Practical II Exam Structures
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
the two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex, joined by the corpus callosum
cerebral hemispheres
2
New cards
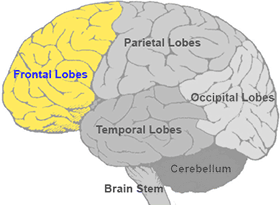
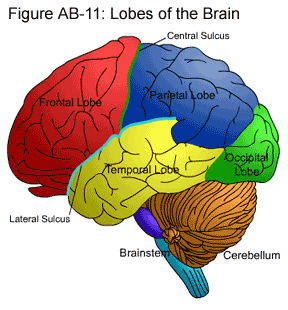
Largest lobe of the cerebral cortex. Executive function, information processing, higher cognition. Located superior to the temporal lobe and anterior to the parietal lobe.
frontal lobe
3
New cards
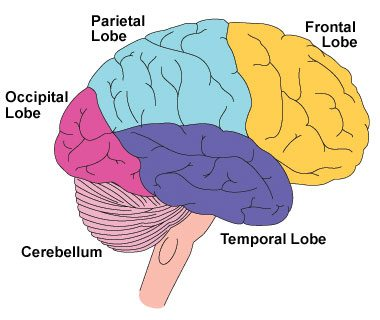
Located posterior to the frontal lobe and anterior to the occipital lobe. Information integration, somatosensation, proprioception. Left and right halves are responsible for information coming from the respective opposite side of the body.
parietal lobe
4
New cards
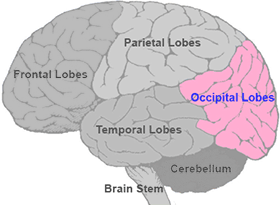
Located at the back of the head. Decodes visual signals.
occipital lobe
5
New cards
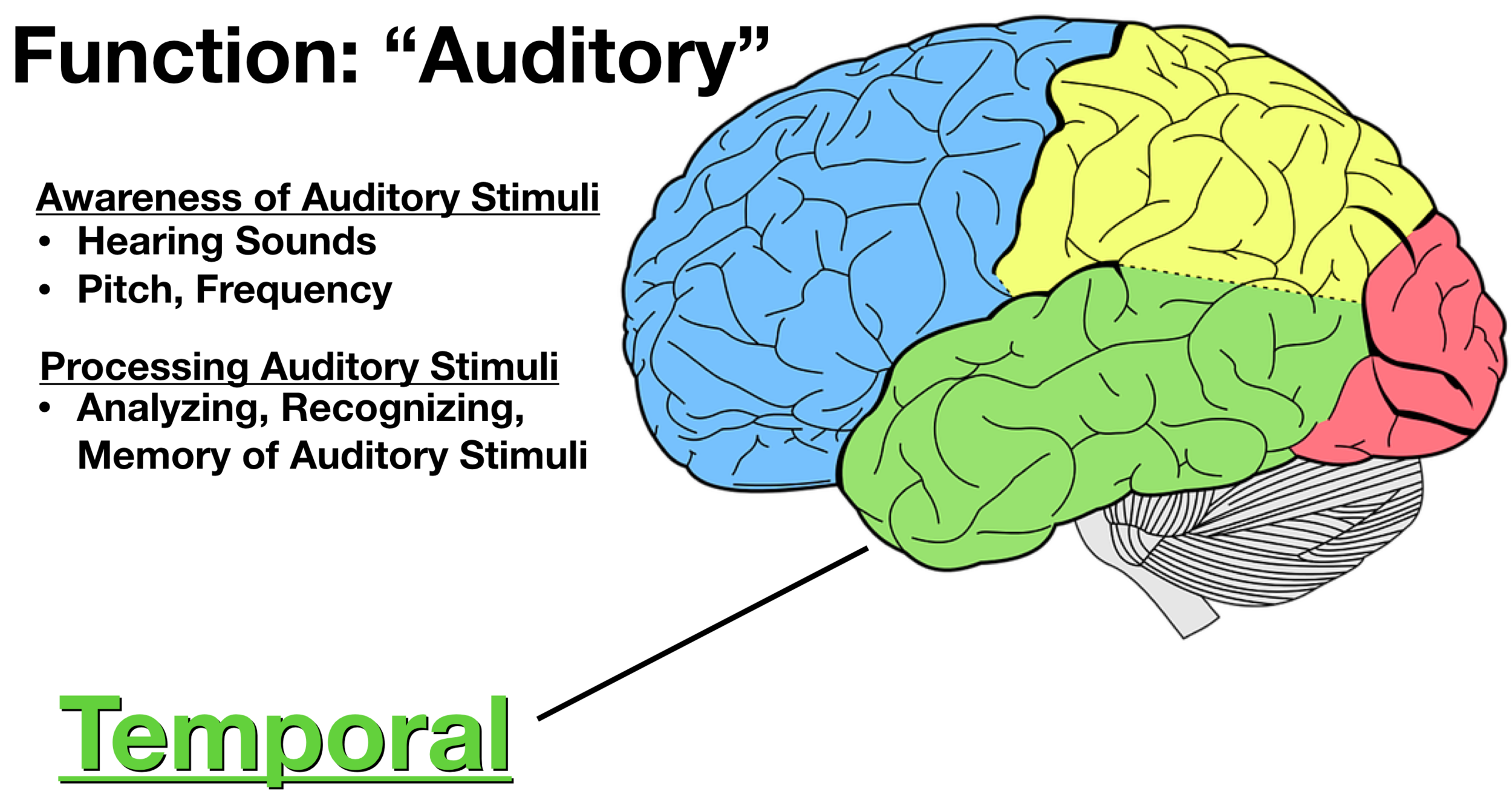
Sits behind the ears/temples. Houses memories, emotion, and language comprehension. Houses the hippocampus, the primary auditory cortex, and Wernicke's area.
