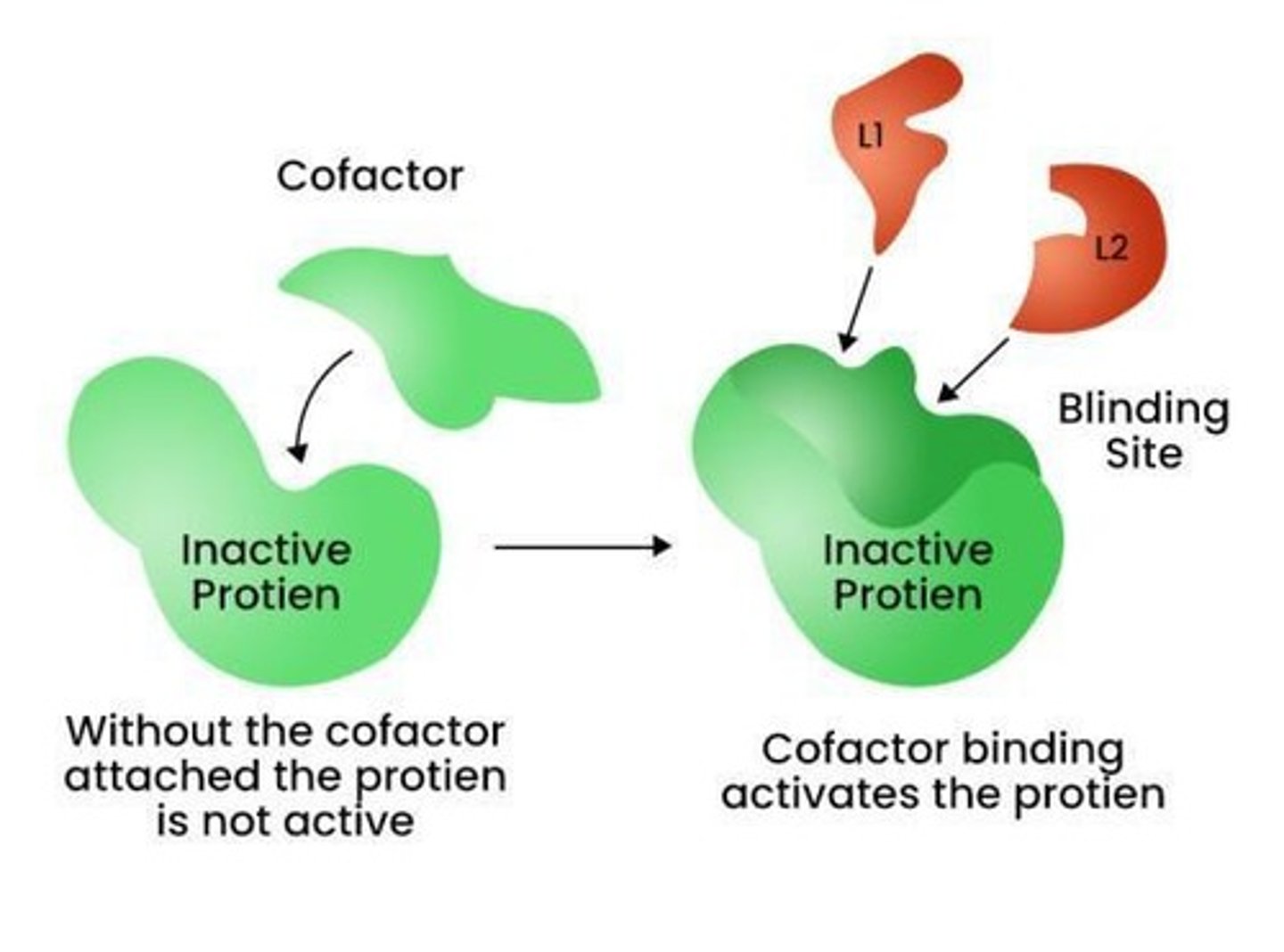
What are cofactors?
Non-protein components that assist enzymes, often metal ions or organic molecules.
What is the difference between an apoenzyme and a holoenzyme?
An apoenzyme is an enzyme lacking a cofactor, while a holoenzyme includes a cofactor.