temporal lobe
6
New cards
Forms the boundary between the frontal and parietal lobes on the lateral and medial surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres. This separates the primary motor cortex from the primary somatosensory cortex.
central sulcus
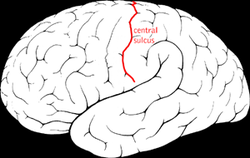
7
New cards
Separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes.
lateral sulcus/sylvian fissure
8
New cards
A deep groove that divides the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
longitudinal fissure
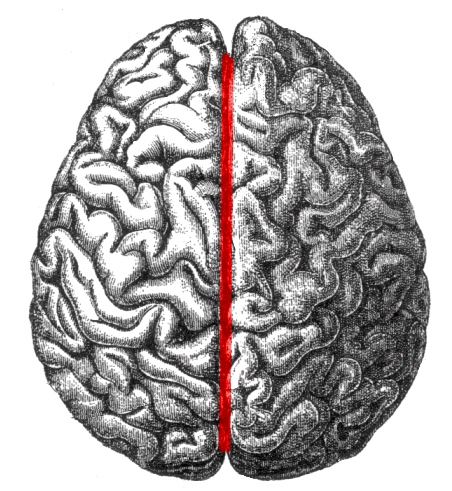
9
New cards
A bundles of axons that connects the two temporal lobes across the midline. Interconnects the amygdalas and temporal lobes, contributing to the role of memory, emotion, speech, and hearing.
anterior commissure
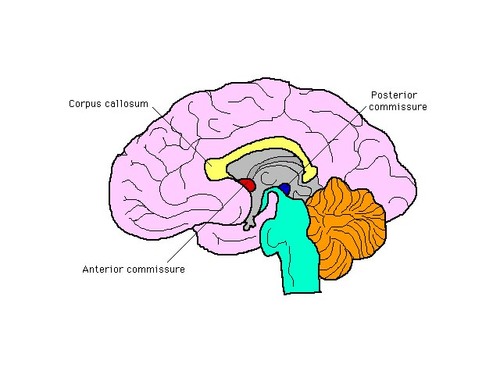
10
New cards
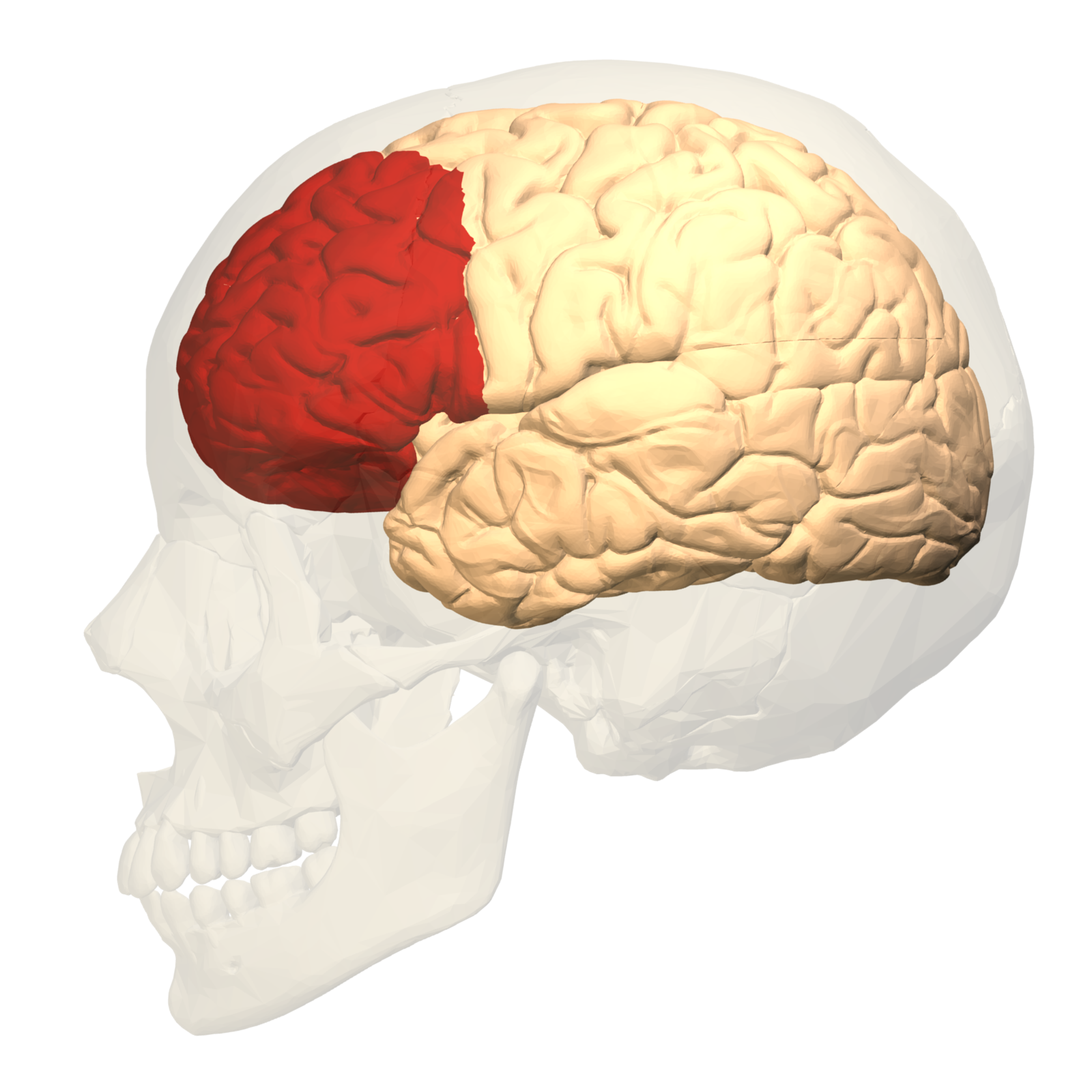
Left hemisphere. Anterior part of the brain. Involved in functions of cognitive control such as decision making. Influences personality traits.
prefrontal cortex (frontal lobe)
11
New cards
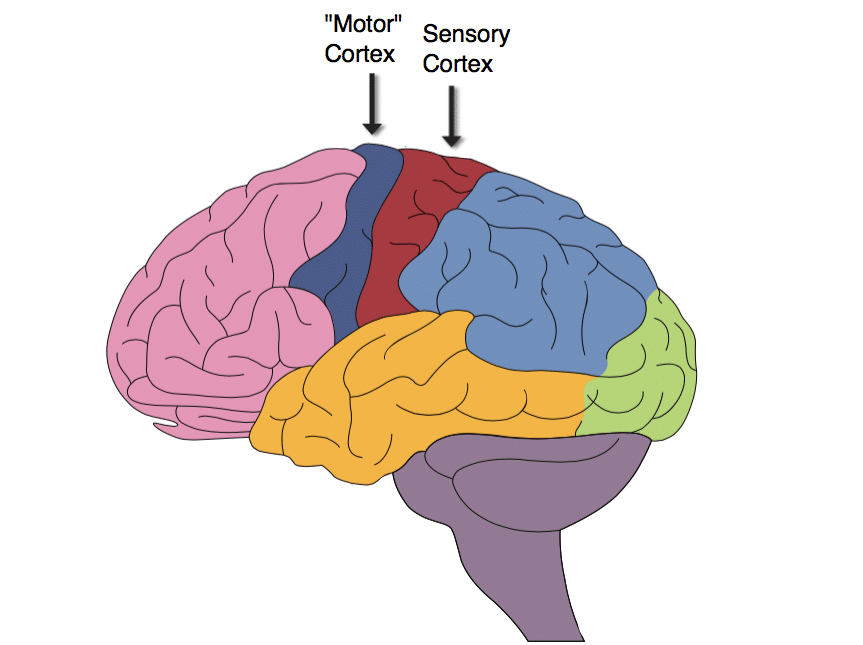
Left hemisphere. Anterior part of the parietal lobe. Where sense of touch is processed.
somatosensory cortex/postcentral gyrus (parietal lobe)
12
New cards
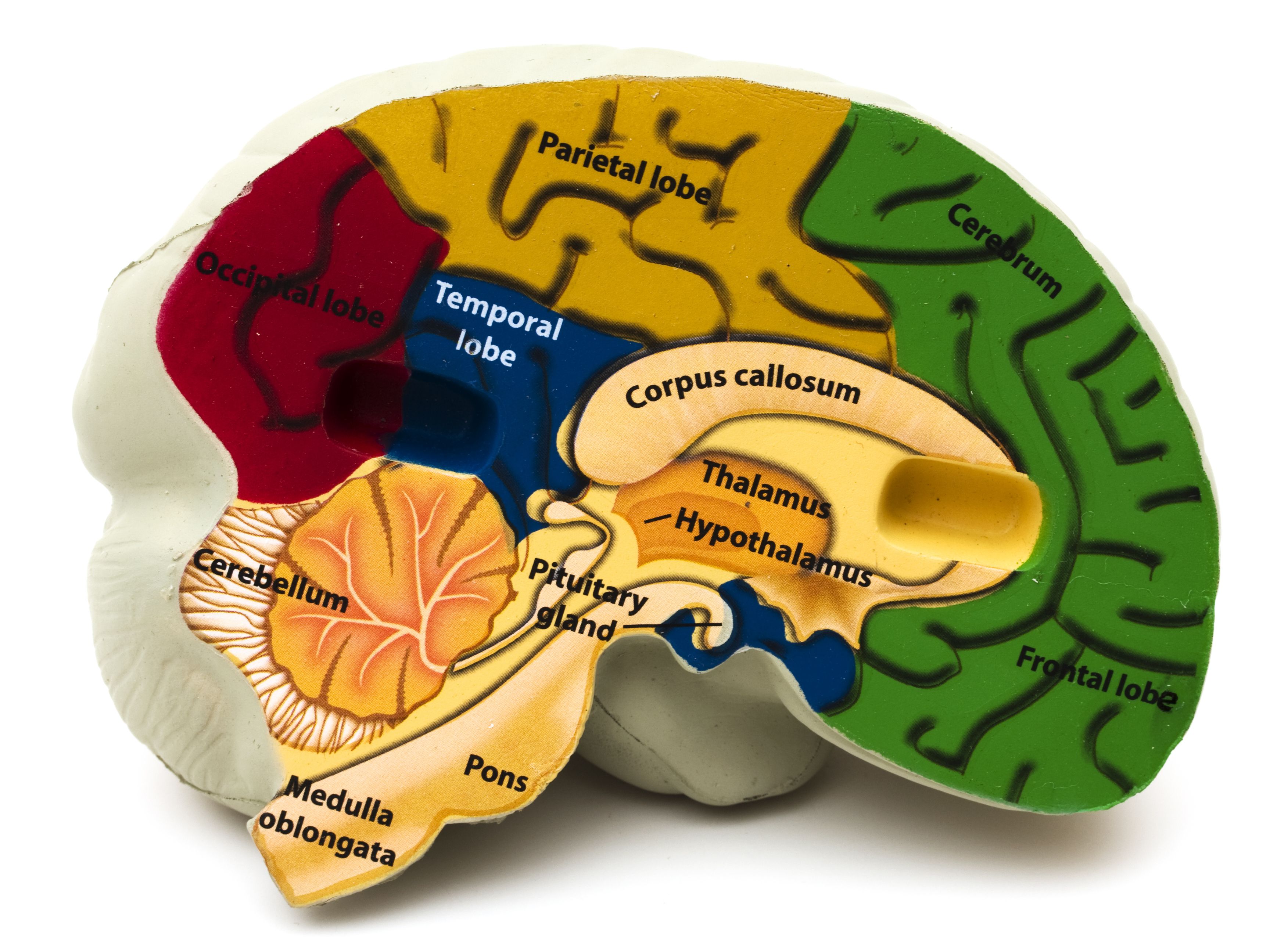
Lower or hindmost part of the brain; continuous with spinal cord. Controls functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure.
medulla oblongata
13
New cards
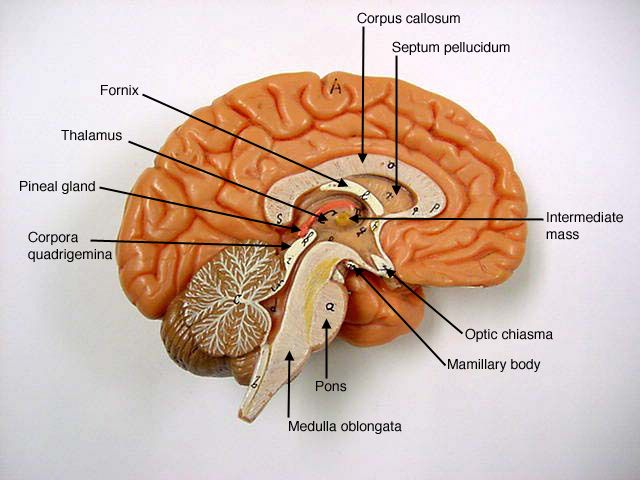
corpus callosum
A thick bundle of nerve fibers that connects the two hemispheres of the brain and ensures both sides of the brain can communicate.
14
New cards
pre central gyrus/primary motor cortex
Directs movements by controlling muscle contractions. Located in the most posterior part of the frontal lobe, anterior to the central sulcus.