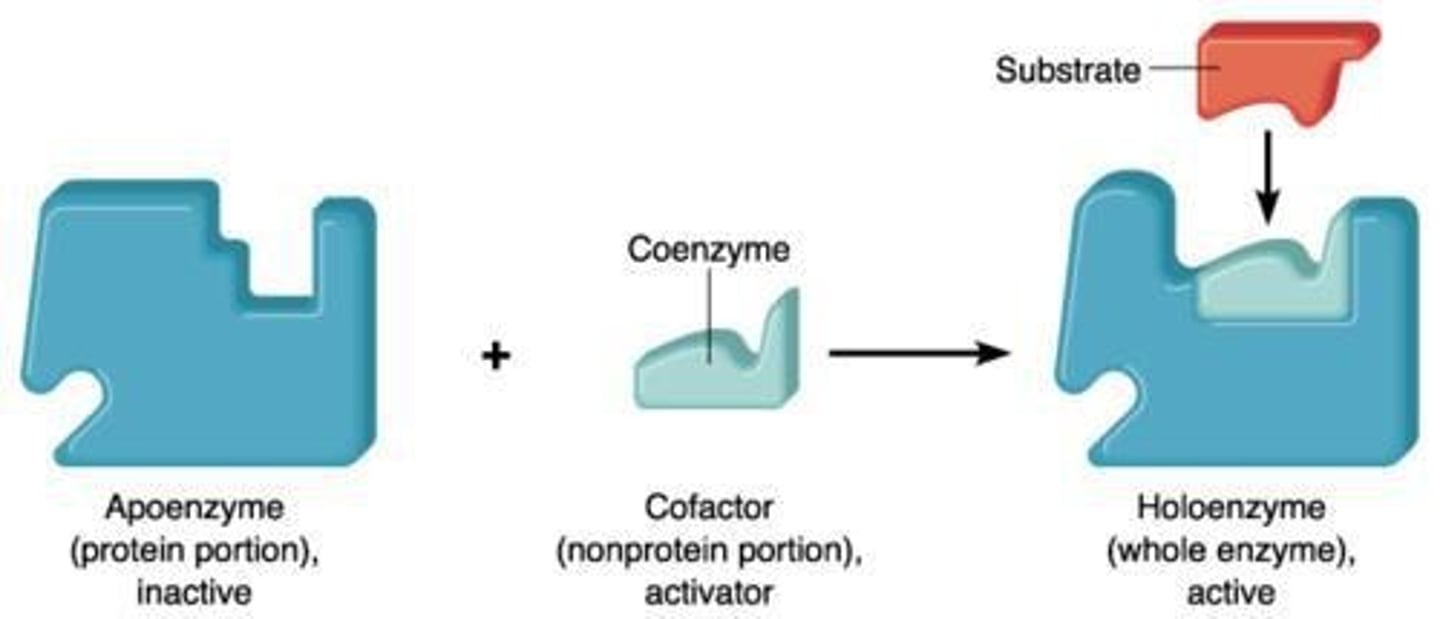
What is the active site of an enzyme?
The region responsible for interacting with the substrate and initiating the reaction.
What is a proenzyme?
An inactive form of an enzyme that requires activation to function.
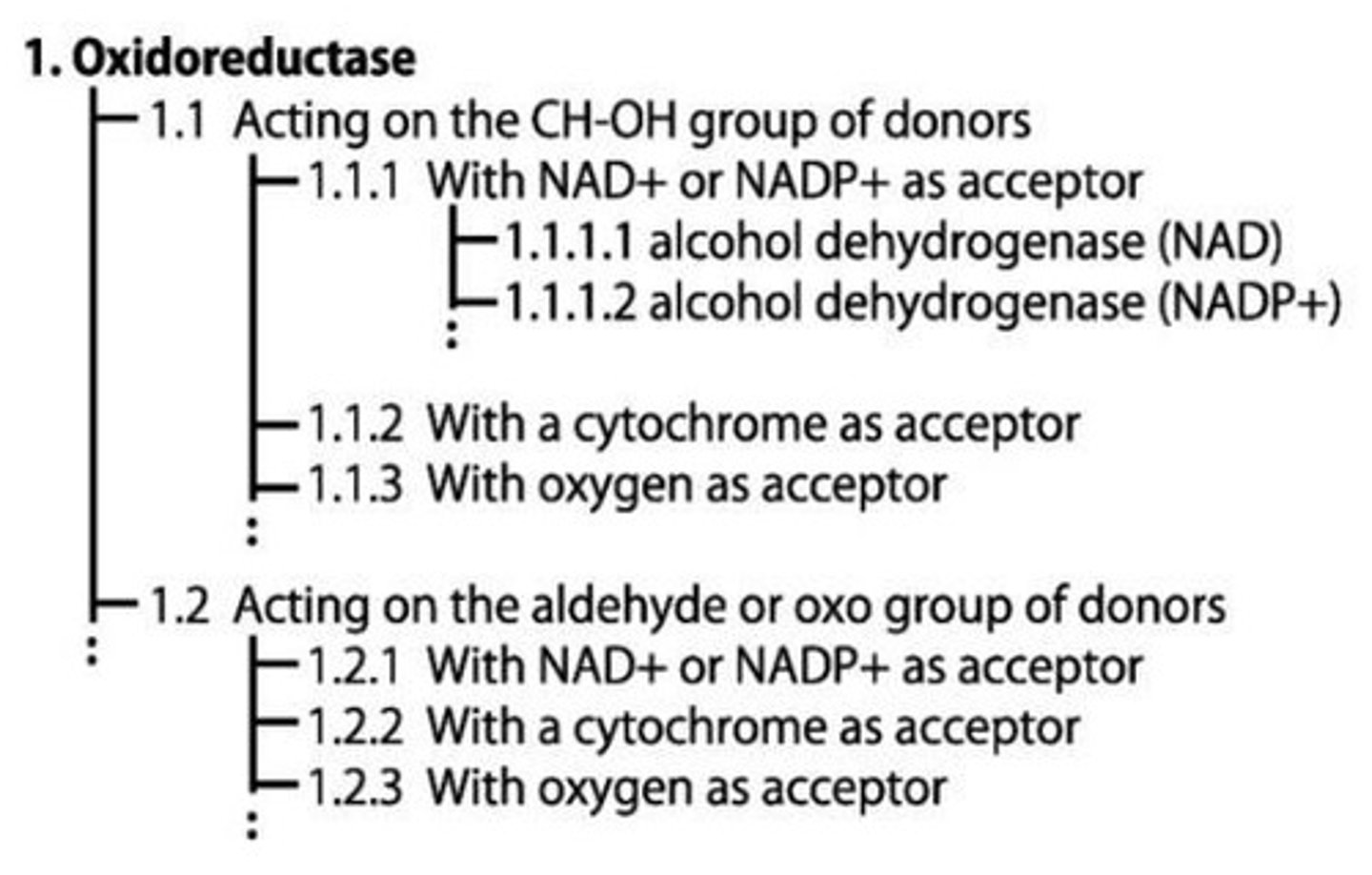
What does the first number in an EC number represent?