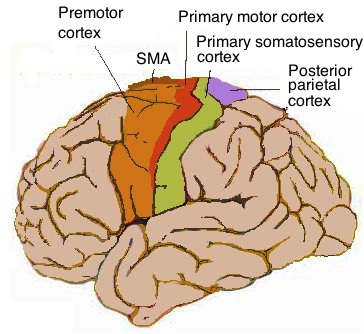
15
New cards
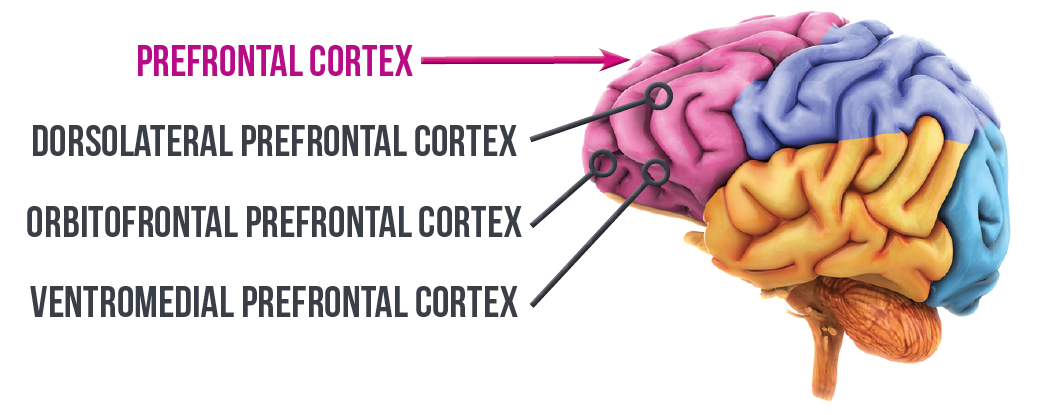
prefrontal cortex
executive function. "upstairs brain". Allows us to make rational decisions.
The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex tells your limbic system what is worth fearing.
Behavior and personality traits.
The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex tells your limbic system what is worth fearing.
Behavior and personality traits.
16
New cards
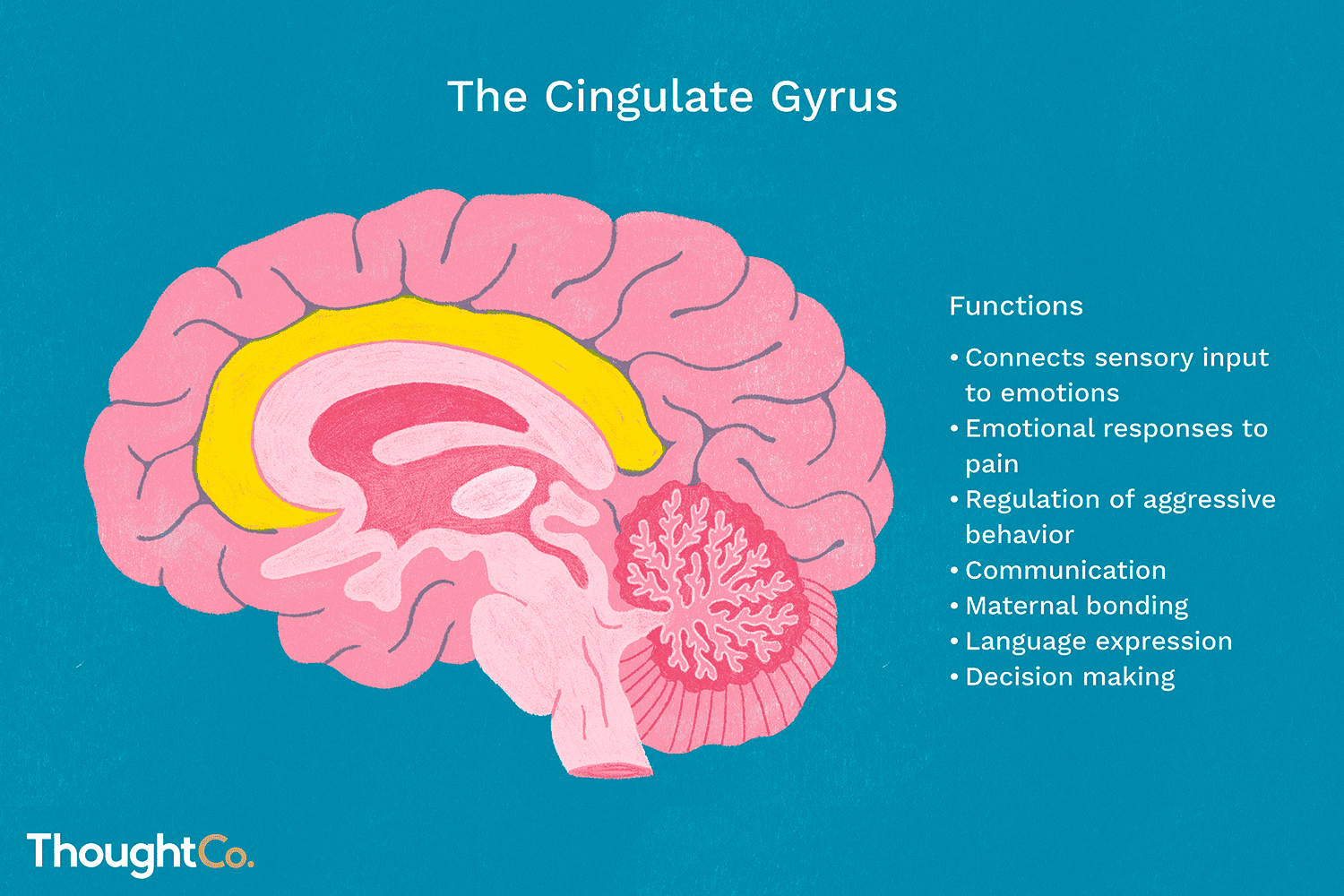
cingulate cortex/gyrus
sits above the corpus callossum, a component of the limbic system that is involved in processing emotions and behavioral regulation.