The enzyme class, such as EC1 for oxidoreductases.
What type of reaction do oxidoreductases catalyze?
EC1 - Simultaneous oxidation and reduction reactions.
What do transferases do?
EC2 - Catalyze the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another.
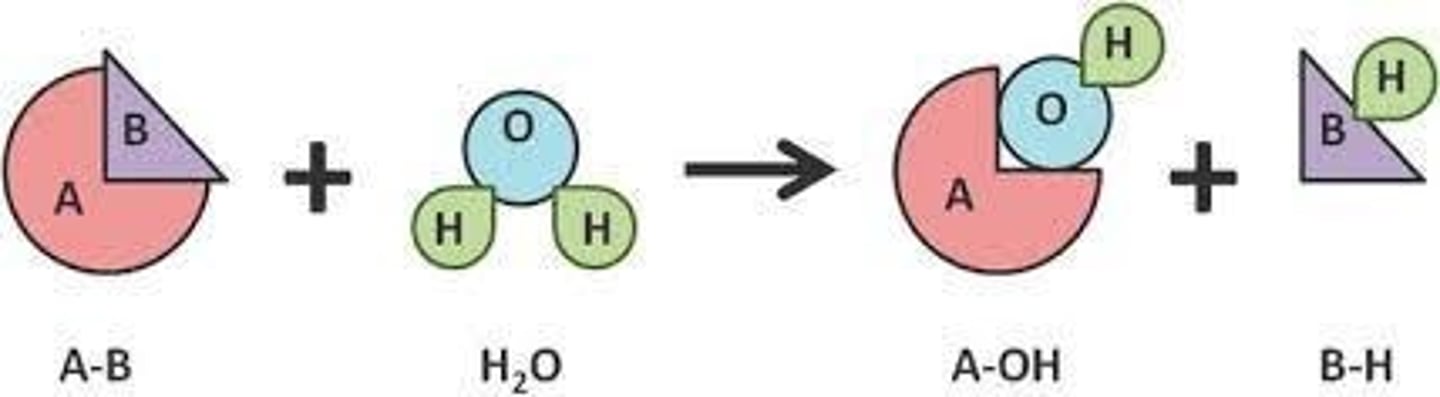
How do hydrolases function?
EC3 - They catalyze the cleavage of a bond through the insertion of a water molecule.
What is the role of lyases?
EC4 - They catalyze the cleavage of bonds without hydrolysis or oxidation.
What do isomerases do?
EC5 - Catalyze structural rearrangements within a single molecule.
What is the function of ligases?
EC6 - Catalyze the joining of two molecules by forming a new covalent bond, usually requiring ATP.
What do translocases facilitate?
EC7 - The movement of ions or molecules across membranes or between compartments.
What are the two main types of enzyme cofactors?
Inorganic cofactors (metal ions) and organic cofactors (coenzymes).
What is a prosthetic group?
A tightly bound cofactor that is permanently attached and crucial for enzyme function.
Why is enzyme regulation important?
To maintain metabolic balance, prevent harmful accumulation, control energy use, and coordinate signaling pathways.
How do cofactors enhance enzyme activity?
They stabilize substrate binding, participate in reactions, and maintain enzyme structure.
What is the significance of the second and third numbers in an EC number?
The second number indicates the type of group or bond the enzyme interacts with, while the third specifies the outcome of the reaction.
What is bioavailability in the context of enzymes?
The proportion of the enzyme that is available to have an active effect in the body.
What is covalent modification of enzymes?
Covalent modification is the attachment of a small molecule to an enzyme, which may stimulate or inhibit its activity.
What is the role of proteolytic processing in enzyme activity?
Proteolytic processing involves the cleavage of an enzyme's polypeptide chain by proteases, which can activate or deactivate the enzyme.
What is allosteric regulation of enzymes?
Allosteric regulation involves the binding of a molecule at a site other than the active site, changing the enzyme's shape and activity.
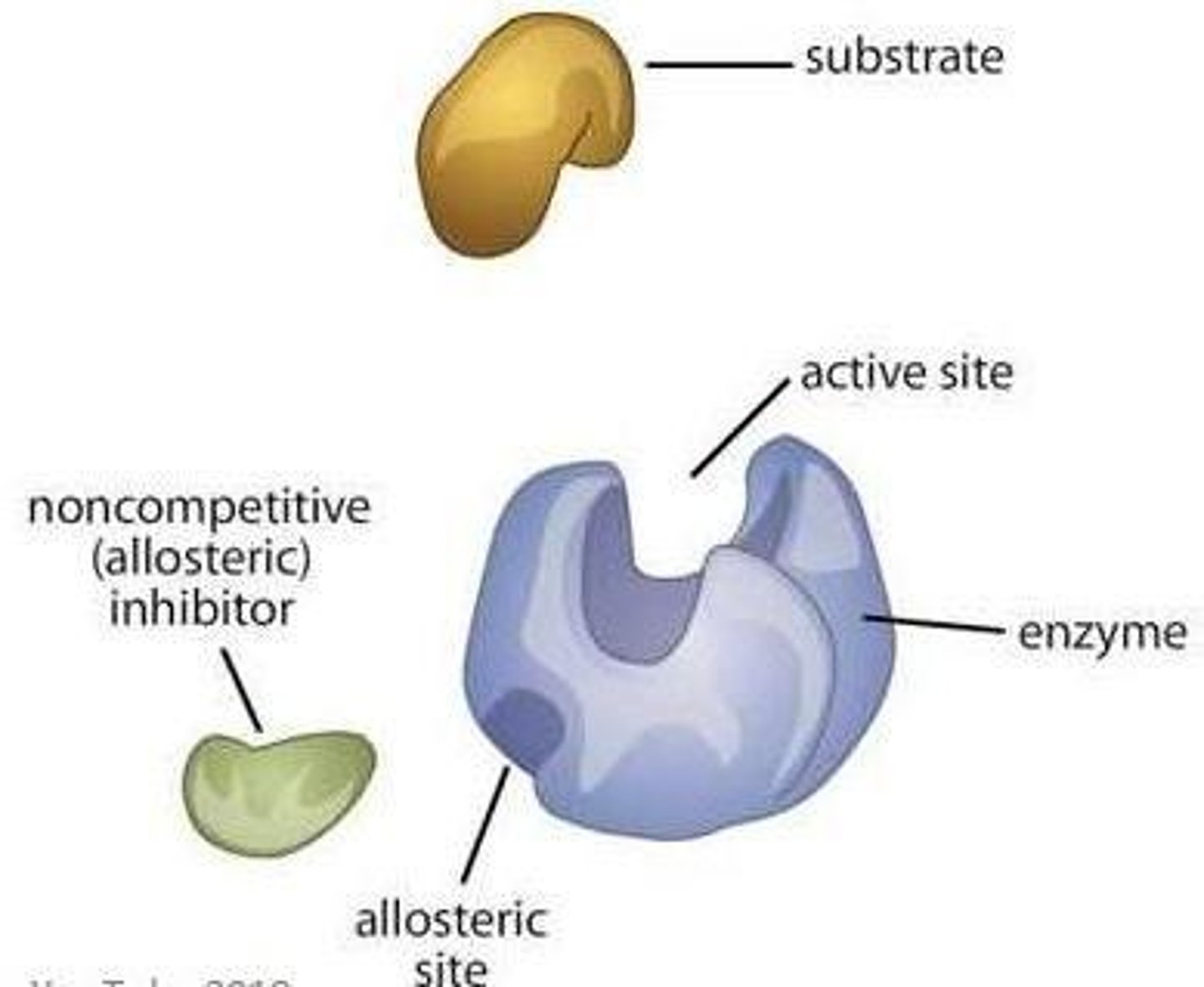
What is the difference between an allosteric activator and an allosteric inhibitor?