17
New cards
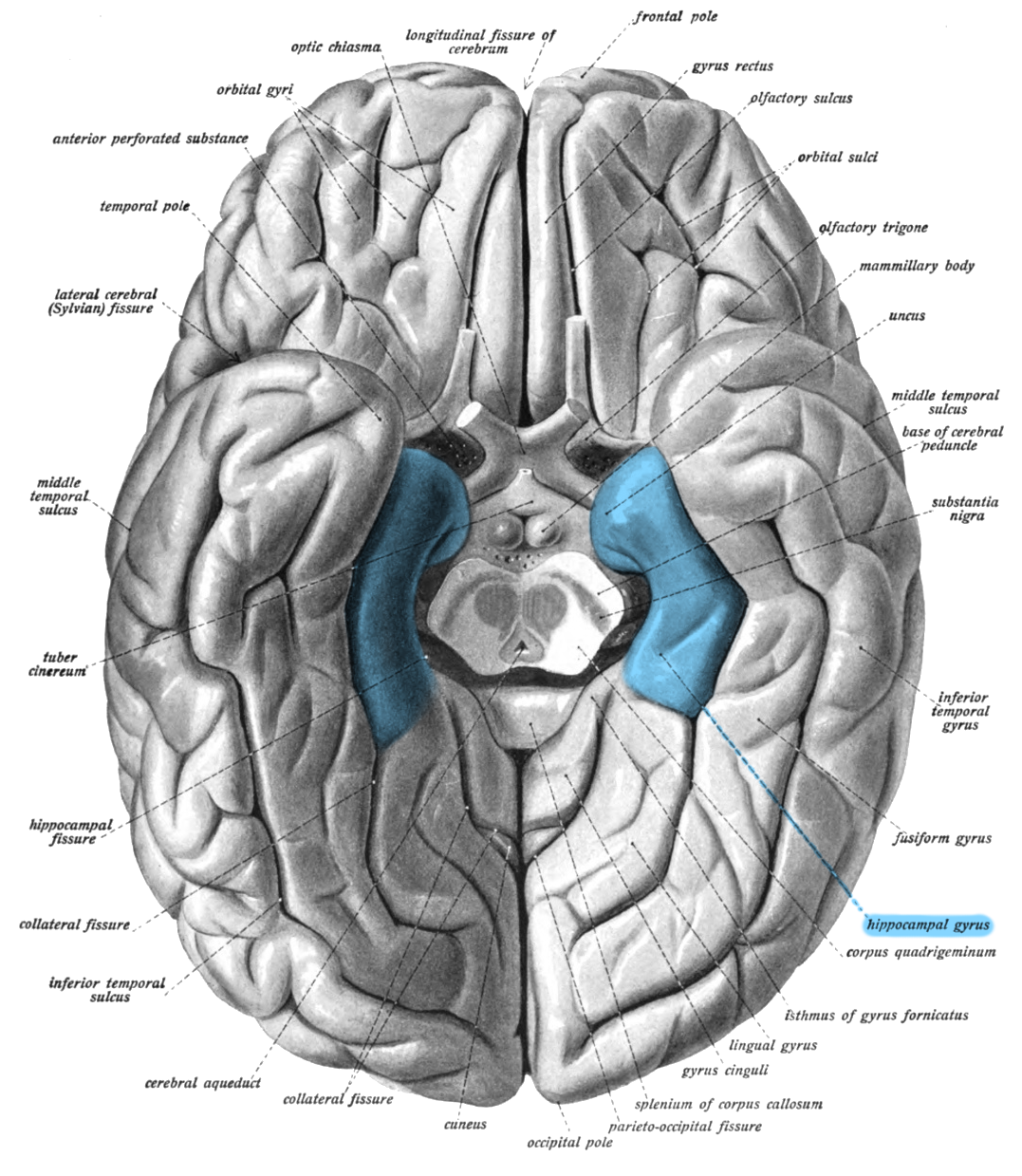
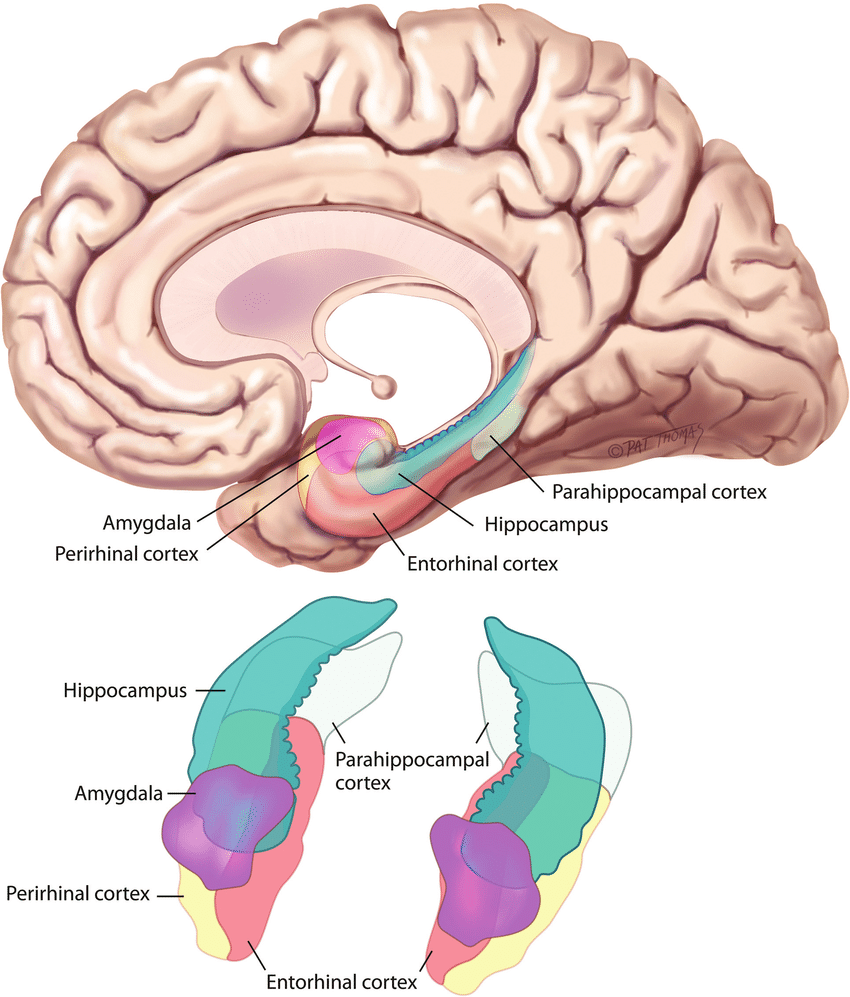
hippocampal gyrus
A grey matter cortical region that surrounds the hippocampus. Part of the limbic system. Plays an important role in memory encoding and retrieval.
18
New cards
trisynaptic circuit of the hippocampus
The hippocampus is important for the consolidation of short-term to long-term memory. The trisynaptic circuit involves 3 major cell groups: granule cells