An allosteric activator stabilizes the enzyme's active form, while an allosteric inhibitor stabilizes its inactive form.
What is compartmentalization in enzyme regulation?
Compartmentalization controls where in the cell an enzyme or substrate is located, preventing unwanted reactions and allowing for optimal activity.
What is the 'lock and key' model of enzyme action?
The 'lock and key' model suggests that enzymes and substrates have specific complementary shapes that fit exactly into one another.
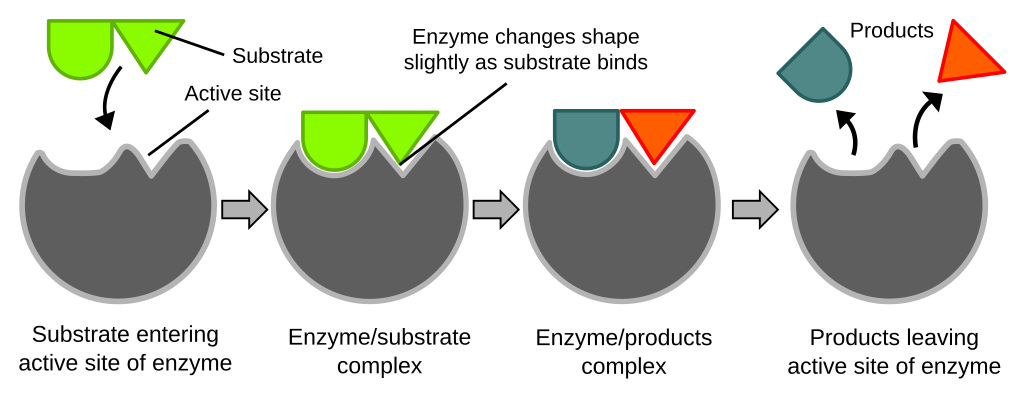
What is the 'induced fit' model of enzyme action?
The induced fit model describes how an enzyme changes shape when a substrate binds to its active site.
Initially, the active site is not a perfect fit for the substrate.
When the substrate approaches, interactions between its chemical groups in the active site cause the enzyme to alter its conformation.
This change in shape allows the active site to fit more tightly around the substrate.
The enzyme–substrate complex formed stabilizes the transition state, lowering the activation energy required for the reaction.
After the reaction, the products are released, and the enzyme returns to its original shape, ready to catalyse another reaction.
What is the significance of the transition state in enzyme reactions?
The transition state is a short-lived, unstable chemical state that requires less activation energy to reach the product than if the enzyme were absent.
What does ΔG represent in biochemical reactions?
ΔG represents the amount of energy needed to reach the transition state; a higher ΔG indicates a slower reaction.
How do enzymes affect the activation energy of a reaction?
Enzymes lower the activation energy by transforming substrates and applying proper orientation for the reaction to occur.
What happens if the system does not have enough energy to meet the ΔG?
If insufficient energy is available, the substrate may leave the transition state and return to its original form.
What is the modern view of enzyme action known as 'conformational selection'?