of the dentate gyrus, pyramidal cells of CA3, and pyramidal cells of CA1.
19
New cards
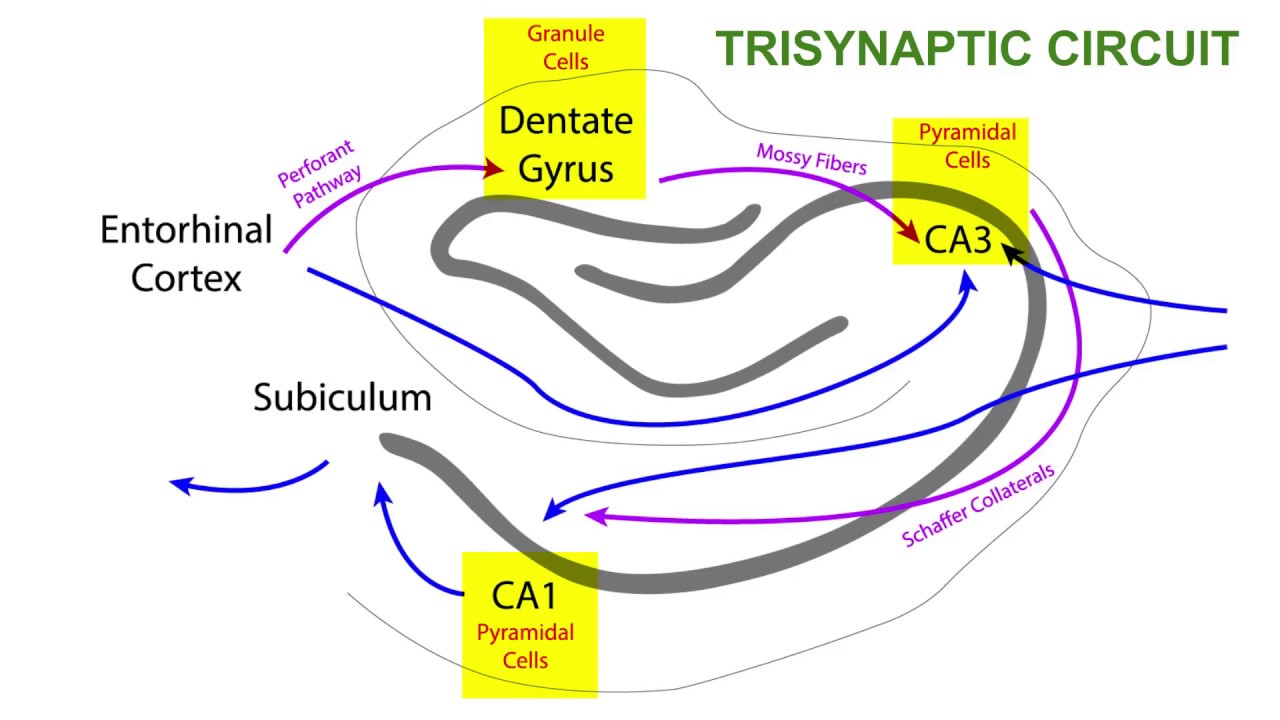
3 synapses of the trisynaptic circuit
synapse 1: entorhinal cortex to the dentate gyrus via the perforant pathway
synapse 2: from the dentate gyrus to CA3 via mossy fibers
synapse 3: from CA3 to CA1 via Schaffer collaterals.
synapse 2: from the dentate gyrus to CA3 via mossy fibers
synapse 3: from CA3 to CA1 via Schaffer collaterals.