Conformational selection considers the variety of conformations an enzyme can adopt, with the specific conformation depending on the environment and regulatory molecules.
What are enzyme assays used for?
To determine the catalytic activity of an enzyme.
What are the two types of enzyme assays?
Fixed Time Assays and Kinetic Assays.
What do Fixed Time Assays measure?
The amount of reaction in a fixed amount of time.
What do Kinetic Assays monitor?
The progress of a reaction continuously.
Why is it important to control conditions during enzyme assays?
Minor changes in variables like temperature or pH can drastically alter enzyme activity.
What does the substrate concentration [S] represent in enzyme reactions?
The concentration of the substrate that starts high and decreases over time as it is converted to product.
What does the product concentration [P] represent in enzyme reactions?
It starts at zero and increases over time, mirroring the substrate curve.
What happens to the enzyme-substrate complex concentration [ES] during an enzyme reaction?
[ES] rapidly rises to a steady state and then falls to zero once the substrate is used up.
What is V0 in enzyme kinetics?
The initial rate of reaction at time zero when substrate concentration is very high.
How is V0 determined?
By recording substrate disappearance/product appearance with known [S] and [E] concentrations.
What does reaction order describe?
How the reaction rate depends on reactant concentrations.
What is zero order in reaction kinetics?
The rate is independent of substrate concentration [S]; adding more substrate has no effect.
What is first order in reaction kinetics?
The rate is proportional to substrate concentration [S]; doubling substrate doubles the rate.
What is second order in reaction kinetics?
The rate is proportional to two reactant concentrations.
What does the Michaelis-Menten equation describe?
The relationship between reaction rate (V0) and substrate concentration under physiological conditions.
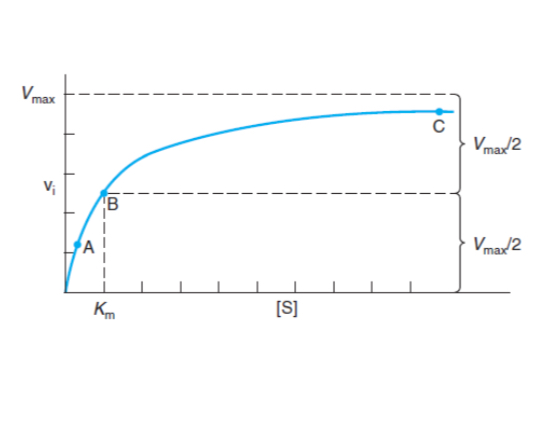
What does Km represent in enzyme kinetics?
The substrate concentration at which the reaction proceeds at half maximal velocity. mol/L or µM).
Low Km is a high affinity for substrate as it easily binds. High Km means low enzyme affinity as it requires more substrate.
What does Kcat represent?
The turnover number of the enzyme, indicating the number of substrate molecules cleaved per enzyme molecule per unit time.
s⁻¹
Kcat = Vmax/ [E]T
What is the Lineweaver-Burk plot used for?
To calculate Vmax and Km from concentrations less than those required for saturating conditions.
\frac{1}{V_0} = y-axis
\frac{1}{[S]} = x-axis
Slope = \frac{K_m}{V_{max}}
Y-intercept = \frac{1}{V_{max}}
X-intercept = -\frac{1}{K_m}
![<p>To calculate Vmax and Km from concentrations less than those required for saturating conditions.</p><p></p><p></p><ul><li><p><span>\frac{1}{V_0} = y-axis</span></p></li><li><p><span>\frac{1}{[S]} = x-axis</span></p></li><li><p><span>Slope = \frac{K_m}{V_{max}}</span></p></li><li><p><span>Y-intercept = \frac{1}{V_{max}}</span></p></li><li><p><span>X-intercept = -\frac{1}{K_m}</span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7bdce169-3879-479c-ab4e-8ec2704cfcee.jpg)
What is the Hanes-Woolf plot?
A linear transformation of the Michaelis-Menten plot, typically plotted as [S] vs. V0.
![<p>A linear transformation of the Michaelis-Menten plot, typically plotted as [S] vs. V0.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f0f27410-0c93-431e-aee0-b052ad5d5c00.jpg)
What is the Eadie-Hofstee plot?
Another linear transformation of the Michaelis-Menten plot, typically plotted as V0 vs. [S].
![<p>Another linear transformation of the Michaelis-Menten plot, typically plotted as V0 vs. [S].</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/54a55d77-87ac-4bc6-a122-3fb8d88ee369.jpg)