20
New cards
entorhinal cortex
the main gateway of communication between the hippocampus and the neocortex
21
New cards
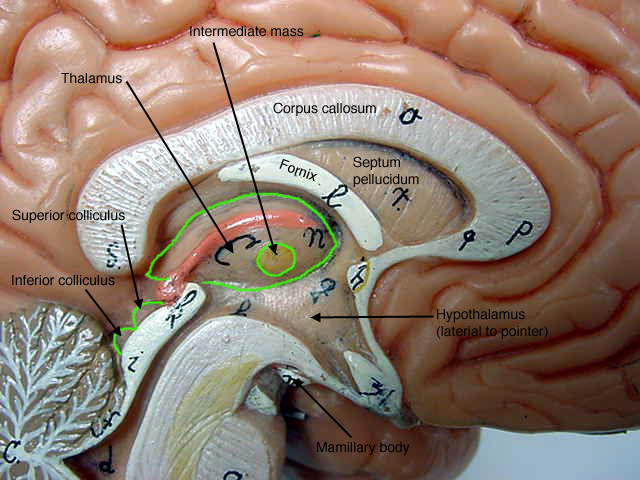
fornix
a bundle of nerve fibers that act as a major tract of the hippocampus
22
New cards
subiculum
most inferior part of the hippocampus
23
New cards
dentate gyrus
formation of new episodic memories. Produces new neurons in adulthood.
24
New cards
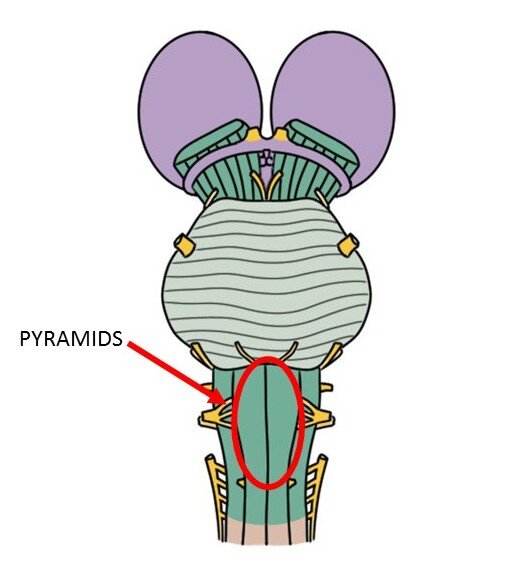
medullary pyramids
Paired white matter structures of the medulla oblongata. Contain the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts.
25
New cards
structures of the limbic system
HAThippo
26
New cards
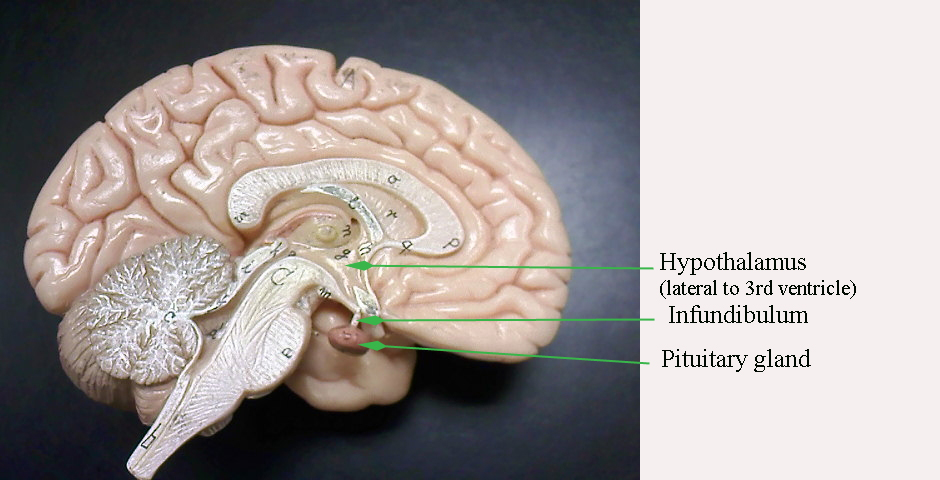
hypothalamus
controls hormone release via the anterior pituitary; regulates ANS
27
New cards
amygdala
Fear, anxious emotions, anxiety.
28
New cards
thalamus
sensory relay station. Directs senses to appropriate areas in the cortex. Your sense of smell is the only sense that bypasses your thalamus.
29
New cards
hippocampus
next to and interconnected with the amygdala: memory.
30
New cards
pituitary gland
produces and secretes hormones. Relays signals from the hypothalamus to glands throughout the body.